
Symptoms
This result clearly shown that ampicilin is the most effective antibiotic to inhibit the growth of E.coli. Besides that, E.coli is a gram negative bacteria.
Causes
E. coli can cause dehydration, bloody diarrhea and abdominal cramps 2–8 days after exposure, officials said. Anyone concerned about an illness should contact a healthcare provider.
Prevention
coli
- Diagnosis. To diagnose illness caused by E. coli infection, your doctor sends a sample of your stool to a laboratory to test for the presence of E. ...
- Treatment. For illness caused by E. ...
- Lifestyle and home remedies. Drink clear liquids. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. Most people don't seek medical attention for E. ...
Complications
One strain, E. coli O157:H7, produces a powerful toxin (poison), and can cause severe illness, kidney failure and even death. The symptoms of E. coli O157:H7 are diarrhea or bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and malaise.
What is the most effective antibiotic against E coli?
What is E coli and how bad is it?
What antibiotics are used to treat E coli infection?
How dangerous is ecoli in the sputum?

Is there a medical treatment for E. coli?
Antibiotics can be an effective treatment for E. coli infections that reside outside of the digestive system, like urinary tract infections. But there is no specific drug treatment recommended for a STEC infection. Antibiotics should not be used to treat an E.
How can E. coli infection be resolved?
Most cases of E. coli infections are mild and do not cause a serious health risk. Cases resolve on their own with rest and drinking plenty of fluids. However, some strains can cause severe symptoms and even life-threatening complications, such as hemolytic uremic syndrome, which can lead to kidney failure and death.
Can you get rid of E. coli with antibiotics?
Antibiotics can effectively treat E. coli infections outside the digestive tract and most intestinal infections but are not used to treat intestinal infections by one strain of these bacteria.
What is the best antibiotic to treat E. coli?
Fluoroquinolones, such asciprofloxacin, andlevofloxacin, are usually the first-line therapy. Azithromycin is also commonly used as treatment for invasive E. coli infections.
How long does it take to recover from E. coli?
Most people recover from E. coli infection without treatment within five to 10 days. Antibiotics should not be used to treat this infection because they may lead to kidney complications. Antidiarrheal treatments should also be avoided.
Is E. coli UTI hard to treat?
UTIs caused by this bacteria can be extremely difficult to treat. Research also shows that E. coli develops drug resistance very quickly. To prevent UTIs, make sure you drink lots of water and always wipe front to back.
What are the first signs of E. coli?
Symptoms of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) infection vary for each person, but often include severe stomach cramps, diarrhea (often bloody), and vomiting. Some people may have a fever, which usually is not very high (less than 101˚F/38.5˚C). Most people get better within 5 to 7 days.
How did I get E. coli in my urinary tract?
coli often gains entry into the urinary tract via stool. Women are particularly at risk for UTIs because their urethra sits close to the anus, where E. coli is present. It's also shorter than a man's, giving the bacteria easier access to the bladder, where the majority of UTIs occur, and the rest of the urinary tract.
How to treat E. coli infection?
Staying hydrated and getting plenty of rest are key when treating E. coli infection. Shutterstock
What is the cause of intestinal E. coli?
For instance, intestinal E. coli infections caused by Shiga toxin–producing E. coli, or STEC — which spurs an estimated 265,000 foodborne infections each year in the United States — does not require antibiotic treatment. ( 1)
Why do people get traveler's diarrhea?
That includes people with diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, cirrhosis of the liver, or a weakened immune system. Individuals on acid blockers or antacids are also at an increased risk because the reduction in stomach acid can make it easier for bacteria such as E. coli to survive . (12)
How to avoid cross contamination?
Avoid cross-contamination. Use separate cutting boards for meats and produce, and clean counters and utensils after contact with raw meat.
How to stop vomiting from a syringe?
These include apple and pear juices, caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, dairy, fatty foods, and high-fiber foods. Gradually add bland food into your diet. Start with items like soda crackers, toast, eggs, and rice.
Where is E. coli high risk?
Preventing E. coli–Related Traveler’s Diarrhea. Many areas of Central and South America, Mexico, Africa, the Middle East, and most of Asia are considered high-risk destinations for traveler's diarrhea. (There is some risk when traveling to Eastern Europe and a few Caribbean islands as well.)
Can pregnant women get E. coli?
Preventing Intestinal E. coli Infection and Its Complications. While preventive measures are the same for everyone, know that pregnant women, newborns, children, the elderly, and individuals who have a compromised immune system have a higher risk of contracting a foodborne E. coli illness.
How to prevent E. coli?
coli infections by being careful about the foods that carry the greatest chance of contamination: Cook hamburgers until they’re 160 F inside. Drink only pasteurized milk, juice, and cider. Wash all of your produce before you eat it.
