
What are the methods of removing turbidity from water?
Techniques to Reduce Pond Turbidity
- Pond filtration. A mechanical pump can help to keep the water clear in ornamental ponds, though it may not be sufficient if turbidity levels are abnormally high.
- Use of chemical additives. Chemical treatment should be considered when mineral turbidity levels are exceedingly high. ...
- Surface application of hay. ...
- Culture-beneficial bacteria. ...
What is turbidity and how does it effect water?
Turbidity is the capacity of water to disperse and absorb light, preventing its transmission in depth. It depends on suspended and dissolved solids including pelagic organisms (plankton). Turbidity is a parameter measured in situ, and is directly related to the visual appearance of water. The total suspended solids (TSS) is a parameter measured ...
How to reduce the turbidity?
- Obtain a clear container (Mason jar, soda bottle, etc.) about 1 pint (16 oz) size.
- Fill with tap water.
- Add a small amount of PAM (a few granules or a “pinch”).
- Add a teaspoon of soil from the site.
- Shake for 10-20 seconds or until the water begins to clear, then allow to settle.
How can you remove the turbidity of water?
Simple Options to Remove Turbidity
- Cloth Filtration. A simple option to pre-treat turbid water is to filter through a locally available cloth. ...
- Sand Filtration. Filtration through clean sand is a fast and simple pre-treatment option. ...
- Settling & Decanting. ...
- Moringa Flocculation. ...
- Raket Flocculation. ...
- Alum Flocculation. ...
- Resources. ...
How can we reduce turbidity in water?
Settling and decanting is a method to reduce turbidity by letting the water sit for 2-24 hours so that the particulates settle to the bottom of the container.
What is the possible treatment method of turbidity?
There are three ways to reduce this turbidity: Store the runoff long enough for the sediment to settle (weeks to years in many cases). Store the runoff and filter it (high maintenance and expensive). Treat it with chemical flocculants.
What chemical removes turbidity?
Aluminum sulfate (alum) and ferric chloride are the most widely groups of chemical coagulant and have been extensively used to remove turbidity.
How do you reduce turbidity in a pond?
Treatment with coagulants, particularly alum, almost always clears turbidity from ponds. Eliminate sources of turbidity in culture ponds and use coagulants only if the turbidity remains. Excessive turbidity in ponds caused by suspended soil particles is a frequent occurrence – especially in freshwater aquaculture.
Which type of filtration is suitable for higher turbidity?
Ultrafiltration SystemUltrafiltration System: Removes higher levels of Turbidity: This system is more advanced and is able to filter out more turbid water than Media Filters. Removes bacteria & viruses: UF systems have the capacity to filter fine particles, suspended solids (including silt & colloids), and organic matter.
How does coagulation reduce turbidity?
Turbidity reduction by coagulation-flocculation in drinking water reduces microbes and organic matter, increasing effectiveness of downstream treatment. Chitosan is a promising household water coagulant, but needs parameters for use.
What is turbidity water purification?
Turbidity can act as a shield to pathogens and the particles that cause turbidity can harbor bacteria and viruses. Turbidity is removed through our multi-barrier water treatment process which includes coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
How do you reduce turbidity in a creek?
Conventional media filtration with anthracite, sand and garnet is the most common filtration system for turbidity reduction. Typically used with any surface or bore water, this filtration method responds well to changes in the source water quality.
How is turbidity and color removed from impure water?
Filtration Rapid Mixing Slow Mixing Settling Cleaning The primary purpose of the coagulation/flocculation process is the removal of turbidity from the water. The process removes many bacteria which are suspended in the water and can be used to remove color from the water.
What is flocculant for?
Flocculants. Flocculation and coagulation treatment chemicals are used in effluent wastewater water treatment processes for solids removal, water clarification, lime softening, sludge thickening, and solids dewatering.
Why is turbidity important in water treatment?
Turbidity in water treatment is critically needed as it is the most visible form of contamination. There are many sources that require turbidity removal for their intended applications. For example, treated wastewater and surface water are common sources used for a multitude of different applications; however, these sources are generally filled with visible contaminants that can negatively affect the application and must be removed. Increased levels of turbidity can facilitate microbial growth which leads to unhealthy water. Paying attention to turbidity levels and taking it into consideration enables the following processes to run smoothly and efficiently, whether it be an RO system, irrigation, or even drinking water purposes. A turbidity monitor that will alert the customer when the turbidity levels have reached an undesirable level is available upon request. This feature can prevent internal damage from occurring and ensure optimal permeate quality.
What is turbidity in water?
Turbidity refers to how clear or cloudy water is depending on the amounts of contaminants like suspended solids, organic matter, dirt, clay, and grit; and is typically measured in NTUs (Nephelometric turbidity units) while some companies like to refer to it as SDIs (Silt Density Index).
Why does water turn yellow?
