The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved about 100 monoclonal antibodies for therapies, with about a third of those treating different types of cancer. Another 570 are being studied, with roughly 70 percent of those designed as cancer treatments.
Why are monoclonal antibodies so expensive?
Monoclonal antibodies can also cause: mouth and skin sores that can lead to serious infections. high blood pressure. congestive heart failure. heart attacks. inflammatory lung disease. Monoclonal antibodies can cause mild to severe allergic reactions while …
What to expect from monoclonal antibody treatment?
Jul 20, 2020 · Monoclonal antibody-based immunotherapy is now considered to be a main component of cancer therapy, alongside surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Monoclonal antibodies possess a diverse set of clinically relevant mechanisms of action. In addition, antibodies can directly target tumor cells while simultaneously promoting the induction of long ...
What are monoclonal antibodies and how do they treat CLL?
May 01, 2012 · Monoclonal antibody-based treatment of cancer has been established as one of the most successful therapeutic strategies for both hematologic malignancies and solid tumors in the last 20 years. The initial combining of serological techniques for cancer cell surface antigen discovery with hybridoma technology led to a series of landmark clinical ...
Are there side effects of monoclonal antibody treatment?
The multifaceted properties of antibodies as a therapeutic platform have led to the development of new cancer treatment strategies that will have major impacts on cancer care. This review focuses on the known mechanisms of action, current clinical applications for the treatment of cancer, and mechanisms of resistance of monoclonal antibody therapy.

Does cancer treatment use monoclonal antibodies?
How many monoclonal antibodies are approved for cancer?
Which cancers are treated with monoclonal antibodies?
Does chemotherapy use monoclonal antibodies?
Is monoclonal antibody therapy safe?
How long have monoclonal antibodies been used to treat cancer?
Why are monoclonal antibodies not widely used?
What is a disadvantage of monoclonal antibodies?
What happens after monoclonal antibody treatment?
How do you feel after monoclonal antibodies?
Are monoclonal antibodies considered immunotherapy?
Do monoclonal antibodies stay in your body?
How do monoclonal antibodies work against cancer?
Monoclonal antibodies are immune system proteins that are created in the lab. Antibodies are produced naturally by your body and help the immune sy...
Which cancers are treated with monoclonal antibodies?
Many monoclonal antibodies have been approved to treat a wide variety of cancers. To learn about specific treatments for your cancer, see the PDQ®...
What are the side effects of monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies can cause side effects, which can differ from person to person. The ones you may have and how they make you feel will depend...
Is monoclonal antibody a cancer treatment?
Monoclonal Antibodies in Cancer Therapy. Monoclonal antibody-based immunotherapy is now considered to be a main component of cancer therapy, alongside surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Monoclonal antibodies possess a diverse set of clinically relevant mechanisms of action.
Can antibodies target tumors?
In addition, antibodies can directly target tumor cells while s …. Monoclonal antibody-based immunotherapy is now considered to be a main component of cancer therapy, alongside surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Monoclonal antibodies possess a diverse set of clinically relevant mechanisms of action. In addition, antibodies can directly target ...
When was the first monoclonal antibody approved?
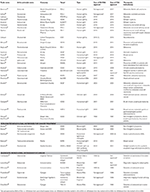
Home Oncology Antibodies Monoclonal Antibodies. In 1986, muromonab-CD3 (OKT3) wins the first therapeutic monoclonal antibody approval from the US FDA, which works as an immunosuppressive for the prevention of transplant rejection. Since from past more than three decades from the first approval, till now more than 100 antibodies are approved by US ...
What is the FDA approved drug for refractory B cell lymphoma?
In June 2019, US FDA approved Polivy , a CD79b-directed antibody–drug conjugate, in combination with bendamustine and rituximab for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, who have received at least two prior therapies. 34. Sintilimab**.
When was CD3 approved?
In 1986, muromonab-CD3 (OKT3) wins the first therapeutic monoclonal antibody approval from the US FDA, which works as an immunosuppressive for the prevention of transplant rejection. Since from past more than three decades from the first approval, till now more than 100 antibodies are approved by US FDA, which includes largest 42 approvals ...
When was ibritumomab tiuxetan approved?
ibritumomab tiuxetan was the first radioimmunotherapy drug approved by the FDA in 2002 , for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory, low‑grade or follicular B‑cell non‑Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), including patients with rituximab refractory follicular NHL. 5.
When was Gemtuzumab ozogamicin approved?
2000. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin was the first antibody-drug conjugate to be approved for the treatment of Acute myeloid leukemia. In June 2010, Pfizer withdrew Mylotarg from the market at the request of the US FDA, but in In 2017, Pfizer reapplied for approval, based on new clinical findings.
Is Gemtuzumab a conjugate?
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin was the first antibody-drug conjugate to be approved for the treatment of Acute myeloid leukemia. In June 2010, Pfizer withdrew Mylotarg from the market at the request of the US FDA, but in In 2017, Pfizer reapplied for approval, based on new clinical findings.
When will Rybrevant be approved?
In May 2021, FDA Approves Rybrevant as the First Targeted Treatment for Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. In April 2021, FDA approved Zynlonta, a CD19-directed ADC, for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma.
What is the purpose of monoclonal antibodies?
