- You notice an increase in swelling, discoloration or pain.
- Your symptoms don't go away a few days after starting antibiotics.
- Your cellulitis infection spreads to surrounding areas of your body.
Medication
An infection like athlete’s foot or impetigo can lead to cellulitis, so you want to treat it as soon as you notice signs. Dry, itchy skin between your toes can mean athlete’s foot. Sores, red and swollen skin, or blisters can be a sign of an infection. Treat other medical conditions.
Procedures
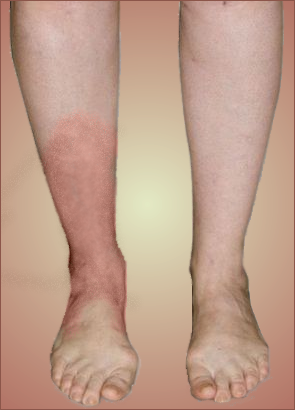
In general, cellulitis appears as a red, swollen, and painful area of skin that is warm and tender to the touch. The skin may look pitted, like the peel of an orange, or blisters may appear on the affected skin. Some people may also develop fever and chills.
Self-care
See a doctor if you have symptoms of cellulitis. Seek medical attention immediately if the red area of the skin spreads quickly or you develop a fever or chills. Anyone can get cellulitis, but some factors can increase the risk of getting this infection.
Nutrition
In some cases, he or she may suggest blood tests or other tests to help rule out other conditions. Cellulitis treatment usually includes a prescription oral antibiotic. Within three days of starting an antibiotic, let your doctor know whether the infection is responding to treatment.
What are the symptoms of cellulitis and how is it treated?
What does cellulitis look like on the skin?
When should I see a doctor for cellulitis?
How do you test for cellulitis?

How do you tell if antibiotics are working for cellulitis?
Cellulitis symptoms should gradually get better. Symptoms usually begin to improve within 1 to 3 days of starting antibiotics. Pain and firmness will begin to subside. You should see the area become less red and swollen.
Should cellulitis be completely gone after antibiotics?
Symptoms of cellulitis usually disappear after a few days of antibiotic therapy. However, cellulitis symptoms often get worse before they get better, probably because, with the death of the bacteria, substances that cause tissue damage are released.
How long does cellulitis take to heal completely?
Treatment for cellulitis It's important to keep taking antibiotics until they're finished, even when you feel better. Most people make a full recovery after 7 to 10 days. If cellulitis is severe, you might be referred to hospital for treatment.
What should I monitor for cellulitis?
The IDSA recommends bloodwork for patients with skin or soft tissue infection (SSTI) who have signs and symptoms of systemic toxicity; such tests include blood cultures, complete blood cell (CBC) with differential, and levels of creatinine, bicarbonate, creatine phosphokinase, and C-reactive protein (CRP).
How do you know if cellulitis is healing?
The healing process of cellulitis can be tracked visually. In most cases, symptoms will disappear after a few days on antibiotics....Signs of healing to look for include:Reduced pain.Less firmness around the infection.Decreased swelling.Diminished redness.
What happens if antibiotics don't work for cellulitis?
Without antibiotic treatment, cellulitis can spread beyond the skin. It can enter your lymph nodes and spread into your bloodstream. Once it reaches your bloodstream, bacteria can cause quickly cause a life-threatening infection known as blood poisoning.
Will my skin go back to normal after cellulitis?
Cellulitis can take weeks to get better. The swelling, weeping and discolouration of the skin may last for many weeks, even once the infection is fully treated. You will not need to take antibiotics for all this time. Normally the course is 7 – 10 days but may be longer in severe cases.
Does cellulitis go purple when healing?
The second is due to a polymicrobial infection of different bacteria that often starts just forward of the anus following surgery or rectal abscesses. Necrotizing cellulitis starts as an extremely painful, red swelling that soon turns purple and then black as the skin and flesh die.
What are the signs that cellulitis is getting worse?
You have signs that your infection is getting worse, such as:Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness.Red streaks leading from the area.Pus draining from the area.A fever.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work for cellulitis?
Most people with cellulitis respond to the antibiotics in 2 to 3 days and begin to improve. In rare cases, the cellulitis may spread through the bloodstream and become serious. Even more rarely, surgery is required to drain an abscess or remove dead tissue.
Does cellulitis peel when healing?
