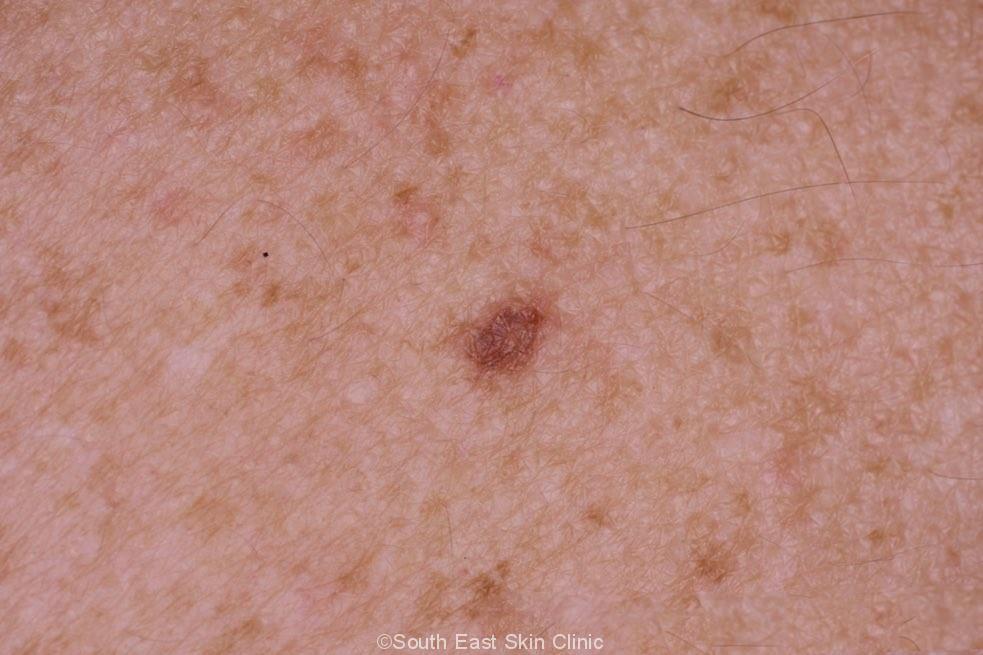
The best way to treat a dysplastic nevus
Nevus
Nevus is a nonspecific medical term for a visible, circumscribed, chronic lesion of the skin or mucosa. The term originates from nævus, which is Latin for "birthmark", however, a nevus can be either congenital or acquired. Common terms, including mole, birthmark, and beauty mark, are used to describe nevi, but these terms do not distinguish specific types of nevi from one another.
Should dysplastic nevus be removed?
The best way to treat a dysplastic nevus depends on its category. Mildly dysplastic nevi do not need further treatment, while severely dysplastic nevi should be surgically removed. There is less consensus among leading physicians on the best treatment option for moderately dysplastic nevi.
What is melanocytic nevus and how to treat it?
Melanocytic nevi are benign neoplasms or hamartomas composed of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells that constitutively colonize the epidermis. Melanocytes are derived from the neural crest and migrate during embryogenesis to selected ectodermal sites (primarily the skin and the CNS), but also to the eyes and the ears.
Will your nevus develop into a skin issue?
These moles are frequently found on the trunk or limbs, although they can appear anywhere on the body. Most congenital nevi usually do not cause health problems, but a small percentage may develop into skin cancer (melanoma) later in life. The risk of melanoma increases with the size of the nevus.
Should you have an atypical mole removed?
People with 10 or more atypical moles have 12x the risk of developing melanoma. Atypical moles resemble melanoma, which is why mole removal is so critical. If your dermatologist identifies an atypical mole during your annual skin cancer check, he or she will suggest a mole removal procedure to perform a biopsy of the mole. During a mole biopsy, the doctor examines the cells in the mole to determine whether the mole is malignant or benign.
What is a mildly dysplastic nevus?
What does this mean? Dysplastic nevi are categorized as mild, moderate, or severe. Remember, a dysplastic nevus is a mole that exists in the spectrum between a benign mole and melanoma. A mildly dysplastic nevus is closer on that spectrum to a benign mole, whereas a severely dysplastic nevus is closer to a melanoma.
Should a dysplastic nevus be removed?
Should people have a doctor remove a dysplastic nevus or a common mole to prevent it from changing into melanoma? No. Normally, people do not need to have a dysplastic nevus or common mole removed. One reason is that very few dysplastic nevi or common moles turn into melanoma (1, 3).
How serious is dysplastic nevus?
Atypical or dysplastic nevi are not skin cancers, and often do not become melanoma, although having them appears to increase your risk of developing melanoma, an aggressive and potentially deadly form of skin cancer.
Should I be worried about dysplastic nevus?
Atypical moles, also known as dysplastic nevi, are unusual-looking moles that have irregular features under the microscope. Though benign, they are worth more of your attention because individuals with atypical moles are at increased risk for melanoma, a dangerous skin cancer.