The contaminants responsible for turbidity surround multiple surface water sources like wells, rivers, lakes, and sometimes seawater. Color change also falls under turbidity which occurs from the presence of heavy metals like iron that can cause the water to turn yellow and orange.
How to reduce turbidity in water?
Settling and decanting is a method to reduce turbidity by letting the water sit for 2-24 hours so that the particulates settle to the bottom of the container. The clear water is then decanted off the top into a second container. The benefit of settling and decanting is that it requires no equipment besides the containers. The drawbacks of settling and decanting are the need for multiple containers, the time it takes the water to settle, and, if the containers are opaque, the difficulty in observing the effect of settling. In laboratory studies, the use of settling and decanting significantly reduced both the turbidity and the chlorine demand of turbid waters.
How does inadequate water sanitation affect children?
The health consequences of inadequate water and sanitation services include an estimated 4 billion cases of diarrhea and 1.9 million deaths each year, mostly among young children in developing countries. Diarrheal diseases lead to decreased food intake and nutrient absorption, malnutrition, reduced resistance to infection, and impaired physical growth and cognitive development. Since 1996, a large body of published work has proven the effectiveness of interventions to improve water quality through household water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) at reducing diarrheal disease. However, not all of these interventions remove the turbidity that causes water to look dirty. Although the following options are not proven to reduce diarrheal disease incidence on their own, they can be used to pre-treat water to reduce turbidity before the use of household water treatment products. These options mechanically (through filtration) or chemically (through flocculation and settling of suspended material) remove particles and reduce turbidity. These pre-treatment methods may also increase the efficacy of household water treatment products by removing contaminants that interfere with disinfection and physical filtration processes. For more information, contact //safewater [at] cdc [dot] gov "> [email protected] .
What are the drawbacks of sand filtration?
The drawback of sand filtration is that it requires three containers and a spigot. In laboratory studies, the use of sand filtration significantly reduced both the turbidity and the chlorine demand of turbid water.
What is aluminum sulfate used for?
Aluminum sulfate is widely used as a flocculant in water treatment plants in the United States and Europe. It is also widely available in developing countries, sold in naturally occurring mineral blocks of soft white stone, and generally called ‘alum’.
Does alum reduce chlorine?
In laboratory studies , the use of alum significantly reduced the turbidity of water, and also significantly reduced the chlorine demand of turbid waters.
Does HWTS help with diarrhea?
Since 1996, a large body of published work has proven the effectiveness of interventions to improve water quality through household water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) at reducing diarrheal disease. However, not all of these interventions remove the turbidity that causes water to look dirty. Although the following options are not proven ...
Types of Pond Turbidity
Mineral turbidity is common in new ponds and can be recognised by the pond water turning reddish to light brown. Doug Beckers / CC BY-SA 2.0
Techniques to Reduce Pond Turbidity
A mechanical pump can help to keep the water clear in ornamental ponds, though it may not be sufficient if turbidity levels are abnormally high. Crinklecrankle.com / CC BY 2.0
Importance of Maintaining a Clear Pond
Turbid water can prevent fish owners from spotting sickly fish and quarantining them before they spread disease to others. Ivan Radic / CC BY 2.0
Why is turbidity important in water treatment?
Therefore, removing turbidity serves a two-fold purpose in water treatment: it removes some microbes, while reducing the levels of organic matter and other particles, increasing the effectiveness of downstream treatment processes.
Why is turbidity important in drinking water?
Effective reduction of turbidity is one of the primary goals in effective drinking water treatment because of potential interference with downstream treatment processes and negative effects on consumer acceptance. Turbidity might interfere with filtration by clogging the filter prematurely.
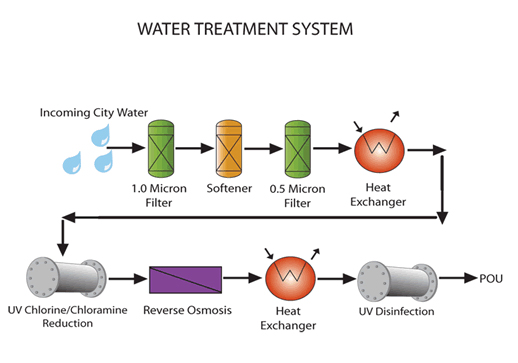
What is POU treatment?
In areas without water treatment systems or with impaired sources of drinking water, water may need treatment at the household level, or point of use (POU) to render it safe to drink. This household level treatment can include turbidity reduction, which should be followed by POU filtration and ideally disinfection.
Does chitosan increase turbidity?
Also, simply increasing the solubility of the polymer in water does not necessarily increase turbidity reduction efficacy. The best of the studied chitosan dosages for reduction of both bentonite and kaolinite turbidity was 3 mg/L, although there was a broader effective dose range for bentonite than kaolinite.
