Medication
However, they should be advised to avoid factors that can aggravate hypercalcemia, including thiazide diuretics and lithium carbonate therapy, volume depletion, prolonged bed rest or inactivity, and a high calcium diet (>1000 mg/day).
Procedures
Denosumab — Denosumab is an option for patients with hypercalcemia that is refractory to zoledronic acid (ZA) or in whom bisphosphonates are contraindicated due to severe renal impairment.
Nutrition
Moderate hypercalcemia — Asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic individuals with chronic moderate hypercalcemia (total albumin-corrected calcium between 12 and 14 mg/dL [3 to 3.5 mmol/L]) may not require immediate therapy. However, they should follow the same precautions described above for mild hypercalcemia.
What should patients with hypercalcemia be advised to avoid?
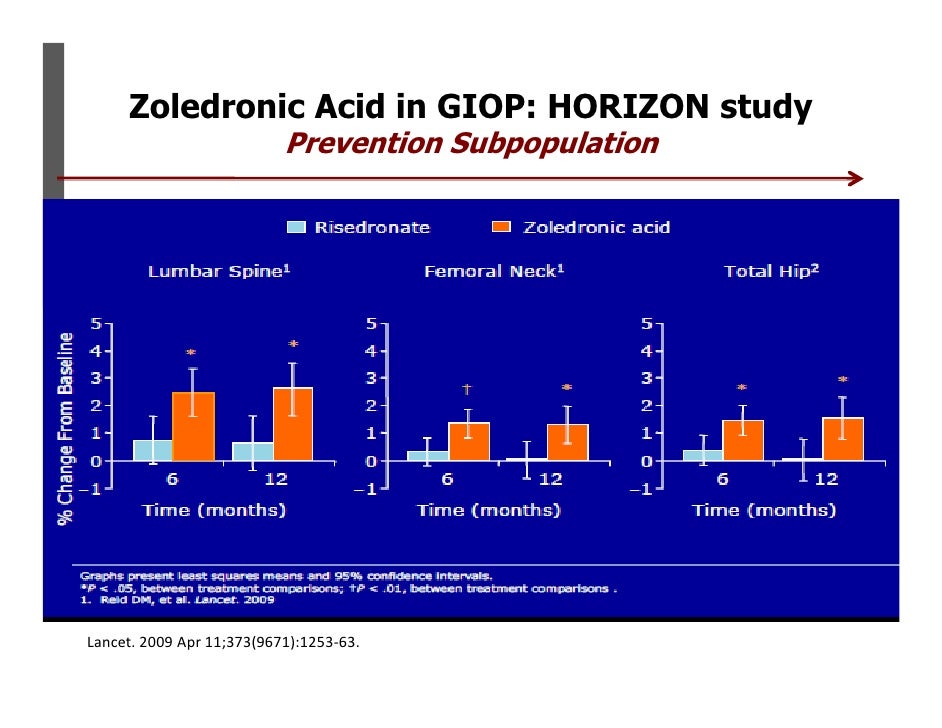
Another prophylactic approach would be to treat patients at risk of developing hypercalcemia with drugs, such as the bisphosphonates, that inhibit bone resorption.
Which medications are used to treat hypercalcemia?
What is moderate hypercalcemia?
What is the prophylactic approach to the treatment of hypercalcemia?

What drugs affect calcium levels?
Increased calcium in your blood can occur in one of three ways: Increased absorption from your intestines. Decreased excretion through your kidneys....The medicines that have been associated with increased blood calcium levels (hypercalcemia) are:Lithium.Thiazide diuretics.Teriparatide.Estrogens.Tamoxifen.
What is the first line treatment for hypercalcemia?
Intravenous bisphosphonates are the treatment of first choice for the initial management of hypercalcaemia, followed by continued oral, or repeated intravenous bisphosphonates to prevent relapse.
Why are bisphosphonates contraindicated in hypocalcemia?
Bisphosphonates (applies to Fosamax) hypocalcemia The use of bisphosphonates is contraindicated for the treatment of osteoporosis in patients with hypocalcemia. These agents increase bone mineral density, a process that requires an adequate supply of calcium in the body.
What is the most common treatment for hypercalcemia?
Although bisphosphonates are most commonly used to treat established hypercalcemia, they have also been given to prevent hypercalcemia and adverse skeletal events, particularly in patients with metastatic cancer to bone.
How does Lasix help with hypercalcemia?
Furosemide, a potent natriuretic agent, also increases calcium excretion in direct proportion to sodium excretion. It seemed reasonable, therefore, to use this diuretic to increase calcium excretion and to lower serum calcium acutely in patients with hypercalcemia.
How do bisphosphonates treat hypercalcemia?
Bisphosphonates inhibit osteoclastic bone resorption and are effective in the treatment of hypercalcemia due to conditions causing increased bone resorption and malignancy-related hypercalcemia. Pamidronate and etidronate can be given intravenously, while risedronate and alendronate may be effective as oral therapy.
