Microscope magnification required to view: 400x, 1000x preferable In wastewater, the presence of spirillum or spirochetes usually indicates septicity. This is bacterial spirillum, captured under the microscope at 1000x magnification.
What is a wastewater treatment microscope?
Wastewater treatment microscopes are used to identify particulate matter, bacteria, protozoa and rotifers while treating wastewater. The wastewater treatment microscope typically uses phase contrast to aid in identifying bacteria. Each of these wastewater treatment microscope packages has been built specifically with wastewater treatment in mind.
What is the BOD of wastewater treatment?
As an example of expected standards, the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of average wastewater effluent is 200 mg/L and the effluent after treatment is expected to be >30 mg/L. It is crucial a wastewater facility meets these expectations or risk stiff penalty.
Can magnetite-based coagulants be used in wastewater treatment?
With regard to the kinetics results, magnetite-based coagulants (F, FA, FE, and FEA) exhibited greater floc formation and agglomeration. Therefore, the incorporation of F or E into coagulants and coagulation treatment was found to have potential applications in the wastewater setting.
What are the objectives of waste water treatment?
The objective of municipal and industrial waste water treatment is to extract pollutants, remove toxicants, neutralise coarse particles, kill pathogens so that quality of discharged water is improved to reach the permissible level of water to be discharged into water bodies or for agricultural land.
How do you size a wastewater treatment plant?
Multiply your Minimum Population (P) by 150 to get your daily estimated wastewater production. For example, a three bed house with a Minimum Population (P) of 5 people would have a daily estimated wastewater production of 750 litres per day (5 x 150).
What parameters are to be used to measure strength of wastewater?
Analytical tests aimed at establishing the concentration (typically in mg/L or ppm) of organic (i.e., carbon-containing) matter have traditionally been used to determine the relative "strength" of a wastewater sample.
What is the size of the course screen used in treatment of water?
Coarse screens remove large solids, rags, and debris from wastewater, and typically have openings of 6 mm (0.25 in) or larger. Types of coarse screens include mechanically and manually cleaned bar screens, including trash racks.
What is the most important parameter for wastewater analysis?
The most popular sum parameter in waste water analysis are the BOD (biochemical oxygen demand), COD (chemical oxygen demand), TOD (total oxygen demand) and TOC (total organic carbon). The TOC reflects the organic pollution on the basis of a direct carbon determination.
How do you measure quality of wastewater?
Tests can measure physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the wastewater. Physical characteristics include temperature and solids. Chemical characteristics include pH value, dissolved oxygen concentrations, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD), nitrogen, phosphorus, chlorine.
What is considered high strength wastewater?
Residential strength wastewater influent examples range from BOD5 100 mg/L – 400 mg/L, TSS 100 – 400 mg/L, and FOG 50 – 150 mg/L. High strength wastewater influent examples range from BOD5 100 – 3685 mg/L, TSS 142 – 4375 mg/L, and FOG 25 – 14,958 mg/L.
What is the size of coarse screens?
Coarse screens. Coarse screens have a clear openings ranging from 6 to 150 mm (0.25 t0 6 in). Coarse screen consist of parallel bars, rods or wires, wire mesh or a perforated plates with openings generally of circular or rectangular shapes.
What is Micro screening in wastewater treatment?
Micro screening is defined as the physical blockage of particles in a mesh with a specific pore size (Mäkinen et al., 1988; Ljunggren, 2006) . Several filters are associated with the physical entrapment of particles in aquaculture, though drum filters are the most common option for solid waste removal. ... ...
What is the size and spacing of the coarse screen used in pretreatment of wastewater?
40 mm is the correct answer.
What is the limit of COD?
According to standards of Central Pollution Control Board, permissible value of BOD is 30 mg/l and COD is 250 mg/l.
What are the 6 main indicators of water quality?
They include dissolved oxygen, pH, temperature, salinity and nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus). They also include measures of toxicants such as insecticides, herbicides and metals. Physico-chemical indicators provide information on what is impacting on the system.
What is the ratio of BOD and COD?
BOD : COD (Chemical oxygen demand) ratio using the formulated seed comes in the range of 0.7-0.8 whereas that using BODSEED comes in the ratio of 0.5-0.6. The ultimate BOD (UBOD) was also performed by exceeding the 3-day dilution BOD test.
What is the objective of wastewater treatment?
Objective of Waste Water Treatment: The objective of municipal and industrial waste water treatment is to extract pollutants, remove toxicants, neutralise coarse particles, kill pathogens so that quality of discharged water is improved to reach the permissible level of water to be discharged into water bodies or for agricultural land.
How is dissolved organic matter removed from sewage?
The dissolved and colloidal organic matter in waste water/sewage is removed by aerobic or anaerobic processes. The effluent from primary sedimentation tank is first subjected to aerobic oxidation in processes such as aerated lagoons, trickling filters, activated sludge units, oxidation ponds etc.
