
Medication
You can help prevent the spread of germs that cause respiratory illnesses like influenza by:
- Covering your nose and mouth with a tissue when you cough or sneeze. Throw the tissue in the trash after you use it.
- Washing your hands often with soap and water, especially after you cough or sneeze. ...
- Avoiding touching your eyes, nose or mouth. ...
- Trying to avoid close contact with sick people.
- Staying home from work or school if you are sick.
Therapy
Interferons produced to fight the rhinovirus had been beating back the flu. A number of viruses trigger the interferon response, and it’s possible that any of them could make the body put up stiff resistance to a new infection for some period of time.
Nutrition
These groups include:
- adults over age 65
- children under 5 years old
- young adults and children under age 19 who are receiving long-term aspirin (Bufferin) therapy
- people with compromised immune systems (due to a disease such as AIDS)
- pregnant women
- people with chronic illnesses such as asthma, heart disease, diabetes mellitus, or neuromuscular disease
What are the measures to prevent the propagation of H1N1?
What are the emergency warning signs?
- Fast breathing or trouble breathing
- Bluish skin color
- Not drinking enough fluids
- Not waking up or not interacting
- Being so irritable that the child does not want to be held
- Flu-like symptoms improve but then return with fever and worse cough
- Fever with a rash
How does interferon protect us from H1N1?
How contagious is H1N1?
What are the first symptoms of H1N1?

What was the treatment for H1N1 virus?
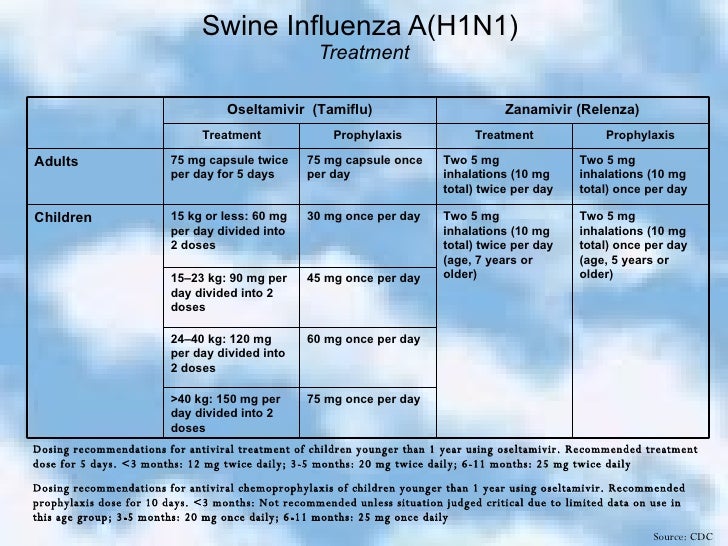
Drugs indicated for treatment of H1N1 influenza A virus include neuraminidase inhibitors (ie, oseltamivir and zanamivir). Oseltamivir and zanamivir inhibit neuraminidase, which is a glycoprotein on the surface of influenza virus that destroys an infected cell's receptor for viral hemagglutinin.
How long does it take for H1N1 to go away?
The symptoms of swine flu (H1N1), including fever, chills, cough, and body aches, last about eight days, on average. Some symptoms may continue longer than that. However, most people can go back to school or work 24 hours after their fever goes away completely without using medications that reduce fever.
What are the chances of surviving H1N1?
H1N1 influenza (swine flu) tends to cause high morbidity but low mortality rates (1%-4%).
Was there a vaccine for the H1N1 virus?
The 2009 influenza A (H1N1) monovalent vaccine was released in mid October. The immunization series consisted of 2 doses for children younger than 10 years, consisting of an initial dose and a booster to be administered several weeks later. Adults and children 10 years and older received a single dose.
Can H1N1 be treated at home?
Most people with flu, including H1N1 flu (swine flu), require only symptom relief. Supportive care such as drinking liquids, taking pain relievers for fever and headache, and resting may be helpful.
Is H1N1 still around in 2021?
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed on November 5, 2021, three human infections with novel influenza A viruses occurred during the 2020-21 influenza season. However, no human-to-human transmission was associated with these 'swine flu' patients.
Is H1N1 still around?
The A/H1N1pdm09 virus is now one of the seasonal flu viruses that circulate each winter. If you've had flu in the last few years, there's a chance it was caused by this virus.
Is H1N1 life threatening?
Severe cases of swine flu can be fatal. Most fatal cases occur in those with underlying chronic medical conditions, such as HIV or AIDS. The majority of people with swine flu recover and can anticipate a normal life expectancy.
