
Healthline.com
1. Yogurt...
2. Probiotics...
3. Garlic...
4. Hydrogen peroxide...
5. Tea tree oil...
6. Breathable cotton underwear...
7. Boric acid...
8. Don't douche...
Learn More...Medicalnewstoday.com
1. Know when to see a doctor...
2. Know how sex can cause bacterial vaginosis...
3. Use safe hygiene practices...
4. Try a probiotic...
5. Apple cider vinegar...
6. Garlic...
7. Boric acid...
8. Tea tree oil...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. Yogurt...
2. Apple Cider Vinegar...
3. Cold Compress...
4. Garlic...
5. Boric Acid...
6. Chamomile...
7. Hydrogen Peroxide...
8. Tea Tree Oil...
Learn More...Tinyqualityhomes.org
1. Cold Compress...
2. Yogurt...
3. Garlic...
4. Echinacea...
5. Hydrogen Peroxide...
6. Maintain Good Hygiene...
7. Tea Tree Oil...
8. Apple Cider Vinegar...
Learn More...What is Gardnerella and why does it affect me?
Gardnerella vaginalis is the specific type of bacteria strain that causes a vaginal infection on the female genital tract, called bacterial vaginosis or simply, BV. The bacteria is usually harmless, however when they start to multiply, they may cause some serious health symptoms. Gardnerella vaginalis infection produces a grayish or yellowish discharge with a fishy vaginal odor, which intensity may increase after washing the area with alkaline soaps.
Is Gardnerella a sexually transmitted disease?
Gardnerella is basically a kind of gram variable bacteria and causes Gardnerella Vaginalis. It is a disease usually found in women and it can be sexually transmitted to the partner.but it doesnot cause any complications to the partner. You do need to see a doctor as he will see through test whether you actually have it or not.
How to treat and cure vaginitis?
Yeast infection (vaginal)
- Diagnosis. Ask questions about your medical history. ...
- Treatment. Treatment for yeast infections depends on the severity and frequency of your infections. ...
- Alternative medicine. No alternative medicine therapies have been proved to treat vaginal yeast infections. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
How to treat bacterial vaginosis naturally at home?
How to use garlic as one of the strongest home remedies for bacterial vaginosis:
- Make a mixture of some drops of garlic oil with a half teaspoon of coconut and vitamin E oil. ...
- Add garlic to your cooking daily as well as consume few cloves of garlic on a daily basis.
- Take garlic supplementary pills after consulting the doctor.
See more

What is the best treatment for Gardnerella?
Metronidazole and clindamycin are the preferred medications used to treat Gardnerella infections.
Why do I keep getting Gardnerella vaginitis?
Not having enough lactobacilli bacteria causes your vaginal PH to increase to 4.6 or more, so that your vagina isn't acidic enough. In this environment, Gardnerella starts to multiply, and other bacteria begin to cling to the Gardnerella bacteria and grow, too.
Does Gardnerella require treatment?
Asymptomatic Gardnerella colonization does not need to be treated as nearly 30% of cases resolve spontaneously. All symptomatic patients need treatment but despite treatment, recurrences are common. These patients need to be followed by the nurse practitioner until all symptoms have disappeared.
Does Gardnerella vaginitis go away on its own?
What Happens. Bacterial vaginosis often clears up on its own. But in some women it doesn't go away on its own. And for many women it comes back after it has cleared up.
How serious is Gardnerella?
If left untreated, the infection can make you more susceptible to contracting other STIs including HIV, Chlamydia and Gonorrhoea. In women, Gardnerella can lead to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) and can also cause some complications in pregnancy, including premature labour and delivery.
How long does it take for Gardnerella to go away?
Generally, treatment with an oral antibiotic lasts about 7 days,, or 5 days for the ointments.
What happens if Gardnerella is left untreated?
If Gardnerella is left untreated, there is an increased risk of getting other STIs, including HIV. A long term infection in pregnant women can cause premature rupture of membranes, preterm labour and delivery, along with a range of other potentially dangerous complications.
How did I get Gardnerella vaginosis?
Risk factors that seem to increase the likelihood of bacterial vaginosis include a history of multiple sex partners, a sexual relationship with a new partner, cigarette smoking, vaginal douching and the use of the intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD).