How to protect against E. coli?
Prevention. One of the most important things you can do to protect yourself and your family against E. coli is wash your hands, particularly in these situations: Before you prepare food.
What is the name of the strain of E. coli that makes the toxin?
The strains of E. coli that make the toxin are sometimes called STEC, which is short for “Shiga toxin-producing E. coli.”. One especially bad strain, O157:H7, can make you very sick. It causes abdominal cramps, vomiting, and bloody diarrhea. It is the leading cause of acute kidney failure in children.
What happens when you eat meat that has E. coli?
Among the ways this can happen: Ground meat: You eat ground meat that carries E. coli, and the meat wasn’t cooked enough to kill the bacteria. When meat is processed, sometimes bacteria from the animals’ intestines make their way into the meat.
How long does it take for E. coli to make you sick?
You’ll probably start to feel ill 2 to 5 days after you’ve taken in the E. coli bacteria. The most common symptoms are:
How do you know if you have E. coli?
The only way your doctor can know for sure if you have an E. coli infection is to send a sample of your stool to a lab to be analyzed.
Where does E. coli live?
E. coli ( Escherichia coli ), is a type of bacteria that normally lives in your intestines. It’s also found in the gut of some animals.
What is the best home remedy for E. coli?
Supportive care is the primary treatment for E. coli, so the most universal treatments are home remedies. The goal of E. coli treatment is to prevent dehydration and loss of electrolytes.
Why is E. coli treated with supportive care?
E.coli infections are treated with supportive care to replace fluids and electrolytes lost because of watery diarrhea.
What is the best medication for E. coli?
Medications are only rarely used for E. coli infections. Antibiotics and antidiarrheal medications may make the problem worse. There is, then, no “best” medication for E. coli.
What are the common side effects of E. coli medication?
coli infection are treated with supportive care alone. Medications are rarely used or actively discouraged, so medication side effects are only rarely an issue.
How many people die from E. coli each year?
coli, particularly a Shiga toxin-producing strain called E. coli O157:H7. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 73,000 people in the United States are infected each year with Escherichia coli O157:H7. Most people ride out the infection, but about 2,000 people will be hospitalized and about 60 will die each year. The number of people infected annually with less deadly pathogenic E. coli is uncertain.
How many Escherichia coli infections are spread from person to person?
Person-to-person contact. Although animals are the main source of Escherichia coli infections, anywhere from 10% to 15% of infections are spread from person to person. The most common cause of person-to-person spread is poor hygiene.
Why is ETEC called traveler's diarrhea?
coli (EAEC) attach themselves to the lining of the intestines and secrete toxins that cause intestinal membranes to lose ions and water, leading to watery diarrhea, but without any fever. ETEC and EAEC infections are commonly called “traveler’s diarrhea” because the infection is usually picked up by traveling to a developing country.
How long does it take for E. coli to recover?
Healthy adults usually recover from infection with E. coli O157:H7 within a week. Young children and older adults have a greater risk of developing a life-threatening form of kidney failure.
When does E. coli occur?
Time of year. Though it's not clear why, the majority of E. coli infections in the U.S. occur from June through September.
Where does E. coli live?
Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria normally live in the intestines of healthy people and animals. Most types of E. coli are harmless or cause relatively brief diarrhea. But a few strains, such as E. coli O157:H7, can cause severe stomach cramps, bloody diarrhea and vomiting. You may be exposed to E. coli from contaminated water or food — ...
How to avoid a bout with a bacterial infection?
Dr. Rajapakse says the best way to avoid a bout with the bacteria is to wash your hands and thoroughly cook your hamburgers.
Can E. coli get into raw milk?
Unpasteurized milk. E. coli bacteria on a cow's udder or on milking equipment can get into raw milk.
Can E. coli cause problems?
E. coli can affect anyone who is exposed to the bacteria. But some people are more likely to develop problems than are others. Risk factors include:
Can E. coli cause a weakened immune system?
People who have weakened immune systems — from AIDS or from drugs to treat cancer or prevent the rejection of organ transplants — are more likely to become ill from ingesting E. coli. Eating certain types of food.
How to get rid of E. coli infection?
coli, scrub your hands vigorously with soap and clean under your fingernails where bacteria can get caught. Dry your hands with paper towels instead of cloth towels to avoid transferring bacteria.
How to protect against E. coli?
The most important thing you can do to protect against E. coli infection is to wash your hands – frequently. Always wash your hands thoroughly before and after cooking and after handling raw meat or poultry. Wash your hands after using the restroom, changing diapers or after contact with animals.
How do you get E. coli?
