
There is general agreement that RBC transfusion is typically not indicated for hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin; also spelled haemoglobin and abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates (with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae) as well as the tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in the blood …
Red blood cell
Red blood cells, also known as RBCs, red cells, red blood corpuscles, haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes, are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or gills of fish, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries.
Full Answer
What is a red blood cell (RBC) count?
A red blood cell (RBC) count measures the number of red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, in your blood. Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to every cell in your body. Your cells need oxygen to grow, reproduce, and stay healthy.
Are there clinical practice guidelines for red blood cell transfusion (RBC)?
The development of clinical practice guidelines for RBC transfusion has been challenged by a limited availability of high-quality evidence to support practice recommendations.
What are the treatments for high RBC count?
High RBC Count Treatment If you have a high RBC count: Exercise to improve heart and lung function. Eat less red meat and iron-rich foods.
What is the normal range of red blood cells?
The normal RBC range for men is 4.7 to 6.1 million cells per microliter (mcL). The normal RBC range for women who aren’t pregnant is 4.2 to 5.4 million mcL. The normal RBC range for children is 4.0 to 5.5 million mcL. These ranges may vary depending on the laboratory or doctor.
At what level of RBC Do you transfuse?
Based on these two trials, as well as other smaller randomized controlled trials and observational studies, the AABB guidelines recommend a restrictive RBC transfusion threshold of 8 g/dL for patients undergoing cardiac or orthopedic surgery.
What level of RBC is dangerously low?
A severe low hemoglobin level for men is 13.5 gm/dL or lower. For women, a severe low hemoglobin level is 12 gm/dL.
What hematocrit level requires a transfusion?
Because tissue oxygen delivery is dependent on hemoglobin and cardiac output, past medical practice has supported the use of the “golden 10/30 rule,” by which patients are transfused to a hemoglobin concentration of 10 g/dL or a hematocrit of 30%, regardless of symptoms.
Is 3.8 RBC low?
A normal RBC count would be: men – 4.7 to 6.1 million cells per microlitre (cells/mcL) women – 4.2 to 5.4 million cells/mcL.
What happens if RBC count is low?
A low RBC count, also known as anemia, can affect the body's ability to transport oxygen and nutrients around the cardiovascular system. It can cause fatigue, dizziness, and heart palpitations. The most common form of anemia is iron deficiency anemia. This can result from blood loss, malnutrition, or kidney problems.
What is a critically low hematocrit?
Hematocrit: critical low and high values: A hematocrit of less than 15% can result in cardiac failure. A hematocrit of over 60% may result in spontaneous blood clotting.
What is dangerously low hematocrit?
In adults, normal levels for men range from 41%-50%. For women, the normal range is slightly lower: 36%-44%. A hematocrit level below the normal range, meaning the person has too few red blood cells, is called anemia.
What is the lowest hemoglobin level before transfusion?
Some doctors believe that hospital patients who fall below 10 g/dL should get a blood transfusion. But recent research found that: Many patients with levels between 7 and 10 g/dL may not need a blood transfusion.
What is a red blood cell (RBC) count?
A red blood cell (RBC) count measures the number of red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, in your blood. Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to every cell in your body. Your cells need oxygen to grow, reproduce, and stay healthy. An RBC count that is higher or lower than normal is often the first sign of an illness.
What is it used for?
A red blood cell (RBC) count is almost always part of a complete blood count, a group of tests that measure many different parts and features of your blood. The RBC measurement is used to help diagnose red blood cell disorders, such as anemia, a condition in which your body does not make enough healthy red blood cells.
Why do I need a red blood cell count?
You may get this test as part of a complete blood count, which is often included in a routine checkup. You may also need this test if you have symptoms of a low or high red blood cell count.
What happens during a red blood cell count?
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
Will I need to do anything to prepare for this test?
You don't need any special preparations for a red blood cell (RBC) count.
Are there any risks to this test?
There is very little risk to having a blood test. There may be slight pain or bruising at the spot where the needle was put in, but most symptoms go away quickly.
What do the results mean?
Your results will show whether you have a normal red blood cell count or a count that is too low or too high.
How to increase RBC?