How many people died from H1N1 in 2009?
284,000Swine flu pandemic / Number of deaths
Are antibiotics effective against the H1N1 virus?
Swine flu (H1N1) and other types of influenza are caused by viruses, so antibiotics do not treat these illnesses.
Who made the H1N1 vaccine?
Injectable H1N1 vaccines are manufactured by CSL, Sanofi Pasteur or Novartis. They are inactivated H1N1 virus vaccines used for immunization of individuals 6 months of age and older against influenza disease caused by H1N1 2009 virus.
Was there a vaccine for SARS?
"There Was No Vaccine For Sars Or Mers.
How to care for H1N1 patients?
Recommended measures for care of patients with suspected or confirmed H1N1 influenza include the following: Place patients in a single-patient room with the door kept closed. An airborne-infection isolation room with negative-pressure air handling can be used, if available .
How to control H1N1?
While in home isolation, patients and other household members should be given infection control instructions, including frequent hand washing with soap and water. Use alcohol-based hand gels (containing at least 60% alcohol) when soap and water are not available and hands are not visibly dirty. Patients with H1N1 influenza should wear a face mask when within 6 feet of others at home.
Why was H1N1 needed for 2009/2010?
A separate seasonal influenza vaccine was needed for the 2009/2010 influenza season because it was too late to incorporate the new strain into the regular influenza vaccine already in production. Now H1N1 is a component of the trivalent and quadrivalent influenza vaccines.
What to do when H1N1 is confirmed in a community?
The CDC recommends the following actions when human infection with H1N1 influenza (swine flu) is confirmed in a community [ 1] : Household contacts who are not ill. Remain home at the earliest sign of illness. Minimize contact in the community to the extent possible.
What should a patient wear to prevent conjunctival exposure?
Personnel providing care to or collecting clinical specimens from patients should wear disposable nonsterile gloves, gowns, and eye protection (eg, goggles) to prevent conjunctival exposure.
How to help a patient with respiratory infection?
Encourage patients to wash their hands frequently and to follow respiratory hygiene practices. Cups and other utensils used by the ill person should be washed with soap and water before use by other persons.
How to seek medical care?
To seek medical care, patients should contact their health care providers to report illness (by telephone or other remote means) before seeking care at a clinic, physician's office, or hospital.
What are the symptoms of H1N1?
Symptoms. The signs and symptoms of flu caused by the H1N1 virus are similar to those of infections caused by other flu strains and can include: Fever, but not always. Chills. Cough. Sore throat. Runny or stuffy nose. Watery, red eyes. Body aches.
Where does H1N1 enter the body?
Influenza viruses such as H1N1 infect the cells that line your nose, throat and lungs. The virus enters your body when you inhale contaminated droplets or transfer live virus from a contaminated surface to your eyes, nose or mouth.
What to do if you have the flu while pregnant?
Call your doctor, however, if you have flu symptoms and you're pregnant or you have a chronic disease, such as asthma, emphysema, diabetes or a heart condition, because you have a higher risk of flu complications. If you have emergency signs and symptoms of the flu, get medical care right away. For adults, emergency signs and symptoms can include: ...
Treatment Is Important for High Risk Groups
People in high risk groups should talk to their health care provider as soon as possible if they think they may have the flu because they have a greater chance of getting serious flu complications than other persons.
Side Effects of Flu Antiviral Drugs
The most common side effects of oseltamivir (Tamiflu®) are nausea and vomiting, which can also be symptoms of the flu. Nausea and vomiting can be minimized by taking the medication with food.
Treatment May Be Needed Even if Test Results are Negative
Your health care provider may diagnose you with flu based on your symptoms and their clinical judgment or they may choose to use an influenza diagnostic test. Health care providers can use rapid flu tests (15 minutes or less) to test a specimen from your nose or throat in their offices.
What are the health conditions that H1N1 has caused?
This includes pregnancy, diabetes, heart disease, asthma and kidney disease. In one study, fifty-seven percent of children who had been hospitalized as a result of 2009 H1N1 have had one or more “higher risk” medical conditions.
What is the 2009 H1N1?
What is 2009 H1N1 (swine flu)? 2009 H1N1 (sometimes called “swine flu”) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new virus was first detected in people in the United States in April 2009.
How did the 2009 H1N1 virus spread?
Flu viruses are spread mainly from person to person through coughing, sneezing or talking by people with influenza. Sometimes people may become infected by touching something – such as a surface or object – with flu viruses on it and then touching their mouth or nose.
