
Nutrition
Treatment. impurities in rifampin and rifapentine, two important anti-tuberculosis (TB) medications. People with TB disease or latent TB infection taking rifampin or rifapentine should continue taking their current medication, and should …
What medications are used to treat TB?
Apr 08, 2020 · If you have an active TB disease you will probably be treated with a combination of antibacterial medications for a period of six to 12 months. The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three …
What is TB and how it is treated?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a primordial infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs. M. tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) is the etiological agent of TB and currently more than one-third of the world population is suffering from TB. For the treatment of TB, administration of …
What is the current treatment for TB?
Jan 18, 2010 · People with TB meningitis are given a 12 month course of treatment consisting of two months’ quadruple therapy, followed by isoniazid and rifampicin for the rest of the treatment. The use of glucocorticoids (such as prednisolone) is also recommended for the first 2-3 weeks of treatment, followed by gradual withdrawal (NICE, 2006).
What are the side effects of TB treatment?
Some programmes or clinicians may choose to use a shorter (eg. 9–12 months) MDR-TB treatment regimen consisting of combinations of later-generation fluoroquinolones (moxifloxacin or gatifloxacin), clofazimine, ethambutol and pyrazinamide throughout the treatment period supplemented by prothionamide, kanamycin, and high-dose isoniazid during …
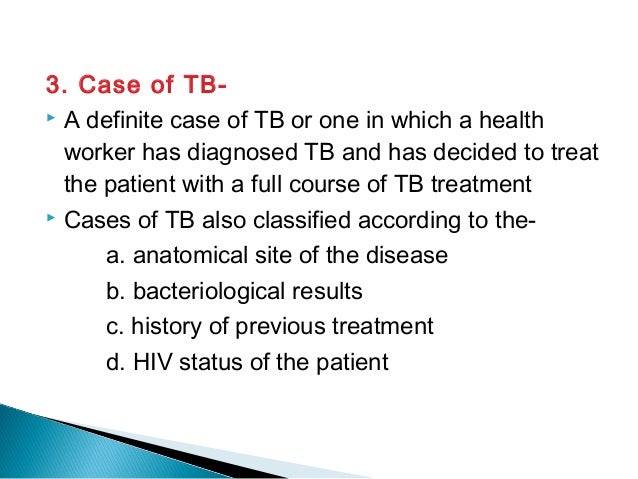
How many TB treatments are there?
Your doctor may order a test that shows which antibiotics will kill the TB strain. Based on the results, you'll take three or four medications for 2 months. Afterward, you'll take two medications for 4 to 7 months. You'll probably start to feel better after a few weeks of treatment.Sep 19, 2021
What is first line treatment for TB?
Of the approved drugs, isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), ethambutol (EMB), and pyrazinamide (PZA) are considered first-line anti-TB drugs and form the core of standard treatment regimens (Figure 6.4) (Table 6.2). Rifabutin (RBT) and rifapentine (RPT) may also be considered first- line drugs under certain circumstances.
What is the most effective method to monitor TB treatment?
The use of sputum smear microscopy and culture rather than sputum smear microscopy alone is recommended for the monitoring of patients with multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) during treatment (conditional recommendation/very low quality evidence) (2).
What is the main medicine for TB?
The usual treatment is: 2 antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampicin) for 6 months. 2 additional antibiotics (pyrazinamide and ethambutol) for the first 2 months of the 6-month treatment period.
Is there a vaccine for TB?
Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) disease. This vaccine is not widely used in the United States, but it is often given to infants and small children in other countries where TB is common. BCG does not always protect people from getting TB.
How is extrapulmonary TB treated?
TreatmentAnti-TB drugs. Anti-TB treatment is the mainstay in the management of EPTB. ... Paradoxical reaction. ... Corticosteroids. ... Surgery. ... Monitoring during treatment.
How is tuberculosis prevented?
Wash your hands after coughing or sneezing. Don't visit other people and don't invite them to visit you. Stay home from work, school, or other public places. Use a fan or open windows to move around fresh air.Dec 16, 2020
Why is multidrug therapy used for TB?
What is multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and how do we control it? The bacteria that cause tuberculosis (TB) can develop resistance to the antimicrobial drugs used to cure the disease. Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) is TB that does not respond to at least isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful anti-TB drugs.Jan 16, 2018
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
What is the test for TB?
Sputum tests. If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria. Sputum samples can also be used to test for drug-resistant strains of TB.
How long does ethambutol last?
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
What test is used to test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just ...
Can a TB test be wrong?
Results can be wrong. The TB skin test isn't perfect. Sometimes, it suggests that people have TB when they don't. It can also indicate that people don't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Can TB drugs cause liver damage?
Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. All tuberculosis medications can be toxic to your liver. When taking these medications, call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
Is TB a serious disease?
TB is a serious disease, and can be fatal if not treated properly. It is important to remember that all medications have risks and benefits. Learn more from CDC’s Dear Colleague letter. Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick. As a result, two TB-related conditions exist: latent TB infection and TB disease.
Can rifampin be used for TB?
Treatment. impurities in rifampin and rifapentine, two important anti-tuberculosis (TB) medications. People with TB disease or latent TB infection taking rifampin or rifapentine should continue taking their current medication, and should talk with their healthcare provider about any concerns.
What is the best treatment for TB?
The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol. You may begin to feel better only a few weeks after starting to take the drugs but treating TB takes much longer than other bacterial infections.
How long does it take to treat TB?
The treatment for this type of TB takes much longer, 20 to 30 months to complete, and you may experience more side effects.
What are the side effects of TB?
While you are in treatment for active TB disease, you will need regular checkups to make sure your treatment is working. Everyone is different, but there are side effects associated with taking the medications, including: 1 Upset stomach, nausea and vomiting or loss of appetite 2 Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet 3 Itchy skin, rashes or bruising 4 Changes in your eyesight or blurred visions 5 Yellowish skin or eyes 6 Dark-colored urine 7 Weakness, fatigue or fever that for three or more days
What are the symptoms of TB?
Yellowish skin or eyes. Dark-colored urine. Weakness, fatigue or fever that for three or more days. It is important to tell your doctor or TB nurse immediately if you begin having any unusual symptoms while taking medicine for either preventive therapy or for active TB disease.
Can TB cause liver damage?
TB drugs can be toxic to your liver, and your side effects may be a warning sign of liver damage . If you are having trouble with tingling and numbness, your doctor may prescribe a vitamin B6 supplement while you are in treatment. It may also be possible to change TB medications if your side effects are serious.
Can you get TB from taking too much medicine?
You must finish your medicine and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If you stop taking the drugs too soon you can become sick again and potentially spread the disease to others. Additionally, by taking the drugs incorrectly, TB germs that are still alive may become drug-resistant, making it harder for you to get better next time.
What antibiotics are used to treat TB?
For the treatment of TB, administration of multiple antibiotics such as isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol is required for a long period of time to kill bacteria. However, antibiotic resistance is an emerging problem in multiple drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) infections.
What is the etiological agent of TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a primordial infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs. M. tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) is the etiological agent of TB and currently more than one-third of the world population is suffering from TB. For the treatment of TB, administration of multiple antibiotics such as isoniazid, rifampicin, ...
What is the most effective anti-TB drug?
Fluoroquinolones are often the most effective anti-TB drugs in an MDR-TB regimen. There are two important recommendations regarding fluoroquinolone use from the 2011 update of the Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis(1).
How early can you start anti-TB treatment?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is recommended for all patients with HIV and drug-resistant TB, irrespective of CD4 cell-count, as early as possible (within the first eight weeks) following initiation of the anti-TB treatment (strong recommendation) (1). The drug dosage is usually determined by age and weight.
How long does it take to treat TB?
The current poor global control of TB is due in part to the lack of research innovation over the past few decades; current DS-TB treatment guidelines have been essentially unchanged for 35 years and treatment still takes a minimum six months.
How many people have TB in the world?
According to WHO estimates, in 2018 10 million people developed TB globally, for an incidence of 132/100 000 people. This global average, however, hides the vast disparities between developed and developing countries. Almost all cases are concentrated in South East Asia (44%), Africa (24%), and the western Pacific (18%) regions.
Is TB latent or active?
While TB treatment and control efforts are currently dichotomized around “latent” and “active” TB infection, neither of the two available methods to identify latent TB infection (tuberculin skin test and interferon gamma release assays) distinguish the few asymptomatic individuals who will develop active TB (estimated to be 5-10% lifetime risk) from the majority of individuals who will never develop active TB. Treating all M tuberculosis latently infected individuals for months is not feasible in most areas of the world. Rather, evidence is emerging of a spectrum of TB disease activity, and new approaches attempt to predict asymptomatic individuals who will progress to active TB disease (incipient TB infection).
Does XDR-TB have a control arm?
Of the three XDR-TB trials, however, only endTB-Q has a concurrent WHO standard control arm. Both Nix-TB and ZeNix only include experimental arms with no concurrent SOC control arm, with the primary outcome being relapse or failure at 12 months after enrollment.
Is DS TB decreasing?
Although global rates of DS-TB are slowly decreasing, rates of MDR-TB are decreasing less quickly, affecting 3.4% of new TB cases and 18% of previously treated cases. Even more challenging to treat is XDR-TB: MDR-TB with additional resistance to fluoroquinolones and injectable aminoglycosides.
Can you treat tuberculosis for months?
Treating all M tuberculosis latently infected individuals for months is not feasible in most areas of the world. Rather, evidence is emerging of a spectrum of TB disease activity, and new approaches attempt to predict asymptomatic individuals who will progress to active TB disease (incipient TB infection).
What to do if you have TB?
Actions to be taken 1 Houses should be adequately ventilated; 2 Anyone who coughs should be educated on cough etiquette and respiratory hygiene, and should follow such practice at all times; 3 While smear positive, TB patients should:#N#Spend as much time as possible outdoors;#N#If possible, sleep alone in a separate, adequately ventilated room;#N#Spend as little time as possible on public transport;#N#Spend as little time as possible in places where large numbers of people gather together.
What are some ways to prevent TB?
Other TB prevention activities. There are several other TB prevention activities. This includes preventing people with latent T B from developing active, and infectious, TB disease. TB infection control including the use of masks & respirators, which means preventing the transmission of TB in such settings as hospitals & prisons.
Why is isoniazid used for TB?
Isoniazid is a cheap drug, but in a similar way to the use of the BCG vaccine, it is mainly used to protect individuals rather than to interrupt transmission between adults. This is because children rarely have infectious TB, and it is hard to administer isoniazid on a large scale to adults who do not have any symptoms.
What precautions should be taken to prevent TB?
If someone is not on treatment, then precautions such as cough etiquette, must be taken to prevent TB spreading from one adult to another. Anything which increases the number of people infected by each infectious person, such as ineffective treatment because of drug resistant TB, reduces the overall effect of the main TB prevention efforts. ...
How to stop TB from one person to another?
This is done through firstly, identifying people with active TB, and then curing them through the provision of drug treatment. With proper TB treatment someone with TB will very quickly not be infectious ...
What is TB prevention?
TB prevention in health care facilities. Doctors and other health care workers who provide care for patients for TB, must follow infection control procedures to ensure that TB infection is not passed from one person to another.
How to prevent TB?
Spend as little time as possible on public transport; Spend as little time as possible in places where large numbers of people gather together . Educating people about TB is also an important part of TB prevention, as well as ensuring that people who need treatment receive it as soon as possible.
What is the best treatment for TB?
Treatment for Tuberculosis. Drug treatment is one of the most efficient ways to treat this infectious disease. For patients with Latent TB infections, doctors generally prescribe an antibiotic called isoniazid for preventing the latent infection from becoming active. Active TB Diseases will be deadly if left untreated.
What are the different types of TB?
Types of Tuberculosis (TB) There are two different types of tuberculosis: Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis.
What is TB in the body?
What is Tuberculosis (TB)? Tuberculosis (TB) is a dangerous and highly contagious bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs, but if left untreated, it might spread to different parts of the body.
How long does ethambutol last?
The procedure involved is taking a combination of ethambutol, INH, priftin and pyrazinamide for a term of three months, followed by a mix of INH and pyrazinamide for 12 months.
What is the most common test for TB?
Skin Test : It is the most common type of test. In this procedure, a small sample of Tuberculin – a purified protein is injected under the patient’s skin. If the skin around the site of the injection gets swollen more than five millimetres, then it is a clear indication of TB infection.
What tests are used to test for infectious disease?
These tests include certain body fluids test – blood and sputum, skin test and chest X-rays.
Can a weak immune system cause TB?
Individuals with a weak immune system are at increased risk. Metabolic diseases such as diabetes can also increase the risk of contracting TB. Tuberculosis is a contagious airborne disease, which can be acquired from close contact with an infected person.
