
What is the treatment for a vaso-occlusive crisis?
Vaso-occlusive crisis is treated with vigorous intravenous hydration and analgesics. Intravenous fluids should be of sufficient quantity to correct dehydration and to replace continuing loss, both insensible and due to fever. Normal saline and 5% dextrose in saline may be used.
Are standard medical texts adequate for the treatment of vaso-occlusive crisis?
Nonetheless, most standard medical texts provide neither adequate information for the treatment or prevention of pain due to vaso-occlusive crisis in SCD nor reassurance of the unlikelihood of addiction in this population. Nor is this need met by easily obtained review articles in core medical journals.
Is inhaled nitric oxide an effective treatment for vaso-occlusive crisis?
Role of inhaled nitric oxide Inhaled nitric oxide may serve as a potential medication in the treatment of vaso-occlusive crisis.
What are vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs)?
These SCD-related painful episodes, also referred to as vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs), have multifactorial causes, and they often occur as a result of multicellular aggregation and vascular adherence of red blood cells, neutrophils, and platelets, leading to recurrent and unpredictable occlusion of the microcirculation.
What is the treatment of vaso-occlusive crisis?
Vaso-occlusive crisis is treated with vigorous intravenous hydration and analgesics. Intravenous fluids should be of sufficient quantity to correct dehydration and to replace continuing loss, both insensible and due to fever. Normal saline and 5% dextrose in saline may be used.
What are the main treatments for a patient with sickle cell crisis?
TreatmentHydroxyurea (Droxia, Hydrea, Siklos). Daily hydroxyurea reduces the frequency of painful crises and might reduce the need for blood transfusions and hospitalizations. ... L-glutamine oral powder (Endari). ... Crizanlizumab (Adakveo). ... Voxelotor (Oxbryta). ... Pain-relieving medications.
What is most likely a potential intervention for a sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis?
Opioids are commonly used for this purpose. Acute management also may involve administering supplementary oxygen to combat low bodily oxygen levels, and/or fluids to manage dehydration. A blood transfusion also may be necessary in some cases.
How can vaso occlusion be prevented?
Anti-adhesion agents. Molecules that inhibit selectin binding and adhesion are a potential method for reducing or improving vaso-occlusion. These molecules are especially appealing given their potential for use in combination with RBC-targeting agents described above.
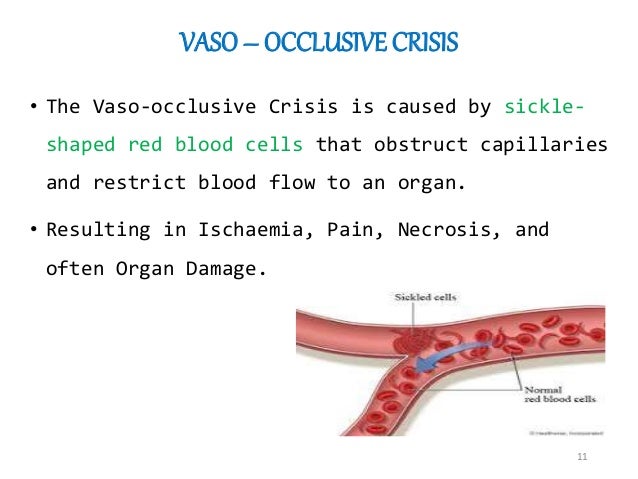
What is vaso occlusive crisis?
A vaso-occlusive crisis occurs when the microcirculation is obstructed by sickled RBCs, causing ischemic injury to the organ supplied and resultant pain.
What medication should sickle cell patients avoid?
Morphine is considered the drug of choice for the treatment of acute sickle cell pain (Table 2), whereas meperidine (Demerol, Sanofi-Synthelabo) should be avoided because of the increased risk of seizures in patients with renal dysfunction, which can occur in patients with SCD.
How does hydroxyurea treat sickle cell?