You may be able to increase your RBC with the following dietary changes: adding iron-rich foods (such as meat, fish, poultry), as well as dried beans, peas, and leafy green vegetables (such as spinach) to your diet. increasing copper in your diet with foods like shellfish, poultry, and nuts.
Where to get RBC count?
An RBC count is a simple blood test performed at your doctor’s office. You doctor will draw blood from your vein, usually on the inside of your elbow. The steps involved in the blood draw are: The healthcare provider will clean the puncture site with an antiseptic.
What is the purpose of blood smears?
Blood smears can help detect abnormalities in the blood cells (such as sickle cell anemia), white blood cell disorders such as leukemia, and bloodborne parasites like malaria. Anemia is a condition in which there are not enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout the body. Types of anemia include:
What are the effects of blood cancer on the blood?
Blood cancers can affect the production and function of red blood cells. They can also result in unusual RBC levels. Each type of blood cancer has a unique impact on RBC count. The three main types of blood cancer are: leukemia, which impairs the bone marrow’s ability to produce platelets and red blood cells.
What is CBC test?
A CBC test measures the number of all components in the blood, including: red blood cells. white blood cells. hemoglobin. hematocrit. platelets. Your hematocrit is the volume of red blood cells in your body. A hematocrit test measures the ratio of RBCs in your blood.
Why is a blood test called a red blood cell count?
It’s also known as an erythrocyte count. The test is important because RBCs contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to your body’s tissues . The number of RBCs you have can affect how much oxygen your tissues receive.
Why is my RBC high?
A high RBC count may be a result of sleep apnea, pulmonary fibrosis, and other conditions that cause low oxygen levels in the blood. Performance-enhancing drugs like protein injections and anabolic steroids can also increase RBCs. Kidney disease and kidney cancers can lead to high RBC counts as well.
What is CBC blood test?
A complete blood count (CBC) is a blood test that measures your hemoglobin level and other characteristics of your red blood cells (such as their size). This test not only shows if you have anemia, but it can also help your doctor figure out what might be causing it.
Why do you need a blood transfusion?
Whether a blood transfusion might be needed depends on how severe your symptoms are and your hemoglobin level.
How to treat anemia in cancer patients?
Raise the hemoglobin level so that symptoms get better. The most common treatments of anemia in patients with cancer include: Iron therapy. Red blood cell transfusion, commonly known as blood transfusion.
What to do if you have anemia and can't reach your doctor?
If you can’t reach your cancer care team right away, you may need to get immediate care at an emergency room.
What does it mean when you don't have enough red blood cells?
What is anemia? When you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells, you have a condition called anemia. This means your blood has lower than normal hemoglobin (Hgb) levels. Hemoglobin is the part of the red blood cell (RBC) that carries oxygen to all the cells in your body.
What causes red blood cells to be destroyed?
Red blood cells (RBCs) being destroyed by the body before they’re replaced. The body making fewer RBCs. Having chronic kidney disease. Having conditions like sickle cell disease or thalassemia (inherited disorders of red blood cells) A combination of any of these factors.
What is the blood test called to check for vitamin levels?
Blood chemistry tests to check organ function and levels of vitamins and minerals. A blood test called a reticulocyte count (Reticulocytes are very young red blood cells just released from the bone marrow, so this test shows how many new red cells your body is making.)
How to reduce red blood cell count?
1. Medical Treatments. Phlebotomy is the quickest and simplest way of reducing your red blood cell count, and it may be recommended if you have a history of blood clots. Phlebotomy involves removing about a pint of blood at a time, similar to the procedure used for blood donation.
What is the normal blood cell count for a newborn?
Adult females: 4.2 to 5.0 million/microliter. Children: 3.8 to 5.5 million/microliter. Newborns: 4.8 to 7.2 million/microliter. Pregnancy: Slightly lower than normal adult cell counts. If you exceed the upper limit of your range, you may have a high blood cell count.
What is the difference between erythrocytosis and polycythaemia?
Polycythaemia is an abnormally high concentration of hemoglobin in the blood through an increase in red cell numbers, whereas erythrocytosis only refers to a documented increase of red cell mass. The number of red cells you have varies according to sex and age. Women have lower levels than men and newborn babies often will have more than adults.
What is a primary polycythemia?
Primary polycythemias are abnormally high levels of red blood cell precursors resulting from inherited or acquired genetic mutations. This category also includes polycythemia vera, and primary familial and congenital polycythemia.
Why does EPO cause red blood cells to increase?
A lack of oxygen or secreting tumor can cause your body to make more of the hormone erythropoietin, and high levels of EPO can prompt your body to make more red blood cells than normal. Chronic hypoxia.
What causes high red blood cell count?
In primary polycythemia, abnormalities in the production of red blood cells cause a high red blood cell count. The cause of secondary polycythemia is the result of external factors such as sleep apnea, hypoxia, and certain tumors, affecting red blood cell production. 1.
Why do people with high altitudes have high red blood cells?
At high altitudes, increased red blood cell production occurs in order to compensate for the low oxygen levels and low level tissue oxygenation. Certain tumors often release increased amounts of erythropoietin.
Study Questions
What is the target hemoglobin level for red blood cell (RBC) transfusion among hospitalized adult patients who are hemodynamically stable, and the length of time RBCs should be stored prior to transfusion?
Methods
Reference librarians conducted a literature search for randomized clinical trials (RCTs) evaluating hemoglobin thresholds for RBC transfusion (1950-May 2016) and RBC storage duration (1948-May 2016) without language restrictions. The results were summarized using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation method.
Results
The summary estimates across trials demonstrated that restrictive RBC transfusion thresholds were not associated with higher rates of adverse clinical outcomes, including 30-day mortality, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, rebleeding, pneumonia, or thromboembolism.
Conclusions
The authors concluded that a restrictive transfusion threshold is safe in most clinical settings, and that the current blood banking practices of using standard-issue blood should be continued.
Perspective
These guidelines suggest that it is good practice to consider the hemoglobin level, the overall clinical context, patient preferences, and alternative therapies when making transfusion decisions regarding an individual patient.
What is the hemoglobin level for RBC transfusion?
There is general agreement that RBC transfusion is typically not indicated for hemoglobin (Hb) levels of > 10 g/dL and that transfusion of RBCs should be considered when Hb is < 7 to 8 g/dL depending on patient characteristics. 6, 7 The decision to transfuse RBCs should be based on a clinical assessment of the patient that weighs the risks associated with transfusion against the anticipated benefit. As more studies addressing RBC transfusion become available, it becomes increasingly clear that liberal transfusion strategies are not necessarily associated with superior outcomes and may expose patients to unnecessary risks.
What is clinical practice guidelines?
Clinical practice guidelines are defined as systematically developed statements to assist with practitioner and patient decisions about appropriate health care for specific clinical circumstances. 1-3 There is a growing body of literature on the best approaches to develop clinical practice guidelines.
Is transfusing blood a medical procedure?
Transfusion of blood and blood components (ie, RBCs, platelets, plasma, and cryoprecipitate) is one of the most common medical procedures performed in the developed world. However, the decision to transfuse or not to transfuse is one of the more complex decisions made by medical practitioners. Clearly no medical intervention is without risks, but in principle, these risks should be offset or justified by immediate or long-term benefits.
Is there a high quality clinical practice guideline for transfusion of blood components?
There are an increasing number of high-quality clinical practice guidelines addressing transfusion of blood components. These guidelines are based on increasing numbers of high-quality randomized clinical trials that have been completed over the past 15 years.
Is platelet transfusion a prophylactic?
It has been shown that patients with severe thrombocytopenia are at increased risk of bleeding. Platelet transfusions can be administered either as a prophylactic to minimize the risk of bleeding or as a therapeutic to control bleeding . It has been assumed for many years that transfusion of platelets should decrease the bleeding risk in the patients with hypoproliferative thrombocytopenia (eg, post myelosuppressive chemotherapy). Early guidelines for platelet transfusion developed in 1980s and 1990s relied primarily on systematic reviews of the literature available at the time, which primarily consisted of small trials. 16 The initial guidelines recommended transfusion of nonbleeding patients at the level of 20 000/μL. This value was extrapolated from the observation that there is significantly increased risk of bleeding when the platelet count is < 5000/μL and the risk of bleeding does not seem to change between 10 000/μL and 100 000/μL. 16 Several studies in different patient populations has shown that there is no difference in bleeding risk between a platelet count of 10 000/μL and a count of 20 000/μL. 17, 18 It has been also observed that ∼ 7100/μL/d is necessary for interaction with the endothelium. 16, 19
What is the RBC test?
Red blood cells (RBCs), also called erythrocytes, are cells that circulate in the blood and carry oxygen throughout the body. The RBC count totals the number of red blood cells that are present in your sample of blood. It is one test among several that is included in a complete blood count (CBC) and is often used in the general evaluation ...
How long does a RBC last?
The typical lifespan of an RBC is 120 days.
What causes low RBC count?
Some causes of a low RBC count (anemia) include: Trauma that leads to loss of blood. Conditions that cause red blood cells to be destroyed, such as hemolytic anemia caused by autoimmunity or defects in the red cell itself; the defects could be a hemoglobinopathy (e.g., sickle cell anemia), thalassemia, an abnormality in the RBC membrane (e.g., ...
What causes the RBCs to rise?
Dehydration —as the volume of fluid in the blood drops, the count of RBCs per volume of fluid artificially rises. Lung (pulmonary) disease —if someone is unable to breathe in and absorb sufficient oxygen, the body tries to compensate by producing more red blood cells.
What is the purpose of RBC count?
An RBC count can be used to detect a problem with red blood cell production and/or lifespan, but it cannot determine the underlying cause . In addition to the full CBC, some other tests may be performed at the same time or as follow up to help establish a diagnosis. Examples include:
What happens if you lose your RBCs?
If RBCs are lost or destroyed faster than they can be replaced, if bone marrow production is disrupted, or if the RBCs produced do not function normally, or do not contain enough hemoglobin, then you may develop anemia, which affects the amount of oxygen reaching tissues.
What are the signs of CBC?
Some common signs and symptoms associated with anemia that generally lead to a healthcare practitioner ordering a CBC are: Weakness or fatigue. Lack of energy.
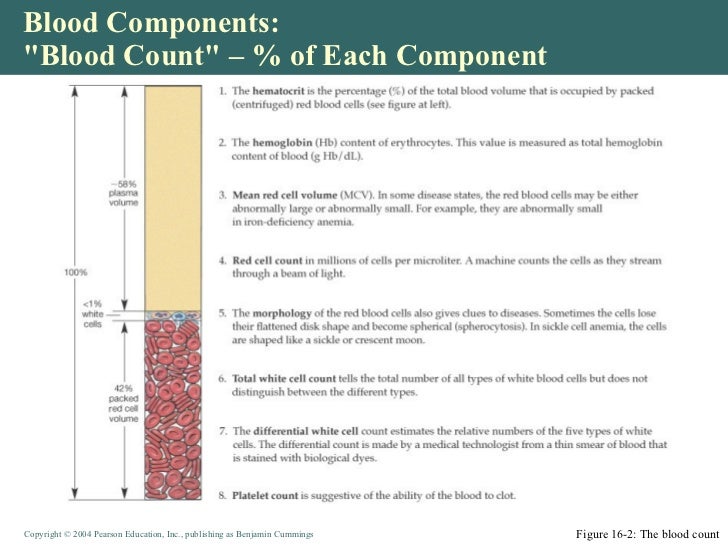
Complete Blood Count
High Or Low RBC Counts
- When the RBC count is higher or lower than the average range, it alerts the doctor that a medical condition could be the cause. The other values from the CBC will be considered, as well as other diagnostic tests.
Treatment
- Treatment of an abnormal RBC count is typically focused on addressing the underlying condition. These treatments will vary widely depending on the cause. But if the cause is a nutritional deficiency, medication use, or a chronic condition, there may be things you can do to not only improve your blood countbut your overall health too.
Summary
- A red blood cell count is used to measure the number of oxygen-carrying red blood cells in your body. When you have a high blood count or a low blood count, it's a sign that you may be sick. Your doctor will also monitor your RBC count when you have a blood disorder or you're taking medicines that affect it. If you have an abnormal RBC count, your doctor will treat the medical co…