Medication
Fasting hypoglycemia is a type of hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, that occurs when the stomach is empty. Fasting hypoglycemia is diagnosed as a blood glucose level of less than 50mg/dL, according to the National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse.
Therapy
You may also receive a hormone called glucagon that helps raise your blood sugar level. Treatment will depend on the cause of the hypoglycemia. For example, if a medicine you take is causing hypoglycemia, healthcare providers may change or stop giving you the medicine. If hypoglycemia is caused by low hormone levels, you may need to take hormones.
Self-care
Hormonal deficiencies that cause fasting hypoglycemia are usually a problem in children rather than in adults. These deficiencies include decreased cortisol, growth hormone, epinephrine or glucagon. Hormone replacement therapy is usually prescribed as a treatment option.
Nutrition
What is fasting hypoglycemia?
What are the treatment options for hypoglycemia?
How is fasting hypoglycemia treated in children?

What can hypoglycemia be treated by?
How do I treat hypoglycemia? A mild case of hypoglycemia can be treated through eating or drinking 15-20g of fast acting carbohydrate such as glucose tablets, sweets, sugary fizzy drinks or fruit juice. Some people with diabetes may also need to take 15-20g of slower acting carbohydrate if the next meal is not due.
What is the first line treatment for hypoglycemia?
As the main counter-regulatory hormone to insulin, glucagon is the first-line treatment for severe hypoglycemia in insulin-treated patients with diabetes.
What is hypoglycemia How is it treated?
Hypoglycemia is a condition in which your blood sugar (glucose) level is lower than the standard range. Glucose is your body's main energy source. Hypoglycemia is often related to diabetes treatment. But other drugs and a variety of conditions — many rare — can cause low blood sugar in people who don't have diabetes.
How do they treat hypoglycemia without diabetes?
Non-diabetic hypoglycemia dieteating small meals regularly, rather than three large meals.eating every 3 hours.eating a variety of foods, including protein, healthful fats, and fiber.avoiding sugary foods.
Is insulin given for hypoglycemia?
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin continuously and with food. Some people have frequent and severe hypoglycemia despite medication adjustments. In these circumstances, your health care provider may recommend that you keep your blood sugar in a higher than usual range.
What are the three classic signs of hypoglycemia?
Initial signs and symptoms of diabetic hypoglycemia include: Looking pale (pallor) Shakiness. Dizziness or lightheadedness.
Is there medication for reactive hypoglycemia?
One study reports that certain people with reactive hypoglycemia may also benefit from taking antidiabetic drugs, such as metformin. These individuals include those who doctors suspect may have prediabetes. Metformin may help reduce symptoms, as prediabetes is a possible cause of this type of hypoglycemia.
How can I raise my blood sugar quickly?
Among the foods you can try for a quick blood sugar boost are:a piece of fruit, like a banana, apple, or orange.2 tablespoons of raisins.15 grapes.1/2 cup apple, orange, pineapple, or grapefruit juice.1/2 cup regular soda (not sugar-free)1 cup fat-free milk.1 tablespoon honey or jelly.15 Skittles.More items...•
What is the treatment for severe hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia is considered severe if you need help from someone to recover. For example, if you can't eat, you might need glucagon injection or intravenous glucose. In general, people with diabetes who are treated with insulin should have a glucagon kit for emergencies.
How to treat hypoglycemia?
Immediate treatment. If you have symptoms of hypoglycemia, do the following: Eat or drink 15 to 20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates. These are sugary foods without protein or fat that are easily converted to sugar in the body. Try glucose tablets or gel, fruit juice, regular — not diet — soft drinks, honey, and sugary candy.
How to prevent recurrent hypoglycemia?
Depending on the underlying cause, treatment may involve: Medications. If a medication is the cause of your hypoglycemia, your doctor will likely suggest changing or stopping the medication or adjusting the dosage. Tumor treatment.
What to do if you don't have glucagon?
If there's no glucagon kit available or you don't know how to use it, call for emergency medical help.
What to do if you have type 1 diabetes?
If you haven't been diagnosed with diabetes, make an appointment with your primary care doctor.
How to stabilize blood sugar?
Repeat these steps until the blood sugar is above 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Have a snack or meal. Once your blood sugar is normal, eating a snack or meal can help stabilize it and replenish your body's glycogen stores.
Can you fast if you have hypoglycemia?
If you don't have signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia during your initial visit with your doctor, he or she might have you fast overnight or longer. This will allow low blood sugar symptoms to occur so that he or she can make a diagnosis.
How to treat low blood sugar with a carbohydrate diet?
If your blood sugar is still below 70 mg/dl, eat another 15 grams of fast acting carbohydrate food. If you still do not feel better, call your doctor. Step3: Eat a meal or snack 30-60 minutes after treating low blood sugar.
