You may have any of the below:
- Chest X-ray
- Chest fluoroscopy
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
Full Answer
What care should a patient receive after a thoracentesis?
You may have any of the below: Chest X-ray Chest fluoroscopy Ultrasound CT scan
What are the risks of a thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis (pleural tap) is a medical procedure sometimes used to diagnose or treat certain lung problems. During a thoracentesis, a needle is pushed through your chest wall and into the pleural space, typically to remove excess pleural fluid. Find procedure specialists Why would I need thoracentesis?
What to expect after thoracentesis?
May 18, 2020 · A thoracentesis is a relatively simple procedure that involves using a needle to remove fluid from the pleural space. Doctors may use the …
What is the best position for thoracentesis?
The use of wall suction, in comparison to evacuated bottles, may decrease the incidence of transient chest pain or cough. Image-guided thoracentesis performed with wall suction is safe when compared to evacuated bottles.
What is a thoracentesis?
Interpreting Results. Thoracentesis is a medical procedure to remove some fluid between the lungs and the chest wall. The name derives from the Greek words thorax (“chest”) and centesis (“puncture”). It is used to help diagnose and treat medical conditions causing this fluid buildup, called a “pleural effusion.”.
Where is thoracentesis performed?
Depending on the situation, it may be performed in a hospital or at a doctor’s office. 3
How does thoracentesis help with pleural effusion?
Thoracentesis removes some of the excess fluid surrounding the lungs when there is a pleural effusion. Sometimes thoracentesis is used as a treatment to decrease symptoms from a pleural effusion. All that extra fluid may make you feel short of breath. Removing some of it may help you feel more comfortable. 1 .
What are the complications of thoracentesis?
The most common potentially serious complication of thoracentesis is pneumothorax. Some other possible problems include: 1 Re-expansion pulmonary edema (REPE) 2 Damage to the spleen or liver 3 Infection 4 Air embolism 5 Shortness of breath 6 Pain 7 Bleeding 5
Is a thoracentesis diagnostic inconclusive?
Sometimes a diagnostic thoracentesis is inconclusive. That just means that your physician needs more information to determine the cause of your medical problems. Depending on the context, you might need one or more of the following:
Can thoracentesis be done at the bedside?
Someone will surgically drape the area and get it ready for the procedure. In the past, thoracentesis was often performed at the bedside without any kind of imaging. However, now it is frequently done with the help of ultrasound.
Can you have thoracentesis with severe respiratory failure?
For example, thoracentesis is not usually recommended for people with severe respiratory failure or people who don’t have adequate blood pressure. People who are unable to sit still for the procedure are also not able to have it safely.
Thoracentesis
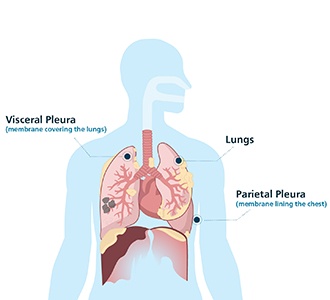
Your lungs are surrounded by a double layer of membranes called the pleura. In between the two pleural membranes is a narrow space called the pleural space. The pleural space has a small amount of fluid that acts as a lubricant as your lungs breathe in and out.
Why would I need thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis is both a diagnostic tool and a treatment. It is mainly used to treat pleural effusion, or the buildup of excess pleural fluid.
The thoracentesis procedure
Thoracentesis is a safe procedure. Although it usually takes place at a hospital, it is an outpatient procedure, so probably you will go home the same day.
Thoracentesis: possible complications
Although thoracentesis is a safe and minimally invasive procedure, it does come with some risks. Possible complications of thoracentesis include:
What to do when preparing for a thoracentesis?
When preparing a person for a thoracentesis, a doctor may: review all medications that the person is taking and make changes to the types or dosages where appropriate. order blood tests to check whether the person’s blood clots normally. ask whether the person may be pregnant.
Why do doctors do thoracentesis?
Doctors may perform a thoracentesis for one of two reasons: Diagnostic reasons: A thoracentesis can help doctors identify the cause of the pleural effusion. Therapeutic reasons: Too much fluid in the pleural space compresses the lungs, making it difficult for a person to breathe properly. Removing the fluid reduces pressure on the lungs, ...
What to do after thoracentesis?
A person will receive an X-ray after the thoracentesis to check that the procedure was a success. They will then undergo a period of careful monitoring to ensure that they do not develop complications. A doctor will send fluid samples to a lab to help identify the cause of the pleural effusion.
What is the procedure to remove fluid from the pleural space?
A doctor may suggest a thoracentesis to remove fluid from the pleural space. A thoracentesis is a procedure that involves the use of a needle to remove excess fluid from the pleural space between the lungs and the chest wall. The medical term for a buildup of fluid in the pleural space is pleural effusion.
How long does a thoracentesis take?
A thoracentesis usually takes between 10 and 15 minutes. Trusted Source. , depending on the amount of fluid in the pleural space. The more fluid there is to drain out, the longer the procedure will take.
What is a pleural tap?
It can cause several symptoms, including an inability to breathe properly. A thoracentesis, also called a pleural tap, is a procedure to remove this fluid. Read on to find out how a thoracentesis works, how to prepare for the procedure, and the potential risks and complications.
Why do you need to stay still during pleural surgery?
It is very important to stay as still as possible throughout the procedure to avoid any accidental damage to the lungs. If there is a lot of fluid to remove from the pleural space, a doctor may attach a tube to the needle to aid drainage. The person may feel a pulling sensation as the fluid leaves their chest.
Types of pleural effusion
There are clinical cases in which the patient does not develop any specific symptoms. However, the individual usually suffers from a series of characteristic signals. For example, difficulty breathing, cough, hiccups, severe discomfort in the chest area, chills and even moderate fever. In any case, we can differentiate between:
What is thoracentesis?
Also known as “pleural paracentesis,” “thoracic paracentesis,” or “pleurocentesis,” torococentesis is a medical procedure in which a variable amount of pleural fluid is removed.
Why do you need a thoracentesis?
If there’s excess fluid, it can compress the lungs and cause difficulty breathing. The goal of a thoracentesis is to drain the fluid and make it easier for you to breathe again. In some cases, the procedure will also help your doctor discover the cause of the pleural effusion.
How long does it take to get a pleural effusion?
The amount of fluid drained varies depending on the reasons for performing the procedure. It typically takes 10 to 15 minutes, but it can take longer if there’s a lot of fluid in the pleural space.
What is a pleural tap?
Thoracentesis, also known as a pleural tap, is a procedure done when there’s too much fluid in the pleural space. This allows a pleural fluid analysis to be performed in the lab to figure out the cause of fluid accumulation around one or both of the lungs. The pleural space is the small space between the lungs and the chest wall.
What is abnormal on a pleural biopsy?
Abnormal results on a pleural biopsy can indicate certain causes for the effusion, including: the presence of cancer cells, such as lung cancer.
Can you drive home after pleural surgery?
You’ll need someone else to drive you home after the procedure if you’re sedated. After sitting in a chair or lying on a table, you’ll be positioned in a way that allows the doctor to access the pleural space. An ultrasound may be done to ascertain the correct area where the needle will go.
Can you go home after a thoracentesis?
Most people who have a thoracentesis can go home the same day. You’ll be able to return to most of your normal activities soon after the procedure. However, your doctor may recommend that you avoid physical activity for several days after the procedure. Your doctor will explain how to take care of the puncture site.
Can you stay overnight after thoracentesis?
To ensure there are no complications, you may be asked to stay overnight in the hospital to be monitored. A follow-up X-ray may be performed right after the thoracentesis.
How does thoracentesis work?
From there, most cases happen this way: You'll sit up on a bed or chair, with your arms resting on a table. This position spreads out the space between the ribs. The area where the needle will be inserted is cleaned and numbed.
What happens during thoracentesis?
During the thoracentesis, your doctor removes fluid from the pleural space. This eases your shortness of breath, chest pain, and pressure on your lungs. That fluid is then tested to figure out the reason behind the build-up.
How many teaspoons of fluid are in the pleural space?
There are normally 4 teaspoons of fluid in this area, known as the “pleural space.”. A variety of things can cause that amount to go up.
Is thoracentesis surgery safe?
Every surgical procedure has some potential problems. Though thoracentesis is generally considered safe, these complications can happen: Pulmonary edema, or fluid in the lungs. Pneumothorax, or collapsed lung. Infection at the site where the needle pierced your skin.

Purpose of Thoracentesis
Risks and Contraindications
- People with certain medical conditions cannot have thoracentesis safely. For example, thoracentesis is not usually recommended for people with severe respiratory failure or people who don’t have adequate blood pressure. People who are unable to sit still for the procedure are also not able to have it safely. Healthcare providers are also very cautious in giving thoracentesi…
Before The Procedure
- Before the thoracentesis, your healthcare provider will talk to you about all your medical conditions, perform a physical exam, and assess your health. This will help ensure that thoracentesis makes sense for you. You should also review your medications with your clinician. If you take medications that affect your blood (like Coumadin), you might n...
During The Procedure
- Your medical team will include your healthcare provider, one or more nurses, and health aids or clinic personnel.
After The Procedure
- People need to be monitored after getting thoracentesis, even if they are having the procedure as an outpatient. That’s because thoracentesis sometimes causes complications. If you are doing well, you may be able to go home in an hour or so.
Interpreting Results
- If you are having a diagnostic thoracentesis, your fluid will be sent to the lab for analysis. The tests done here may take a day or more to come back. Your clinician can let you know about the specific results in your situation. These results may help your healthcare provider diagnose your specific medical condition.