When are bisphosphonates contraindicated?
Avoid oral bisphosphonates in patients with esophageal disorders such as achalasia, esophageal stricture, esophageal varices, Barrett's esophagus, inability to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes, history of bariatric surgery (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass).
Does alendronate cause hypocalcemia?
Alendronate (and other bisphosphonates) may lead to symptomatic hypocalcaemia in patients with pre-existing subclinical hypoparathyroidism. In this patient the most likely explanation of hypocalcaemia is the unmasking of pre-existing subclinical hypocalcaemia caused by hypopar- athyroidism, by alendronate therapy.
Who should not take bisphosphonates?
Don't take bisphosphonates if you:Are allergic to them.Have disorders of the food pipe (esophagus), including tears, holes, narrowing, or difficulty swallowing.Have severe kidney disease.Can't sit in an upright position for at least 30 minutes.Have low levels of calcium in your bloodstream.
Does Lasix lower calcium levels?
The most commonly used diuretic, furosemide (Lasix®), causes the kidneys to produce more urine. As a result, the amount of free water in the body is reduced. Along with an increase in urine volume, furosemide causes loss of calcium, sodium and potassium.
Can steroids cause hypercalcemia?
Chronic hypercalcemia can be an important complication of anabolic steroid and vitamin supplement abuse.
How does calcitonin treat hypercalcemia?
In response to hypercalcemia, calcitonin is secreted by the parafollicular C cells. Calcitonin lowers serum calcium by decreasing renal calcium and phosphorus reabsorption and also by decreasing bone reabsorption. Calcitonin is not significant in overall calcium homeostasis, but it is an important therapeutic option.
What IV is used for hypercalcemia?
Initial therapy of severe hypercalcemia includes the simultaneous administration of intravenous (IV) isotonic saline, subcutaneous calcitonin, and a bisphosphonate (typically, IV zoledronic acid [ZA]) (table 1).
How do you lower hypercalcemia?
These include:Drinking plenty of water: Staying hydrated may lower blood calcium levels, and it can help prevent kidney stones.Quitting smoking, if applicable: Smoking can increase bone loss. ... Exercising, including strength training: Resistance training promotes bone strength and health.More items...
Does Lasix lower calcium levels?
The most commonly used diuretic, furosemide (Lasix®), causes the kidneys to produce more urine. As a result, the amount of free water in the body is reduced. Along with an increase in urine volume, furosemide causes loss of calcium, sodium and potassium.
When does hypercalcemia need to be treated?
If calcium levels are lower than 12 mg/dL and a patient has no symptoms, it is unnecessary to treat the hypercalcemia. In patients with moderate hypercalcemia (12 to 14 mg/dL) and symptoms, specific treatment is necessary. Patients with moderate calcium level elevation but no symptoms may only need adequate hydration.
What is the best treatment for hypercalcemia?
Denosumab (Prolia, Xgeva). This drug is often used to treat people with cancer-caused hypercalcemia who don't respond well to bisphosphonates. Prednisone. If your hypercalcemia is caused by high levels of vitamin D, short-term use of steroid pills such as prednisone are usually helpful. IV fluids and diuretics.
How to treat hypercalcemia?
If your hypercalcemia is mild, you and your doctor might choose to watch and wait, monitoring your bones and kidneys over time to be sure they remain healthy . For more severe hypercalcemia, your doctor might recommend medications or treatment of the underlying disease, including surgery.
What to do if your calcium is too high?
IV fluids and diuretics. Extremely high calcium levels can be a medical emergency. You might need hospitalization for treatment with IV fluids and diuretics to promptly lower the calcium level to prevent heart rhythm problems or damage to the nervous system.
How to cure parathyroid problems?
Surgical and other procedures. Problems associated with overactive parathyroid glands often can be cured by surgery to remove the tissue that's causing the problem. In many cases, only one of a person's four parathyroid glands is affected.
How does calcitonin work?
Calcitonin works largely via reduction of bone calcium reabsorption (similar to bisphosphonates). It also reduces renal calcium reabsorption. Calcitonin is an excellent agent to control calcium while waiting for the bisphosphonate to take effect (typically both agents will be initiated simultaneously ).
Is albumin corrected calcium?
Calcium is partially bound to albumin. This formula attempts to adjust the calcium level for changes in albumin. Corrected calcium may be calculated at MDCalc here. Albumin-corrected calcium is somewhat better than uncorrected calcium level, but it's not terrific. It may tend to overestimate the calcium level.
Is LR safe for hypercalcemia?
Thus, LR will will not elevate the patient's calcium level, so LR remains safe to use in patients with hypercalcemia. Plasmalyte is an excellent choice in most patients, since this is a balanced crystalloid that doesn't contain calcium.
