
What is treatment for calcified heart valve?
- ultrasound investigation of the heart;
- chest x-ray;
- cardiac catheterization;
- ventrikulografii;
- aortography;
- ultrasonography.
What are the symptoms of a calcified heart valve?
chest pain as the heart strains to pump enough blood through the compromised valve feeling tired after exertion, as when you exercise or move feeling short of breath, especially after exertion
What causes mitral valve calcification?
- Severe MAC can complicate mitral valve replacement. ...
- Severe MAC has been considered a contraindication for percutaneous mitral valve intervention with the MitraClip.
- MAC is an independent predictor of permanent pacemaker implantation following transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
What causes calcified heart valves?
Calcium buildup on the valve. Calcium is a mineral found in your blood. As blood repeatedly flows over the aortic valve, calcium deposits can build up on the heart valves (aortic valve calcification). The calcium deposits may never cause any problems.

Can you reverse valve calcification?
Currently no clinical therapy is available to prevent or reverse this type of vascular calcification. Some possible targets to block and regress calcification include local and circulating inhibitors of calcification as well as factors that may ameliorate vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis [2].
How do you treat aortic valve calcification?
Currently, the only established treatment for calcific aortic stenosis is surgical valve replacement. Due to the increasing number of ongoing basic scientific and clinical studies, the cellular mechanisms responsible for this disease clearly demonstrate that medical therapy may be an option for these patients.
How serious is a calcified heart valve?
Aortic valve calcification is a condition in which calcium deposits form on the aortic valve in the heart. These deposits can cause narrowing at the opening of the aortic valve. This narrowing can become severe enough to reduce blood flow through the aortic valve — a condition called aortic valve stenosis.
Can a calcified aortic valve be repaired?
The novel repair technique of calcified bicuspid aortic valve is described, in which the calcified body of the cusps is repaired with autologous pericardium leaving the native free margin and commissures in place for anchoring. The technique has been used in 48 consecutive patients offering excellent early results.
How serious is calcification of the aorta treatment?
Calcific aortic stenosis (AS) is a progressive disease with no effective medical therapy that ultimately requires aortic valve replacement (AVR) for severe valve obstruction.
How long can you live with aortic calcification?
Severe symptomatic aortic stenosis is associated with a poor prognosis, with most patients dying 2–3 years after diagnosis.
How is calcification of the heart treated?
Although healthcare providers don't have a standard treatment for coronary artery calcification, some are using intravascular lithotripsy to treat severe cases. This newer procedure uses a catheter (tube) with a device at the end that sends pressure waves out to make the calcification come apart.
How long can you live with coronary artery calcification?
As follow-up lengthened, all-cause mortality rates increased: Patients with a CAC score of 0 had a mortality rate of 0.7% at 7 years (11). The incident mortality curves revealed very low mortality through 5 years, but mortality seemed to increase substantively between 5 and 15 years of follow-up.
What causes a heart valve to calcify?
As blood repeatedly flows over the aortic valve, calcium deposits can build up on the heart valves (aortic valve calcification). The calcium deposits may never cause any problems. Aortic valve stenosis that's related to increasing age and calcium deposit buildup usually doesn't cause symptoms until ages 70 or 80.
How can I strengthen my heart valve naturally?
9 Natural Ways to Strengthen Your Heart ValvesLook at Your Plate. ... Pop Some Fish Oil. ... Keep Your Weight in Check. ... Decrease Salt Intake. ... Get Better Sleep. ... Move Around. ... Try Meditation. ... Up Your Dental Hygiene.More items...•
What foods to avoid if you have aortic stenosis?
Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables, low-fat or fat-free dairy products, poultry, fish, and whole grains. Avoid saturated and trans fat, and excess salt and sugar.
Does vitamin D cause aortic stenosis?
Conclusions: Vitamin D and or Calcium supplement intake worsens aortic stenosis progression and increases the need for AVR. It does not have a significant impact on mortality.
What Is A Calcified Heart Valve?
Dr. Borger Says: A calcified heart valve is one in which a large amount of calcium has been deposited over many years. Heart valves are normally fo...
How Does A Heart Valve Get calcified?
Dr. Lamelas Says: There are multiple reasons that valves calcify. One particular reason is attributed to the normal wear and tear of the heart valv...
Can Each of The Four Heart Valves Get calcified?
Dr. Lamelas Says: The left sided heart valves (aortic and mitral) are usually the valves that calcify. The aortic valve, which is the main valve or...
How Does A Calcified Heart Valve Impact Patients?
Dr. Borger Says: Once the calcification and valve stenosis become severe, patients will develop increasing shortness of breath on exertion. Lighthe...
How Are Calcified Heart Valves Treated?
Dr. Lamelas Says: A valve replacement is indicated in patients where the calcium on the valve progresses to the point where its function is impaire...
If A Calcified Valve Is Replaced, Can It Get Calcified Again?