Cellulitis may be associated with lymphangitis and lymphadenitis, which are due to bacteria within lymph vessels and local lymph glands. A red line tracks from the site of infection to nearby tender, swollen lymph glands. After successful treatment, the skin may flake or peel off as it heals. This can be itchy.
Is it normal for cellulitis to blister?
Signs and symptoms In general, cellulitis appears as a red, swollen, and painful area of skin that is warm and tender to the touch. The skin may look pitted, like the peel of an orange, or blisters may appear on the affected skin.
How long does it take for cellulitis to heal?
You should start to see improvement in 3 days. If cellulitis is not treated, the infection can spread through your body and become life-threatening. You may need any of the following medicines: Antibiotics help treat the bacterial infection. Acetaminophen decreases pain and fever.
What is the cause of cellulitis?
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Cellulitis is a skin infection caused by bacteria. Cellulitis is common and can become severe. Cellulitis usually appears on the lower legs. It can also appear on the arms, face, and other areas. Cellulitis develops when bacteria enter a crack or break in your skin, such as a scratch, bite, or cut.
How to get rid of swelling in a swollen ear?
This will help decrease swelling and pain. Prop the area on pillows or blankets to keep it elevated comfortably. Place a cool, damp cloth on the area. Use clean cloths and clean water. You can do this as often as you need to. Cool, damp cloths may help decrease pain. Apply cream or ointment as directed.
How do you know if you have a wound?
Your wound gets larger and more painful. You feel a crackling under your skin when you touch it. You have purple dots or bumps on your skin, or you see bleeding under your skin. You see red streaks coming from the infected area.
How long does it take for a fever to go away after antibiotics?
The red, warm, swollen area gets larger. Your fever or pain does not go away or gets worse. The area does not get smaller after 3 days of antibiotics. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
How to take medicine if you are allergic to it?
Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell him or her if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them.
How do doctors diagnose cellulitis?
Doctors diagnose it by examining the infected skin and asking questions. This information can help make sure you get the treatment you need and prevent problems. Medical tests: While a test cannot tell whether you have cellulitis, testing can tell what germs are causing an infection.
How to treat cellulitis?
It can help you avoid serious medical problems like blood poisoning and severe pain. To treat cellulitis, doctors prescribe: Antibiotics: An oral (you take by swallowing) antibiotic can effectively clear cellulitis. The type of antibiotic you need and how long you’ll need to take it will vary.
How long does it take for cellulitis to clear?
If you fail to notice improvement after 24 – 48 hours, let your doctor know. While cellulitis will clear with treatment, anyone who has had it has a higher risk of getting cellulitis again. You can find out what helps to prevent this at Cellulitis: How to prevent it from returning. Images.
How long do you stay in hospital for cellulitis?
Most people are hospitalized for just over one week. Wound care: This is an important part of treating cellulitis. Covering your skin will help it heal. If you need special wound coverings or dressings, you’ll be shown how to apply and change them.
Can a doctor tell if you have cellulitis?
Medical tests: While a test cannot tell whether you have cellulitis, testing can tell what germs are causing an infection. A referral to a dermatologist: If you are seeing a doctor other than a dermatologist, you may be sent to a dermatologist. Cellulitis can look like other skin conditions and infections.
Can cellulitis look like other skin conditions?
Cellulitis can look like other skin conditions and infections. Dermatologists have extensive training in diagnosing the many conditions that can look like cellulitis. An accurate diagnosis is essential to clear your skin condition.
How do doctors diagnose cellulitis?
Doctors Diagnose Cellulitis by How It Looks. Doctors typically diagnose cellulitis by doing a physical examination and looking at the affected skin. Blood or other lab tests are usually not needed.
How is cellulitis treated?
Cellulitis is treated with antibiotics. Most cellulitis infections can be treated with antibiotics that are taken by mouth (oral antibiotics). More serious infections may need to be treated in the hospital with intravenous (IV) antibiotics, which are given directly into a vein.
What does it mean when your skin is red and swollen?
In general, cellulitis appears as a red, swollen, and painful area of skin that is warm and tender to the touch. The skin may look pitted, like the peel of an orange, or blisters may appear on the affected skin. Some people may also develop fever and chills. Cellulitis can appear anywhere on the body, but it is most common on the feet and legs.
What is the condition that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the infected area of the skin?
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the infected area of the skin. If untreated, it can spread and cause serious health problems. Good wound care and hygiene are important for preventing cellulitis.
How do you get cellulitis?
How People Get Cellulitis. Experts do not know how the bacteria get into the body for many people who get cellulitis. Sometimes the bacteria get into the body through openings in the skin, like an injury or surgical wound. In general, people cannot catch cellulitis from someone else.
What are the factors that increase the risk of cellulitis?
Other factors that increase someone’s risk for cellulitis include: Problems with the lymphatic system so it does not drain the way it should (lymphedema); the lymphatic system is a part of the body’s immune system that helps move fluid that contains infection-fighting cells throughout the body.
How to prevent cellulitis?
Common sense and good wound care are the best ways to prevent bacterial skin infections, including cellulitis. Clean all minor injuries that break the skin with soap and water. Clean all minor cuts and injuries that break the skin (like blisters and scrapes) with soap and water.
What is the best antibiotic for cellulitis?
Narrow spectrum penicillins targeting streptococci and staphylococci (in the case of purulent infection) should be the mainstay of antimicrobial therapy. The natural history of cellulitis is one of slow resolution. Fever and inflammation often persist during the first 72 hours of treatment.
What is the term for an acute infection of the skin involving the dermis and subcutaneous tissues?
Cellulitis is simply defined as an acute infection of the skin involving the dermis and subcutaneous tissues. Erysipelas classically refers to a more superficial cellulitis of the face or extremities with lymphatic involvement, classically due to streptococcal infection.
Can you have a culture of blood with sepsis?
Cultures of blood, aspirates or biopsies are not recommended but should be considered in patients who have systemic features of sepsis, who are immunosuppressed or for cases associated with immersion injuries or animal bites.12. Cellulitis mimics.
Is cellulitis a clinical condition?
Cellulitis is a frequently encountered condition, but remains a challenging clinical entity. Under and overtreatment with antimicrobials frequently occurs and mimics cloud the diagnosis. Typical presentation, microbiology and management approaches are discussed. KEYWORDS: infection, cellulitis, OPAT, antibiotics.
How do you know if you have cellulitis?
Cellulitis tends to progress quickly, so early identification is key. At first, you might just feel some pain and tenderness. But over the course of a few hours, you may start to notice: skin that’s warm to the touch. blistering. skin dimpling. growing area of redness.
How to heal cellulitis at home?
Covering your wound. Properly covering the affected skin will help it heal and prevent irritation.
How long does it take for cellulitis to go away?
With antibiotic treatment, the symptoms of cellulitis should begin to disappear within 48 hours, but it’s very important to continue taking your antibiotics until all the pills are gone. Otherwise, it may come back, and the second course of antibiotics may not be as effective as the first.
What is cellulitis on legs?
What is cellulitis? Cellulitis is a type of bacterial infection that can quickly become serious. It affects your skin, causing inflammation, redness, and pain. This type of infection occurs when bacteria enters your body through broken skin. It can affect any part of the body, but it’s most common on the lower legs.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work on cellulitis?
Sometimes oral antibiotics don’t work as well as they should. If your cellulitis is not improving after two or three days, your doctor may prescribe a different antibiotic or have you admitted for IV treatment.
What is it called when you have a deep infection of the fascia?
An infection of the fascia, a deep layer of tissue surrounding your muscles and organs, is known as necrotizing fasciitis, or flesh-eating disease. People with necrotizing fasciitis usually need multiple surgeries to remove dead tissue, often entire limbs.
What is the best treatment for athlete's foot?
A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve), can help reduce pain and inflammation. Treating any underlying conditions. Treat any underlying conditions, such as athlete’s foot or eczema, that caused the wound that got infected. Taking all your antibiotics.
How to prevent cellulitis?
Preventing cellulitis can be as simple as following the surgeon’s instructions for caring for your surgical incision, including taking the time to keep it clean and changing your bandage as appropriate. 6 .
What is cellulitis in the body?
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin that typically happens after a break in the integrity of the skin. A break in the skin can be something as small as a paper cut or a similar wound or could be a crack in dry skin. Essentially, any break in the skin can become a doorway for bacteria to enter and create an infection in the skin.
Why is cellulitis more likely to occur in diabetics?
Diabetics, in particular, are at risk for cellulitis because their immune system is often impaired and they may have diminished sensation, which can result in the infection being further along before it is first noted. 3 .
What causes cellulitis on the skin?
Causes. Most cellulitis infections are caused by one of two strains of bacteria: streptococcus and staphylococcus. These two types of bacteria cause the vast majority of cases and are present on the skin of many healthy individuals, but other types of bacteria can also be responsible. Knowing the type of bacteria responsible for ...
What are the risks of cellulitis?
Risk Factors. Any condition that causes a break in the skin can be a risk factor for cellulitis. 1 Surgery is a major risk factor for any type of skin infection due to the incision (s) necessary to perform a procedure. Incisions are sometimes large, or in some cases, there are multiple incisions, which increase the risk of an incision.
What happens when the skin is not healthy?
When skin is not healthy or has an opening such as a wound, the bacteria that make up the normal flora can penetrate to the lower levels of the skin, where the infection begins and, in some cases, becomes cellulitis .
Where does cellulitis occur?
Most cellulitis occurs in the legs, but it can occur almost anywhere on the body. 2 For the surgery patient, the site of an incision is by far the most common site of infection. This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
How to get rid of cellulitis?
While there is no cure for lymphedema, it can be treated with exercise, compression bandages, elevation, and drainage. Lose weight.
How to treat cellulitis in a wound?
Wash the wound with soap and water. Apply an antibiotic ointment. Cover the wound with a bandage. Clean and change the bandage every day (or as often as your doctor recommends) until the wound heals. Keep your skin clean and moisturized. Keeping your skin clean washes away bacteria that cause cellulitis.
How to reduce the risk of getting cellulitis?
This can help reduce your risk of getting cellulitis again. The following can help decrease your risk of getting cellulitis again: Avoid injuring your skin. Skin injuries include cuts, scrapes, burns, sunburns, frostbite, stings from bees and other insects, and abrasions.
How to prevent dry skin from forming?
An effective way to prevent or reduce dry skin is to apply moisturizer within three minutes of taking showers or baths.
Can you get cellulitis again?
If you’ve had cellulitis, you have a higher risk of getting it again. Even after successful treatment, some people get cellulitis again and again. For most people, the cellulitis develops in the same place every time.
Can antibiotics help with cellulitis?
Repeat flares of cellulitis can be reduced with daily antibiotics. If you continue to get cellulitis after doing what you can to reduce your risk, research shows that taking a low-dose antibiotic can help. This treatment may be recommended for someone who has had cellulitis three or four times in one year.
Does smoking cause cellulitis?
While more research is needed to know whether smoking increases your risk of getting cellulitis again, research suggests it might. If you drink alcohol, drink in moderation. More research is also needed to know whether alcohol increases your risk of getting cellulitis again.
How do you know if you have cellulitis?
The most common symptoms of cellulitis include: itching. swelling or red, inflamed areas of skin. pain and tenderness. tight, glossy skin over infected area. feeling of warmth. fever. abscess or pus-filled pocket. Some symptoms may indicate you’re experiencing side effects or complications of cellulitis.
How long does it take for cellulitis to heal?
Most cases of cellulitis will heal in 7 to 10 days with a regular course of antibiotics. Some infections may require longer treatment if the infection is not responding well. People with severe infections or those with a weakened immune system may also need longer or stronger doses of antibiotics.
What is the cause of cellulitis?
Cellulitis is often caused by Staphylococcus, a type of bacteria. A more serious type of staph bacteria, known as MRSA, can also cause cellulitis. MRSA is resistant to many of the antibiotics that can treat normal staph infections.
What causes redness on the legs?
Prevention. Summary. Cellulitis is a common bacterial infection that develops in the layers of skin. It can cause painful, hot to the touch, and red swelling on your body. It’s most common on the lower legs, but it can develop anywhere.
What are the complications of cellulitis?
Complications of cellulitis. These complications or side effects of a cellulitis infection are the most common. They can occur in people who don’t seek treatment, and they may also occur when treatment isn’t effective. Some of these complications are medical emergencies, and you should seek immediate attention if you show symptoms.
How to help a swollen limb?
Injections, pills, or topical antibiotics may be used to help end the infection and prevent complications. Rest can go a long way to helping promote healing, too. Lying with your affected limb raised above your heart may reduce swelling. This will cut down on irritation, itching, and burning.
What are the conditions that make you more susceptible to infection?
Manage underlying medical conditions. People with conditions like diabetes, cancer, and vascular disease may have a weakened immune system. This can make you more susceptible to infection. If you manage those conditions, you may be more capable of handling secondary issues, such as cellulitis, when they occur.