Is a dysplastic nevus precancerous?
There are several skin conditions that can be a “precancer” or an indicator that one may be prone to skin cancers. Two of the most common are known as actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevus.
Can dysplastic nevus come back?
Abstract. Melanocytic nevi, including dysplastic or atypical nevi (DN), can recur or persist following shave removal procedures, and recurrence may resemble melanoma, both clinically and histologically (pseudomelanoma).
Can dysplastic nevus change?
Once dysplastic nevi are identified, routine care should include the use of total body photography to track changes of nevi over time. These lesions will change over time(37), but most changes are not worrisome for melanoma. The majority of dysplastic nevi undergo involution over years.
What is a moderately dysplastic nevus?
Dysplastic nevi can be identified clinically as mild, moderate, or severe. Mildly dysplastic nevi are nevi that show this tendency to become very much larger than a normal nevus yet there is some central maturation. This can produce a "fried egg" appearance to the nevus.
Can dysplastic nevus be raised?
Dysplastic nevi symptoms They tend to appear on skin exposed to sun regularly, but they sometimes show up on the scalp, breasts or buttocks as well. These atypical moles tend to be: Larger than common moles. Flat with some parts that are raised.
Can dysplastic nevi appear suddenly?
Moles, or nevi, typically form during childhood and adolescence, but new moles can appear in adulthood. Although most moles are noncancerous, or benign, the development of a new mole or sudden changes to existing moles in an adult can be a sign of melanoma.
Is a severely dysplastic nevus melanoma?
Yes — but most dysplastic nevi do not turn into melanoma. Most types of atypical moles remain stable over time. Patients with five or more dysplastic nevi are 10 times more likely to develop melanoma than individuals with no atypical moles.
What is a high grade dysplastic nevus?
There is a small sub-group of high grade dysplastic naevi. that, when seen in association with melanomas, show similar. genetic mutations as melanomas do in their evolution.1. This suggests that some high grade dysplastic naevi are an. intermediate between benign naevus and melanoma, and.
How wide is a dysplastic nevus?
The institute also specifies that a dysplastic nevus may often be more than 6 mm wide.
What to do if you see a mole on your body?
Early detection is the key to fighting skin cancer. If you see a strange mole on your body, see a doctor right away,” says Dr. Bobby Buka, a board-certified dermatologist practicing in NYC. “Generally, dermatologists follow the ‘ugly duckling’ rule.
Can a biopsy be removed if you have multiple moles?
However, your doctor may recommend surgical removal of a precancerous mole if a biopsy is determined to be highly dysplastic, i.e., the mole is very likely to develop into cancer. Your doctor may also recommend removal of a moderately dysplastic nevus if you have multiple atypical moles, if you have a family history of skin cancer ...
Can a dysplastic nevus turn into skin cancer?
While a dysplastic nevus is more likely to develop into skin cancer, this outcome is by no means a given. Dr. Jena Martin, a dermatopathologist practicing in Minnesota, notes that only about 20% of melanomas develop in moles that have been present since childhood. However, the more precancerous moles an individual has, ...
Do you have to remove nevi?
In general, dysplastic nevi do not need to be surgically removed because the risk of them developing into cancer is so limited. In fact, according to the American Osteopathic College of Dermatology, “Most of the melanomas found on people with atypical moles arise from normal skin and not an atypical mole.”.
Can a dysplastic mole become cancerous?
Cells in dysplastic nevi behave abnormally, and are therefore referred to as precancerous. If the cells undergo further mutations, they may develop into cancer and spread to other areas of the body. The good news is that the odds of a precancerous mole developing into cancer are really very low—many moles will remain nothing more ...
What is dysplastic nevus syndrome?
Facts About Dysplastic Nevus Syndrome You Should Know. If you're not familiar with dysplastic nevus syndrome, you're not alone. It's also known as atypical mole syndrome (AMS) and was first brought to the attention of a doctor in the early 1820s.
How many moles are there in a person with dysplastic nevus?
A diagnosis of dysplastic nevus requires that a person have at least 50 or more of the atypical moles on their body called dysplastic nevi. To make it more confusing, if a patient has five or more atypical melanocytic nevi, they are considered to have dysplastic nevus syndrome.
What is atypical nevi?
Known as atypical nevi or dysplastic nevi, they're essentially atypical moles. They have an unusual shape, are typically larger, and have a pebble-like surface. Many have a tan color, but the shades vary. It is these clinical features that serve as a basis for diagnosis.
Do moles need to be removed?
Some moles require surgical removal while others require nothing more than observation. The important thing is to be vigilant and to report any suspicious spots to your doctor. By providing your email address, you are agreeing to our privacy policy. We never sell or share your email address.
What is a mildly dysplastic nevus?
