
If a patient has a high-grade cytology (Pap test) result (i.e., HSIL) and an HPV test that is positive for HPV type 16, then treatment with a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) is preferred. A colposcopy with biopsy is not necessary to confirm the diagnosis first.
Can you get rid of HPV 16?
Cervarix is a vaccine that only protects against HPV strains 16 and 18, which primarily cause cervical cancer. Since the HPV vaccine is a preventative measure against HPV, a sexually transmitted disease, the vaccine is intended for young children before they become sexually active to ensure immunity.
What does a positive HPV 16 mean?
The HPV (human papilloma virus) results show that you are infected with a type of genital HPV virus that is associated with cervical cancer. Types 16 and 18 are the ones that are the causative agent in the vast majority of cervical cancers.
What to do if you have HPV?
Your health care provider may recommend more frequent screening if you:
- are HIV positive
- have a weakened immune system
- were exposed before birth to a medicine called diethylstilbestrol, (DES) which was prescribed to some pregnant women through the mid 1970s
- had a recent abnormal cervical screening test or biopsy result
- have had cervical cancer
What are my treatment options for HPV?
Some of the places you can go to recieve STI testing include:
- Planned Parenthood. STI testing is available at Planned Parenthood. ...
- Doctor’s office. For quick testing, you can schedule an appointment with your doctor, or visit your local urgent care center.
- Local health clinics. Most government-funded healthcare clinics offer free or low-cost STI testing for gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, and HIV. ...
- Pharmacy. ...
- At home. ...
How do I get rid of persistent HPV 16?
If your doctor decides to treat the abnormal cells, they may use one of these methods:Cryotherapy. This involves freezing the abnormal cells with liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide.Conization. This procedure removes the abnormal areas.Laser therapy. ... Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP).
Can you recover from HPV 16?
In most cases, your body can produce antibodies against the virus and clear the virus within one to two years. Most strains of HPV go away permanently without treatment. Because of this, it isn't uncommon to contract and clear the virus completely without ever knowing that you had it.
How long does it take to clear HPV16?
Abbreviation: HPV16, human papillomavirus type 16. Of the 33 women with redetection, 75.6% (95% CI, 58.0%–89.9%) of women cleared their second detection within 1 year and 87.8% (95% CI, 76.0%–96.9%) cleared within 3 years.
What does it mean to be HPV 16 positive?
What if I Test Positive for HPV 16 or 18 of the Cervix? Testing positive for HPV 16 or 18 doesn't mean you'll develop cervical cancer, but it does mean that any dysplasia found in a Pap test carries a higher risk of becoming a cancer.
Should I be worried if I have HPV 16?
HPV 16 is the most common high-risk type of HPV and usually doesn't result in any noticeable symptoms, even though it can bring about cervical changes. It causes 50 percent of cervical cancers worldwide.
How did I get HPV 16?
You can get HPV by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the virus. It is most commonly spread during vaginal or anal sex. It also spreads through close skin-to-skin touching during sex. A person with HPV can pass the infection to someone even when they have no signs or symptoms.
What are symptoms of HPV 16?
Other types, such as HPV-16 and HPV-18, don't cause warts but can lead to certain cancers....With oral HPV, symptoms may include:an earache.hoarseness.a sore throat that won't go away.pain when swallowing.unexplained weight loss.swollen lymph nodes.
How common is HPV 16?
RESULTS: The prevalence of HPV 16 in the study group was 65.3%, and the prevalence of HPV 18 was 33.3%. The prevalence of infection with both viruses was 26.9%. Overall survival at 5 years was 91% among women with HPV 18 and 96% among those without this virus type (p = 0.133).
Do I need a colposcopy if I have HPV?
If you test positive for HPV 16/18, you will need to have a colposcopy. If you test positive for HPV (but did not have genotyping performed or had genotyping and tested negative for 16/18), you will likely have a colposcopy.
What do I do if I test positive for high risk HPV?
If you got a positive HPV test and your Pap test was abnormal, your doctor will probably follow up with a colposcopy. Try to see a physician who specializes in this procedure. During a colposcopy, your doctor will look more closely at the cervix, vagina or vulva with a special microscope called a colposcope.
Should I be worried about high risk HPV?
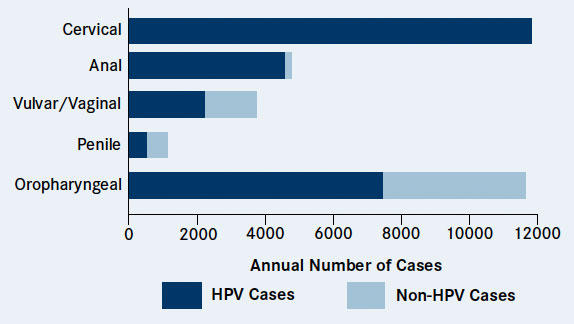
High-risk HPV can cause cervical cancer, penile cancer, anal cancer, and cancers of the mouth and throat. It's also a great idea to get the HPV vaccine. Getting the HPV vaccine can help prevent certain types of cancer and genital warts.