Is ionized calcium biologically active?
Only ionized calcium is biologically active, so ionized calcium is the most clinically relevant measurement. iCa is the preferred measurement of calcium among critically ill patients, if it is available.
How to prevent hypercalcemia?
Talk to your doctor regularly to stay informed and ask questions. Be sure to keep up with any recommended follow-up tests and appointments. You can do your part to help protect your kidneys and bones from damage due to hypercalcemia by making healthy lifestyle choices. Make sure you drink plenty of water.
What causes high calcium levels?
Taking too much vitamin D or calcium in the form of supplements can raise your calcium level. Excessive use of calcium carbonate, found in common antacids like Tums and Rolaids, can also lead to high calcium levels. High doses of these over-the-counter products are the third most common cause.
What hormones are involved in calcium?
Your body uses the interaction between calcium, vitamin D, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) to regulate calcium levels. PTH helps the body control how much calcium comes into the blood stream from the intestines, kidneys, and bones. Normally, PTH increases when the calcium level in your blood falls and decreases when your calcium level rises.
Why does the body make calcitonin?
Your body can also make calcitonin from the thyroid gland when your calcium level gets too high. When you have hypercalcemia, there is excess calcium in your blood stream and your body can’t regulate your calcium level normally. There are several possible causes of this condition:
How to stop kidney stones?
Make sure you drink plenty of water. This will keep you hydrated, keep blood levels of calcium down, and decrease your risk of developing kidney stones. Since smoking can speed up bone loss, it’s important to quit as soon as possible. Smoking also causes many other health issues.
Why is calcium important?
Calcium is essential for the normal function of organs, cells, muscles, and nerves. It’s also important in blood clotting and bone health. However, too much of it can cause problems. Hypercalcemia makes it hard for the body to carry out its normal functions. Extremely high levels of calcium can be life-threatening.
How does bisphosphonate lower calcium levels?
Intravenous bisphosphonates lower blood calcium levels by regulating bone calcium. Dialysis can be performed to rid your blood of extra calcium and waste when you have damaged kidneys. This is usually done if other treatment methods aren’t working.
What causes hypercalcemia?
Severe hypercalcemia is a potentially life-threatening complication of several diseases. Most commonly it is caused by cancers that enhance bone resorption. Impaired renal calcium excretion resulting from a combination of volume contraction and calcium-induced renal injury (nephrocalcinosis) plays a critical role in the genesis and aggravation ...
How long does it take for calcium to be reduced?
One of these agents in combination with volume expansion can reduce serum calcium concentrations to near normal in most patients within 3 to 6 days.
Can narcotics raise calcium levels?
Sedatives and narcotic analgesics, by reducing activity and oral intake, can raise serum calcium levels. In the future it may be possible to predict which patients with cancer are likely to develop accelerated local tumor-mediated or humorally mediated osteolysis.
Can glucocorticoids help with bone resorption?
Bone resorption also can be reduced by getting patients out of bed to stand or walk. Glucocorticoids may be effective in patients with hypercalcemia associated with high levels of vitamin D, such as sarcoidosis, some lymphomas, or vitamin D intoxication. Patients with mild to moderate hypercalcemia may be asymptomatic.
Is hypercalcemia asymptomatic?
Patients with mild to moderate hypercalcemia may be asymptomatic. Therapy in these patients should be directed at the primary disease as well as at preventing complications that could raise the level of serum calcium. Efforts should be made to prevent volume contraction and prolonged bed rest.
Does calcitonin help with bone resorption?
Combining calcitonin with plicamycin or a bisphosphonate can enhance the rate of decline of the serum calcium level. Bone resorption also can be reduced by getting patients out of bed to stand or walk.
What is the best treatment for cancer hypercalcemia?
Certain conditions, including numerous cancer-related hypercalcemias, can be treated with calcium-lowering agents, such as mithramycin and glucocorticoids. Anesthetic management: avoidance of thiazide diuretics and maintenance of hydration and urine output with sodium-containing fluids.
What are the primary treatments for renal failure?
These primary treatments also are useful because sodium inhibits the renal reabsorption of calcium. Additional therapies include 1)bisphosphonates (pa midronate is the most commonly used) 2)calcitonin 3)ambulation 4)hemodialysis 5)treatment of the underlying condition.
What percentage of hypercalcaemia is due to primary hyperparathyroidism?
Ninety percent of hypercalcaemia is due to primary hyperparathyroidism or malignancy. #. Adjusted calcium <3mmol/L: often asymptomatic and does not require urgent correction, however discuss with the endocrine team. #.
What is the normal calcium concentration?
Serum calcium concentration is tightly regulated within a normal reference range of between 2.2-2.6mmol/L. # Abnormalities of parathyroid function, bone resorption, renal calcium reabsorption or dihydroxylation of vitamin D may cause the regulatory mechanisms to fail and serum calcium to rise.
