What are the treatment options for a stroke?
1. Exercise Regularly...
2. Eat Healthy...
3. Reduce Weight...
4. Manage Stress...
5. Quit Smoking...
Learn More...What are the stroke management guidelines?
Stroke Treatment 1 On the Way to the Hospital. If someone you know shows signs of stroke, call 9-1-1 right away. 2 What Happens Next. The risk of stroke within 90 days of a TIA may be as high as 17%,... 3 Stroke Rehabilitation. After a stroke, you may need rehabilitation (rehab) to help you recover. 4 More Information. Learn about CDC programs...
How is stroke treated in the emergency department (ED)?
These guidelines cover the management of stroke in adults (over 18 years) from onset to chronic care and focus on patients with a new clinical event (first stroke or recurrent stroke). Goal and objectives of the guidelines The primary goal of the guidelines is to continuously improve the quality of care in patients with stroke nationally.
Why is it important to treat the underlying causes of stroke?
Emergency medical services (EMS) should be developed and upgraded for stroke care at the hospital or district level to include transport and triage of patients from peripheral medical centers. Emergency department ED personnel should be trained to diagnose and treat all types of stroke.

What is the first line treatment for ischemic stroke?
The main very early treatments for ischemic stroke are: Thrombolytic therapy – This involves giving a medication called alteplase (also known as tPA, for "tissue plasminogen activator"), or a similar medication called tenecteplase, by IV (through a vein).
What is the gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke?
An IV injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) — also called alteplase (Activase) or tenecteplase (TNKase) — is the gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke. An injection of TPA is usually given through a vein in the arm within the first three hours.
What is the most powerful treatment for ischemic stroke?
Alteplase is most effective if started as soon as possible after the stroke occurs – and certainly within 4.5 hours.
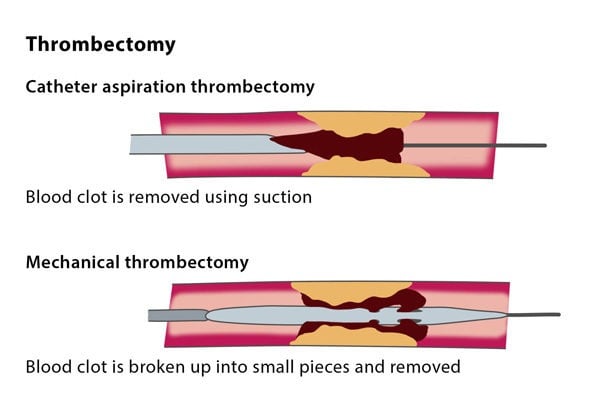
What is catheter based stroke treatment?
Catheter-based therapies include local intra-arterial thrombolysis, mechanical thrombectomy, and angioplasty techniques. Intravenous thrombolysis is limited to the first three hours after symptom onset, which excludes many patients with disabling stroke deficits.
What is the best treatment to give a possible stroke patient who is not in the hospital CPR?
A clot-busting medication called tPA, or tissue plasminogen activator, can be given to someone if they're having a stroke, potentially reversing or stopping symptoms from developing.
What does tPA do for stroke?
Known by the generic name alteplase and marketed as Activase® (Genentech), tPA is given to patients through an IV in the arm, and it works by dissolving blood clots that block blood flow to the brain.
What are 3 treatments for a stroke?
Stroke treatmentClot-breaking drugs. Thrombolytic drugs can break up blood clots in your brain's arteries, which will stop the stroke and reduce damage to the brain. ... Mechanical thrombectomy.Stents. ... Surgery. ... Medications. ... Coiling. ... Clamping. ... Surgery.
What is the difference between stroke and ischemic stroke?
A stroke is a bleeding or clotting event that interferes with blood flow to the brain. An ischemic stroke is when blood vessels to the brain become clogged. A hemorrhagic stroke is when bleeding interferes with the brain's ability to function.
What is the best treatment option for hemorrhagic strokes?
Options include physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy. The primary goal of therapy is to restore as much function as possible.
Who performs mechanical thrombectomy?
In a nationally representative cohort of elderly patients with stroke, most mechanical thrombectomies were performed by radiologists, neurologists, and neurosurgeons.
Is Ischemic Stroke?
Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks or narrows an artery leading to the brain. A blood clot often forms in arteries damaged by the buildup of plaques (atherosclerosis). It can occur in the carotid artery of the neck as well as other arteries. This is the most common type of stroke.
What is the most common reason for a stroke patient being ineligible for thrombolysis?
The most common reason for ineligibility for systemic thrombolysis was symptom onset >180 minutes (50%), followed by recent surgery (19%), recent gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding (19%), and recent arteriotomy at a noncompressible site (12%).
What is IV line?
An intravenous (IV) line is inserted so, if necessary, you can be given medications quickly. Electrodes will be placed on your body to monitor your heart, and a small device called a pulse oximeter may be clipped on a finger or ear to track the oxygen level in your blood.
Why do we need PCI?
Why is it done? PCI improves blood flow, thus decreasing heart-related chest pain (angina), making you feel better and increasing your ability to be active. PCI is usually scheduled ahead of time.
How long do you stay in bed after PCI?
