What can I do to prevent drug interactions?
Communication with your healthcare provider is key in helping to prevent drug interactions. Keep an up-to-date list of your medications, over-the-counter products, vitamins, herbals, and medical conditions. Share this list with your doctor, pharmacist, and nurse at each visit so that they can also screen for drug interactions.
What is a drug interaction?
Key Points A drug interaction is a reaction between two (or more) drugs or between a drug and a food, beverage, or supplement. A drug interaction can affect how a drug works or cause unwanted side effects. Treatment with HIV medicines (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) helps people with HIV live ...
What is an example of drug-condition interaction?
Drug-condition interaction: A reaction that occurs when taking a drug while having a certain medical condition. For example, taking a nasal decongestant if you have high blood pressure may cause an unwanted reaction. A drug interaction can affect how a drug works or cause unwanted side effects. Do HIV medicines ever cause drug interactions?
How can I find out more about drug interactions?
However, you can also use our online drug interaction checker to learn more about possible drug interactions, too. This tool explains what the interaction is, how it occurs, the level of significance (major, moderate, or minor) and usually a suggested course of action.
What is the purpose of each active ingredient?
Why do you need to know all the medicines you take?
What is an OTC label?
What does the directions section on a drug label mean?
What is the other information on a food label?
What is the best medicine for sour stomach?
What is the H2 receptor antagonist?
See more
About this website
What happens when you have a drug interaction?
Drug interactions involve combinations of a medication with other substances that alter the medication's effect on the body. This can cause the medication to be less or more potent than intended or result in unexpected side effects.
How do you manage common drug side effects?
Eat small, frequent meals rather than large meals three times a day. Drink clear liquids cold and sip slowly. Try Popsicles or gelatine. Eat bland foods, such as dry toast and crackers and avoid fatty, fried, spicy, strong-smelling or very sweet foods.
What are 3 common drug interactions?
Which are Some Common Drug-Drug interactions?Angiotensin Converting Enzymes (ACE) inhibitors and Potassium Supplements. ... Angiotensin Converting Enzymes (ACE) inhibitors and Spironolactone. ... Digoxin and Amiodarone. ... Digoxin and Verapamil. ... Theophylline and Quinolones. ... Warfarin and Macrolides.More items...•
Will medication side effects go away?
Some side effects go away over time as your body gets used to a new drug, so your doctor may recommend you stick with your current plan for a little longer. In other cases, you may be able to lower your dose, try a different drug, or add another one, like an anti-nausea medicine, to your routine.
How long after stopping a medication to the side effects go away?
Withdrawal symptoms usually come on within 5 days of stopping the medicine and generally last 1 to 2 weeks. Some people have severe withdrawal symptoms that last for several months or more. See your doctor if you get severe withdrawal symptoms after you stop taking antidepressants.
What causes drug interactions?
Most of the important drug interactions result from a change in the absorption, metabolism, or elimination of a drug. Drug interactions also may occur when two drugs that have similar (additive) effects or opposite (canceling) effects on the body are administered together.
What is the most common type of drug interaction?
pharmacokinetic – defined as an alteration in the absorption, distribution, metabolism or excretion of one drug by another. This is the most common type of drug interaction.
What is it called when two drugs interact badly?
Pharmacodynamic interactions. Drug interactions can be additive (the result is what you expect when you add together the effect of each drug taken independently), synergistic (combining the drugs leads to a larger effect than expected), or antagonistic (combining the drugs leads to a smaller effect than expected).
Drug Interaction Checker - Find Interactions Between Medications
Use WebMD’s Drug Interaction Checker tool to find and identify potentially harmful and unsafe combinations of prescription medications by entering two or more drugs in question.
Drug Interactions Checker - Check Your Brand and Generic Drugs - RxList
Drug Interactions. Pharmacy Author: Omudhome Ogbru, PharmD Medical and Pharmacy Editor:Jay W. Marks, MD Drug interactions overview. Whenever two or more drugs are being taken, there is a chance that there will be an interaction among the drugs.