How to treat low blood sugar?
How to treat a low blood sugar: Step 1: Check your glucose. If your glucose is between 51-70 mg/dl, eat or drink 15 grams of carbohydrate to raise glucose. If you your glucose is less than 50 mg/dl, take 30 grams of carbohydrate. Good sources of 15 grams fast acting carbohydrate are: Step 2: Wait 15 minutes, and check your glucose.
What is hypoglycemia in diabetes?
What is Hypoglycemia? Hypoglycemia, or low blood glucose, happens when blood glucose levels drop too low. For most people with diabetes this means a glucose less than 70 mg/dl. Hypoglycemia can be caused by skipping a meal or a snack, eating less than usual, taking too much diabetes medication, or more exercise than usual.
Why do people with hypoglycemia need to take extra care to check blood sugar frequently?
People with hypoglycemia unawareness need to take extra care to check blood sugar frequently. This is especially important prior to and during critical tasks such as driving. A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can sound an alarm when blood sugar levels are low or start to fall.
What is glucagon used for?
Glucagon is used to treat someone with diabetes when their blood sugar is too low to treat using the 15-15 rule.
What does it mean when your blood sugar is high?
Other causes of symptoms. Other people may start to have symptoms of hypoglycemia when their blood sugar levels are higher than 70 mg/dL. This can happen when your blood sugar levels are very high and start to go down quickly. If this is happening, discuss treatment with your diabetes care team.
Why is my blood sugar low?
One reason newer insulins are preferred over NPH and regular insulin is that they’re less likely to cause blood sugar lows , particularly overnight. Insulin pumps may also reduce the risk for low blood sugar. Accidentally injecting the wrong insulin type, too much insulin, or injecting directly into the muscle (instead of just under the skin), can cause low blood sugar.
How long does it take for blood sugar to rise?
Treatment—The "15-15 Rule". The 15-15 rule—have 15 grams of carbohydrate to raise your blood sugar and check it after 15 minutes. If it’s still below 70 mg/dL, have another serving. Repeat these steps until your blood sugar is at least 70 mg/dL.
How many carbs should a child have to fix low blood sugar?
Young children usually need less than 15 grams of carbs to fix a low blood sugar level: Infants may need 6 grams, toddlers may need 8 grams, and small children may need 10 grams. This needs to be individualized for the patient, so discuss the amount needed with your diabetes team.
How to get blood sugar back to normal?
This may be: Glucose tablets (see instructions) Gel tube (see instructions) 4 ounces (1/2 cup) of juice or regular soda (not diet) 1 tablespoon of sugar, honey, or corn syrup.
What is the term for the state of ketosis?
Your cells have to adapt to running on ketones for energy and not glucose. This state is called ketosis and it can come along with what is commonly called keto flu. Keto flu includes lightheadedness and headaches. These are two known symptoms of hypoglycemia. Which is logical, since hypoglycemia = low blood sugar.
What happens to blood sugar when you fast?
What happens to your blood sugar when you fast. Let’s get rid of the elephant in the room: fasting causes hypoglycemia. As in low blood sugar. When you fast, your body needs to transition from using glucose for energy to using ketones. Your cells have to adapt to running on ketones for energy and not glucose.
What happens if you eat too much after a heavy meal?
Reactive hypoglycemia happens typically a few hours after a heavy meal. What happens is that your body might produce too much insulin, lowering your blood sugar. Reactive hypoglycemia doesn’t happen overnight, it’s a condition that can mean that you’re at risk of developing diabetes.
How to get energized during fasting?
Hydrating is a huge component of fasting and it’s a go-to when feeling down. Drink green tea or coffee (black of course), might help you feel full or more energized. Get electrolytes, mainly sodium, potassium, magnesium. Simple salted water could do wonders, trust me. Have a vegetable broth.
What is the average blood sugar level for diabetics?
This amount may vary from person to person, the average value is around 70 mg/dl. It’s usually caused by mismatched medicine, food, drinks and exercise, which can result in really low blood sugar.
Why do I get lightheaded when I fast?
Lightheadedness can also come from low electrolytes, meaning low potassium and sodium levels. As your sodium levels decrease, the body tends to lower blood volume, which can add to the low blood sugar. I myself experienced lightheadedness on a 5 day fast.
Is keto flu hard?
Keto flu can be hard, as I said earlier if your body is not used to fasting. A friend of mine who never experimented with fasting tried a 5 day fast and stopped after 3 days. She was not prepared to fast physically and mentally, her body wasn’t used to it.
How did a nurse bring his diabetes into remission?
One nurse explains how he brought his type 2 diabetes into remission with a combination of intermittent fasting and walking after meals. He said that intermittent fasting ( OMAD fasting) for a week lowered his blood sugars. He was also following a keto diet plan. INTERMITTENT FASTING PDF.
