Treatment may involve one or more of the following types of antibiotics: ceftazidime ciprofloxacin (Cipro) or levofloxacin gentamicin
Full Answer
Does Keflex treat Pseudomonas?
This new quinolone seems to be suitable for single drug treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in patients with normal host defense mechanisms, while its therapeutic potential in compromised hosts requires further evaluation. MeSH terms
How can Pseudomonas aeruginosa be prevented?
To prevent P. aeruginosa, there are several steps you can take. Wash your hands often. This is the best way to prevent the spread of germs. Use soap and water and scrub for at least 20 seconds; or,...
How are Pseudomonas infections treated?
Antibiotics that you swallow or receive by IV are commonly used to treat Pseudomonas infections. Topical creams are used to treat skin infections. Ear and eye infections require drops. Certain symptoms, such as hot tub folliculitis, go away without treatment. Lung, heart, and blood issues may require weeks of antibiotics.
What is the treatment for Pseudomonas infection?
Seek prompt medical care for any of the following:
- A rash that comes back after getting better
- A rash that gets worse or persists for more than a few days despite home treatment
- A rash that occurs with fever, fatigue or malaise
See more

Natural Products Structural Diversity-I Secondary Metabolites: Organization and Biosynthesis
Pseudomonas fluorescens produces the PK antibiotic mupirocin (mup) which is active against Gram-positive bacteria including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. It is a mixture of pseudomonic acids, each of which comprise a C 17 monic acid (MA) and a C 9 9-hydroxynonanoic acid (9-HN) joined by an ester linkage.
Transfusion- and Transplantation-Transmitted Infections
Matthew J. Kuehnert, Sridhar V. Basavaraju, in Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases (Eighth Edition), 2015
Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenesis in Plants: Familiar Foes in a Foreign Kingdom
When nonpathogenic bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens, or disarmed pathogen mutants are introduced into the intercellular spaces of a plant leaf, they neither grow nor trigger the strong defense reactions associated with avirulent pathogens [ 5, 6 ].
PLANT DISEASES CAUSED BY PROKARYOTES: BACTERIA AND MOLLICUTES
Erwinia carotovora pv. carotovora, E. chrysanthemi, and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Bacteria E. carotovora pv. carotovora and P. fluorescens cause the most common and the most destructive soft rots. Erwinia caratovora pv. atroseptica, the cause of blackleg of potato ( Figs. 12-31B–12-31D ), may be thought of as a cool temperature variant of E.
Synthetic Methods IV – Asymmetric Oxidation Reduction, C–N
Desymmetrization of 1,7-type diol derivatives using PFL was reported by Bonini (equations 12 and 13 ). 13,54 Acylation of the diols and hydrolysis of the corresponding diacetates gave the monoacetates in high ee s. The resulting monoacetates were used for the synthesis of the C1–C13 fragments of nystatin A1 and amphotericin B.
Therapeutic Areas II: Cancer, Infectious Diseases, Inflammation & Immunology and Dermatology
Mupirocin (pseudomonic acid A) 12, produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens, 30 is bactericidal against S. aureus and S. epidermidis, including methicillin-resistant and beta-lactamase producing strains, and some Streptococcus species, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, and S.
Natural Product Biosynthesis by Microorganisms and Plants, Part A
For characterizing the phloroglucinol synthase PhlD and phl gene cluster from Pseudomonas fluorescens, Achkar et al. (2005) expressed phlD and part or the whole of the phl gene cluster in E. coli by using the pET system (Novagen). Following is an example of the method for heterologous expression of a type III PKS gene or gene cluster in E.
What is the name of the infection caused by pseudomonas?
Blood. A bacterial infection of the blood is called bacteremia. A blood infection is one of the most severe infections caused by pseudomonas. Symptoms may include: fever. chills. fatigue. muscle and joint pain.
What is the most common species of pseudomonas?
Only a few of the many species cause disease. The most common species that causes infection is called Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Trusted Source.
Where are pseudomonas found?
The bacteria are found widely in the environment, such as in soil, water, and plants. They usually do not cause infections in healthy people. If an infection does occur in a healthy person, it is generally mild. More severe infections occur in people who are ...
How to prevent infection in hospital?
Thoroughly washing hands and cleaning equipment in hospitals can help prevent infection. Outside a hospital, avoiding hot tubs and swimming pools that are poorly cared for can help prevent infections. You should remove swimming garments and shower with soap after getting out of the water.
What type of antibiotics are used in a lab?
Treatment may involve one or more of the following types of antibiotics: ceftazidime. ciprofloxacin ( Cipro) or levofloxacin. gentamicin. cefepime. aztreonam. carbapenems.
Is a pseudomonade a pathogen?
More severe infections occur in people who are already hospitalized with another illness or condition, or people who have a weak immune system. Pseudomonades are fairly common pathogens involved in infections acquired in a hospital setting. ...
Is pseudomonas an opportunistic infection?
Pseudomonas infections are considered opportunistic infections. This means that the organism only causes disease when a person’s immune system is already impaired. Conditions that may increase the risk of infection include: Infections can be severe in people whose immune systems are already compromised.
Abstract
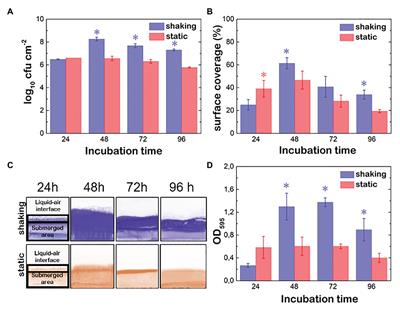
Infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa have become a real concern in hospital-acquired infections, especially in critically ill and immunocompromised patients. The major problem leading to high mortality lies in the appearance of drug-resistant strains. Therefore, a vast number of approaches to develop novel anti-infectives is currently pursued.