Technically, you develop an E. coli infection by ingesting (taking in by mouth) certain strains of E. coli bacteria. The bacteria travel down your digestive tract, releases a destructive toxin, called the Shiga toxin, which damages the lining of your small intestine. The growing infection causes your symptoms.
How long does it take for E. coli to heal?
Other strains of E. coli, the Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC), cause bloody diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain and cramps. If you are otherwise healthy, you should recover from an E. coli infection within about a week without any treatment.
What is the name of the bacteria that produces E. coli?
Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC): This is the bacteria most commonly known for E. coli food contamination. This strain is also called enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) and verocytotoxin-producing E. coli (VTEC).
What are the most common infections caused by E. coli?
The most common urinary tract infections caused by E. coli are a bladder infection (cystitis), infection of the urethra (urethritis) and kidney infection.
How to avoid E. coli?
The best and easiest way to avoid getting an E. coli infection is to frequently wash your hands with soap and water. Wash your hands before and after handling foods ( including prepping, cooking and serving foods), after using the bathroom, after touching animals (especially farm or zoo animals), after changing diapers and after shaking hands or being touched by others (you never know what their hands have touched). Washing your hands can not only prevent contracting E. coli, but also many other infectious disease that are spread from person to person. Make frequent hand washing a new habit.
Where does E. coli live?
Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria normally live in the intestines of people and animals. Most E. coli are harmless and actually are an important part of a healthy human intestinal tract. However, some E. coli are pathogenic, meaning they can cause illness, either diarrhea or illness outside of the intestinal tract.
What is the pathogenic E. coli strain?
Pathogenic E. coli strains are categorized into pathotypes. Six pathotypes are associated with diarrhea and collectively are referred to as diarrheagenic E. coli. Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC)—STEC may also be referred to as Verocytotoxin-producing E. coli (VTEC) or enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC).
What is the name of the bacteria that produce toxins?
The bacteria that make these toxins are called “Shiga toxin-producing” E. coli, or STEC for short. You might hear these bacteria called verocytotoxic E. coli (VTEC) or enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC); these all refer generally to the same group of bacteria.
How long does it take for STEC to get in your system?
The incubation period is usually 3-4 days after the exposure, but may be as short as 1 day or as long as 10 days. The symptoms often begin slowly with mild belly pain or non-bloody diarrhea that worsens over several days.
Why do public health experts rely on estimates rather than actual numbers of infections?
Public health experts rely on estimates rather than actual numbers of infections because not all STEC infections are diagnosed, for several reasons. Many infected people do not seek medical care; many of those who do seek care do not provide a stool specimen for testing, and many labs do not test for non-O157 STEC.
Is E. coli harmful to water?
coli are used as markers for water contamination—so you might hear about E. coli being found in drinking water, which are not themselves harmful, but indicate the water is contaminated. It does get a bit confusing—even to microbiologists.
Can E. coli make you sick?
Escherichia coli (abbreviated as E. coli) are a large and diverse group of bacteria. Although most strains of E. coli are harmless, others can make you sick. Some kinds of E. coli can cause diarrhea, while others cause urinary tract infections, respiratory illness and pneumonia, and other illnesses.
Why does E. coli spread?
Outbreaks often are caused by food that has gotten the bacteria, E coli, in it. Bacteria can get accidentally mixed into ground beef before packaging. Eating undercooked meat can spread the bacteria, even though the meat looks and smells normal. E. coli can also live on cows’ udders. It may get into milk that is not pasteurized.
How many people died from E. coli in 1999?
You can become very sick if it gets into your food or water. In 1999 it was estimated that about 73,000 people in the U.S. got sick each year from E. coli. About 60 died. It’s believed that the number of illnesses and deaths has been dropping since then.
How long does it take for E. coli to spread to playmates?
Children can pass the bacteria in their stool to another person for 2 weeks after they have gotten well from an E. coli O157:H7 illness. Older children and adults rarely carry the bacteria without symptoms.
How long to boil vegetables for E. coli?
During an outbreak of E. coli O157:H7, vegetables should be boiled for at least 1 minute before serving. Cook ground beef to 160° F Test the meat by putting a food thermometer in the thickest part of the meat. Do not eat ground beef that is still pink in the middle.
How long does it take to get well after diarrhea?
People who have only diarrhea and stomach ache usually get completely well in 5-10 days. They do not have problems later. For those people who get very sick and have kidney failure, about 1 out of 3 may have kidney problems later.
What to do if you have blood in your diarrhea?
Anyone who suddenly has diarrhea with blood in it should call or see a doctor.
Can E. coli live in milk?
E. coli can also live on cows’ udders. It may get into milk that is not pasteurized. Raw vegetables, sprouts, and fruits that have been grown or washed in dirty water can carry E. coli O157:H7. It can get into drinking water, lakes, or swimming pools that have sewage in them.