Why does my body release insulin after eating?
For some reason, the body keeps releasing insulin even after you’re meal has digested. And this extra boost of insulin causes your body to fall below normal levels.
How long does it take to check glucose levels?
You have to drink a cold, syrupy (and nauseating) liquid, then wait at the doctor’s office, having your blood drawn multiple times, at 1-hour intervals to check your glucose levels.
Does intermittent fasting help with diabetes?
Another study shows how IF can improve insulin resistance. These fasting benefits are beneficial for anyone, but particularly people dealing with blood sugar issues and type 2 diabetes.
What is fasting hypoglycemia?
Fasting hypoglycemia is a type of hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, that occurs when the stomach is empty. Fasting hypoglycemia is diagnosed as a blood glucose level of less than 50mg/dL, according to the National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse. Symptoms of fasting hypoglycemia include inability to concentrate, lack of energy and headache.
Why does insulinoma raise insulin levels?
These tumors may raise insulin levels because there is not enough glucose to balance out this increased insulin. Treatment for insulinomas is complete removal of the tumor, according to Tufts University. Advertisement.
How long does it take for alcohol to deplete glycogen?
This process takes approximately 12 to 24 hours, after which the symptoms of fasting hypoglycemia become apparent.
How long does it take for alcohol to cause hypoglycemia?
This process takes approximately 12 to 24 hours, after which the symptoms of fasting hypoglycemia become apparent. In order to decrease the probability of fasting hypoglycemia as a result of alcohol intake, food should always be consumed with alcohol.
What causes hypoglycemia in the body?
Liver, heart and kidney disease can be underlying causes for hypoglycemia, according to the NDIC. In these diseased states, the process of gluconeogenesis, which is a metabolic pathway in the body that results in the creation of glucose, is hindered.
Can you have a headache while fasting?
It is a normal state when awakening from a night of sleep, after exercising or between meals; however, there are some medications and other underlying conditions that can cause fasting hypoglycemia.
Can aspirin cause hypoglycemia?
Some kinds of aspirin taken in large doses can also cause fasting hypoglycemia. When fasting hypoglycemia occurs as a result of medication, it is advised to either change the medication or dosage. Advertisement.
Symptoms of reactive hypoglycemia
While reactive hypoglycemia is different than hypoglycemia, they share similar symptoms, including:
What causes it?
While we know what causes hypoglycemia, the cause of reactive hypoglycemia remains a bit of a mystery, says Zumpano. “Alcohol and high sugar intake are potential triggers for some, but the exact cause is still unknown,” she notes.
Other ways to prevent reactive hypoglycemia
Using extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil or nut- or seed-based oils for cooking can deliver healthy fats to your body, says Zumpano. Use these to cook your lean meats or add to cooked vegetables and salads to make a healthy, delicious combo.
How does attention to fasting hyperglycemia help with diabetes?
Attention to fasting hyperglycemia coupled with appropriate individualization of treatment should improve the long-term outcome of individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes by reducing the risk of complications . Normalization of the fasting blood glucose, through whatever strategy, minimizes glucotoxicity and insulin resistance, ...
What insulin is used for hepatic glucose?
Hepatic glucose output and disposal in the fasting state may be controlled via bedtime administration of either an intermediate-acting insulin such as NPH or a long-acting true basal insulin such as insulin glargine. Attention to fasting hyperglycemia coupled with appropriate individualization of treatment should improve the long-term outcome ...
Why does fasting cause hyperglycemia?
Fasting hyperglycemia is a phenomenon that has been observed in essentially all individuals with diabetes and may be due to dysregulation of the normal circadian hormonal patterns resulting in increased hepatic glucose output.
