
What are my treatment options for kidney failure?
Dec 02, 2021 · Treatment involves removing the obstruction and draining the collected urine. Duplex kidney is the presence of four kidneys instead of two. This often produces no complications, but treatable urinary tract infections occur occasionally. Duplicated ureter is the most common kidney abnormality. Here, two ureters drain a single kidney.
What is conservative management for kidney failure?
Jul 05, 2014 · The embolic material used for the treatment of RAVMs may be Gelfoam, absolute alcohol, polyvinyl alcohol ... There was a slight increase of serum creatinine levels in 14 patients, but renal function remained within normal limits. ... delayed complication from coil and guidewire occlusion of renal arteriovenous malformation. Am J Kidney Dis ...
How are renal arteriovenous malformations (AVM) treated?
Your doctor may prescribe: Phosphate binders: a medicine to help your body get rid of extra phosphorus in your blood. When your kidneys are not... Calcium and Vitamin D: supplements to help balance the calcium and vitamin D in your body. When your kidneys are not...
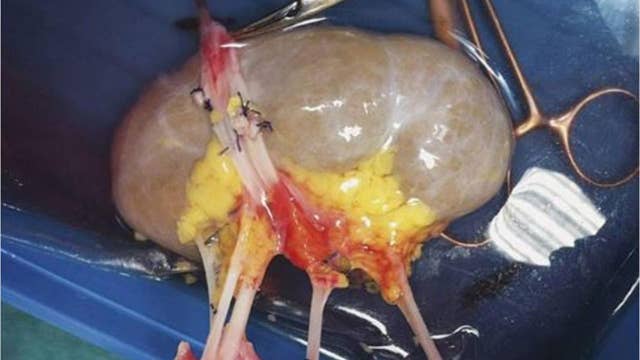
What is malformation in kidney?
What is the most common congenital abnormality of the kidney?
How do you fix a duplex kidney?
- Nephrectomy – kidney removal. ...
- Heminephrectomy – part of the affected kidney and duplicated ureter are removed.
- Ureteroureterostomy – in the case of an ectopic ureter, it is split near the bladder and joined to the normal ureter, allowing urine from the upper kidney to drain as normal.
What is congenital renal malformation?
Which of the following are the tubes inside the kidney?
What would be the long term effects of chronic infection or inflammation of the kidneys?
How many tubes are coming out from kidney fissure?
Is duplex kidney serious?
What are the symptoms of duplex kidney?
Symptoms include: Urinary tract infections (UTIs). An obstruction of the urinary tract resulting in poor urine flow. Urinary incontinence is marked by frequent leaking of urine.
What are the first signs of kidney problems?
What are the symptoms of kidney diseases?
- High blood pressure.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- A metallic taste in your mouth.
- Fatigue.
- Weakness.
- Trouble thinking.
- Sleep issues.
What happens if baby is born with kidney problems?
Can kidney disease be treated?
Depending on the underlying cause, some types of kidney disease can be treated. Often, though, chronic kidney disease has no cure. Treatment usually consists of measures to help control signs and symptoms, reduce complications, and slow progression of the disease.
What is the treatment for end stage kidney disease?
At that point, you need dialysis or a kidney transplant. Dialysis.
What is a kidney biopsy?
Kidney biopsy. During a kidney biopsy, your doctor uses a needle to remove a small sample of kidney tissue for lab testing. The biopsy needle is inserted through your skin and is often directed using the guidance of an imaging device, such as ultrasound. As a first step toward diagnosis of kidney disease, your doctor discusses your personal ...
What is the procedure for a kidney biopsy?
The biopsy needle is inserted through your skin and is often directed using the guidance of an imaging device, such as ultrasound.
What is the first step in a kidney diagnosis?
As a first step toward diagnosis of kidney disease, your doctor discusses your personal and family history with you. Among other things, your doctor might ask questions about whether you've been diagnosed with high blood pressure, if you've taken a medication that might affect kidney function, if you've noticed changes in your urinary habits, ...
What tests are needed for kidney disease?
For kidney disease diagnosis, you may also need certain tests and procedures, such as: Blood tests. Kidney function tests look for the level of waste products, such as creatinine and urea, in your blood. Urine tests.
Where is the donor kidney placed?