How to kill E. coli bacteria?
Because antibiotics are not advised in E. coli infections, it will be up to your immune system to kill off the infection. Fortunately, your immune system is very capable of doing this, given adequate time and proper support. Rest, follow your doctor's instructions, and allow your immune system to do its job!
How do you know if you have E. coli?
E. coli infections occur most frequently while traveling to areas of the world with poorer hygiene than we have here in North America. It is transmitted via fecal contamination of food, water, etc. Symptoms of an E. coli infection include: Abdominal pain. Nausea and/or vomiting. Diarrhea. Fever. Abdominal cramps. ...
Why do you need electrolytes?
Electrolytes are substances that are found in the body and help to maintain the normal functioning of the body. You may be required to get a blood transfusion in cases of severe bloody diarrhea (which some strains of E. coli can cause). Your blood will be checked to determine hemoglobin levels.
What is supportive treatment?
Rather, the treatment offered by medical professionals is "supportive," meaning it consists of rest, fluids, and medications for symptom management such as pain and/or nausea. This is counter-intuitive for many people, who often expect medical drugs as a "cure" for illnesses such as an E. coli infection.
Why are antidiarrheal medications not helpful?
Antidiarrheal medications are not helpful because they delay the passage of the infection and a worsening of symptoms. Your best bet, counter-intuitive as it may seem, is to allow the diarrhea to continue to get rid of the infection as soon as possible.
What is the best medicine for abdominal pain?
Take pain and anti-nauseant medications as needed. To help with symptom relief, you can take pain medication such as Acetaminophen (Tylenol) for abdominal pain. This is available over-the-counter at your local drugstore or pharmacy. Follow the dosing directions on the bottle. You can also try anti-nauseant medications such as Dimenhydrinate (Gravol) to help combat nausea.
Can E. coli be cured?
Do not take anit-diarrheals and antibiotics. It is important to understand that E. coli infections are not able to be "cured" (and the bacteria cannot be "killed") with typical medical drugs such as antibiotics or even antidiarrheals.
What are the symptoms of E. coli?
UTIs can cause a range of symptoms, including: an urgent, frequent need to pee, often with little urine output. bladder fullness. burning urination. pelvic pain. foul-smelling, cloudy urine. urine that’s brownish, pink, or tinged with blood.
What is the best treatment for a UTI?
Treatment for a UTI caused by E. coli. The first line of treatment for any bacterial infection is antibiotics. If your urinalysis comes back positive for germs, a doctor will likely prescribe one of several antibiotics that works to kill E. coli, since it’s the most common UTI culprit.
What bacteria are responsible for UTI?
Other bacteria that cause a UTI. While infection with E. coli accounts for most UTIs, other bacteria can also be the cause. Some that might appear in a urine culture include: Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Can UTIs be treated with antibiotics?
Takeaway. UTIs are some of the most common infections doctors see. Most are caused by E. coli and are successfully treated with a round of antibiotics. If you have symptoms of a UTI, see a doctor. Most UTIs are uncomplicated and don’t cause any lasting harm to your urinary tract.
Can you send urine to a lab for a recurrent infection?
In some cases, especially if you don’t seem to be improving with treatment or you get recurrent infections, a doctor may send your urine out to a lab to be cultured. This can pinpoint exactly what bacteria is causing the infection and what antibiotic effectively fights it.
Is urine sterile?
While researchers used to think of urine as sterile, it’s now known that even a healthy urinary tract can host a variety of bacteria. But one type of bacteria not normally found in the urinary tract is E. coli. E. coli often gains entry into the urinary tract via stool.
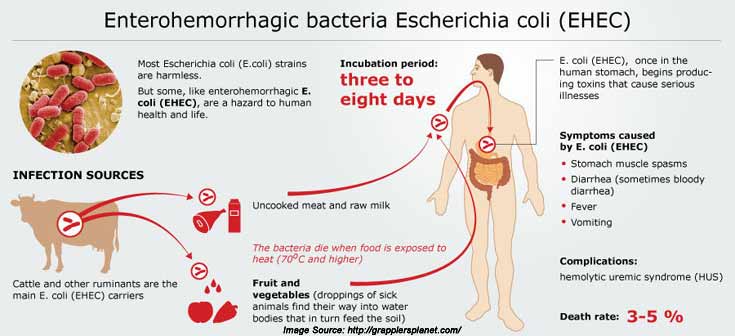
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- To diagnose illness caused by E. coli infection, your doctor sends a sample of your stool to a laboratory to test for the presence of E. coli bacteria. The bacteria may be cultured to confirm the diagnosis and identify specific toxins, such as those produced by E. coliO157:H7.
Prevention