Newer anti-androgens
- All of these drugs can be helpful in men with cancer that has not spread but is no longer responding to other forms of hormone therapy (known as non-metastatic castrate-resistant ...
- Enzalutamide can also be used for metastatic prostate cancer (cancer that has spread), whether it is castrate-resistant or castrate-sensitive (still responding to other forms of hormone therapy).
- Apalutamide can also be used for metastatic castrate-sensitive prostate cancer.
- Leuprolide (Eligard, Lupron Depot, others)
- Goserelin (Zoladex)
- Triptorelin (Trelstar)
- Histrelin (Vantas)
- Degarelix (Firmagon)
What hormone is used to treat prostate cancer?
This is known as hormone therapy, also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), and is the standard first treatment when prostate cancer has spread (metastatic prostate cancer). Testosterone is a male sex hormone (or androgen), which is mostly produced by the testicles, and is vital in reproduction and sexual function.
What are the side effects of prostate hormone therapy?
- Decreased mental capacity, tiredness, and feelings of depression. Talk to your doctor about taking a mild antidepressant to battle these symptoms. ...
- Decreased muscle mass and decreased bone mass (osteoporosis). ...
- Gaining weight. ...
- Hot flashes. ...
- Anemia. ...
- Growth of excess breast tissue and sore breasts. ...
- Sexual problems. ...
What is the best treatment for prostate cancer?
Treating advanced prostate cancer
- Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is often used to treat prostate cancer that's spread to other parts of the body (metastatic prostate cancer).
- Steroids. Steroid tablets are used when hormone therapy no longer works because the cancer is resistant to it.
- Other medical treatments. ...
What is the success rate of hormone therapy?
When it comes to early stages of disease, patients very frequently do well with either brachytherapy or external beam radiation. Success rates of around 90% or higher can be achieved with either approach.

Which hormone therapy is best for prostate cancer?
Abiraterone (Zytiga) blocks an enzyme (protein) called CYP17, which helps stop these cells from making androgens. Abiraterone can be used in men with advanced prostate cancer that is either: High risk (cancer with a high Gleason score, spread to several spots in the bones, or spread to other organs)
What drugs are used for hormone therapy?
Common LHRH drugs include goserelin (Zoladex) and leuprolide (Lupron). They can be used alone or with other hormone drugs (tamoxifen, aromatase inhibitors, fulvestrant) as hormone therapy in pre-menopausal women.
How long do you take bicalutamide for prostate cancer?
Reducing tumour flare During this time they can make your symptoms worse. This is called tumour flare. If you are having bicalutamide to stop tumour flare, you take it for a few days before starting the luteinising hormone blocker, and stay on it for about 4 to 6 weeks.
How Long Can prostate cancer be treated with hormones?
Doctors usually recommend that you have the treatment for between 3 months and 3 years. How long depends on the risk of your cancer coming back and how many side effects you get.
What is the success rate of hormone therapy?
Hormone replacement therapy users had a 100% survival rate at 6 years as opposed to 87% in nonusers. Both groups of tumors were detected by screening mammography, thus detected "early" by current convention. Yet, we observed a survival benefit for those women who had received HRT.
How is hormone therapy given?
Hormone therapy can be given in a few ways: Oral medication – Taken by mouth. Injection – Given by an injection under the skin (subcutaneous) or in the muscle (intramuscular). Surgical intervention – Removal of the ovaries in women, or testicles in men, causes lower levels of hormones being made.
Why is bicalutamide not used now?
Bicalutamide, the most recent antiandrogen to be approved for use in the United States, is also used in therapy of prostate cancer, but has not been approved for use in nonmalignant hyperandrogenic states. All three nonsteroidal antiandrogens have been linked to instances of liver injury.
How do u feel when taking bicalutamide?
You may feel sick when you are having this treatment. This is usually mild. If you feel sick, your doctor can give you tablets to help. It may also help to take your bicalutamide tablets with food.
Is bicalutamide a chemo drug?
No, Casodex is not a form of chemotherapy, Casodex (bicalutamide) is an anti-androgen which is a type of hormone therapy used to treat prostate cancer. When you have cancer there are different options of cancer treatment including: hormone therapy. chemotherapy.
Can prostate cancer spread while on hormone therapy?
In 85% to 90% of cases of advanced prostate cancer, hormone therapy can shrink the tumor. However, hormone therapy for prostate cancer doesn't work forever. The problem is that not all cancer cells need hormones to grow. Over time, these cells that aren't reliant on hormones will spread.
