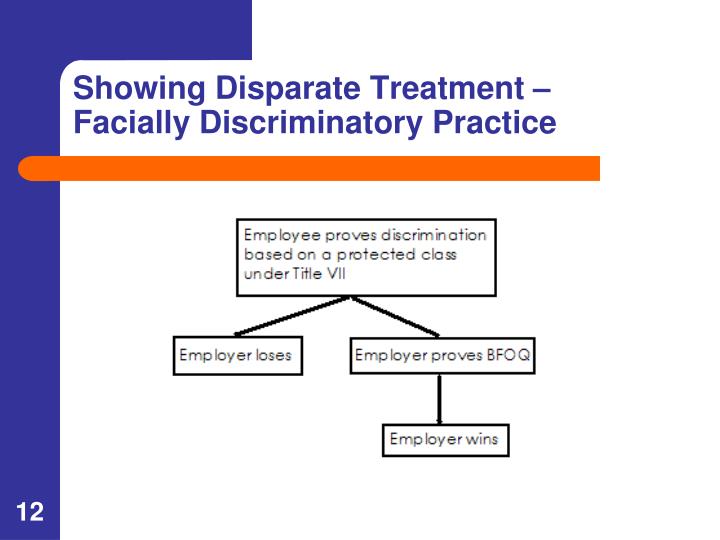
What is disparate treatment in employment law?
§ 1607.11 Disparate treatment. The principles of disparate or unequal treatment must be distinguished from the concepts of validation. A selection procedure - even though validated against job performance in accordance with these guidelines - cannot be imposed upon members of a race, sex, or ethnic group where other employees, applicants, or members have not been …
What are the arguments in a disparate treatment lawsuit?
Oct 18, 2017 · Following is an excerpt from a recent EEOC publication describing its precedent on “disparate treatment” of federal employees to establish a case …
How do you prove disparate treatment?
Feb 16, 2021 · Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibits employers from discriminating against individuals based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. Title VII prohibits an employer from discriminating with regard to any term, condition, or privilege of employment.
When did unlawful disparate treatment of workers with caregiving responsibilities take effect?
May 23, 2007 · UNLAWFUL DISPARATE TREATMENT OF CAREGIVERS This section illustrates various circumstances under which discrimination against a worker with caregiving responsibilities constitutes unlawful disparate treatment under Title VII or the ADA. Part A discusses sex-based disparate treatment of female caregivers, focusing on sex-based …
What is disparate treatment?
Disparate treatment occurs where members of a race, sex, or ethnic group have been denied the same employment, promotion, membership, or other employment opportunities as have been available to other employees or applicants. Those employees or applicants who have been denied equal treatment, because of prior discriminatory practices or policies, ...
What does it mean when an employee is denied equal treatment?
Those employees or applicants who have been denied equal treatment, because of prior discriminatory practices or policies, must at least be afforded the same opportunities as had existed for other employees or applicants during the period of discrimination.
Can a selection procedure be imposed on a race?
A selection procedure - even though validated against job performance in accordance with these guidelines - cannot be imposed upon members of a race, sex, or ethnic group where other employees, applicants, or members have not been subjected to that standard.
How to establish prima facie discrimination?
The complainant must initially establish a prima facie case of discrimination by demonstrating that he or she was subjected to an adverse employment action under circumstances that would support an inference of unlawful intent. Proof of a prima facie case will vary depending upon the circumstances of the particular case.
What is the most common issue that the Commission must address in a federal sector appeal?
Apart from procedural dismissals, the most common issue that the Commission must address in a federal sector appeal is whether a complainant has been subjected to disparate treatment discrimination because of his or her statutorily protected status or activity.
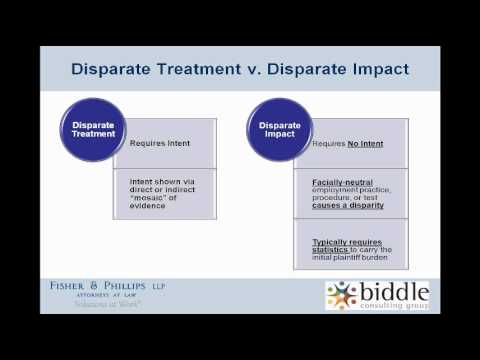
What is disparate treatment?
A disparate treatment claim argues that the individual suffered less favorable treatment than similarly situated individuals. The basis for the less favorable treatment may be due to the individual’s race, religion, sex, color, or national origin. In disparate treatment claims, the employer’s intent is the matter at issue.
How to substantiate disparate impact claim?
You can substantiate a disparate impact claim by proving that a policy has negative consequences for a particular class. For instance, suppose a company institutes a hiring policy requiring a strength test. A female applicant fails the strength test and is subsequently eliminated from the hiring process.
What are the two forms of discrimination in the workplace?
There are two forms of discrimination in the workplace: disparate treatment and disparate impact. An experienced California employment discrimination attorney can aid in analyzing evidence and building a case for the discrimination you’ve experienced.
What is an alternative effective employment policy?
An alternative effective employment policy or practice exists that would be non-discriminatory. There is a defense to a disparate impact claim: the employer must prove that a legitimate and non-discriminatory purpose exists for the contested policy or practice.
How to contact a discrimination lawyer in California?