How is industrial waste water removed?
The toxic, non-biodegradable chemicals in industrial waste water can be removed by adsorption (on activated charcoal), ion exchange, ultra-filtration, reverse osmosis and electrodialysis.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary Treatment: Tertiary treatment is the final treatment meant for abolishing the secondary effluents and removal of fine suspended solids, traces of organics and bacteria. The sewage effluent from secondary treatment plant is introduced into a flocculation tank where lime is added to eliminate calcium phosphate.
What happens after a wastewater treatment plant meets all permit specifications?
After meeting all permit specifications, clean water is reintroduced into the environment. Although testing is continuous throughout the wastewater treatment process to ensure optimal water flow, clarification and aeration, final testing is done to make sure the effluent leaving the plant meets permit specifications.
Why is wastewater pumped into a secondary clarifier?
Treated wastewater is pumped into a secondary clarifier to allow any remaining organic sediment to settle out of treated water flow. As the influent exits the aeration process, it flows into a secondary clarifier where, like the primary clarifier, any very small solids (or fines) sink to the bottom of the tank.
What is activated sludge?
These small solids are called activated sludge and consist mostly of active bacteria. Part of this activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank to increase the bacterial concentration, help in propagation, and accelerate the breakdown of organic material. The excess is discarded.
What is the process of removing large items from the influent?
Removal of large items from the influent to prevent damage to the facility’s pumps, valves and other equipment .#N#The process of treating and reclaiming water from wastewater (any water that has been used in homes, such as flushing toilets, washing dishes, or bathing, and some water from industrial use and storm sewers) starts with the expectation that after it is treated it will be clean enough to reenter the environment.#N#The quality of the water is dictated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Clean Water Act, and wastewater facilities operate to specified permits by National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES). According to the EPA, The Clean Water Act (CWA) establishes the basic structure for regulating discharges of pollutants into the waters of the United States and regulating quality standards for surface waters. Under the CWA, EPA sets wastewater standards for industry. The EPA has also developed national water quality criteria recommendations for pollutants in surface waters. EPA's National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permit program controls discharges.#N#As an example of expected standards, the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of average wastewater effluent is 200 mg/L and the effluent after treatment is expected to be >30 mg/L. It is crucial a wastewater facility meets these expectations or risk stiff penalty.#N#The physical process of wastewater treatment begins with screening out large items that have found their way into the sewer system, and if not removed, can damage pumps and impede water flow. A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from the influent and ultimately taken to a landfill.
What is the function of an aeration tank?
The primary function of the aeration tank is to pump oxygen into the tank to encourage the breakdown of any organic material (and the growth of the bacteria), as well as ensure there is enough time for the organic material to be broken down.
What is a bar screen in wastewater treatment?
A bar screen is usually used to remove large items from ...
Where do organics sink in a clarifier?
Solids known as organics/sludge sink to the bottom of the tank and are pumped to a sludge digestor or sludge processing area, dried and hauled away. Proper settling rates are a key indicator for how well the clarifier is operating.
Algae
Algae are common in waste treatment systems and come in many forms including a filamentous form. They are usually green or brown in color and the filaments are larger than bacterial filaments. Some have flagella and are sometimes classified as flagellated algae.
Amoeba
Amoebae range in size from 100 to 300 micrometers. They are unique in that they have no distinct shape. They continually range from round to oval to irregular shapes with protrusions periodically extending from the main cell mass and then withdrawing. They move by the use of foot-like protrusions called pseudopodia (false feet).
Free Swimming Ciliate and Crawling Ciliates
The ciliates are so named because of the cilia, small hairs that are distributed over the entire body. Ciliates are generally ovoid or pear-shaped and maintain their shape by means of a tough but flexible pellicle. Cilia protrude through the pellicle in a variety of patterns. The term ciliate comes from the Latin word “ciliate” which means eyelash.
Stalked Ciliates
Stalked ciliates can be seen in single organism form or can grow in colonies. Each “head” in a colony of stalked ciliates is considered one organism. Therefore, when counting higher life forms for maturity index calculations every organism is counted in the colony. Colonies can range from three to over three hundred organisms each.
Chaetonotus
Chaetonotus is a group of poorly understood metazoans. Their size range overlaps that of ciliates, with which they are often confused because of the cilia and spines. They are distinguished by two adhesive structures, like a forked tail, at the posterior end of the cell and by the presence of a discrete pharynx. They usually glide rather than swim.
Flagellate
Flagellates belong to the class Mastigophora and range in size from 5-20 micrometers in diameter. They are commonly ovoid or pear-shaped with one to four flagella, hair-like projections used for locomotion, attached to one or both ends of the cell. The flagella can usually be observed at 1000X magnification.