These are known as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs or Moabs). Monoclonal antibodies are used to treat many diseases, including some types of cancer. To make a monoclonal antibody, researchers first have to identify the right antigen to attack.
What are monoclonal antibodies made of?
There are 4 different ways they can be made and are named based on what they are made of. Murine: These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in -omab. Chimeric: These proteins are a combination of part mouse ...
What are the side effects of mAbs?
It can cause side effects such as high blood pressure, bleeding, poor wound healing, blood clots, and kidney damage.
How does the immune system attack foreign substances?
One way the body's immune system attacks foreign substances is by making large numbers of antibodies. An antibody is a protein that sticks to a specific protein called an antigen. Antibodies circulate throughout the body until they find and attach to the antigen. Once attached, they can force other parts of the immune system to destroy ...
What is an antibody?
An antibody is a protein that sticks to a specific protein called an antigen. Antibodies circulate throughout the body until they find and attach to the antigen. Once attached, they can force other parts of the immune system to destroy the cells containing the antigen. Researchers can design antibodies that specifically target a certain antigen, ...
How do antibodies work?
Antibodies circulate throughout the body until they find and attach to the antigen. Once attached, they can force other parts of the immune system to destroy the cells containing the antigen. Researchers can design antibodies that specifically target a certain antigen, such as one found on cancer cells.
What is a moab?
These are known as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs or Moabs). Monoclonal antibodies are used to treat many diseases, including some types of cancer. To make a monoclonal antibody, researchers first have to identify the right antigen to attack.
Can monoclonal antibodies be used for cancer?
Monoclonal antibody treatments have been developed for some but not all cancers, and certain types of cancer cells are more vulnerable than others to monoclonal antibody interventions. Nonetheless, treatments have been approved for a number of cancers, including the following: Brain cancer. Breast cancer.
What is monoclonal antibody therapy?
Monoclonal antibody drugs are cancer treatments that enlist natural immune system functions to fight cancer.
What is the function of an antibody?
An antibody attaches itself to a specific molecule (antigen) on the surface of a problematic cell. When an antibody binds to the antigen, it serves as a flag to attract disease-fighting molecules or as a trigger that promotes cell destruction by other immune system processes.
What is the role of monoclonal antibodies in the immune system?
Monoclonal antibodies are designed to function in different ways. A particular drug may actually function by more than one means. The role of the drug in helping the immune system may include the following: Flagging cancer cells. Some immune system cells depend on antibodies to locate the target of an attack.
What is the function of monoclonal antibodies?
Some monoclonal antibodies block the connection between a cancer cell and proteins that promote cell growth — an activity that is necessary for tumor growth and survival. Preventing blood vessel growth. In order for a cancerous tumor to grow and survive, it needs a blood supply. Some monoclonal antibody drugs block protein-cell interactions ...
What is the connection between cancer and immune cells?
This connection may promote immune system attacks on the cancer cells.
How are monoclonal antibodies administered?
Monoclonal antibodies are administered through a vein (intravenously). How often you undergo monoclonal antibody treatment depends on your cancer and the drug you're receiving. Some monoclonal antibody drugs may be used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy.
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) joined to a chemotherapy drug or to a radioactive particle are called conjugated monoclonal antibodies. The mAb is used as a homing device to take one of these substances directly to the cancer cells. The mAb circulates throughout the body until it can find and hook onto the target antigen.
What are the side effects of monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies are given intravenously (injected into a vein). The antibodies themselves are proteins, so giving them can sometimes cause something like an allergic reaction. This is more common while the drug is first being given. Possible side effects can include: 1 Fever 2 Chills 3 Weakness 4 Headache 5 Nausea 6 Vomiting 7 Diarrhea 8 Low blood pressure 9 Rashes
What are the different types of antibodies?
Chemolabeled antibodies used to treat cancer include: 1 Brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris®), an antibody that targets the CD30 antigen (found on lymphocytes), attached to a chemo drug called MMAE. This drug is used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. 2 Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla®, also called TDM-1), an antibody that targets the HER2 protein, attached to a chemo drug called DM1. It’s used to treat some breast cancer patients whose cancer cells have too much HER2.
Can mAbs be used for cancer?
For cancer, this is not always easy, and so far mAbs have proven to be more useful against some cancers than others. Over the past couple of decades, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved more than a dozen mAbs to treat certain cancers. As researchers have found more antigens linked to cancer, they have been able ...
What is an antibody?
An antibody is a protein that sticks to a specific protein called an antigen. Antibodies circulate throughout the body until they find and attach to the antigen. Once attached, they can recruit other parts of the immune system to destroy the cells containing the antigen. Researchers can design antibodies that specifically target a certain antigen, ...
How do antibodies work?
Antibodies circulate throughout the body until they find and attach to the antigen. Once attached, they can recruit other parts of the immune system to destroy the cells containing the antigen. Researchers can design antibodies that specifically target a certain antigen, such as one found on cancer cells. They can then make many copies of that ...
What is the function of Alemtuzumab?
Alemtuzumab binds to the CD52 antigen, which is found on cells called lymphocytes (which include the leukemia cells). Once attached, the antibody attracts immune cells to destroy these cells. Some naked mAbs boost the immune response by targeting immune system checkpoints.