Kidney transplant. During kidney transplant surgery, the donor kidney is placed in your lower abdomen. Blood vessels of the new kidney are attached to blood vessels in the lower part of your abdomen, just above one of your legs. The new kidney's urine tube (ureter) is connected to your bladder.
Can renal anomalies be detected on ultrasound?
Renal anomalies are often detected on antenatal ultrasound examination, but many are incidental changes such as minor dilatation of the renal pelvis, usually nonpathological. 41 The differential diagnosis of anomalies is reviewed in Chapter 33, but a brief outline is given here in relation to their pathogenesis.
What is bilateral renal agenesis?
Bilateral renal agenesis is the extreme, leading to fetal, or immediate neonatal death. Other abnormalities are those of the collecting system and include duplication or absence of the ureter, megaureter, ureteral-pelvic junction obstruction, calyceal cyst or diverticulum and calyectasis, and extra or bifid pelvis.
What causes polyhydramnios?
Polyhydramnios is caused by renal anomalies in a small percentage of cases but can indicate the presence of a renal concentrating defect associated with renal dysplasia, nephrotic syndrome, or inherited renal tubular defects ( Cole and Quamme, 2000; van Eijk et al., 2002; Deshpande and Hennekam, 2008 ).
What is the diagnosis of genetic disease with renal and urinary tract manifestations?
The diagnosis of most genetic disease with renal and urinary tract manifestations is based on the characteristic multiorgan findings on imaging. With an increasing number of conditions, analysis of DNA or tissue from amniocentesis or chorionic villus biopsy can be utilized to confirm a suspected disorder or determine prognosis. Examples include:
What are the most common anomalies of cloacal exstrophy?
Renal anomalies are much more common with cloacal exstrophy than with bladder exstrophy. They include anomalies of location such as pelvic kidneys or crossed fused ectopia. Horseshoe kidneys, renal agenesis, and ureteropelvic junction obstruction may occur as well.
What are the features of bladder exstrophy?
In addition to the features seen with bladder exstrophy, patients with cloacal exstrophy can have other skeletal abnormalities. Skeletal anomalies are seen in as many as half of patients with cloacal exstrophy. Anomalies include congenital hip dislocation, talipes equinovarus, and a variety of limb deficiencies. 116
What are fascial anomalies associated with cloacal exstrophy?
The fascial anomalies associated with cloacal exstrophy include those described previously for bladder exstrophy. In addition, an omphalocele is often associated. 117,118 This omphalocele can be closed during the initial bladder closure if it is small. If the omphalocele is large, it may require closure as a primary procedure with the reapproximated bladder halves acting as a silo to decompress the increased intra-abdominal pressure. Alternatively, the omphalocele can be treated with antiseptic paint to promote skin overgrowth. Our preference is to proceed with staged surgical correction of the omphalocele and primary reconstruction of the bladder at a later date. In our opinion, the degree of increased intra-abdominal pressure after omphalocele closure determines whether we can proceed with primary bladder closure at the same time as the omphalocele repair or whether these operations should be staged. Aggressive one-stage closure of a cloacal exstrophy can lead to organ ischemia from the increased intra-abdominal pressure. Rupture of an omphalocele clearly requires immediate attention and would take precedence over other considerations. Fortunately, this occurs rarely.
What does it mean when you have kidney failure?
When you have kidney failure, it means your kidneys are damaged. They cannot do these important jobs well enough. Having kidney failure means that: 85-90% of your kidney function is gone. Your kidneys don't work well enough to keep you alive.
What is a kidney transplant?
A kidney transplant is an operation that places a healthy kidney from another person into your body. The kidney may come from someone who has died or from a living donor who may be a close relative, spouse or friend. It can even come from someone who wishes to donate a kidney to anyone in need of a transplant.
What are the main functions of kidneys?
Healthy kidneys do many important jobs. They keep your whole body in balance. They remove waste products and extra water from your body, help make red blood cells, and help control blood pressure. When you have kidney failure, it means your kidneys are damaged. They cannot do these important jobs well enough. Having kidney failure means that: 1 85-90% of your kidney function is gone 2 Your kidneys don't work well enough to keep you alive
Can peritoneal dialysis be done at home?