Introduction
One of the most important challenges for physicians is the adequate treatment of infections due to Gram-negative pathogens because of the increasing antimicrobial resistance in the healthcare setting [ 1 ].
Risk factors for antimicrobial resistance in P. aeruginosa
Multi-drug resistance (MDR) has increased dramatically in recent years and is now recognized as a major threat worldwide [ 7 ]. Risk factors for the development of MDR strains have been evaluated in several studies.
Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance
Bacteria exhibit multiple resistance mechanisms to antibiotics including decreased permeability, expression of efflux systems, production of antibiotic inactivating enzymes and target modifications. P.
Laboratory role
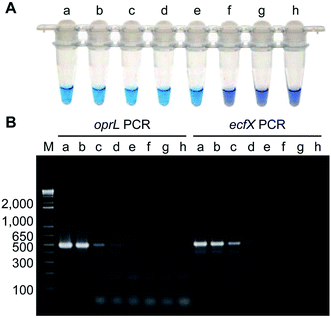
Diagnostic laboratories need to implement several methodologies and procedures to identify P. aeruginosa strains and rapidly provide antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) for the management of antibiotic regimens.
Clinical approaches to P. aeruginosa bacteremia
P. aeruginosa bloodstream infection (BSI) is a serious disease that requires prompt attention and pertinent clinical decisions in order to achieve a satisfactory outcome. Currently, Pseudomonas spp.
Management of P. aeruginosa VAP
P. aeruginosa is one of the leading causes of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) in the US and Europe [ 77 – 79 ]. VAP due to P. aeruginosa is increasing in incidence and poses unique challenges for its clinical management. Risk factors for the development of P.
Why is Pseudomonas fluorescens important?
Pseudomonas fluorescens is interesting and important to study because it produces a particular antibiotic (Mupirocin) which has been proven effective in treating certain kinds of skin, ear, and eye disorders (10).
What is the optimum temperature for Pseudomonas fluorescens?
(2) The optimum growth temperature is between 25-30 degrees Celsius (10) . The Pf-5 strain resides in the plant’s rhizosphere and produces a variety of secondary metabolites including antibiotics against soil borne plant pathogens. (4) Pseudomonas fluorescens PFO-1 is well adapted to the soil where it was first isolated in agricultural soil. (1) Pseudomonas fluorescens strain SBW25 grow on plant leaves and roots where they can contribute to plant growth. Soluble, green fluorescent pigments are produced when the iron concentration is low. The significance of these organisms have increased because of their ability to degrade various pollutants and their use as bio-control against pathogens. (2) Sequencing the genome provided further information of its environmental interaction ands its metabolic capabilities, which can be used against agricultural disease control (1). Pseudomonas fluorescens is interesting and important to study because it produces a particular antibiotic (Mupirocin) which has been proven effective in treating certain kinds of skin, ear, and eye disorders (10).
How many chromosomes are in P. fluorescens?
Currently, two strains of Pseudomonas fluorescens have their genomes sequenced completely. P. fluorescens Pf-5 genome contains one circular chromosome that has 7.1 Mbp and a GC content of 63.3%. It contains 87 RNAs and 6137 proteins. 5.7% of its genome contributes to secondary metabolism which is the largest of the pseudomonas. (2,4) The genome of Pseudomonas fluorescens PfO-1 has one chromosome with 6.43841 Mbp and 60.5% GC content. There are 95 RNAs and 5736 proteins. The genome sequencing of P. fluorescens SBW25 is still in progress. (2)
When did Pseudomonas fluorescens bacteremia start?
Although Pseudomonas fluorescens typically has a low level of virulence, in 1997 four patients at the National Taiwan University Hospital developed Pseudomonas fluorescens bacteremia. These patients had been treated in the chemotherapy room and had begun exhibiting symptoms such as fevers and chills.
Which antibiotics inhibit phytopathogen growth?
Antibiotics such as pyrrolnitrin, pyoluteorin, and 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol that inhibit phytopathogen growth are produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5. Diseases from Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium ultimum that affect cotton plants are inhibited by this strain.
Is pseudomonas effective against mold?
Pseudomonas species are effective against mold causing disease in produce such as apples and pears. This and further studies of Pseudomonas fluorescens will determine its effectiveness an alternative to chemical fungicides. (13) Production of secondary metabolites play an important role in plant disease suppression.
Where do Pseudomonas aeruginosa live?
Their resistance to antibiotics have made them dangerous pathogens. Pseudomonas aeruginosa are commonly seen in the lungs, especially those with cystic fibrosis.
What is the best treatment for pseudomonas?
Antibiotics that you swallow or receive by IV are commonly used to treat Pseudomonas infections. Topical creams are used to treat skin infections. Ear and eye infections require drops. Certain symptoms, such as hot tub folliculitis, go away without treatment.
What to do if you have a Pseudomonas infection?
If you have symptoms of Pseudomonas infection, a health provider will take a sample of your blood or other body fluid and send it to a lab to test. This confirms the type of bacteria that infected you. It may also help determine which medicine will work for you.
What to do when you have a blood pressure cuff infection?
Wash contaminated clothes and sheets with hot water. Everyone should follow these rules for good hygiene: Was h your hands often with soap and water.
Is Pseudomonas a risk factor?
Pseudomonas Risk Factors. Healthy people typically don’t have much risk. However, a few groups may be more susceptible than others, including people who inject drugs. Young black men seem to have greater risk of heart valve infections.
Can a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection be caused by a germ
Pseudomonas infections can occur when the immune system is already weakened. Germs that live in soil and water can cause Pseudomonas infections. You can get these infections in different parts of your body. The most common type that humans get is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The germs may live in pools, hot tubs, and dirty contact lenses.