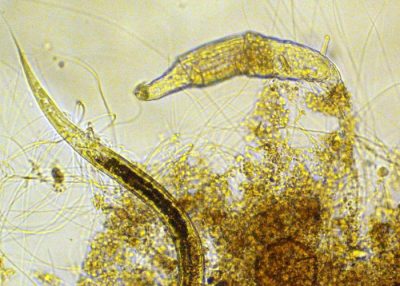
Nematode
Nematodes are common and widespread metazoa. Most are 2-3 mm long and have a long thin shape and a slightly blunt anterior end, resembling earthworms. They are rather stiff and can move either by writhing or gliding through a substrate.
What is the best treatment for bacteria in wastewater?
Bacillus is an excellent treatment of bacteria in wastewater but is best suited for treating fats, oils, greases, and proteins. That is why they are primarily used in wastewater treatment plants. The primary constituents of brewery, winery, and food processor waste are sugars and carbohydrates in very high concentrations.
What is the most cost effective solution for bacterial symbiosis?
If you can adequately control dosing with staff, or with the use of a volumetric doser, the highest strength bacteria is the most cost-effective solution. This option also allows you to use a pseudomona blend if you have oil and grease, or need to aerobically denitrify.
How many filaments are there in activated sludge?
There are only three filaments that are responsible for the majority of the foaming in activated sludge treatment systems. This makes the identification process relatively simple. A simple Gram stain is all that is needed to identify these filaments.
What is the objective of a microscope?
Objectives The objectives on the microscope are used to magnify the specimen. In order to begin observing filaments under the microscope, it would be helpful to have a 10X (magnifies the specimen 100 times) or 20X (magnifies the specimen 200 times) objective along with a 40X (400 times) and an oil immersion objective. The oil immersion objective must be used with a drop of immersion oil and magnifies the specimen 1000 times.

Common Protozoa in Wastewater
Common Bacteria in Wastewater
- All types of bacteria enter the wastewater treatment system. It is the operator's job to create an environment that will favor the floc-forming bacteria that are rod shaped.
Microscope Questions?
- View the wastewater treatment microscopes or contact Microscope Worldwith questions regarding which wastewater treatment microscope is best for your application. 1. Wisconsin Wastewater Operator's Association 2. Biological Wastewater Expert 3. A Guide to Higher Lifeforms
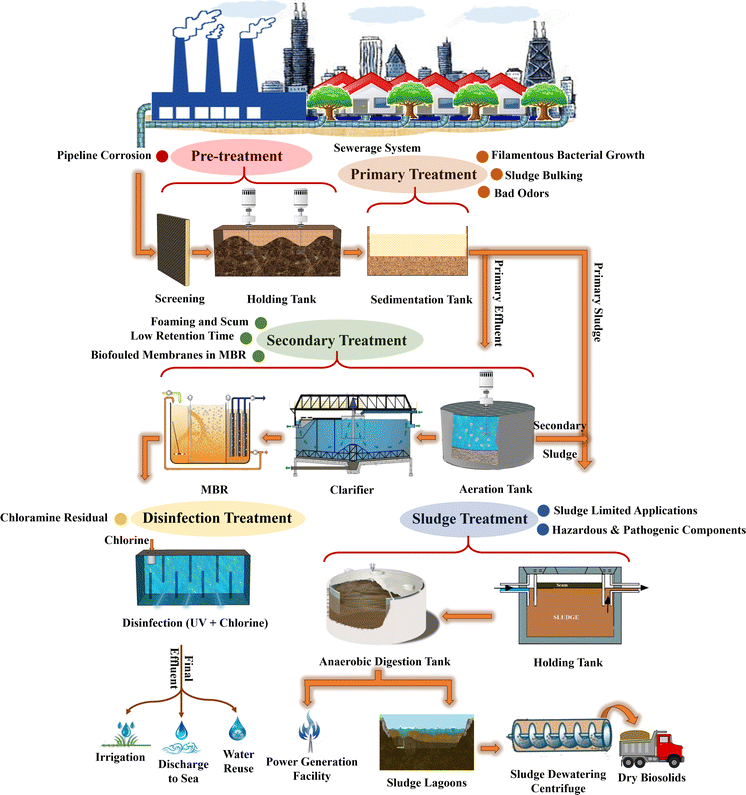
Stage One — Bar Screening
Stage Two — Screening
Stage Three — Primary Clarifier
Stage Four — Aeration
Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier
- Treated wastewater is pumped into a secondary clarifier to allow any remaining organic sediment to settle out of treated water flow. As the influent exits the aeration process, it flows into a secondary clarifier where, like the primary clarifier, any very small solids (or fines) sink to the bottom of the tank. These small solids are called activat...
Stage Six — Chlorination
Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing
Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal