
Several techniques are used for BOD removal in wastewater prior to reuse or safe disposal. Three common BOD reduction methods for wastewater treatment are: Wastewater clarification Wastewater separation (Coagulation & Flocculation) Anaerobic microbial decomposition
What are the methods of BOD removal in wastewater treatment?
Several techniques are used for BOD removal in wastewater prior to reuse or safe disposal. Three common BOD reduction methods for wastewater treatment are: Wastewater clarification. Wastewater separation (Coagulation & Flocculation) Anaerobic microbial decomposition. Wastewater clarification and separation BOD reduction methods are part ...
Why is it important to remove solids and BOD in wastewater?
The importance of removing solids and BOD in wastewater is just as important to a small office park as it is to an entire city. Wastewater treatment utilizes several delicate chemical processes to achieve an acceptable quality of water, which is analogous to an acceptable quality of life.
How do you get rid of CBOD in wastewater treatment?
Wastewater BOD Removal 1 CBOD Conversion Rates. Conversion rates for CBOD are measured in units of kilograms per cubic meter of beads per day (kg/m 3 -day). 2 Recirculating Filtration. Most CBOD removal problems are addressed with filters configured to recycle water multiple times through a PolyGeyser. 3 Concentrating Biosolids. ...
Which process is most widely used for the treatment of sewage?
Among these, the complete-mix anaerobic digestion process is most widely used for the treatment of sewage. Anaerobic digestion is mostly useful for the stabilization of concentrated sludge’s that are produced on the treatment of industrial sewage.
What is the maximum BOD level for wastewater disposal?
How does wastewater clarification work?
What is the name of the agglomerating agent that is added to wastewater to make it clumps
What is the BOD test?
Why do municipalities use a BOD test?
What is flocculation in water?
What is the product of anaerobic digestion?
See more
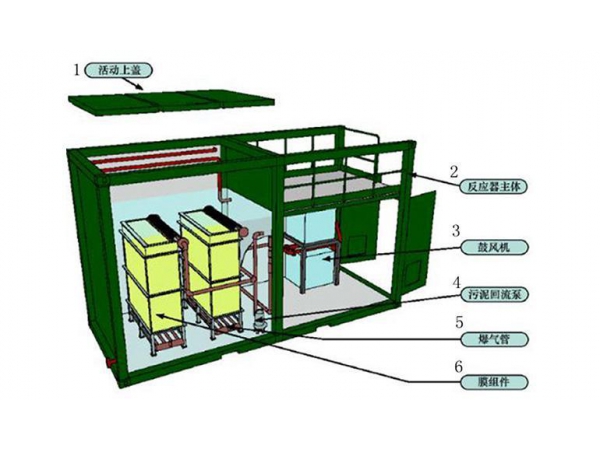
What wastewater treatment Reduces BOD levels the most?
The activated sludge (AS) biological treatment process is the most common process for reducing five-day biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) in wastewater, for both industrial and municipal applications.
How is most BOD removed in a wastewater treatment plant?
Water treatment with ozone is an effective method to reduce BOD and COD levels in industrial and municipal waste water.
How is BOD removed from water?
Three common BOD reduction methods for wastewater treatment are: Wastewater clarification. Wastewater separation (Coagulation & Flocculation) Anaerobic microbial decomposition.
How do you reduce sewage BOD?
These are the best practices for reducing BOD and TSS that facility managers should know:Focus on removing TSS from wastewater first. ... Get a properly sized EQ tank. ... Control the pH of the waste stream. ... Install a modern plate pack DAF made of stainless steel or plastic. ... Use a regenerative turbine air dissolution pump.More items...•
Does aeration remove BOD?
Successful BOD removal in an activated sludge process depends on studying and controlling some basics such as wastewater characteristics. Aeration is used to operate activated sludge process units and is perhaps the most frequently used process to remove biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) from wastewater.
How many of BOD is remove in activated sludge process?
The activated sludge process will often remove 85 to 95% of the BOD from the aeration influent.
What is TSS removal?
Suspended solids carried in stormwater cause a range of harmful effects in rivers, lakes and oceans. TSS capture and removal is a critical component of effective environmental protection.
What is advanced oxidation process in wastewater treatment?
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), in a broad sense, are a set of chemical treatment procedures designed to remove organic (and sometimes inorganic) materials in water and wastewater by oxidation through reactions with hydroxyl radicals (·OH).
How many percentage of BOD removes in primary treatment?
Primary treatment removes about 60 percent of total suspended solids and about 35 percent of BOD; dissolved impurities are not removed. It is usually used as a first step before secondary treatment. Secondary treatment removes more than 85 percent of both suspended solids and BOD.…
Does activated carbon reduce BOD?
The results showed that the activated sludge, sand filter and the activated carbon were very effective for the removal of BOD from the wastewater.
What is flocculation and coagulation?
Coagulation and flocculation are two separate processes, used in succession, to overcome the forces stabilising the suspended particles. While coagulation neutralises the charges on the particles, flocculation enables them to bind together, making them bigger, so that they can be more easily separated from the liquid.
How can we reduce TDS in wastewater treatment?
Various methods such as physical adsorption, reverse osmosis (RO), distillation, precipitation, membrane filtration, and bacteria-based bioremediation have been developed to reduce/remove TDS from water streams (Pinto et al., 2016). Most of those methods, however, are not cost-effective and/ or environmental friendly.
Why is it important to remove solids from wastewater?
The importance of removing solids and BOD in wastewater is just as important to a small office park as it is to an entire city. Wastewater treatment utilizes several delicate chemical processes to achieve an acceptable quality of water, which is analogous to an acceptable quality of life. Wastewater contains many elements which break down ...
What is the most effective way to get inorganic solids out of a septic system?
Inorganic material and other TSS (Total Suspended Solids) are most effectively taken out of wastewater through the use of effluent filters .
What are the elements that make up waste water?
Wastewater contains many elements which break down into two groups, organic and inorganic substances.Organic substances include dish soaps, fecal matter, and food particles. These elements break down and feed bacteria which exist in the septic system. Bacteria naturally decomposes organic matter, but requires oxygen to do so.
Why is BOD important?
BOD is a crucial factor in refining wastewater. The bacteria are important for breaking down substances, however too much BOD can cause unwanted amounts of bacteria. It can also drain receiving waters of oxygen which can kill fish and harm the environment.
Is a septic system aerobic or anaerobic?
Many septic systems have both an aerobic and anaerobic process, while others focus on reducing the need of BOD altogether.
Does bacteria decompose organic matter?
Bacteria naturally decomposes organic matter, but requires oxygen to do so. The larger and more numerous the organic matter, the more oxygen required to eliminate organic matter. The rate at which wastewater requires oxygen is known as the biological oxygen demand (BOD).
BOD Compliance
High concentrations of BOD in wastewater can lead to regulatory issues. By implementing a system to effectively reduce the BOD in the wastewater stream your company will have the ability to remain in compliance and reduce risk. This will save your company regulatory costs.
COD Compliance
Effluent with high concentrations of COD can lead to compliance issues. Our wastewater systems can significantly reduce the Chemical Oxygen Demand in your wastewater. We have saved our customers surcharges and headaches by reducing their COD wastewater.
Visit Our Blog
bioprocessH2O offers innovative wastewater and water reuse treatment technologies to serve a wide variety of industrial and decentralized markets.
What is aerobic BOD?
Aerobic BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) removal is accomplished by direct removal of particulate organics and indirectly through the biological activity of the filter. AST’s bead filters can be configured to do both.
Why is recirculation important?
The need for recirculation is largely driven by the need to supply oxygen to the submerged bed. Recirculation also facilitates a longer contact time with the bacteria-laden bead media. Water is in contact for only about 20 seconds in a single pass through the bed.
Can beads be used as roughing filters?
The PolyGeyser units are virtually impervious to biofouling, and with a high backwashing frequency, they can be effectively used as roughing filters reducing particulate BOD of raw wastes with high BOD and TSS concentrations.
Do bead filters nitrify?
All bead filters nitrify even at high organic loadings as long as oxygen is present in the bed. It must be presumed that a nitrifier seed is available in any effluent sample collected, thus inhibition (CBOD) is required to get an accurate assessment of organic reduction.
Importance of Wastewater Treatment Process
Wastewater contains a large number of toxins that might harm the environment; thus, treatment is essential.
Stages of Wastewater Treatment Process
Unit Operation: It is a process in which wastewater treated by Physical Method
Flow Diagram for Wastewater Treatment Process
Note: – All treatment plants have different equipment depending upon what they want to achieve or other several factors.
What is BOD removal?
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) removal is critical to wastewater treatment. The LemTec™ Biological Treatment Process optimizes BOD removal to meet limits previously thought unattainable in aerated lagoon facilities. Excess BOD causes algae, cyanobacteria and tetrad growth. As a result, stringent regulartory effluent limits can't be met, and additional issues occur including an increase in offensive odors and extended treatment time. The LET approach to each unique project ensures that clients receive a customized design based on their unique objectives and parameters. We tailor our designs and include the best in treatment technologies to provide a comprehensive, innovative solution.
What happens if you have a lot of BOD?
Excess BOD causes algae, cyanobacteria and tetrad growth. As a result, stringent regulartory effluent limits can't be met, and additional issues occur including an increase in offensive odors and extended treatment time.
What are the biological processes of sewage?
The biological treatment processes of sewage are broadly classified as aerobic, anaerobic and pond processes . Depending on the nature of the use of the microorganisms, the biological processes are categorized as suspended growth systems and attached growth systems.
How often is sedimentation done in sewage treatment?
In the normal process of sewage treatment, sedimentation is usually carried out twice-once before the secondary treatment, referred to as primary sedimentation, and then after the secondary treatment is complete, a process known as secondary sedimentation.
What is sequencing batch reactor?
The processes namely aeration and sedimentation are carried out in both the systems . The major difference is that while in the conventional activated sludge system, aeration and sedimentation occur simultaneously in separate tanks, these two processes are carried out sequentially in the same tank in SBR. Thus, the sequencing batch reactor may be regarded as fill- and-draw activated sludge process.
What is an aerated pond?
Aerated lagoons, also called as aerated ponds, are the facultative stabilization ponds wherein surface aerators are installed to overcome the bad adours (due to overload of organic materials). The microbiological treatment of aerated ponds is comparable to the activated sludge process. The major difference is the large surface area in aerated ponds and this is more susceptible for temperature effects. It is possible to carry out continuous nitrification in aerated lagoons. This however, depends on the design and operating conditions of the pond (particularly the temperature).
Why is phosphorus important in sewage treatment?
Thus, during the normal secondary treatment process, 10-30% of the sewage phosphorus is utilized by the microorganisms for growth and energy purposes. Phosphorus removal from waste water is required to control eutrophication and to maintain water quality.
What is a trickling filter?
Trickling Filters: Trickling filters, also known as percolating or sprinkling filters, are commonly used for the biological treatment of domestic sewage and industrial waste water. In a strict sense, trickling filters are not filters, but they are oxidation units.
What is primary treatment?
Primary treatment is aimed at the removal of fine suspended organic solids that cannot be removed in the preliminary treatment. Primary treatment basically involves the process of sedimentation or settling. In the normal process of sewage treatment, sedimentation is usually carried out twice-once before the secondary treatment, referred to as primary sedimentation, and then after the secondary treatment is complete, a process known as secondary sedimentation. It is sometimes necessary to use chemical coagulants to facilitate or aid sedimentation, and this process is referred to as chemical precipitation or coagulation-aided sedimentation.
What is the maximum BOD level for wastewater disposal?
Clean Water Act. Typical maximum values range from 10 mg/L for direct environmental disposal and 300 mg/L for disposal to sewer systems .
How does wastewater clarification work?
Wastewater clarification removes organic solids (primary sludge) from the water by utilizing the force of gravity – in other words, the heavier particles settle to the bottom and are removed first. Wastewater clarification is often followed by a chemical separation process.
What is the name of the agglomerating agent that is added to wastewater to make it clumps
In coagulation, a non-toxic agglomerating agent such as Ferric Chloride (F e Cl) or alum is added to the wastewater causing the suspended particles to come together to form clumps which can easily be removed from the water by filtration.
What is the BOD test?
A BOD test is typically carried out over a standard 5-day incubation period at 20°C (68°F) for the most accurate results.
Why do municipalities use a BOD test?
Municipalities can use a BOD test to detect water contamination in their public supply to ensure that it is safe for human consumption. Industries need to know their BOD value to determine when treated wastewater is safe for reuse or disposal.
What is flocculation in water?
Flocculation uses a chemical polymer (flocculating agent) to precipitate organic particles out of the water by coalescing to form larger particles or flocs. These larger particles can then be deposited into a sedimentation tank for further treatment prior to disposal.
What is the product of anaerobic digestion?
The product of an anaerobic digestion process is the generation of biogas . Anaerobic decomposition is a highly beneficial method because the biofuel generated from the process can be utilized as an alternative energy source for power, heating, and drying applications.