Peritoneal dialysis is a home-based treatment and can be done at home, at work, at school or even during travel. Because of this, peritoneal dialysis may allow for greater flexibility. (For more information on peritoneal dialysis, click here.
What is a PD catheter?
The lining of your abdomen (the peritoneum) acts as a natural filter. A cleansing solution flows into your abdomen (your belly) through a soft tube called a PD catheter.
What to do if you have kidney failure?
If you aren't in the hospital, but have signs or symptoms of kidney failure, make an appointment with your family doctor or a general practitioner.
What tests can be used to diagnose kidney failure?
Analyzing a sample of your urine (urinalysis) may reveal abnormalities that suggest kidney failure. Blood tests. A sample of your blood may reveal rapidly rising levels of urea and creatinine — two substances used to measure kidney function. Imaging tests. Imaging tests such as ultrasound and computerized tomography may be used to help your doctor ...
How to determine if you have kidney failure?
Measuring how much you urinate in 24 hours may help your doctor determine the cause of your kidney failure . Urine tests. Analyzing a sample of your urine (urinalysis) may reveal abnormalities that suggest kidney failure. Blood tests. A sample of your blood may reveal rapidly rising levels of urea and creatinine — two substances used ...
What is the procedure for a kidney biopsy?
The biopsy needle is inserted through your skin and is often directed using the guidance of an imaging device, such as ultrasound.
How is a biopsy needle inserted?
The biopsy needle is inserted through your skin and is often directed using the guidance of an imaging device, such as ultrasound. If your signs and symptoms suggest that you have acute kidney failure, your doctor may recommend certain tests and procedures to verify your diagnosis. These may include:
What happens if you have too much potassium in your blood?
Too much potassium in the blood can cause dangerous irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) and muscle weakness. Medications to restore blood calcium levels. If the levels of calcium in your blood drop too low, your doctor may recommend an infusion of calcium. Dialysis to remove toxins from your blood.
What is the best treatment for toxins in the body?
Dialysis to remove toxins from your blood. If toxins build up in your blood, you may need temporary hemodialysis — often referred to simply as dialysis — to help remove toxins and excess fluids from your body while your kidneys heal. Dialysis may also help remove excess potassium from your body.
What is the treatment for renal arteriovenous malformation?
One indication for the treatment of these malformations is pain. The pain from renal AVMs results from either obstruction of the collecting system by clots or from the expansion of the renal capsule due to intrarenal hemorrhage.
Can contrast cause renal failure?
Contrast used for arteriography may cause acute renal failure, which may necessitate a delay in intervention. Preexisting congenital anomalies, acquired abnormalities, or previous surgery may impair the function of the contralateral kidney. In these cases, global renal function should be assessed by deliberate means.
Is CHF a condition?
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is an unusual yet compelling indication for treatment. Several case reports have described patients in severe heart failure whose cardiac health improved to normal limits after nephrectomy or embolization of the AVM.
How long does PES last?
Postembolization syndrome (PES), a combination of fever, leukocytosis, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, is commonly described and may last 1-3 days. It should be treated with analgesia, rest, and (potentially) intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
What is the best treatment for AVM?
The treatment most likely to cure an AVM is total nephrectomy. Total nephrectomy is indicated for large cirsoid AVMs. In most cases, nephrectomy is reserved for patients in whom more conservative therapy has failed. If the fistula is due to malignancy, then radical nephrectomy is usually indicated.
What are the complications of nephrectomy?
Potential complications of nephrectomy can be classified by organ system, as follows: Cardiac - Dysrhythmia from electrolyte imbalances caused by diuresis, ischemia caused by surgical anemia or anesthetic hypotension. Pulmonary - Atelectasis, pneumonia, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism.
Can alcohol cause headaches?
Alcohol may cause transient headaches and mild intoxication. Recurrence or persistent fistulas are possible. Hematomas and pseudoaneurysm at the puncture site (usually the femoral artery) are not uncommon, with clinical evidence of hematoma occurring in approximately 5% of patients. Previous.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Depending on the cause, some types of kidney disease can be treated. Often, though, chronic kidney disease has no cure. Treatment usually consists of measures to help control signs and symptoms, reduce complications, and slow progression of the disease. If your kidneys become severely damaged, you might need treatment for end-stage kidney disease.