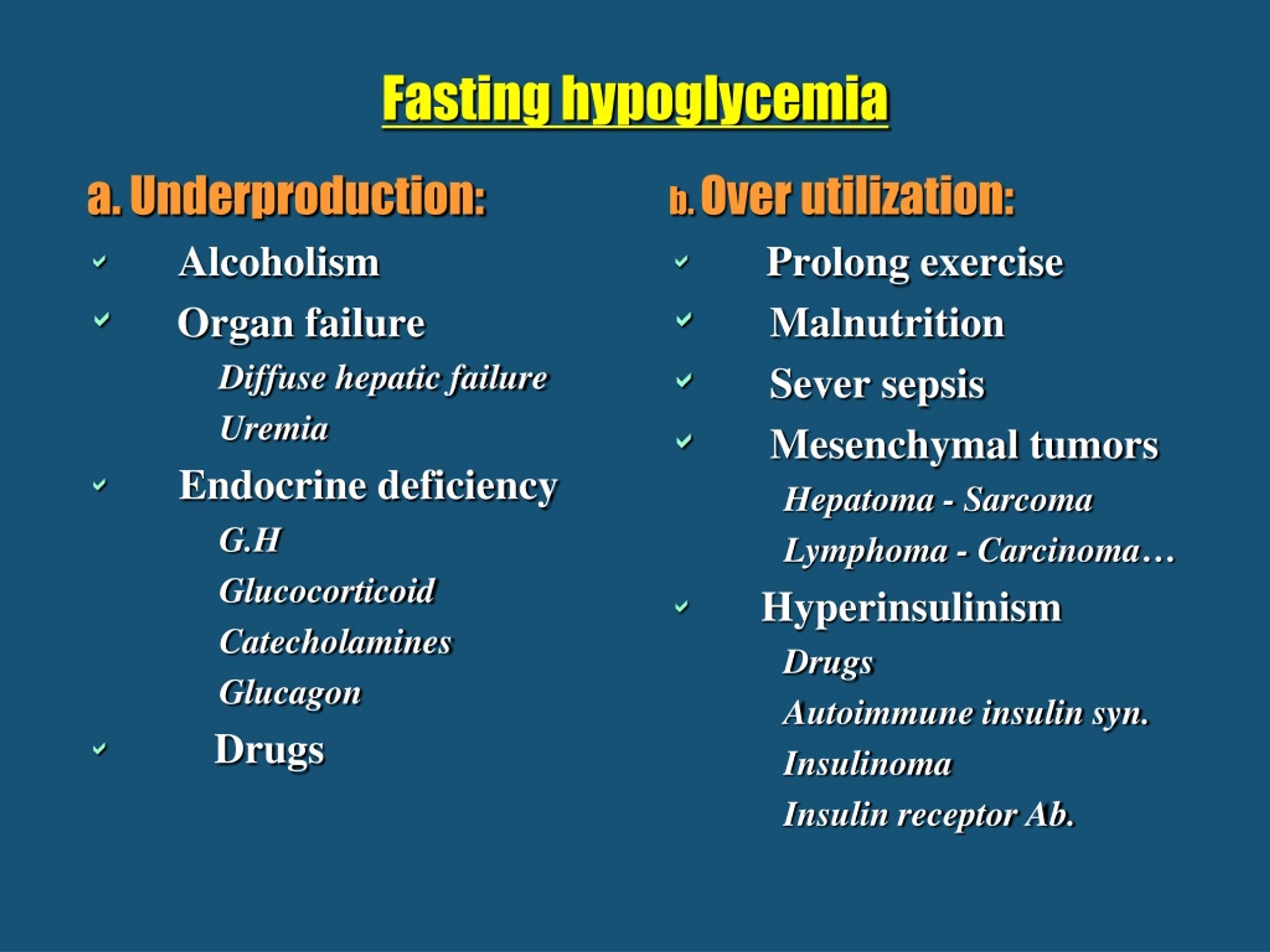
What are the conditions that can cause fasting hypoglycemia?
Alcohol. Exercise. Medical conditions such as liver disease, hypothyroidism, and tumors. Eating disorders or malnutrition. Stomach surgery or hemodialysis.
What happens if you take a medicine that causes hypoglycemia?
For example, if a medicine you take is causing hypoglycemia, healthcare providers may change or stop giving you the medicine. If hypoglycemia is caused by low hormone levels, you may need to take hormones.
How long does it take for blood sugar to go up after fasting?
After you have fasted for 8 hours, your blood sugar level is tested. You are then given a glucose drink. Your blood sugar level is checked after 1 hour and again after 2 hours. Healthcare providers look at how much your blood sugar level increases from the first check.
How long does it take for a person to have hypoglycemia?
Fasting hypoglycemia often happens after the person goes without food for 8 hours or longer. Reactive hypoglycemia usually happens about 2 to 4 hours after a meal. When your blood sugar level is low, your muscles and brain cells do not have enough energy to work well.
How many times can you test your blood sugar after fasting?
After you have fasted overnight, your blood sugar levels will be tested 2 times . For a 72-hour fasting test, you will not be given food for a period of up to 72 hours. During this time, healthcare providers will check to see if your blood sugar drops to a certain level. An oral glucose tolerance test may be done.
What is non diabetic hypoglycemia?
Non-diabetic hypoglycemia is a condition that causes the sugar (glucose) in your blood to drop too low. This can happen in people who do not have diabetes. The 2 types of non-diabetic hypoglycemia are fasting hypoglycemia and reactive hypoglycemia. Fasting hypoglycemia often happens after the person goes without food for 8 hours or longer.
How to control low blood sugar?
The following guidelines may help you keep your blood sugar levels under control. Eat 5 to 6 small meals each day instead of 3 large meals.