What are the symptoms of the 2009 H1N1 virus?
The symptoms of 2009 H1N1 flu virus in people include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, body aches, headache, chills and fatigue. Some people may have vomiting and diarrhea. People may be infected with the flu, including 2009 H1N1 and have respiratory symptoms without a fever.
What are the complications of H1N1?
This includes pregnancy, diabetes, heart disease, asthma and kidney disease.
Can you work with H1N1?
Employees who are well but who have an ill family member at home with 2009 H1N1 flu can go to work as usual. These employees should monitor their health every day, and take everyday precautions including covering their coughs and sneezes and washing their hands often with soap and water, especially after they cough or sneeze. If soap and water are not available, they should use an alcohol-based hand rub. * If they become ill, they should notify their supervisor and stay home. Employees who have an underlying medical condition or who are pregnant should call their health care provider for advice, because they might need to receive influenza antiviral drugs. For more information please see General Business and Workplace Guidance for the Prevention of Novel Influenza A (H1N1) Flu in Workers.
Did cheetahs get H1N1?
In addition, 2009 H1N1 virus infection was reported in a cheetah in the United States. CDC is working closely with domestic and international public and animal health partners to continually monitor reports of 2009 H1N1 in animals and will provide additional information to the public as it becomes available.
What antiviral treatment is needed for 2009 H1N1?
All hospitalized patients with suspected or confirmed 2009 H1N1 should receive antiviral treatment with a neuraminidase inhibitor- either oseltamavir or zanamavir. Moderately ill patients, especially those with risk factors for severe illness, and those who appear to be getting worse can also benefit from neuraminidase inhibi tors.
Can you mix oseltamivir with syrup?
However, there are ample supplies of children's oseltamivir capsules, which can be mixed with syrup at home. Pharmacies can also compound adult oseltamivir capsules into a suspension for treatment of ill infants and children. Additional information on compounding can be found at: http://www.cdc.gov/H1N1flu/pharmacist/.
What is the WHO recommendation for zanamivir?
This recommendation applies to all patient groups, including pregnant women, and all age groups, including young children and infants. For patients with underlying medical conditions that increase the risk of more severe disease, WHO recommends treatment with either oseltamivir or zanamivir.
Do pregnant women need antiviral treatment?
Pregnant women are included among groups at increased risk, and WHO recommends that pregnant women receive antiviral treatment as soon as possible after symptom onset. At the same time, the presence of underlying medical conditions will not reliably predict all or even most cases of severe illness.
Does oseltamivir cause pneumonia?
Evidence indicates that oseltamivir, when properly prescribed, significantly decreases risk of pneumonia (a leading cause of death for both pandemic and seasonal influenza) and the need for hospitalization. In the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, oseltamivir-resistant strains were observed in a small number of patients ...
Is Peramivir a Phase 3 drug?
Peramivir, an investigational, intravenous neuraminidase inhibitor in Phase 3 clinical trials, has been used successfully in adults and children under an emergency investigational new drug program in the United States. It was well tolerated and associated with recovery in the majority of patients hospitalized with severe H1N1 infection.
Is Baloxavir marboxil approved for H1N1?
Baloxavir marboxil is a new antiviral agent approved for the treatment of uncomplicated conventional influenza. Whether it would be an appropriate choice for the 2007-2009 pandemic H1N1 strain is unknown. References. CDC.
Is oseltamivir resistant to H1N1?
In the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, oseltamivir-resistant strains were observed in a small number of patients (especially among strains bearing the H275Y mutation). Most oseltamivir resistance occurred in severely immunocompromised patients with prior exposure to o seltamivir. [ 38]
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Specialist to consult
Complications
- The H1N1 flu, commonly known as swine flu, is primarily caused by the H1N1 strain of the flu (influenza) virus. H1N1 is a type of influenza A virus, and H1N1 is one of several flu virus strains that can cause the seasonal flu. Symptoms of the H1N1 flu are the same as those of the seasonal flu. In the spring of 2009, scientists recognized a particular strain of flu virus known as H1N1. Th…
Prevention
- The signs and symptoms of flu caused by the H1N1 virus are similar to those of infections caused by other flu strains and can include: 1. Fever, but not always 2. Chills 3. Cough 4. Sore throat 5. Runny or stuffy nose 6. Watery, red eyes 7. Body aches 8. Headache 9. Fatigue 10. Diarrhea 11. Nausea and vomiting Flu symptoms develop about one to three days after you're exposed to the …