For immediate assistance, please don’t hesitate to send our California employment discrimination attorneys an online message or call our firm at (818) 290-8904. As a victim of workplace discrimination, understanding the form of discrimination experienced is a crucial element of your legal claim. Contents hide.
What are the federal protections for discrimination?
There are federal protections that protect individuals from discrimination in the workplace. Your employer, or potential employer, has an obligation to prevent and address discrimination against employees. Multiple federal and state protections ensure that if discrimination occurs, victims may file a claim for this treatment.
What happens if a non white employee takes supplies home?
The next week, a non-white employee takes supplies home and is subsequently fired. The non-white employee may have a case for disparate treatment if there is history of the employer’s conduct of treating other employees differently.
Why was Margaret denied compensatory time?
Margaret, an African American employee in the City’s Parks and Recreation Department, files an EEOC charge alleging that she was denied the opportunity to use compensatory time because of her race. She asked her supervisor, Sarah, for the opportunity to use compensatory time so she could occasionally be absent during regular work hours to address personal responsibilities, such as caring for her children when she does not have a sitter. Sarah rejected the request, explaining that Margaret’s position has set hours and that any absences must be under the official leave policy. The investigation reveals that while the City does not have an official compensatory time policy, several White employees in Margaret’s position have been allowed to use compensatory time for childcare purposes. When asked about this discrepancy, Sarah merely responds that those employees’ situations were “different.” In addition, the investigation reveals that while White employees have been allowed to use compensatory time, no African Americans have been allowed to do so. Under the circumstances, the investigator determines that Margaret was unlawfully denied the opportunity to use compensatory time based on her race.
Why was Emily denied tenure?
Emily, an assistant professor of mathematics at the University for the past seven years, files a charge alleging that she was denied tenure based on her sex. Emily applied for tenure after she returned from six months of leave to care for her father. The University’s flexible work program allowed employees to take leave for a year without penalty. Before taking leave, Emily had always received excellent performance reviews and had published three highly regarded books in her field. After returning from leave, however, Emily believed she was held to a higher standard of review than her colleagues who were not caregivers or had not taken advantage of the leave policies, as reflected in the lower performance evaluations that she received from the Dean of her department after returning from leave. Emily applied for tenure, but the promotion was denied by the Dean, who had a history of criticizing female faculty members who took time off from their careers and was heard commenting that “she’s just like the other women who think they can come and go as they please to take care of their families.”
Why is Arnold reluctant to hire?
The employer determines that one of the applicants, Arnold, is the best qualified, but is reluctant to hire him because he disclosed during the interview that he is a divorced father and has sole custody of his son, who has a disability. Because the employer concludes that Arnold’s caregiving responsibilities for a person with a disability may have a negative effect on his attendance and work performance, it decides to offer the position to the second best qualified candidate, Fred, and encourages Arnold to apply for any future openings if his caregiving responsibilities change. Under the circumstances, the employer has violated the ADA by refusing to hire Arnold because of his association with an individual with a disability.
When did the Americans with Disabilities Act of 2008 take effect?
This document was issued prior to enactment of the Americans with Disabilities Act Amendments Act of 2008 (ADAAA), which took effect on January 1, 2009. The ADAAA broadened the statutory definition of disability, as summarized in this list of specific changes.
Why did Carla lose her job?
After Carla, an associate in a law firm, returned from maternity leave, she began missing work frequently because of her difficulty in obtaining childcare and was unable to meet several important deadlines. As a result, the firm lost a big client, and Carla was given a written warning about her performance.
What is disparate treatment?
Disparate treatment is a way to prove illegal employment discrimination. An employee who makes a disparate treatment claim alleges that he or she was treated differently than other employees who were similarly situated, and that the difference was based on a protected characteristic. In other words, the employee alleges ...
How to prove a disparate treatment claim?
To prove a disparate treatment claim, an employee must first present enough evidence to allow the judge or jury to infer that discrimination took place.
Why is an employee denied a promotion?
For instance, an employee is denied a promotion, and the employer claims that it was because the employee lacked an MBA. If the employee who was promoted also didn't have an MBA, the employer's decision looks suspect. Remarks by decision makers.
Why was Horacio fired?
The employer claims that he was fired because he received three customer complaints in the previous quarter. If Horacio can show that other employees who received three or more complaints in a quarter were not fired, and that those employees were not Latino, his argument looks better.
What is the pretext for discrimination?
Once the employer states a legitimate reason for the decision, the employee must prove that it's a pretext for discrimination. This doesn't mean the employee has to come up with absolute proof of an illegitimate motive. Instead, the employee has to present some evidence that calls the employer's stated reason into question and allows the jury to conclude that the employer was really motivated by discrimination. Here are some examples:
What happens if Horacio's supervisor makes derogatory comments about Latino employees?
Similarly, if Horacio can show that his supervisor made derogatory comments about Latino employees or culture, his case is strengthened. On the other hand, if no such comments were made, and the employer can show that it has a strong record of hiring and promoting Latino employees, Horacio will have a tougher time.
What is protected class?
The employee is a member of a protected class (for example, the employee is African American, female, or over the age of 40). The employee was qualified for a job benefit. For example, the employee applied—and was qualified—for an open position, or the employee held a position that he or she was performing adequately.