How do you prevent Gardnerella infection?
Steps that might lower your risk of BV include:Keeping your vaginal bacteria balanced. Use warm water only to clean the outside of your vagina. ... Not douching. Douching upsets the balance of good and harmful bacteria in your vagina. ... Not having sex. ... Limiting your number of sex partners.
Is gardnerella same as BV?
Bacterial vaginosis is a vaginal condition that results from an overgrowth of normal bacteria in the vagina. The condition was formerly referred to as Gardnerella vaginitis, after the bacteria that were believed to cause the condition.
Is gardnerella a yeast infection?
The condition used to be referred to as Gardnerella vaginitis; because Gardnerella is a type of bacteria that sometimes causes the infection. While symptoms are not present in about half of women with bacterial vaginosis, those who do experience symptoms will have vaginal discharge, usually with an unpleasant odor.
Can I get metronidazole over the counter?
No, you cannot buy metronidazole over the counter because you need a prescription to buy it.
How to treat bacterial vaginosis?
Doctors commonly treat bacterial vaginosis with metronidazole ( Flagyl or MetroGel-Vaginal) or clindamycin ( Cleocin ). Either can be taken by mouth or applied as a vaginal cream or gel. However, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that all pregnant women with symptoms be treated with oral medications because the medications are safe and work better than vaginal creams or gels. Studies show that a seven-day treatment with oral metronidazole or a five-day treatment with metronidazole vaginal gel is equally effective in non-pregnant women. Clindamycin vaginal cream is slightly less effective than either type of metronidazole.
What are the risk factors for bacterial vaginosis?
Risk factors that seem to increase the likelihood of bacterial vaginosis include a history of multiple sex partners, a sexual relationship with a new partner, cigarette smoking, vaginal douching and the use of the intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD).
What does it mean when your vagina smells fishy?
In others, it causes an unpleasant "fishy" vaginal odor and a yellow or white vaginal discharge. For some women, these symptoms are especially bothersome during or after intercourse. The discharge seen in bacterial vaginosis tends to be thinner than the "cheesy," thick discharge seen in vaginal yeast (Candida) infections.
Why is bacterial vaginosis considered to be sexually transmitted?
Doctors are not exactly sure why bacterial vaginosis develops. Because it occurs more commonly in people who are sexually active, bacterial vaginosis is considered by some to be sexually transmitted. However, bacterial vaginosis also occurs in people who either are not sexually active or have been in long-term relationships with just one person.
What are some personal hygiene habits?
Personal hygiene habits, such as douching and your use of feminine deodorants. Whether you wear tightly fitting undergarments. Whether you use tampons. Your doctor also may ask if you have any other diseases, such as diabetes, or if you have used antibiotics recently.
Can bacterial vaginosis cause premature labor?
Bacterial vaginosis often occurs during pregnancy. It may cause premature labor and delivery, premature rupture of membranes, and postpartum uterine infections. This is why pregnant women with a history of premature labor or other complications may be checked for bacterial vaginosis even when they don't have any symptoms.
Should women be tested for bacterial vaginosis?
All women with symptoms of bacterial vaginosis should be treated. Some women also should be screened for bacterial vaginosis even if they don't have symptoms. Pregnant women who are at high risk of preterm labor and delivery should be tested for bacterial vaginosis and considered for treatment if it is detected.
What is the purpose of gardnerella DNA probes?
Doctors used tools like gardnerella DNA probes and vaginal pathogen tests (vag path for gardnerella) to measure the prevalence of Gardnerella and diagnose bacterial vaginosis. In the 70 years since that initial discovery, the scientific thinking has shifted.
How long does it take to cure BV?
Bacterial Vaginosis Treatment. BV treatment (or what was formerly and inaccurately known as Gardnerella vaginalis treatment) consists of a five- to seven-day regimen of antibiotics, prescribed either vaginally or orally. Metronidazole (Flagyl) and clindamycin (Cleocin) are two common options, prescribed as 150mg, 300mg, or 500mg tablets.
What is BV testing?
Testing and Diagnosis. BV Treatment. Prevention. It’s a tongue twister of a term, but an important one: Gardnerella vaginalis is the scientific name for a species of bacteria that lives inside your body, working alongside trillions of other microorganisms to keep your vaginal flora (that’s code for the bacteria that typically live in ...