Hydroxyurea makes your red blood cells bigger. It helps them stay rounder and more flexible — and makes them less likely to turn into a sickle shape. The medicine does this by increasing a special kind of hemoglobin called hemoglobin F.
How do you treat a child with sickle cell anemia?
To help your child manage sickle cell disease:Go to all doctor's visits and share any concerns or new symptoms.Make sure your child takes all prescribed medicines.Follow up with any recommended specialists to check for complications.Help your child avoid pain crisis triggers, such as extreme temperatures or stress.More items...
How does oxygen therapy help sickle cell anemia?
But the use of oxygen therapy in sickle cell disease is controversial because high levels of oxygen are known to suppress the formation of new red blood cells. This can worsen the anemia that is seen in these patients. Oxygen therapy is, therefore, only recommended when oxygen levels drop below a critical threshold.
Understanding Common Pain Associated with Sickle Cell Disease
Many patients with chronic diseases suffer pain as a component of the disease process. This is especially true for patients with sickle cell disease, with 90% of hospitalizations due to sickle pain.
MEASUREMENT OF PAIN AND RELIEF
For older children and adults, a verbal pain scale is quite helpful during periods of pain. This involves asking the patient to rate the pain from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst pain imaginable).
What is priapism in emergency room?
The goal of emergency room care is to assess the clinical problem, initiate a trial of oral or IV pain medications, assess the response, and decide with the patient whether or not hospitalization is necessary. ...
Can vasoocclusive pain be diagnosed?
It is not possible to diagnose a painful vaso-occlusive episode with a specific clinical finding or laboratory test. Due to multiple complications of sickle cell disease that present with pain, multiple tests may be done to “rule out” or make sure a patient does not have another complication.
What are the treatment recommendations for von Willebrand disease?
Treatment recommendations for von Willebrand disease (VWD), hemophilia A, β-thalassemia major (β-Thal), thrombotic thromobocytopenic purpura (TTP), idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) were also reviewed. Textbook recommendations were considered consistent with current standards of practice if they met all of the recommendations for each disorder ( Table S1 ). As shown in Table 7, with the exception of VWD, these disorders have incidence rates or prevalence rates significantly lower than that of SCD. Nonetheless, treatment recommendations consistent with generally accepted standards of care are given in 53% to 84% of texts. Overall, textbooks were significantly less likely to meet guidelines for both opioid and hydroxyurea therapy in SCD than treatment standards in all the other hematologic disorders reviewed (χ 2 > 4.07; P < .05).
What does VOC mean for morphine?
VOC indicates vaso-occlusive crisis ; SCD, sickle cell disease; and C-section, caesarian section.
How long does it take to take opioids for SCD?
Guideline recommendations for opioid use for VOCs in SCD. The 4 essential features of both guidelines are (1) rapid initiation of opioid therapy (within 15-30 minutes of arrival in the emergency department); (2) use of an adequate opioid starting dose; (3) frequent repeat doses of opioids (every 15-30 minutes) until pain is significantly improved;
Does hydroxyurea help with vaso-occlusive crisis?
Finally, hydroxyurea use to decrease the frequency of vaso-occlusive crises is completely defined only in 2 textbooks. Thus, most medical texts provide neither adequate information for the treatment or prevention of pain due to vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell disease nor reassurance of the unlikelihood of addiction in this population.
What are the effects of hydroxyurea on sclerosis?
Effects of therapy with hydroxyurea. Skeletal sickle cell anemia. Bone-within-bone appearance. Following multiple infarctions of the long bones, sclerosis may assume the appearance of a bone within a bone, reflecting the old cortex within the new cortex.
What fluids should be used for dehydration?
Intravenous fluids should be of sufficient quantity to correct dehydration and to replace continuing loss, both insensible and due to fever. Normal saline and 5% dextrose in saline may be used. Treatment must be in an inpatient setting. Pecker LH, Lanzkron S. Sickle Cell Disease.