Mildly dysplastic nevi are nevi that show this tendency to become very much larger than a normal nevus yet there is some central maturation. This can produce a "fried egg" appearance to the nevus. Mildly dysplastic nevi do not show asymmetrical colour variation or irregularity or edge. Moderately atypical nevi do not show the central maturation ...
What does irregular edge mean in a nevus?
Variable colour, irregularly irregular within a dysplastic nevus, is indicative of genetic instability for the production of melanin. An irregular edge suggests a genetic instability in terms of lateral growth rate. Either are indicative of a tendency to progress to invasive melanoma.
What is junctional nevus?
Junctional nevi are the result of a single abnormal melanocyte that begins to proliferate at the dermal epidermal junction, and are often seen clinically as a dark flat nevus. A junctional nevus will typically evolve over time into a compound nevus, which is a nevus with both epidermal and dermal melanocytes.
Where are the melanocytes in the dermal nevus?
In the dermal nevus all of the melanocytes are in the dermis. Dermal nevi are clinically manifested as pale soft wrinkled polyps on the skin. This sequence is the normal life pattern of a nevus. Dermal nevi can eventually drop off the skin. Dysplastic nevi do not follow this pattern of maturation and self-destruction.
Is a severe nevus melanoma?
A severely dysplastic nevus is indistinguishable from early melanoma. Very often these lesions show considerable irregularity of edge and irregularly irregular colour. The differentiation between a moderate and severely dysplastic nevus is one of degree. Mildly dysplastic nevi can be observed.
Is fried egg nevus atypical?
Moderately atypical nevi do not show the central maturation of the fried egg nevus. They tend to be larger than normal junctional nevi with some variation of colour and edge. Colour is often regularly irregular. A severely dysplastic nevus is indistinguishable from early melanoma. Very often these lesions show considerable irregularity ...
Do dysplastic nevi age properly?
Dysplastic nevi do not age properly. The junctional phase can be prolonged, so that the lesion grows beyond 6 mm. Very often, with increasing size, the lesion shows increasing variation in colour and edge. Variable colour, irregularly irregular within a dysplastic nevus, is indicative of genetic instability for the production of melanin.
What is a dysplastic nevus?
A dysplastic nevus is a type of mole that looks different from a common mole. (Some doctors use the term "atypical mole" to refer to a dysplastic nevus.) A dysplastic nevus may be bigger than a common mole, and its color, surface, and border may be different. It is usually more than 5 millimeters wide ( 1, 3 ).
Where does a dysplastic nevus appear?
A dysplastic nevus may also appear in areas not exposed to the sun, such as the scalp, breasts, and areas below the waist ( 1, 3 ). Some people have only a couple of dysplastic nevi, but other people have more than 10. People who have dysplastic nevi usually also have an increased number of common moles.
Why do doctors remove moles on the skin?
Another reason is that even removing all of the moles on the skin would not prevent the development of melanoma because melanoma can develop as a new colored area on the skin ( 2 ). That is why doctors usually remove only a mole that changes or a new colored area on the skin.
What is a black bump on the left side of the nevus?
A dysplastic nevus with a black bump that was not there 18 months earlier. The black bump is a melanoma that is about 3 millimeters wide (about 1/8 inch). A melanoma with three parts—a dark brown or black area on the left, a red bump on the right, and an area that is lighter than the skin at the top.
How wide is a nevus?
It is usually more than 5 millimeters wide ( 1, 3 ). A dysplastic nevus can have a mixture of several colors, from pink to dark brown. Usually, it is flat with a smooth, slightly scaly, or pebbly surface, and it has an irregular edge that may fade into the surrounding skin.
What kind of doctor treats moles?
A family doctor may refer people with an unusual mole or other concerns about their skin to a dermatologist. A dermatologist is a doctor who specializes in diseases of the skin. Also, some plastic surgeons, general surgeons, internists, cancer specialists, and family doctors have special training in moles and melanoma.
Can a person with a nevus get melanoma?
Although anyone can develop melanoma, people with the following risk factors have an increased chance of melanoma ( 1 ): Having a dysplastic nevus. Having more than 50 common moles. Sunlight: Sunlight is a source of UV radiation, which causes skin damage that can lead to melanoma and other skin cancers.
What is dysplastic nevus?
Dysplastic nevi are pigmented lesions that clinically and histopathologically differ from regular nevi and thus appear atypical. This term is poorly defined and often misused, and a National Institutes of Health consensus conference recommended that the term dysplastic be abandoned and replaced by atypical nevus.
How big is a nevus?
Clinical features suggesting an atypical nevus are their size (>6 mm), irregular borders, and variegated color (shades of brown, tan, and light red).
What color are nevi?
Dysplastic nevi sometimes have slight border irregularity and often exhibit color variability, with various shades of tans and browns, and sometimes hues of pinks and reds, black, and even white. Blue is usually not seen in atypical moles on clinical examination ( Fig. 50.2A ), but may be seen on dermoscopy ( Fig. 50.2B ).