What causes BV in women?
Bacterial vaginosis is caused by an imbalance in vaginal bacteria. One of the leading causes of BV is a bacteria known. Around 30% of women will develop BV at some point during their pre-menopausal years, and some people are unlucky enough to get it on a recurring basis. BV is not technically considered a sexually transmitted infection, ...
What bacteria are responsible for BV?
Research shows that bacteria like Atopobium, Mobiluncus, and Prevotella (among others) also contribute to the development of BV. While it used to be common practice to refer to BV as a Gardnerella vaginalis infection, you won’t hear those terms used interchangeably nowadays.
How do you know if you have BV?
You won’t always know if you have BV— in fact, as many as 84% of women have a totally asymptomatic case of this infection. But if you do have symptoms, here is what to look for: The most characteristic sign of bacterial vaginosis is a thin, grayish vaginal discharge with a strong “fishy” odor.
Why does my vagina smell so bad?
The smell is often stronger after sexual activity and menses or anything that can increase the vaginal pH. BV can also cause itching and discomfort around your vulva and vaginal opening. The odor is really what distinguishes BV from other types of vaginal conditions like yeast infections or STIs.
What are the risk factors for bacterial vaginosis?
Risk factors that seem to increase the likelihood of bacterial vaginosis include a history of multiple sex partners, a sexual relationship with a new partner, cigarette smoking, vaginal douching and the use of the intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD).
Can a woman with no vagina have bacterial vaginosis?
Although most of these risk factors are related to sexual activity, women who have never had vaginal intercourse can also develop bacterial vaginosis. Subscribe to Harvard Health Online for immediate access to health news and information from Harvard Medical School.
Diagnostic Considerations
BV can be diagnosed by using clinical criteria (i.e., Amsel’s diagnostic criteria) ( 999) or by determining the Nugent score from a vaginal Gram stain ( 1000 ).
Treatment
Treatment for BV is recommended for women with symptoms. Established benefits of therapy among nonpregnant women are to relieve vaginal symptoms and signs of infection. Other potential benefits of treatment include reduction in the risk for acquiring C. trachomatis, N. gonorrhoeae, T. vaginalis, M.
Follow-Up
Follow-up visits are unnecessary if symptoms resolve. Because persistent or recurrent BV is common, women should be advised to return for evaluation if symptoms recur. Limited data are available regarding optimal management strategies for women with persistent or recurrent BV.
Management of Sex Partners
Data from earlier clinical trials indicate that a woman’s response to therapy and the likelihood of relapse or recurrence are not affected by treatment of her sex partner ( 998 ). Therefore, routine treatment of sex partners is not recommended.
Special Considerations
Intravaginal clindamycin cream is preferred in case of allergy or intolerance to metronidazole or tinidazole. Intravaginal metronidazole gel can be considered for women who are not allergic to metronidazole but do not tolerate oral metronidazole.
Causes
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common cause of abnormal vaginal discharge in women of childbearing age and affects 30% of women globally ( 1 ).
Clinical presentation
Malodour and/or a thin white or greyish vaginal discharge, although up to 50% of women may be asymptomatic.
Diagnosis
There is currently insufficient evidence to support the recommendation of routine screening for BV at the time of insertion of an intrauterine device or surgical termination of pregnancy to prevent PID or endometritis in asymptomatic women ( 16-18, 19-23) however, where feasible it is reasonable to provide screening and treatment prior to the intervention..
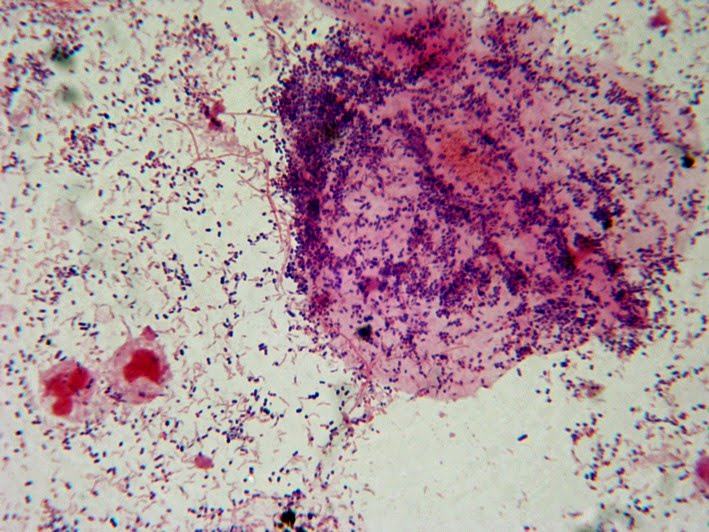
What Is Bacterial Vaginosis (Gardnerella Vaginitis)?
Symptoms
- Up to 50% of women diagnosed with bacterial vaginosis do not have symptoms. In others, it causes an unpleasant "fishy" vaginal odor and a yellow or white vaginal discharge. For some women, these symptoms are especially bothersome during or after intercourse. The discharge seen in bacterial vaginosis tends to be thinner than the "cheesy," thick discharge seen in vaginal …
Diagnosis
- Your doctor will ask you to describe the vaginal odor and discharge. He or she also will ask you about your medical history, including: 1. The date of your last menstrual period 2. The number of sex partners you have 3. Whether you have had any vaginal or urinary tract infections before 4. Whether you have had any sexually transmitted diseases or pelvic infections 5. The method of c…
Prevention
- Doctors are not exactly sure why bacterial vaginosis develops. Because it occurs more commonly in people who are sexually active, bacterial vaginosis is considered by some to be sexually transmitted. However, bacterial vaginosis also occurs in people who either are not sexually active or have been in long-term relationships with just one person. In some women, bacterial vaginosi…
Treatment
- For most women, bacterial vaginosis is simply a nuisance, and the goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms. Doctors commonly treat bacterial vaginosis with metronidazole (Flagyl or MetroGel-Vaginal) or clindamycin (Cleocin). Either can be taken by mouth or applied as a vaginal cream or gel. However, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Preventi...
When to Call A Professional
- Call your doctor whenever you notice any abnormal vaginal odor or discharge, especially if you are pregnant.
Prognosis
- The outlook is excellent. Bacterial vaginosis can return, but repeat treatment is usually successful.
Further Information
- Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Medical Disclaimer
General Information
Causes
- Bacterial vaginosis (gardnerella vaginalis) occurs as an imbalance in the composition of the natural microflora of the vagina, when “non-physiological” types of microorganisms, primarily gardnerella, begin to dominate. External and internal factors can disrupt the normal microflora of the genitourinary organs. Among the external factors contributing to the development of gardne…
Pathogenesis
- Normally, more than 15 types of microorganisms are found in the vagina of an adult woman. Acidophilic lactobacilli predominate, a smaller part are bifidobacteria (10%), peptostreptococci (~ 5%). Lactoflora, thanks to lactic acid, supports the acidic environment of the genital mucosa, which performs local protective and immune functions. Anaerobic bacteria (mobiluncus, bacter…
Symptoms
- Gardnerella vaginalis has a course somewhat similar to other inflammatory diseases of the genitals in women. With this disease, there are: grayish vaginal discharge (homogeneous, pasty, with an unpleasant “fishy” smell); burning, itching, discomfort during urination and sexual contact. Disease is accompanied by inflammatory changes in the vagina, urethra and cervix. When using …
Diagnostics
- To confirm the diagnosis of gardnerella vaginalis, a woman’s vaginal swabs are taken at a gynecologist’s consultation. In the diagnosis of gardnerella vaginalis, it is not so much the presence of gardnerella that matters, as their number and the ratio of microorganisms in the vaginal secretions. Gardnerella are present in the vaginal flora of most healthy women without t…
Treatment
- Early and accurate diagnosis of gardnerella vaginalis allows its timely treatment. The methods of therapy used by modern gynecology make it possible to achieve the patient’s recovery and avoid the development of complications, but they do not guarantee the absence of relapses of the disease in the future. Therapeutic treatment should eliminate the ...
Prevention
- Preventative measures aimed at eliminating the causes of bacterial vaginosis will help to avoid the development of gardnerella vaginalis and its relapses. The widespread prevalence and danger of the consequences of gardnerella vaginalis require not only immediate treatment of the disease, but also its regular household and medical prevention. Women are recommended to: 1. have a p…