
Medication
The pill, which contains quarter doses of four drugs — irbesartan, amlodipine, indapamide and bisoprolol — was used in a large scale study conducted by researchers at the University of Sydney. For the study, 600 people were given either the four-in-one pill or a single standard blood pressure drug (irbesartan).
Nutrition
The following list includes most of the commonly prescribed combination drugs used for hypertension:
- Moduretic (amiloride and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Lotrel (amlodipine and benazepril)
- Tenoretic (atenolol and chlorthalidone)
- Lotensin HCT (benazepril and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Ziac (bisoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Capozide (captopril and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Vaseretic (enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Lexxel (felodipine and enalapril)
What is the best medication to treat hypertension?
Worst Drug # 4: Chlorothiazide, sold as "Diuril". Diuril, like any diuretic or so-called "water pill", increases your risk of painful muscle cramping, paralysis, seizure, and even slipping into a coma because it flushes out vital nutrients that your body needs to keep working properly.
What are the most common medications for hypertension?
- Normal blood pressure (BP): systolic BP is less than 120, and diastolic BP is less than 80.
- Elevated BP: systolic BP 120 to 130 and diastolic BP is less than 80.
- Stage 1 HTN: systolic BP 130 to 139 or diastolic BP 80 to 89.
- Stage 2 HTN: systolic BP at least 140 or diastolic at least 90.
What are the 4 worst blood pressure drugs?
What are the first line medications for hypertension?
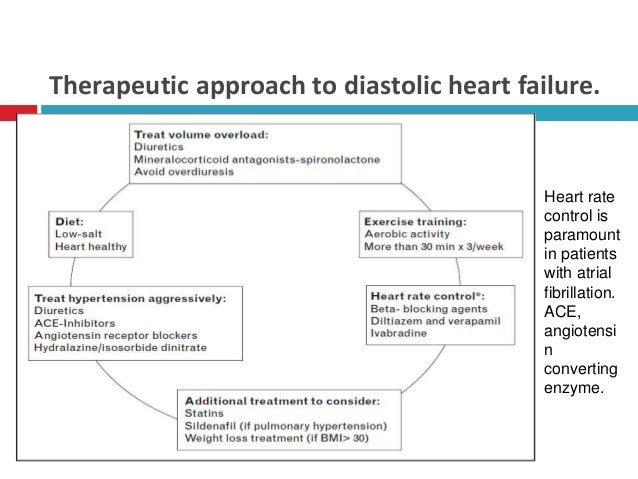
What medication is used first for hypertension?
There are three main classes of medication that are usually in the first line of treatment for hypertension: 1. Calcium Channel Blockers (CCB) 2. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors or ACE-I) and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) 3. Diuretics.
What is the first step in the treatment of hypertension?
Diuretics are the first step in the treatment of most patients with hypertension and the new clinical trials should focus on drugs to be added to them as the second step in the management of hypertension.
Do you need medication for stage 1 hypertension?
If you have stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension, your doctor will likely prescribe medications to lower your blood pressure and recommend healthy lifestyle changes.
What is the most popular medication for high blood pressure?
In terms of prescriptions written, here are the top 4 high blood pressure medications,the ACE inhibitor lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril) tops the list,followed by amlodipine besylate (Norvasc),a calcium channel blocker, and.generic hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ).
Other Medications Sometimes Used to Treat High Blood Pressure
If you're unable to reach your blood pressure goal with one or more of the above medications, other drugs that lower blood pressure include: 1. Alp...
High Blood Pressure and Other Health Problems
High blood pressure often goes hand in hand with other health problems, including: 1. Heart failure 2. Previous heart attack or stroke 3. Coronary...
Keep Trying to Reach Your Blood Pressure Goal
It's not unusual to try several medications or doses before finding what works best for you. An important way for you and your doctor to know if yo...
What is the best medication for hypertension?
Diuretics. There are three classes of diuretic drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Most commonly used are thiazide diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide or chlorthalidone. There is not usually an increased urine flow after the first one or two days of taking these medications. Nevertheless, it is best to take them in ...
Why are ACEIs used for hypertension?