Dr. Lamelas Says: Yes. Bio-prosthetic valves that are implanted in young patients as well as those on dialysis have a greater chance of calcifying...
Is There Anything Else You Feel Patients Should Know About Calcified Heart Valves? Any Tips For Preventing Heart Valve Calcification?
Dr. Borger Says: This is a frequent question of patients, “What can patients do to prevent heart valve calcification?” Unfortunately, there is no k...
What is a calcification of the aortic valve?
Aortic valve calcification is a condition in which calcium deposits form on the aortic valve in the heart. These deposits can cause narrowing at the opening of the aortic valve. This narrowing can become severe enough to reduce blood flow through the aortic valve — a condition called aortic valve stenosis. Aortic valve calcification may be an early ...
Can aortic valve calcification be a sign of heart disease?
Aortic valve calcification may be an early sign that you have heart disease, even if you don't have any other heart disease symptoms. Calcification and stenosis generally affects people older than age 65. When it occurs in younger people, it's often caused by:
What is the condition of a calcified heart valve?
However, if your calcified heart valve causes a condition known as stenosis -- a narrowing of the valve, which impedes blood flow -- then treatment may be necessary. According to MedlinePlus.com, when stenosis occurs, you may need valve replacement surgery.
Why is my heart valve calcified?
Causes of Calcification. Not having enough magnesium in your diet can cause you to suffer from a calcified heart valve. Age also can bring about calcification of your heart valves. In fact, the University of Maryland Medical Center reports that aortic valve calcification is common in people who are older than 75.
What are the four valves in the heart?
Your heart contains four valves: pulmonary, aortic, tricuspid and mitral. According to the Mayo Clinic, calcification of one of these valves can occur as you grow older. However, it also can occur if you do not watch your diet and eat foods high in cholesterol or fat. Heart valve calcification also can occur if you are underweight, ...
What tests are used to check for calcified heart valves?
The Cleveland Clinic reports that your physician may also use a variety of tests to identify the calcified heart valve, including echocardiograms, electrocardiograms and cardiac catheterization. The Cleveland Clinic reports that other diagnostic tests such as ultrasounds, computer tomography and magnetic resonance imaging tests can be used.
Can heart valves cause heart disease?
Heart valve calcification also can occur if you are underweight, including those who suffer from eating disorders. If your heart valves calcify, it can interfere with how your blood flows through your heart, and this can cause you to develop heart disease.
Can a calcified heart valve cause shortness of breath?
According to the Cleveland Clinic, a calcified heart valve will lead to valve disease s, which have symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, coughing, heart palpitations, chest pain or tightness and dizziness. You may also suffer from swollen ankles or feet due to fluid buildup.
What is the best treatment for calcification of the heart valves?
The primary option for treatment of calcification of the heart valves is surgery. For certain patients, focused ultrasound could provide a noninvasive alternative to surgery with less risk of complications – such as surgical wound healing or infection – at a lower cost.
How does cavitational focused ultrasound work?
How it Works. Where the beams converge, pulsed cavitational focused ultrasound (or histotripsy) will deliver mechanical energy to the calcium deposits on the valve. This improves blood flow and the valves' ability to open. This is similar to lithotripsy, which is used on kidney stones.
Is Cardiawave used for kidney stones?
This is similar to lithotripsy, which is used on kidney stones. Cardiawave is treating patients with aortic stenosis that have calcifications on their aortic valves. The initial use is for patients with severe, symptomatic aortic stenosis patients. This study is believed to be the first in human treatment. Advantages.
How to diagnose calcification?
Diagnosing calcification. Calcifications are usually found via X-rays. X-ray tests use electromagnetic radiation to take pictures of your internal organs and usually cause no discomfort. Your doctor will likely detect any calcification issues right away with X-rays. Your doctor may also order blood tests.
What causes calcification in the body?
Causes of calcification. Many factors play a role in calcification. These include: infections. calcium metabolism disorders that cause hypercalcemia (too much calcium in the blood) genetic or autoimmune disorders affecting the skeletal system and connective tissues. persistent inflammation.
What are the soft tissues that are affected by calcium buildup?
soft tissues like breasts, muscles, and fat. kidney, bladder, and gallbladder. Some calcium buildup is harmless. These deposits are believed to be the body’s response to inflammation, injury, or certain biological processes. However, some calcifications can disrupt organ function and affect blood vessels.
What happens when calcium builds up in the body?
Calcification happens when calcium builds up in body tissue, blood vessels, or organs. This buildup can harden and disrupt your body’s normal processes. Calcium is transported through the bloodstream. It’s also found in every cell. As a result, calcification can occur in almost any part of the body. According to the National Academy of Medicine. ...
What is the most common type of breast calcification?
According to the National Cancer Institute, macrocalcifications in the breasts are most common in women over 50 years old.
What medications affect calcium levels?
Some medications can affect your body’s calcium levels. Cholesterol medication, blood pressure medication, and hormone replacement therapy are common medications that affect how calcium is used in your body.
Can you get calcifications at 65?
If you’re under 65 years old and were born with a heart defect or kidney-related issues, calcifications can be more common for you than for others of your age. If you are aware of any of these conditions, ask your doctor about getting tested for calcifications. Some medications can affect your body’s calcium levels.
What causes calcium to be calcified?
existing heart or kidney conditions. taking certain medications that affect the way your body processes calcium, such as high blood pressure and cholesterol medications. injury.
What organs are affected by aortic calcification?
The arteries ( atherosclerosis ) heart valves (calcification of the aortic valve) other organs, such as the kidneys, bladder, and even (though rare) the liver. other soft tissues (muscles, breasts, fatty tissue) joints and tendons. the brain (cranial calcification)
Can kidney stones be removed surgically?
Calcium deposits in the joints and tendons can be removed surgically. While people with kidney stones will likely be prescribed diuretics that stimulate calcium build-up in the bones. Those prone to kidney stones may also be advised to reduce their calcium intake.
Is calcification normal in women?
Almost all adult humans have some calcification of the pineal gland in the brain, and about half of women over 50 have some calcification within their breast tissues.
Can calcification be self diagnosed?
While calcification of any kind is unlikely to produce symptoms that easily lead to self-diagnosis, anyone concerned about their health should see a orthopaedic in Delhi. The detailed description of your symptoms will allow your doctor to decide what kinds of tests should be done, leading to a diagnosis.
What is the best treatment for calcium buildup around the heart valve?
What Are Remedies for Calcium Deposits Around the Valve of the Heart? The only true remedy for calcium buildup around the valve of the heart, also called aortic valve stenosis, is surgery to repair the valve. Low blood pressure medications may ease the symptoms of aortic valve stenosis, but no medications counteract the narrowing ...
How do you know if you have calcium buildup in your heart?
These symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath and heart murmur. Surgeons use a variety of procedures to treat the condition, like aortic valve replacement and balloon valvuloplasty. Overall, doctors effectively treat calcium buildups in the hearts’ valves with surgery, the Mayo Clinic claims. However, patients may still have irregular ...
Can a congenital defect cause calcium buildup?
A congenital defect in the aortic valve may also cause calcium buildup. A defective heart valve causes blood to leak backwards, the Mayo Clinic says, which causes stenosis. Doctors do not always suggest surgery to repair aortic valve stenosis.
Do you need antibiotics after stenosis surgery?
Others may need to take medication for heart failure if the heart has become weak from the stenosis. All patients need to take antibiotics after the surgery to prevent infections in the heart. ADVERTISEMENT.
Can low blood pressure cause aortic valve stenosis?
Low blood pressure medications may ease the symptoms of aortic valve stenosis, but no medications counteract the narrowing of the aortic valve, the Mayo Clinic says. Most people who suffer from calcium deposits around the aortic valve are men older than 65 years old and women older than 75 years old. A congenital defect in the aortic valve may also ...
Lifestyle
Changes to your lifestyle can help prevent and slow the progression of coronary calcification. These can include dieting (especially to limit cholesterol, fat, and sodium), exercising, quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol and losing weight.
Medications
If you’re at risk of coronary calcification your doctor may prescribe cholesterol medications to reduce low density lipoproteins (LDL) known as the "bad" cholesterol (eg, statins) or to increase high density lipoproteins (HDL) known as the "good" cholesterol (eg, niacin).
Procedures & Surgery
For severe atherosclerosis that has caused—or threatens to cause—symptoms or disease, further intervention may be necessary. This can include:
Professor Cathy Shanahan says
When your doctor tells you that you have calcified arteries, it is usually after you have had a coronary calcification scan. This is a type of X-ray that can show how much calcium has built up in the blood vessels of your heart.
Meet the expert
Cathy Shanahan is Professor of Cellular Signalling at King's College, London.
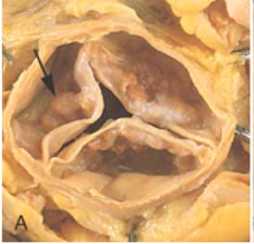
Focused Ultrasound Therapy
Clinical Trials
- A pivotal clinical trialin Europe is organizing for aortic valve calcifications causing severe aortic stenosis. A clinical trialin Serbia is treating patients with severe aortic stenosis.
Regulatory Approval and Reimbursement
- Focused ultrasound treatment for heart valve calcifications is not yet approved by regulatory bodies or covered by medical insurance companies.
Notable Papers
- Messas E, IJsselmuiden A, Goudot G, Vlieger S, Zarka S, Puymirat E, Cholley B, Spaulding C, Hagège AA, Marijon E, Tanter M, Bertrand B, Rémond MC, Penot R, Ren B, den Heijer P, Pernot M, Spaargaren R. Feasibility and Performance of Noninvasive Ultrasound Therapy in Patients With Severe Symptomatic Aortic Valve Stenosis: A First-in-Human Study. Circulation. 2021 Mar 2;143…