Drug Interactions Checker - For Drugs, Food & Alcohol
Drugs.com provides accurate and independent information on more than 24,000 prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines and natural products. This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Data sources include IBM Watson Micromedex (updated 7 June 2022), Cerner Multum™ (updated 3 June 2022), ASHP (updated 16 May 2022 ...
Drug Interactions Checker - Medscape Drug Reference Database
Drug Interaction Checker. Use the search field above to look up prescription or OTC drugs, and herbal supplements; Add a full drug regimen and view interactions
How long after taking dolutegravir can you take milk?
Dolutegravir should be taken 2 hours before or 6 hours after medications that contain calcium or other minerals to help prevent this interaction. In the same manner, many drugs cannot be taken with milk or dairy products because they will bind with the calcium.
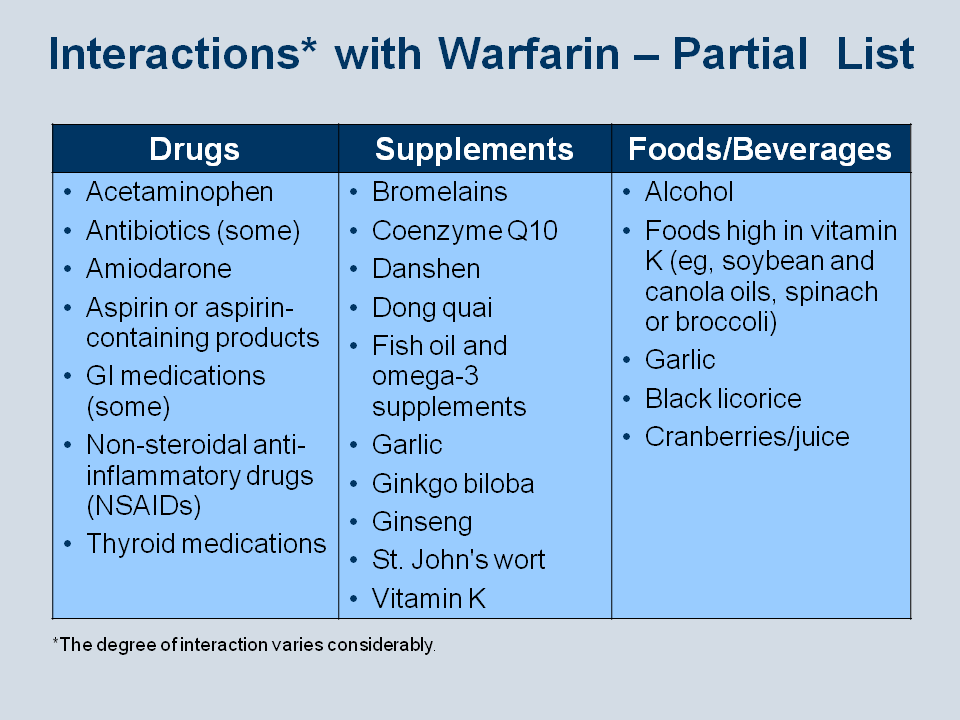
What is the interaction between fenofibric acid and warfarin?
One example of an interaction is between fenofibric acid (Trilipix), used to lower cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, and warfarin, a common blood thinner to help prevent clots. Fenofibric acid can increase the effects of warfarin and cause you to bleed more easily. Metabolism: Drugs are usually eliminated from the body as either ...
Why is it important to check for drug interactions?
Drug interactions are important to check for because they can: Affect how your medication works by changing levels of the drug in your blood. Put you at risk for side effects and toxicity. Worsen a medical condition you may already have.
What is the interaction between two drugs?
A pharmacodynamic interaction occurs when two drugs given together act at the same or similar receptor site and lead to a greater (additive or synergistic) effect or a decreased (antagonist) effect.
What is pharmacokinetic interaction?
A pharmacokinetic interaction may occur if one drug affects another drug’s absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion. Examples can help to explain these complicated mechanisms: Absorption: Some drugs can alter the absorption of another drug into your bloodstream.
Can drug interactions cause side effects?
Drug-drug interactions can decrease how well your medications work, may increase minor or serious unexpected side effects, or even increase the blood level and possible toxicity of a certain drug.
Does diltiazem affect enzymes?
However, enzyme levels may go up or down and affect how drugs are broken down. For example, using diltiazem (a blood pressure medication) with simvastatin (a medicine to lower cholesterol) may elevate the blood levels and side effects of simvastatin.
How does drug interaction affect HIV?
A drug interaction can affect how a drug works or cause unwanted side effects. Treatment with HIV medicines (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) helps people with HIV live longer, healthier lives and reduces the risk of HIV transmission. But drug interactions can complicate HIV treatment.
What to consider before recommending an HIV treatment regimen?
Before recommending an HIV treatment regimen, health care providers carefully consider potential drug-drug interactions between HIV medicines. They also ask about other medicines a person may be taking.
What to tell your health care provider before taking HIV medication?
Before taking HIV medicines, tell your health care provider about all prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take.
How to avoid drug interactions?
You can take the following steps to avoid drug interactions: Tell your health care provider about all prescription and nonprescription medicines you are taking or plan to take. Also tell your health care provider about any vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you take.
What is the treatment for HIV?
Treatment with HIV medicines (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) helps people with HIV live longer, healthier lives and reduces the risk of HIV transmission. But drug interactions, especially drug-drug interactions, can complicate HIV treatment.
What are the different types of drug interactions?
There are three types of drug interactions: Drug-drug interaction: A reaction between two (or more) drugs. Drug-food interaction: A reaction between a drug and a food or beverage. Drug-condition interaction: A reaction that occurs when taking a drug while having a certain medical condition.
Can you take HIV medication with food?
Some HIV medicines can be taken with or without food, because food does not affect their absorption. Conditions such as kidney disease, hepatitis, and pregnancy can affect how the body processes HIV medicines. The dosing of some HIV medicines may need to be adjusted in people with certain medical conditions.
What facts should I know about drug interactions?
Whenever two or more drugs are being taken, there is a chance that there will be an interaction among the drugs. The interaction may increase or decrease the effectiveness of the drugs or their side effects. The likelihood of drug interactions increases as the number of drugs being taken increases.
What are drug interactions?
A drug interaction can be defined as an interaction between a drug and another substance that prevents the drug from performing as expected. This drug interaction definition applies to
How do drug interactions occur?
There are several mechanisms by which drugs interact with other drugs, food, and other substances. An interaction can result when there is an increase or decrease in:
Change in absorption
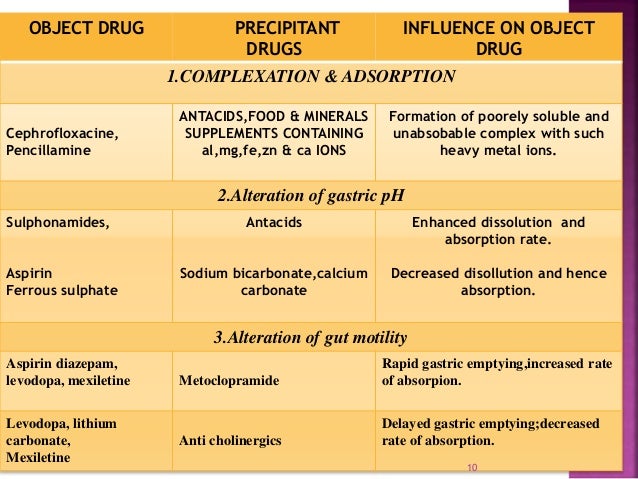
Most drugs are absorbed into the blood and then travel to their site of action. Most drug interactions that are due to altered absorption occur in the intestine. There are various ways that the absorption of drugs can be reduced. These mechanisms include:
Change in drug metabolism and elimination
Most drugs are eliminated through the kidney in either an unchanged form or metabolized by the liver. Therefore, the kidney and the liver are very important sites of potential drug interactions. Some drugs are able to reduce or increase the metabolism of other drugs by the liver or their elimination by the kidney.
How often do drug interactions occur?
The prescribing information for most drugs contains a list of potential drug interactions. Many of the listed interactions may be rare, minor, or only occur under specific conditions and may not be important. Drug interactions that cause important changes in the action of a drug are of greatest concern.
What are the consequences of drug interactions?
Drug interactions may lead to an increase or decrease in the beneficial or the adverse effects of the given drugs. When a drug interaction increases the benefit of the administered drugs without increasing side effects, both drugs may be combined to increase the control of the condition that is being treated.
What are some examples of drug interactions?
Examples of pharmacodynamic interactions are simultaneous administration of a NSAID and phenprocoumon (additive interaction), or of aspirin and ibuprofen (antagonistic interaction).
What is pharmacodynamic interaction?
Pharmacodynamic interactions are those in which drugs influence each other’s effects directly. Often, however, a pharmacodynamic interaction is actually desired, if mutually potentiating effects in the same direction (synergistic effects) are aimed at, e.g., in the use of anti-infectives or in pain therapy.
What is the term for interactions in which drugs influence each other's effects directly?
The term “pharmacodynamic interactions” refers to interactions in which drugs influence each other’s effects directly. As a rule, for example, sedatives can potentiate each other. The same is true of alcohol, which can potentiate the sedative effects of many drugs. Pharmacodynamic interaction.
Why is systematic knowledge important in drug interactions?
The systematic knowledge of drug interaction, in particular on the level of absorption, elimination, transport and drug metabolism may help to prevent adverse effects. Predicting pharmacodynamic interactions often demands a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of effect. Electronic prescribing systems are helpful.
What are the interactions at the absorption level?
Interactions at the absorption level—formation of complexes. Complexes can considerably reduce the bioavailability of drugs. The bisphosphonates used in osteoporosis, such as alendronate, have a very low bioavailability of only 0.5% to 2%. Calcium ions in mineral water or milk reduce this markedly still further.
What are the consequences of interactions between drugs?
A necessary consequence of this is the danger that interactions between drugs will lead to serious adverse effects or will reduce the therapeutic effect of some compounds. Potential interactions can arise at any age in life, but the frequency of polypharmacy in older life increases the risk substantially.
What happens when you interact with drugs?
Interactions between drugs can lead to serious unwanted effects or to a reduction in the therapeutic effects of some drug substances. Polypharmacy, which is common in elderly patients, increases the risk substantially. A necessary consequence of this is the danger that interactions between drugs will lead to serious adverse effects ...
Prescribing Resources
Printable interaction tables, interaction summary charts and clinical prescribing resources
Follow us on Twitter for interaction news and for the latest additions and changes to the website
What is the purpose of each active ingredient?
the purpose of each active ingredient. The " Uses " section of the label: tells you what the drug is used for. helps you find the best drug for your specific symptoms. The " Warnings " section of the label provides important drug interaction and precaution information such as. when to talk to a doctor or pharmacist before use.
Why do you need to know all the medicines you take?
If you take several different medicines, see more than one doctor, or have certain health conditions, you and your doctors need to be aware of all the medicines you take. Doing so will help you to avoid potential problems such as drug interactions.
What is an OTC label?
Over-the-counter (OTC) drug labels contain information about ingredients, uses, warnings and directions that is important to read and understand. The label also includes important information about possible drug interactions. Further, drug labels may change as new information becomes known.
What does the directions section on a drug label mean?
when to stop taking the drug. The " Directions " section of the label tells you: the length of time and the amount of the product that you may safely use.
What is the other information on a food label?
The " Other Information " section of the label tells you: required information about certain ingredients, such as sodium content, for people with dietary restrictions or allergies. The " Inactive Ingredients " section of the label tells you: the name of each inactive ingredient (such as colorings, binders, etc.)
What is the best medicine for sour stomach?
Antacids. (drugs for relief of acid indigestion, heartburn, and/or sour stomach) Ask a doctor or pharmacist before use if you are: allergic to milk or milk products if the product contains more than 5 grams lactose in a maximum daily dose. taking a prescription drug. Ask a doctor before use if you have: kidney disease.
What is the H2 receptor antagonist?
(drugs that prevent or relieve heartburn associated with acid indigestion and sour stomach) For products containing cimetidine, ask a doctor or pharmacist before use if you are: taking theophylline (oral asthma drug), warfarin (blood thinning drug), or phenytoin (seizure drug) Antacids.