ACEIs are widely used to treat hypertension because they are effective, have relatively few side effects and in reduce the complications of hypertension such as heart attacks and strokes. They have a special use in patients with diabetes mellitus who have protein the urine (“diabetic nephropathy”) and in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) in whom they appeared to have beneficial actions in slowing the loss of kidney function above that achieved by other agents.
What is edecrin used for?
Ethacrinic acid (Edecrin) is used in the rare patients who are allergic to diuretics. Loop diuretics are not as effective as thiazides in lowering blood pressure in patients with hypertension. They are used especially to treat edema (swelling of the ankles) or heart failure.
Why are diuretics important?
Diuretics increase the effectiveness of all other categories of antihypertensives. That is why they are an essential part of almost any multidrug regimen for hypertension. Special Points: Diuretics are the original antihypertensives. Therefore, their efficacy and adverse effects are very well understood.
What is beta blocker?
BETA BLOCKERS, ALPHA BLOCKERS AND SYMPATHOLYTIC DRUGS. This group of drugs was introduced next after diuretics, to be used for hypertension. They act on a part of the nervous system that controls blood pressure, known as the sympathetic nervous system. Blockade of the sympathetic nervous system reduces blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels, ...
How often do you give captopril?
There are some small differences in how long these drugs act in the circulation, they are relatively small and, with the exception of the very short acting captopril, any of these agents are usually affective when given once or sometimes twice daily as antihypertensive agents.
Can diuretics cause low blood pressure?
Over treatment with diuretics can lead to low blood pressure , orthostatic hypotension (weakness, dizziness and possibly fainting on standing) and a feeling of tiredness and lethargy, all of which can be prevented or reversed by holding the diuretic for a day or two and resuming, if necessary, at a lower dosage.
What is the best drug for hypertension?
Popular Hypertension Drugs. Prinivil (lisinopril) Drug class: ACE Inhibitors. Lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril) is an inexpensive drug used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. It is also given to reduce the risk of death after a heart attack. It is more popular than comparable drugs.
What is the best drug for high blood pressure?
Drug class: Beta Blockers. Metoprolol ER is an inexpensive drug used to treat high blood pressure and prevent chest pain. It is also used after a heart attack to prevent an additional heart attack from occurring. This drug is more popular than comparable drugs.
What is terazosin used for?
Drug class: Alpha Blockers. Terazosin is an inexpensive drug used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia ( BPH) in men and to treat high blood pressure in both men and women. It is slightly most popular than comparable drugs. Terazosin is only available as a generic drug; all brands have been discontinued.
What is the class of beta blockers?
Drug class: Beta Blockers. Propranolol er is a moderately priced drug used to treat high blood pressure, heart muscle disease, and prevent chest pain caused by angina. it is also used to treat migraines. It is slightly less popular than comparable drugs. it is available in generic and brand versions.
What is the drug class for atenolol?
Tenormin (atenolol) Drug class: Beta Blockers. Atenolol (Tenormin) is an inexpensive drug used to treat high blood pressure and prevent chest pain. It is also used to protect the heart during a heart attack and to prevent an additional heart attack from occurring.
What is Furosemide used for?
Furosemide (Lasix) is an inexpensive drug used to treat high blood pressure and edema or swelling from heart, kidney, or liver disease. It is more popular than comparable drugs. It is available in generic and brand versions.
What is the best medicine for chest pain?
Drug class: Beta Blockers. Lopressor ( Metoprolol) is an inexpensive beta-blocker. Beta-blockers reduce the workload on the heart and help it to beat more regularly. This medicine is used to treat high blood pressure and to prevent chest pain.
What are some examples of blood pressure medications?
Examples are spironolactone (Aldactone, Carospir) and eplerenone (Inspra). How well a drug works for you can depend on your age, sex, race, blood pressure level and overall health.
What are some examples of medications that can cause high blood pressure?
Examples include hydralazine and minoxidil. Aldosterone antagonists. These medications are often used with other drugs, such as a diuretic. Aldosterone antagonists block the hormone aldosterone, which sometimes causes salt and fluid retention, contributing to high blood pressure.
What are some examples of ACE inhibitors?
There are several ACE inhibitors available. Examples include enalapril (Vasotec, Epaned), lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril, Qbrelis) and ramipril (Altace). Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). These drugs block the action of angiotensin, a chemical in your body that narrows your arteries and veins.
What are some examples of beta blockers?
Examples of beta blockers include metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL), nadolol (Corgard) and atenolol (Tenormin). Renin inhibitors. Renin is a substance produced by your kidneys that triggers a series of steps that increases blood pressure.
What are some examples of calcium channel blockers?
Examples of calcium channel blockers include amlodipine (Norvasc), diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac, others), nifedipine (Adalat CC, Procardia) and verapamil (Verelan, Calan). Beta blockers. These drugs work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline.
What are the different types of diuretics?
There are three types of diuretics: thiazide, loop and potassium-sparing. Examples of diuretics include chlorothiazide (Diuril), bumetanide (Bumex) and amiloride (Midamor). If diuretics aren't enough to lower your blood pressure, your doctor might recommend adding other blood pressure medications to your treatment.
How well do drugs work?
How well a drug works for you can depend on your age, sex, race, blood pressure level and overall health. Combining two drugs usually works better than a single drug to get your blood pressure under control. Sometimes additional medication is needed to achieve your blood pressure goal.
How to stop high blood pressure?
Try the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, poultry, fish and low-fat dairy foods. Get plenty of potassium, which can help prevent and control high blood pressure. Eat less saturated fat and trans fat. Decrease the salt in your diet.
What tests are done to confirm if you have high blood pressure?
Ambulatory monitoring. This 24-hour blood pressure monitoring test is used to confirm if you have high blood pressure.
What is elevated blood pressure?
Elevated blood pressure is a systolic pressure ranging from 120 to 129 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure below (not above) 80 mm Hg. Elevated blood pressure tends to get worse over time unless steps are taken to control blood pressure. Elevated blood pressure may also be called prehypertension. Stage 1 hypertension.
What to do if you have chest pain?
If you also have chest pain, vision problems, numbness or weakness, breathing difficulty, or any other signs and symptoms of a stroke or heart attack, call 911 or your local emergency medical number. Both numbers in a blood pressure reading are important. But after age 50, the systolic reading is even more important.
What are Alpha blockers?
Alpha blockers include doxazosin (Cardura), prazosin (Minipress) and others. Alpha-beta blockers. Alpha-beta blockers block nerve signals to blood vessels and slow the heartbeat to reduce the amount of blood that must be pumped through the vessels.
What does blood pressure measure?
A blood pressure reading, as shown in the blood pressure monitor in the image, measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats (systolic pressure) in the first number, and the pressure in your arteries between heartbeats (diastolic pressure) in the second number.
What happens if your blood pressure is high?
If your blood pressure remains stubbornly high despite taking at least three different types of high blood pressure drugs, one of which usually should be a diuretic, you may have resistant hypertension.
What is the best medication for hypertension?
It’s been shown to be a great additive medication for resistant hypertension.”. Centrally acting agents, such as clonidine (Catapres, Kapvay), guanfacine (Intuniv) or methyldopa. These medications help slow your heart rate and keep your blood vessels from constricting by interfering with signals from the brain.
What is the best treatment for blood vessels?
Angiotensin-receptor blockers, such as losartan (Cozaar) or valsartan (Diovan). ARBs help block angiotensin and relax the blood vessels.
What is the role of a vasodilator in the kidney?
Vasodilators relax the muscles in the blood vessel walls, enabling blood to flow more easily. Loop diuretics, such as bumetanide (Bumex) or ethacrynic acid (Edecrin). These diuretics act on a different part of the kidney than thiazide diuretics. “Loop diuretics are secondary players,” Ajithan says.
What is the best medicine for kidneys?
Thiazide diuretics (“water pills”), such as hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) and chlorothiazide (Diuril). Thiazide diuretics help relieve pressure on your blood vessels by prompting the kidneys to remove excess fluid and salt from your body. Calcium channel blockers, such as amlodipine (Norvasc) or diltiazem (Cardizem). ...
How do beta blockers help your heart rate?
Beta blockers help slow your heart rate by reducing the amount of stress hormones (such as adrenaline) in the body. The drugs might be used in people with an abnormal heartbeat or a history of heart attack. “Beta blockers are good at helping the heart remodel.
What to do if blood pressure isn't lowering?
If a medication isn’t doing enough to reduce your blood pressure after one month, your doctor may increase the dose or add another drug to your regimen. Medications in this arsenal include: Beta blockers, such as atenolol (Tenormin) or metoprolol (Lopressor).
What is the standard blood pressure for a high blood pressure patient?
First Lines of Defense. When you’re initially diagnosed with high blood pressure – typically defined as a measurement at or above 130/80 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) – your doctor will consider if you have any underlying conditions.
Who is the first author of the paper "The First Line of Treatment for Hypertension"?
A new paper — the first author of which is Dr. Marc A. Suchard, from the department of biostatistics at the University of California, Los Angeles — showcases some of the pitfalls behind deciding which is the best first line of treatment for hypertension.
Which first line drug has more side effects than thiazide?
The study revealed that angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which are the most commonly prescribed first-line drugs, had more side effects than thiazide diuretics, a class of drugs that are not prescribed as often.
How to reduce high blood pressure?
Simple lifestyle changes can help reduce high blood pressure, although some people may need to take medicine as well. Your GP can advise you about changes you can make to your lifestyle and discuss whether they think you'd benefit from medicine. This patient decision aid (PDF, 132kb) can also help you to understand your treatment options.
How to lower blood pressure?
Some of these will lower your blood pressure in a matter of weeks, while others may take longer. Try to: cut your salt intake to less than 6g (0.2oz) a day, which is about a teaspoonful – find out how you can reduce the amount ...
Why are beta blockers less effective than other blood pressure medications?
They used to be a popular treatment for high blood pressure, but now tend to be used only when other treatments have not worked . This is because beta blockers are considered less effective than other blood pressure medicines. Common examples are atenolol and bisoprolol.
What is the best age to take an ACE inhibitor?
if you're under 55 years of age – you'll usually be offered an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin-2 receptor blocker (ARB) if you're aged 55 or older, or you're any age and of African or Caribbean origin – you'll usually be offered a calcium channel blocker.
When is the next review due for high blood pressure?
Page last reviewed: 23 October 2019. Next review due: 23 October 2022.
Does taking blood pressure medicine make you feel different?
It's really important to take your medicine as directed. If you miss doses, it will not work as well. The medicine will not necessarily make you feel any different, but this does not mean it's not working. Medicines used to treat high blood pressure can have side effects, but most people do not get any.
Can you stop taking blood pressure medicine?
Medicines used to treat high blood pressure can have side effects, but most people do not get any. If you do get side effects, do not stop taking your medicine. Talk to your doctor, who may advise changing your medicine.
Treatment
Interactions
Adverse effects
Types
Specialist to consult
Medical uses
Examples
| DRUG NAME | RATING | REVIEWS | PREGNANCY |
|---|---|---|---|
| View information about Benicar Benicar | 7.2 | 110 reviews | D |
| View information about Toprol-XL Toprol-XL | 6.7 | 34 reviews | C |
| View information about Zestril Zestril | 6.7 | 12 reviews | D |
| View information about atenolol atenolol | 6.6 | 115 reviews | D |
| View information about Diovan Diovan | 6.4 | 60 reviews | D |
| View information about Cozaar Cozaar | 6.2 | 56 reviews | D |
| View information about Lopressor Lopressor | 6.2 | 10 reviews | C |
| View information about clonidine clonidine | 6.1 | 93 reviews | C |
Side effects
- There are three classes of diuretic drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Most commonly used are thiazide diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide or chlorthalidone. There is not usually an increased urine flow after the first one or two days of taking these medications. Nevertheless, it is best to take them in the morning to prevent annoying uri...
Contraindications
- Diuretics increase the effectiveness or all other classes of antihypertensive agents. Therefore, almost any subject, except those with a contraindication, should receive a diuretic if their blood pressure requires more than one drug for its management.
Mechanism of action
- Adverse Effects: Diuretics increase the excretion of potassium and can lead to hypokalemia (low blood potassium concentration) which predisposes to irregular heart beats, and muscular weakness. However, a combination of a thiazide or loop diuretic with a distal, potassium sparing agent (such as in the combined medications, Maxzide or Moduretic), prevents potassium loss a…
Pharmacology
- Different Drugs: Thiazide diuretics include: hydrochlorothiazide (usual starting dose 12.5 to 25 mg daily) or chlorthalidone (similar dose range). Loop diuretics include: furosemide (Lasix), bumetanide (Bumex), and torsemide (Demadex), torsemide has a rather longer duration and is preferred in patients with heart failure. Ethacrinic acid (Edecrin) is used in the rare patients who …
Categories
- ACEIs are widely used to treat hypertension because they are effective, have relatively few side effects and in reduce the complications of hypertension such as heart attacks and strokes. They have a special use in patients with diabetes mellitus who have protein the urine (diabetic nephropathy) and in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) in whom they appeared to have …
Effects
- Individual Drugs: The following are examples of ACEIs in clinical practice: benazepril (Mylan), captopril (Capoten), enalapril (Vasotec), fosinopril (Monopril), Lisinopril (Prinivil), moexipril (Univasc), quinapril (Accupril), ramipril (Altace) and trandolapril (Mavik). There are some small differences in how long these drugs act in the circulation, they are relatively small and, with the e…
Research
- Biochemical changes with ACEIs are usually insignificant in patients with normal kidney function. However, in those with impaired kidneys, they can raise the serum potassium concentration to levels that are dangerous and require either a change in therapy, or increasing thiazide or loop diuretic dosage to promote potassium loss. Such patients should discuss with their physician o…
Pathophysiology
- Special Indications: As these include patients with chronic kidney disease (but see the adverse effects above), early diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, or left ventricular hypertrophy. These drugs will not be discussed in detail since they are used infrequently.
Cause
- This group of drugs was introduced next after diuretics, to be used for hypertension. They act on a part of the nervous system that controls blood pressure, known as the sympathetic nervous system. Blockade of the sympathetic nervous system reduces blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels, and decreasing the rate and force of contraction of the heart. Therefore, beta blockers a…
Resources
- The actions of these agents are enhanced in patients taking diuretic drugs and therefore are a good second or third line selection in those patients who are not controlled with a diuretic and an ACEI or ARB. Unfortunately, alpha blockers have been shown to be less affective than other groups of blood pressure lowering agents in preventing the complications of heart failure and he…
Diagnosis
- Individual drugs: They fall into two categories. The first are called dihydropyridine CCBs and include amlodipine (Norvasc), felodipine (Plendil), nifedipine (Procardia), and nicardipine (Cardene). The second, termed nondihydropyridine CCBs include two drugs, diltiazem (Dilacor, Cardizem, Cartia, and Tiazac), and verapamil (Calan, Covera, Isoptin, Verelan). Both groups are e…
Treatment
- Non-dihydropyridine CCBs cause cardiac slowing. This typically reduces the heart rate by about 10%. It can be beneficial in some patients with a fast heart rate or who have irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation), but in those with a slow initial heart rate, it can cause symptoms of decreased cardiac output (tiredness, lethargy, and dizziness on exertion). This group of drugs also can cau…
Clinical Trials
- This is a rapidly developing field with extensive research, both by Centre scientists in the laboratory and clinical investigators in patients with hypertension. The following outlines some of the areas of research conducted at the Centre at Georgetown. Research at the Hypertension, Kidney and Vascular Research Centre at Georgetown has focused on a different path, namely dr…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Oxidative stress occurs in cells and tissues of the body when oxygen reacts to form toxic molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS). These can inactivate the normal signaling pathways between cells, damage cell membranes and proteins, and alter the DNA that forms the basis of our genes. Therefore, oxidative stress has widespread effects in the body. Increasing ev…
Alternative Medicine
- Amongst those factors that are under our control which influence the probability of developing hypertension, an excessive dietary salt intake is probably the most important. Research in animal models at Georgetown at the Center for Hypertension, Kidney, and Vascular Research has linked dietary salt intake with oxidative stress that may underlie the hypertension and adverse consequ…
Coping and Support
- For further information about how to support the research in Georgetown Universitys Center for Hypertension, Kidney, and Vascular Research, please see Georgetown Universitys Office of Advancement.
Preparing For Your Appointment