How many times can you have hormone treatment for prostate cancer?
Hormone therapy can help shrink the prostate and any cancer that has spread, and make the treatment more effective. You may be offered hormone therapy for up to six months before radiotherapy. And you may continue to have hormone therapy during and after your radiotherapy, for up to three years.
How quickly does PSA drop after hormone therapy?
Median PSA at the end of hormonal therapy for all patients was 0.2 ng/mL (range: 0 - 96.2). A total of 744 patients (70%) reached a PSA-CR at the end of hormonal therapy. The time to reach PSA nadir was 3.7 months, ranging from 0.8 to 8.2 months. With a median follow-up of 7.2 years, higher rates of BF (56% vs.
When Is Hormone Therapy used?
Hormone therapy may be used: 1. If the cancer has spread too far to be cured by surgery or radiation, or if you can’t have these treatments for som...
Possible Side Effects of Hormone Therapy
Orchiectomy and LHRH agonists and antagonists can all cause similar side effects from lower levels of hormones such as testosterone. These side eff...
Current Issues in Hormone Therapy
There are many issues around hormone therapy that not all doctors agree on, such as the best time to start and stop it and the best way to give it....
What is the most common treatment for prostate cancer?
Treatments that reduce androgen production by the testicles are the most commonly used hormone therapies for prostate cancer and the first type of hormone therapy that most men with prostate cancer receive. This form of hormone therapy (also called androgen deprivation therapy, or ADT) includes:
How do androgens help prostate cells grow?
Androgens promote the growth of both normal and cancerous prostate cells by binding to and activating the androgen receptor, a protein that is expressed in prostate cells ( 1 ). Once activated, the androgen receptor stimulates the expression of specific genes that cause prostate cells to grow ( 2 ).
What hormones are released when androgen levels are low?
Normally, when androgen levels in the body are low, the hypothalamus releases LHRH. This stimulates the pituitary gland to produce luteinizing hormone, which in turn stimulates the testicles to produce androgens. LHRH agonists, like the body’s own LHRH, initially stimulate the production of luteinizing hormone.
What hormones block androgen production?
block androgen production (synthesis) throughout the body. Androgen production in men. Drawing shows that testosterone production is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (L HRH). The hypothalamus releases LHRH, which stimulates the release of LH from the pituitary gland.
What does LHRH do to the testicles?
LHRH agonists, like the body’s own LHRH, initially stimulate the production of luteinizing hormone. However, the continued presence of high levels of LHRH agonists actually causes the pituitary gland to stop producing luteinizing hormone. As a result, the testicles are not stimulated to produce androgens.
What is the procedure to remove testicles?
This form of hormone therapy (also called androgen deprivation therapy, or ADT) includes: Orchiectomy, a surgical procedure to remove one or both testicles. Removal of the testicles, called surgical castration , can reduce the level of testosterone in the blood by 90% to 95% ( 5 ).
What are the hormones that control the development and maintenance of male characteristics?
Hormones are substances that are made by glands in the body. Hormones circulate in the bloodstream and control the actions of certain cells or organs. Androgens (male sex hormones) are a class of hormones that control the development and maintenance of male characteristics. The most abundant androgens in men are testosterone ...
What hormones are used to treat prostate cancer?
Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Prostate cancer cells depend on hormones such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) to thrive. Hormone therapy, which is also called androgen deprivation therapy or androgen suppression therapy, for prostate cancer involves depriving the cancer cells of this fuel by either blocking ...
What are the side effects of hormone therapy?
Depression. Elevated cholesterol levels. Most men on hormone therapy experience at least some of these side effects. Before beginning hormone therapy, you should discuss the effects of testosterone loss with your doctor to help minimize them. Exercise is one of the best things you can do to prevent many of these side effects.
What is the name of the LHRH antagonist?
For example, degarelix (Firmagon) is an LHRH antagonist that is given as a monthly injection. Following treatment, patients may experience pain or swelling at the injection site as well as increased liver enzymes.
What is the surgical removal of the testicles?
Orchiectomy involves the surgical removal of the testicles. Since over 90 percent of testosterone is produced by the testicles, this is an effective strategy for blocking testosterone release. Orchiectomy causes most prostate tumors to stop growing or shrink for a period of time.
What antiandrogens are prescribed for an orchiectomy?
Commonly prescribed antiandrogens include flutamide (Eulexin) and bicalutamide (Casodex).
What is Xtandi used for?
This antiandrogen may be used to treat castration-resistant prostate cancer.
How often do you give LHRH?
LHRH agonists are given through regular shots or implants under the skin. They may be administered on a variety of schedules that range from once a month to once a year.
What happens after prostate cancer treatment?
After treatment of prostate cancer, if the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level remains high or starts rising. In locally advanced prostate cancer, to make external beam radiation therapy more effective in reducing the risk of recurrence. In those with a high risk of recurrence after initial treatment to reduce that risk.
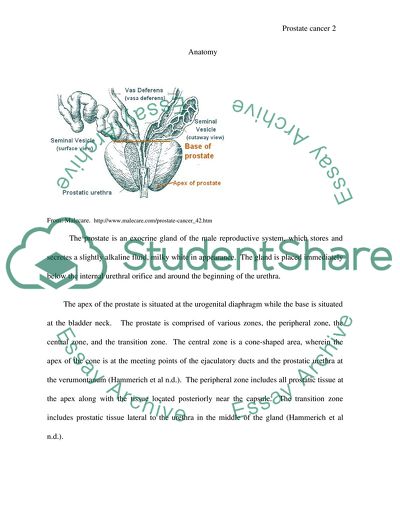
Where is prostate cancer located?
Prostate cancer occurs in the prostate gland, which is located just below the bladder in males and surrounds the top portion of the tube that drains urine from the bladder (urethra). This illustration shows a normal prostate gland and a prostate with a tumor.
What is the effect of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone?
Certain medications — known as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists and antagonists — prevent your body's cells from receiving messages to make testosterone. As a result, your testicles stop producing testosterone. Medications that block testosterone from reaching cancer cells.
Can you get hormone therapy after an orchiectomy?
Orchiectomy is usually performed as an outpatient procedure and doesn't require hospitalization. Typically, no additional hormone therapy is required after orchiectomy.
Can hormone therapy be used for prostate cancer?
Your doctor may recommend hormone therapy for prostate cancer as an option at different times and for different reasons during your cancer treatment. Hormone therapy can be used: In advanced (metastatic) prostate cancer to shrink the cancer and slow the growth of tumors, which also might relieve signs and symptoms.
Does intermittent therapy reduce side effects?
Early research shows this intermittent dosing of hormone therapy medications may reduce the risk of side effects . However, additional studies are needed to determine the long-term survival benefits of intermittent therapy.
Can hormone therapy be adjusted?
Depending on your circumstances, you may undergo tests to monitor your medical situation and watch for cancer recurrence or progression while you're taking hormone therapy. Results of these tests can give your doctor an idea of how you're responding to hormone therapy, and your therapy may be adjusted accordingly.
What hormones are used to treat prostate cancer?
Sometimes you may have these drugs earlier on, when you are first diagnosed. Newer hormonal therapy drugs include: abiraterone. enzalutamide.
What is the best drug for prostate cancer?
leuprorelin (Prostap ® ), Lutrate ®) triptorelin (Decapeptyl ®, Gonapeptyl Depot ®) buserelin (Suprefact ®) for advanced prostate cancer. A nurse or doctor at your GP practice or hospital can give you these drugs. The first time you have one of these drugs, it can cause a temporary increase in testosterone.
How to reduce testosterone in prostate cancer?
Another way of reducing testosterone in men with locally advanced or advanced prostate cancer is to have an operation to remove part or all of the testicles. This is called an orchidectomy and is not commonly done. It may be an option if you find it hard to have regular injections or to take tablets every day.
What is intermittent therapy?
Instead of taking the drugs continuously, you may stop taking the drugs for a while and then start taking them again. This is called intermittent hormonal therapy. It means you get a break from the side effects of hormonal therapy.
Where is testosterone made?
Testosterone is mainly made by the testicles. A small amount is made by the adrenal glands, above each kidney. Hormonal therapies lower your testosterone levels or stop it reaching the prostate cancer cells. Testosterone is important for:
What hormones make testosterone?
The pituitary gland in the brain makes a hormone called luteinising hormone (LH). This hormone tells the testicles to make testosterone. LHRH agonists interfere with this action and stop the testicles making testosterone. You have them as an implant injection or an injection under the skin.
Can you have radiotherapy for prostate cancer?
Doctors often advise having hormonal therapy along with radiotherapy (including brachytherapy ), to make treatment more effective. This is usually if you have intermediate-risk or high-risk early prostate cancer.
When It's Used
Hormone therapy is a common treatment for all stages of prostate cancer. You might get it along with other treatments like radiation and chemotherapy.
How It Works
Hormone therapy stops your body from making androgens or keeps the prostate cancer cells from using these hormones to grow.
Types of Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer
There are many kinds of hormone therapy. Sometimes two or more types are used together. These are the most common ones:
Side Effects of Hormone Treatment
The loss of testosterone that hormone therapy causes leads to side effects in nearly all men. These can include:
What to Expect
You might get hormone therapy in your doctor’s office, in an outpatient treatment center, or as pills you take at home.
Overview
Why It's Done
- Hormone therapy for prostate cancer is used to stop your body from producing the male hormone testosterone, which fuels the growth of prostate cancer cells. Your doctor may recommend hormone therapy for prostate cancer as an option at different times and for different reasons during your cancer treatment. Hormone therapy can be used: 1. In advanced (metastatic) prosta…
Risks
- Side effects of hormone therapy for prostate cancer can include: 1. Loss of muscle mass 2. Increased body fat 3. Loss of sex drive 4. Erectile dysfunction 5. Bone thinning, which can lead to broken bones 6. Hot flashes 7. Decreased body hair, smaller genitalia and growth of breast tissue 8. Fatigue 9. Changes in behavior 10. Problems with metabolism
How You Prepare
- As you consider hormone therapy for prostate cancer, discuss your options with your doctor. Approaches to hormone therapy for prostate cancer include: 1. Medications that stop your body from producing testosterone.Certain medications — known as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists and antago...
What You Can Expect
- LHRH agonists and antagonists
LHRHagonist and antagonist medications stop your body from producing testosterone. These medications are injected under your skin or into a muscle monthly, every three months or every six months. Or they can be placed as an implant under your skin that slowly releases medication ov… - Anti-androgens
Anti-androgens block testosterone from reaching cancer cells. These oral medications are usually prescribed along with an LHRH agonist or before taking an LHRHagonist. Anti-androgens include: 1. Bicalutamide (Casodex) 2. Nilutamide (Nilandron) 3. Flutamide
Results
- You'll meet with your cancer doctor regularly for follow-up visits while you're taking hormone therapy for prostate cancer. Your doctor will ask about any side effects you're experiencing. Many side effects can be controlled. Depending on your circumstances, you may undergo tests to monitor your medical situation and watch for cancer recurrence or progression while you're taki…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiesof tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.
Overview
Why It's Done
- Hormone therapy for prostate cancer is used to stop your body from producing the male hormone testosterone, which fuels the growth of prostate cancer cells. Your doctor may recommend hormone therapy for prostate cancer as an option at different times and for different reasons during your cancer treatment. Hormone therapy can be used: 1. In advanced (metastatic) prosta…
Risks
- Side effects of hormone therapy for prostate cancer can include: 1. Loss of muscle mass 2. Increased body fat 3. Loss of sex drive 4. Erectile dysfunction 5. Bone thinning, which can lead to broken bones 6. Hot flashes 7. Decreased body hair, smaller genitalia and growth of breast tissue 8. Fatigue 9. Changes in behavior 10. Problems with metabolism
How You Prepare
- As you consider hormone therapy for prostate cancer, discuss your options with your doctor. Approaches to hormone therapy for prostate cancer include: 1. Medications that stop your body from producing testosterone.Certain medications — known as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists and antago...
What You Can Expect
- LHRH agonists and antagonists
LHRHagonist and antagonist medications stop your body from producing testosterone. These medications are injected under your skin or into a muscle monthly, every three months or every six months. Or they can be placed as an implant under your skin that slowly releases medication ov… - Anti-androgens
Anti-androgens block testosterone from reaching cancer cells. These oral medications are usually prescribed along with an LHRH agonist or before taking an LHRHagonist. Anti-androgens include: 1. Bicalutamide (Casodex) 2. Nilutamide (Nilandron) 3. Flutamide
Results
- You'll meet with your cancer doctor regularly for follow-up visits while you're taking hormone therapy for prostate cancer. Your doctor will ask about any side effects you're experiencing. Many side effects can be controlled. Depending on your circumstances, you may undergo tests to monitor your medical situation and watch for cancer recurrence or progression while you're taki…