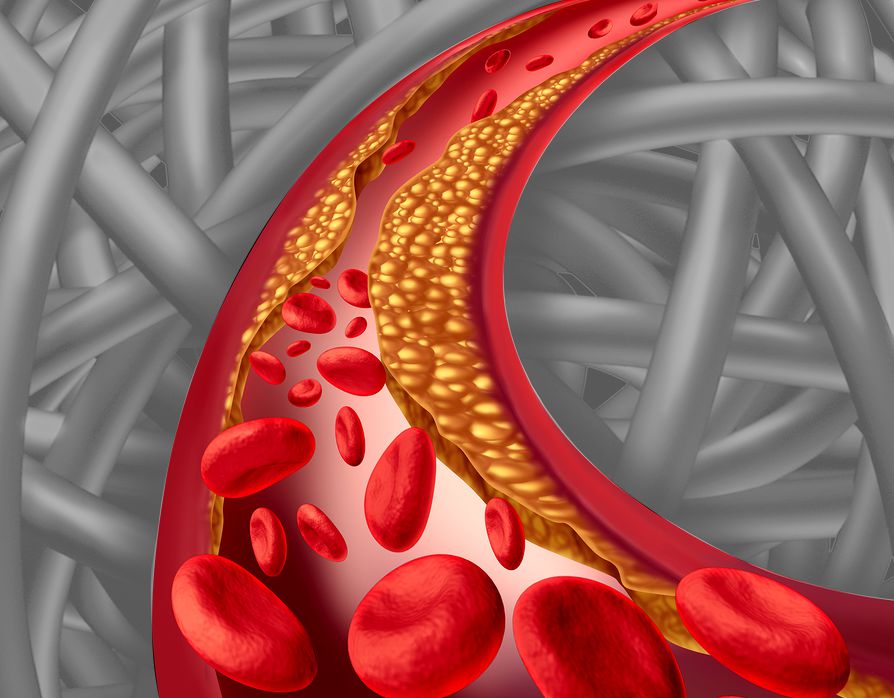
- Cholesterol drugs. ...
- Aspirin. ...
- Beta blockers. ...
- Calcium channel blockers. ...
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). ...
- Nitroglycerin. ...
- Ranolazine.
Medication
Procedures
Self-care
Nutrition
See more

What are the two most common treatments of coronary heart disease?
Procedures and surgery Interventional procedures are nonsurgical treatments to get rid of plaque buildup in the arteries and prevent blockages. Common procedures are balloon angioplasty and stenting.
Is there any treatment for artery disease?
Unfortunately, there isn't a cure for coronary artery disease, and you can't reverse this condition once you're diagnosed. But you can make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk of developing further health problems, such as a heart attack.
Can coronary artery disease be treated without surgery?
Through angioplasty, our cardiologists are able to treat patients with blocked or clogged coronary arteries quickly without surgery. During the procedure, a cardiologist threads a balloon-tipped catheter to the site of the narrowed or blocked artery and then inflates the balloon to open the vessel.
Can you reduce coronary artery disease?
You can absolutely prevent CAD from worsening, and with some hard work, you might even be able to reverse some of the damage, says Gregg Fonarow, MD.
How long can you live with coronary artery disease?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is treatable, but there is no cure. This means that once diagnosed with CAD, you have to learn to live with it for the rest of your life. By lowering your risk factors and losing your fears, you can live a full life despite CAD.
Is there a drug that removes plaque from arteries?
29, 2020, by the European Heart Journal. The findings may explain why the drug, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa), lowers the risk of heart attack and stroke by 26% in people at high risk for those serious problems. The study included 80 people with fatty plaque in the arteries of the heart (coronary artery disease).
How do you detect coronary artery disease?
Coronary Angiography Coronary angiography, also called cardiac catheterization, is a minimally invasive study that is considered the gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease.
What is the best test to check for clogged arteries?
A CT coronary angiogram can reveal plaque buildup and identify blockages in the arteries, which can lead to a heart attack. Prior to the test, a contrast dye is injected into the arm to make the arteries more visible. The test typically takes 30 minutes to complete.
Can an ECG detect a blocked artery?
No, an electrocardiogram cannot detect blocked arteries. Blocked arteries are usually diagnosed with a nuclear stress test, cardiac pet scan, coronary CT angiogram or traditional coronary angiogram.
What foods clean your arteries?
Eat These 10 Foods to Cleanse Your ArteriesAsparagus. Asparagus is one of the best foods to cleanse your arteries. ... Avocado. Avocado helps reduce the “bad” cholesterol and increase the “good cholesterol” that helps to clear the arteries. ... Broccoli. ... Fatty Fish. ... Nuts. ... Olive Oil. ... Watermelon. ... Turmeric.More items...•
Is coronary artery disease serious?
This often preventable disease causes the dangerous thickening and narrowing of the coronary arteries—the vessels that bring blood to the heart—which disrupts the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart, causing serious problems. Without enough blood, coronary artery disease can lead to angina (chest pain).
Which fruit is good for heart blockage?
Berries include blueberries, strawberries, cranberries, raspberries, and blackberries. These fruits are associated with an impressive amount of health benefits, including their ability to reduce inflammation and improve heart health. Berries are packed with fiber, vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- To diagnose coronary artery disease, a health care provider will examine you. You'll likely be asked questions about your medical history and any symptoms. Blood tests are usually done to check your overall health.
Causes
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Clinical significance
- Making certain lifestyle changes can help keep the arteries healthy and can prevent or slow coronary artery disease. Try these heart-healthy tips: 1. Don't smoke.Smoking is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease. Nicotine tightens blood vessels and forces the heart to work harder. Not smoking is one of the best ways to lower the risk of a heart attack. 2. Control blood …
Signs and symptoms
- Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of unsaturated fatty acid. It's thought that they can lower inflammation throughout the body. Inflammation has been linked to coronary artery disease. However, the pros and cons of omega-3 fatty acids for heart disease continue to be studied. Sources of omega-3 fatty acids include: 1. Fish and fish oil.Fish and fish oil are the most effectiv…
Epidemiology
- If you have symptoms of coronary artery disease or any risk factors, make an appointment with your health care provider. You may be referred to a heart specialist (cardiologist). Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and to know what to expect from your doctor.
Sources
Symptoms
Pathophysiology
Definition
Prognosis