How do I boost my immune system to fight HPV?
To help boost your immune system so your body can fight HPV, you may consider quitting smoking, decreasing your stress level, and altering your diet. Keep in mind that HPV is very common and you are not alone.
How to treat HPV?
There is no treatment for the virus itself. However, there are treatments for the health problems that HPV can cause: 1 Genital warts can be treated by your healthcare provider or with prescription medication. If left untreated, genital warts may go away, stay the same, or grow in size or number. 2 Cervical precancer can be treated. Women who get routine Pap tests and follow up as needed can identify problems before cancer develops. Prevention is always better than treatment. For more information visit www.cancer.org#N#external icon#N#. 3 Other HPV-related cancers are also more treatable when diagnosed and treated early. For more information visit www.cancer.org#N#external icon
Is Pap test better than treatment?
Women who get routine Pap tests and follow up as needed can identify problems before cancer develops. Prevention is always better than treatment. For more information visit www.cancer.org. . Other HPV-related cancers are also more treatable when diagnosed and treated early. For more information visit www.cancer.org.
Can genital warts be treated?
Genital warts can be treated by your healthcare provider or with prescription medication. If left untreated, genital warts may go away, stay the same, or grow in size or number. Cervical precancer can be treated. Women who get routine Pap tests and follow up as needed can identify problems before cancer develops.
How long does it take to get clear of HPV?
Be diligent about well-woman checks and regular pap smears. In most cases, women are clear of HPV within about eight- to 24-months. So your positive test may mean nothing more than, “take care of yourself, eat well, exercise and get good sleep so your immune system can do its job well.”.
What happens if you test positive for HPV?
And, we also know that while HPV is a common link in those that have cervical cancer, most cases of HPV DO NOT become cancerous.
How long does it take for HPV to run?
In 90% to 95% of those cases, HPV runs its course, the immune system fights it off within one to two years, and that’s that. This is most common for women in their teens and in their 20s. For others, the virus is more persistent and it will continue to multiply and build in their system until it’s ultimately detectable via screening tools.
Can HPV be detected with a pap smear?
A chronic case of HPV often shows up in the form of an abnormal pap smear, which will lead to further investigation and treatment. There is nothing different about your pap smear when we test for HPV – we use the same cell sample that we do to look for cervical cell abnormalities.
Does condom help HPV?
So, while using a condom can help to prevent the spread, it’s not 100% effective in preventing the transmission of HPV. There are vaccines out now that help the immune system develop immunity to some of the most common and high-risk strains of HPV. These are recommended for teens and women into their mid-20s.
Can you test positive for HPV if you are monogamous?
As testing methods improve, there’s a chance you could test positive for HPV, even if you’re over the age of 30 and in a completely monogamous relationship.
Is a pap smear good for cervical cancer?
The good news is that pap smears have been amazingly effective at detecting – and stopping – the most dangerous strains of HPV in their tracks, preventing the development of cervical cancer. Developing a comfortable rapport with your OB/GYN and observing routine well-woman visits and pap smear schedules is the best way forward for women with – or without – HPV.
How to check for HPV?
If a woman tests positive for cervical HPV infection but has a normal Pap smear, the doctor may do one of two things: 4 1 Schedule another round of tests in 12 months. If the results are normal, you can return to normal screening. If they are not, additional testing will be needed. 2 Perform an HPV test to identify the two high-risk HPV strains (HPV 16 and HPV 18) that account for 70% of all cervical cancers. 5 If the results are negative (meaning you have not been infected with these specific viruses), you can be retested in 12 months as a safeguard. If the results are positive, additional testing will be needed.
How long does it take for HPV to clear?
What to Do If You Have HPV. In most cases, the immune system will be able to clear human papillomavirus (HPV) on its own within 18 to 24 months, usually with no long-term consequences, though that is not always the case. 1 . Because there are no drugs available to treat an active HPV infection, HPV treatment involves resolving HPV symptoms ...
What is the best treatment for warts?
Cryotherapy (freezing warts with liquid nitrogen) Electrocautery (using electricity to burn warts away) Surgery. Laser therapy. Trichloracetic acid (applied topically to gradually remove a wart) Genital warts should never be considered normal, and you should not treat them at home without first seeing a doctor.
What is the treatment for dysplasia?
For persons with moderate- to high-grade dysplasia, treatment would involve the removal of affected tissue using either a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), cone biopsy, cryotherapy, or other surgical techniques. 11 . It is important to remember that dysplasia is not cancer.
Can you treat genital warts at home?
Genital warts should never be considered normal, and you should not treat them at home without first seeing a doctor. While most warts will turn out to be benign, others may require further investigation, particularly if they are bleeding, inflamed, spreading, resistant to treatment, or have an atypical appearance.
Is HPV a long term problem?
There are typically no long-term consequences associated with HPV, infection does come with risk. Learn more about HPV infection below. 1
Does Verywell Health use peer reviewed sources?
Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
What is HPV 16 and 18?
Persistent HPV 16 and 18 infections markedly increase in the risk of cervical, vaginal, vulvar, and penile cancers. Alamy. HPV is short for human papillomavirus, a very common virus that infects nearly everyone at some point. There are many different strains of the virus, each identified with a number. HPV 16 and 18 are high-risk types known ...
What age can you get the HPV?
The CDC recommends that all boys and girls get the HPV vaccine at age 11 or 12. However, it can be given through age 26 in women and through age 21 in men.
How long does it take for HPV to clear?
If you get diagnosed with HPV, and everything else tests okay, then most likely the HPV will clear on its own within one to two years, if you don't have a suppressed immune system.
Is HPV more common in men than women?
Both oral HPV infection and HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer are much more common among men than women. In addition, oral HPV 16 infection is six times more common in men than women ages 18 to 69, according to a report published in November 17 in Annals of Internal Medicine. ( 2)
Can you shed HPV from your cervix?
Even though HPV is common, many women will never know they’ve contracted it, since HPV-infect ed cells are often shed from the cervix with no intervention.
Is HPV a STD?
It's the most commonly diagnosed sexually transmitted disease ( STD) in the United States and abroad. HPV also causes common skin warts, which are not considered STDs. In spite of its ubiquity, though, HPV is widely misunderstood.
Does HPV 16 cause cancer?
HPV 16 and 18 have been shown to significantly increase the risk of cervical cancer as well as genital cancers.
What age should I get tested for HPV?
USPSTF screening recommendations apply to persons with a cervix at average risk, defined as those with no previous cervical cancer or high-grade precancer, not currently under close follow-up for a recent abnormal result, not immunocompromised (e.g., persons with HIV), and who had no exposure to diethylstilbestrol in utero. Among these persons, screening should be performed starting at age 21 years and continue through age 65 years. Testing can be performed using either conventional or liquid-based cytologic tests (i.e., Pap tests). For persons aged ≥30 years, screening can include FDA-cleared tests for high-risk, oncogenic types of HPV. For cytopathologic testing, clinics should use CLIA-certified laboratories using acceptable terminology (Bethesda 2001 or LAST terminology) ( 1239 ).
What is HPV test?
Positive cytology and HPV tests are markers of cervical precancerous lesions, which often do not cause symptoms until they become invasive. Appropriate follow-up is essential to ensure that cervical cancer does not develop.
How long does it take to follow up a negative HPV test?
If a patient has a minimally abnormal test result (i.e., negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy HPV positive, ASC-US HPV positive, LSIL, or HPV positive) that was preceded by a negative screening HPV test or cotest within the past 5 years, follow-up in 1 year instead of colposcopy is recommended (a negative HPV test or cotest performed during follow-up of abnormal results would not similarly reduce risk).
How can cervical cancer be prevented?
Cervical cancer can be prevented with regular screening tests, like the Pap test (cytology) and HPV tests. Those at average risk should start getting cytology tests at age 21 years.
What happens if you have a positive HPV test?
An abnormal cytology test or a positive HPV test can cause short-term anxiety, stress, fear, and confusion, possibly decreasing the patient’s ability to absorb and retain information and acting as a barrier to follow-up care ( 1258 – 1261 ). A positive HPV test might elicit concerns about partners, worries about disclosure, and feelings of guilt, anger, and stigmatization ( 1260 ). Providers should frame HPV positivity in a neutral, nonstigmatizing context and emphasize its common, asymptomatic, and transient nature. Providers also should emphasize that HPV infections often are shared between partners but it is often not possible to know the origin of an HPV infection; HPV tests might become positive many years after initial exposure due to reactivation of latent infections in both male and female partners. Having an HPV infection should not raise concerns about a male partner’s health ( 1262 ). Providers should communicate the meaning of both the cytology and HPV test results to patients at screening.
What is the best way to obtain satisfactory cytology results?
Health care facilities that train providers on cytology test collection and use simple quality assurance measures are more likely to obtain satisfactory test results (as determined by the laboratory).
How long after menstruation should you do a cytology test?
A conventional cytology test (in which the sample is smeared onto a dry slide) should ideally be scheduled for 10–20 days after the first day of menses. Liquid-based cytology can be performed at any time during the menstrual cycle.
What happens if you get a positive HPV test?
If you get a positive HPV test, your physician has detected one or more high risk strains of the virus on the Pap test of your cervix. If the virus stays with you for a long time, it can cause cell changes that can lead to several types of cancer.
What happens if HPV comes back negative?
Once your HPV tests come back negative, continuing with regular Pap and HPV tests mean any abnormalities that develop later can be found and treated before they become cancer.
How many people have HPV?
Right now, 80 million people in the United States have HPV. What you need to know is that in most cases, your immune system clears the virus before any health problems develop. The risk for cancer increases if your body cannot fight off the virus for some reason, and it stays in your system.
Can your partner catch HPV?
Your partner can catch it from you. However, he or she has probably already been exposed by you or someone else. If your partner is a woman, she should be sure to follow screening guidelines and keep up with her own Pap and HPV testing so if a problem does develop, it is found early.
Is HPV a surprise?
I have HPV, now what? A positive HPV test can be a surprise, but knowing the facts can give you relief. Four out of five people will get it at some point. BY Heather Alexander. We all hope the awkwardness is over after we get our Pap and HPV tests. So hearing that you have tested positive for HPV can be a blow.
How long does it take to recover from HPV?
Like Mendelsohn, the large majority of people with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer return to relatively good health within a year of completing treatment, Dr. Yom said.
What was the treatment for cancer in the early 2000s?
As a consequence, by the early 2000s, surgery had largely been supplanted by high-dose radiation therapy coupled with chemotherapy. This approach was as effective in treating the cancer, but it didn’t carry the baggage of disfigurement and fatality.
What is the ECOG 3311 trial?
Several trials have also tested deintensification approaches involving robotic surgery. In a trial called ECOG 3311, led by Dr. Ferris, all trial participants initially underwent TORS. The intensity of any additional treatment they received was based on factors—such as size of the original tumor or extent of cancer in neck lymph nodes—that have been shown to predict whether the cancer is likely to spread or return.
What was Mendelsohn's tumor?
Mendelsohn’s tumor was in his tonsils, the most common site of oropharyngeal cancer. The burns in his throat were the result of the radiation therapy he underwent as part of his treatment. Before having radiation therapy, Mendelsohn underwent surgery to remove cancerous lymph nodes in his neck.
Is HPV related oropharyngeal cancer?
Therein lies the rub of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, said Robert Ferris, M.D., Ph.D., the director of the UPMC Hillman Cancer Center in Pittsburgh, who specializes in treating head and neck cancers. The prognosis is excellent but, for some, the treatment can have a detrimental impact on their quality of life.
Can immune checkpoint inhibitors treat cancer?
Several immune checkpoint inhibitors are already approved to treat people with advanced forms of certain head and neck cancers, and other types of immunotherapy drugs have also shown promise for HPV- related cancers . An electron micrograph of HPV particles.
Is Mendelsohn's cancer positive?
Mendelsohn’s cancer was HPV positive and now, at the age of 51, although he continues to experience some problems related to the treatments he received, he is largely healthy—and thriving. He runs his family business and is very active in the cancer advocacy community.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
Prescriptions
- Genital warts and anal warts are caused by human papillomavirus. There are roughly 40 different low-risk HPV types that can cause genital warts, the vast majority of which are caused by HPV6 and HPV11.8 The HPV types that cause genital warts rarely cause cancer. Even so, they can be itchy, painful, or unsightly.8 Most genital warts will resolve on their own without treatment withi…
Surgery and Specialist-Driven Procedures
- Specialist procedures, including surgery, are sometimes used to treat genital warts that are not responsive to at-home treatments. The same applies to HPV-related changes in cells that can lead to cancer, referred to as dysplasia.
Vaccination
- Scientists have long been trying to develop a therapeutic vaccine that can prevent high-risk HPV from causing cancer. Despite advances in research, there are currently no therapeutic HPV vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).21 This doesn't mean that the current preventive vaccine, called Gardasil-9, doesn't play a role in people who already have HPV…
Summary
- There is no cure for human papillomavirus (HPV). The treatment is instead focused on managing the conditions that HPV can cause. This includes genital and HPV warts. These conditions may be treated with topical prescription drugs or removed with procedures like cryotherapy, laser therapy, electrocautery, and surgery. There are also procedures used ...
A Word from Verywell
- While an HPV diagnosis can be distressing, it helps you catch any problems before they become serious or even life-threatening. By and large, treatments for HPV-associated conditions have few complications. Many of the treatments are covered, at least in part, by health insurance. Patient assistance and co-pay assistance programsare also available to reduce your out-of-pocket cost…