You will be asked to remain in bed for 2 to 6 hours, depending upon your specific condition. Pain medication may be given if you experience any discomfort. You will be encouraged to drink water and other fluids to help flush the contrast dye from your body. Most people spend the night in hospital after a PCI.
What is the best medicine for a stroke?
If you get to the hospital within 3 hours of the first symptoms of an ischemic stroke, you may get a type of medicine called a thrombolytic (a “clot-busting” drug) to break up blood clots. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a thrombolytic. tPA improves the chances of recovering from a stroke.
What do you need to do after a stroke?
After a stroke, you may need rehabilitation ( rehab) to help you recover. Before you are discharged from the hospital, social workers can help you find care services and caregiver support to continue your long-term recovery.
What is the best way to get to the hospital for a stroke?
Stroke Treatment. Calling 9-1-1 at the first symptom of stroke can help you get to the hospital in time for lifesaving stroke care. Your stroke treatment begins the moment emergency medical services (EMS) arrives to take you to the hospital. Once at the hospital, you may receive emergency care, treatment to prevent another stroke, ...
Why do people go to the hospital for stroke?
Stroke patients who are taken to the hospital in an ambulance may get diagnosed and treated more quickly than people who do not arrive in an ambulance. 1 This is because emergency treatment starts on the way to the hospital. The emergency workers may take you to a specialized stroke center to ensure that you receive the quickest possible diagnosis ...
What is a tube used for?
The tube is then used to install a device, such as a coil, to repair the damage or prevent bleeding. Surgical treatment. Hemorrhagic strokes may be treated with surgery. If the bleeding is caused by a ruptured aneurysm, a metal clip may be put in place to stop the blood loss.
What type of doctor treats strokes?
Brain scans will show what type of stroke you had. You may also work with a neurologist who treats brain disorders, a neurosurgeon that performs surgery on the brain, or a specialist in another area of medicine.
How many days after TIA can you get a stroke?
The risk of stroke within 90 days of a TIA may be as high as 17%, with the greatest risk during the first week. 6. That’s why it’s important to treat the underlying causes of stroke, including heart disease, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation (fast, irregular heartbeat), high cholesterol, and diabetes.
How do doctors remove a clot from the brain?
In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever. They thread a catheter through an artery in the groin up to the blocked artery in the brain. The stent opens and grabs the clot. Special suction tubes may also remove the clot.
How does Alteplase IV work?
Doctors administer Alteplase IV r-tPA through an IV in the arm, dissolving the clot and improving blood flow to the part of the brain being deprived. Many people don’t arrive at the hospital in time to receive the medication, which can save lives and reduce long-term effects of stroke.
What is Alteplase IV?
Medication Treatment with Alteplase IV r-tPA. Considered the gold standard, tissue plasminogen activator, r-tPA, (known as alteplase) is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat ischemic stroke.
What is the best way to remove a clot?
Mechanical Treatment to Remove the Clot. An endovascular procedure or a mechanical thrombectomy is a strongly recommended option to remove a clot in eligible patients with a large vessel occlusion, or LVO. In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever.
What Are the Types of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention?
The main goal of PCI is to open up clogged arteries, but there are different ways your doctor can do that. PCI types include:
How Are Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Procedures Done?
Percutaneous coronary intervention procedures vary depending on the type. In most cases, you’ll be awake for the procedure, though you’ll be given a sedative to help you relax.
What Are the Risks of a Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Procedure?
Most people don’t have any serious complications from PCI, but they can happen. Some possible risks are:
What is the purpose of the stroke guidelines?
Their aim is to help clinicians, at any level – primary, secondary or tertiary - to make the best decisions for each patient, using the evidence currently available.
How long does it take to treat a disabling stroke?
All patients with disabling acute ischemic stroke who can be treated within 3 hours (4.5 hours as soon as approved by the Drug Controlling authority) after symptom onset should be evaluated without delay to determine their eligibility for treatment with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (alteplase).
What is the best medication for TIA?
All patients with ischemic stroke or TIA should receive antiplatelet therapy unless there is indication for anticoagulation. Aspirin (30-300 mg/day) or combination of aspirin (25 mg) and extended release dipyridamole (200 mg) twice or clopidogrel (75 mg OD) are all acceptable options for initial therapy.
What should the total cholesterol be for TIA?
All patients with history of TIA or ischemic stroke should be treated with a statin if they have a total cholesterol of > 200 mg%, or LDL cholesterol > 100 mg%. The treatment goals should be a total cholesterol of <200 mg%, and LDL cholesterol of <100 mg% (<70 mg% for very high risk individuals).
What scales are used to determine the degree of neurological deficit?
Validated stroke scales like NIHSS may be used to determine the degree of neurological deficit. All patients should have neuroimaging, complete blood count, blood glucose, urea, serum creatinine, serum electrolytes, ECG and markers of cardiac ischemia.
When should anticoagulation be used?
Anticoagulation should not be used for patients in sinus rhythm unless cardiac embolism is suspected.
How long should you give gastrostomy fluids?
Patients with altered sensorium should be given only intravenous fluids (Dextrose saline or normal saline) for at least 2-3 days. Evidence:Dennis,[73] Hamidon,[74] Norton,[75] Paciaroni,[76] Smithard.[77] Oral care.