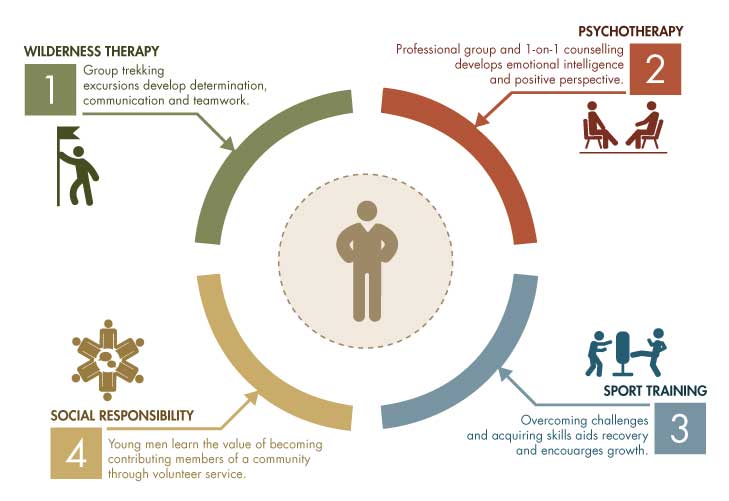
What treatment is best?
- Being sick or depressed. How you feel mentally and physically can affect your willingness to stick to your treatment plan. ...
- Alcohol or drug use. ...
- If you need help finding substance use disorder treatment or mental health services, use SAMHSA’s Treatment Locator external icon .
What is the rehab treatment model?
- The ability to recognize and admit that one is experiencing an addiction problem
- A surrender to the fact that the addiction exists and a decision to seek control through an outer guide
- Self-observation and awareness of the behaviors that were part of and arose from the addiction, as well as those that help promote self-restraint
What are the three models of addiction?
The three-stages of addiction are: 3, 4
- Binge/Intoxication: an individual uses an intoxicating substance and experiences its rewarding or pleasurable effects
- Withdrawal/Negative Affect: an individual experiences a negative emotional state in the absence of the substance
- Preoccupation/Anticipation: an individual seeks substance use again after a period of abstinence
What is the measure of a model?
In tabular models, a measure is a calculation created using a DAX formula for use in a reporting client. Measures are evaluated based on fields, filters, and slicers users select in the reporting client application.
What are some treatment models for addiction?
These techniques and practices include:Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) ... Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) ... Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) ... Motivational Enhancement and Interviewing. ... Medication-Assisted Therapies (MAT) ... Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) ... Solution Focused Brief Therapy/Solution Focused Therapy.More items...
What are the five stages of treatment?
Stage-Matched Care. Developed from the Trans-theoretical Model of Change1, the Stage of Change model includes five stages: pre-contemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, and maintenance.
What are some treatment methods?
This article will provide an overview of the different types of therapy available.Cognitive-behavioral therapy. ... Dialectical behavior therapy. ... Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy. ... Exposure therapy. ... Interpersonal therapy. ... Mentalization-based therapy. ... Psychodynamic therapy. ... Animal-assisted therapy.More items...•
What are the four stages of treatment?
Various models exist describing the overall phases of treatment, but most have elements in common. The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) describes four stages of treatment: initiation, early abstinence, maintenance of abstinence, and advanced recovery.
What is the first step of treatment?
In the early stage of treatment, clients may be in the precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, or early action stage of change, depending on the nature of the group. Regardless of their stage in early recovery, clients tend to be ambivalent about ending substance use.
What are the five stages of change model?
Five stages of change have been conceptualized for a variety of problem behaviors. The five stages of change are precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, and maintenance.
What is health treatment?
[trēt´ment] 1. the management and care of a patient; see also care. 2. the combating of a disease or disorder; called also therapy.
What are the three most common therapy treatments?
The Most Common Types of TherapyClient-Centered Therapy (Person-Centered Therapy, PCT, CCT or Rogerian Therapy) ... Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) ... Existential Therapy (part of the Humanistic-existential Approach) ... Psychoanalytic or Psychodynamic Therapy. ... Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)More items...•
How many types of medical treatments are there?
Three principal types of medical treatment Curative – to cure a patient of an illness. Palliative – to relieve symptoms from an illness. Preventative – to avoid the onset of an illness.
What are the 5 stages of drug dependence?
Stages of AddictionFirst Use. The first step to addiction is trying the substance. ... Regular Use. As people become regular users, they begin to display a pattern. ... Risky Use. As use deepens, people may begin to exhibit dangerous behavior, such as driving while drunk or high. ... Dependence. ... Substance Use Disorder.
What are targets in DBT?
In DBT, there are 3 categories of targets: life-threatening behavior, therapy-interfering behavior, and quality-of-life-interfering behavior. Imminent and upcoming risk takes precedence for discussion over past patient behavior and urges.
What are the 4 stages of drug abuse?
While there are many factors that contribute to drug and alcohol addiction, including genetic and environmental influences, socioeconomic status, and preexisting mental health conditions, most professionals within the field of addiction agree that there are four main stages of addiction: experimentation, regular use, ...
THE FOCUS OF TREATMENT IS TO
Assist the child or adolescent to develop coping strategies for traumatic stress reactions
WHAT IS EXPECTED OF A PARENT OR CAREGIVER?
Participation of the caregiver is a helpful way to assist the child in treatment. If a caregiver participates, the child is more likely to succeed. TF-CBT assists caregivers by:
How to treat addiction and mental health issues at the same time?
Treating both the addiction and any mental health issues at the same time is often effective for co-occurring disorders because of the ways that these conditions interact with each other. If one disorder is left untreated, it can worsen and negatively affect any progress made to treat the other disorder. Additionally, the two conditions may be related to each other in complex ways, so treating them simultaneously offers the person the best opportunity to address these relationships and figure out how best to manage both disorders on a daily basis.
Why are medications important?
Treatment plans must be reviewed often and modified to fit the patient’s changing needs. Treatment should address other possible mental disorders.
What is a co-occurring disorder?
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) defines co-occurring disorders as any time a person has “at least one mental disorder as well as an alcohol or drug use disorder,” and each “can be diagnosed independently of the other.”.
Is there a single treatment for everyone?
No single treatment is right for everyone. Effective treatment addresses all of the patient’s needs, not just his or her drug use. Staying in treatment long enough is critical. Counseling and other behavioral therapies are the most commonly used forms of treatment.
What is goal oriented therapy?
A goal-oriented therapy focusing on a person's present and future, rather than past. This is considered goal-oriented therapy (the symptoms or issues that brought a person to their current situation are usually not the target in this approach
What is the treatment of self destructive behavior?
A form of treatment that focuses on exploring patterns of thinking that lead to self-destructive actions, identifying the beliefs that direct these thoughts, and learning to modify patterns of thinking to improve coping skills
What is Betty Ford Foundation?
The Hazelden Betty Ford Foundation is a force of healing and hope for individuals, families and communities affected by addiction to alcohol and other drugs. As the nation's leading nonprofit provider of comprehensive inpatient and outpatient treatment for adults and youth, the Foundation has 17 locations nationwide and collaborates with an expansive network throughout health care. With a legacy that began in 1949 and includes the 1982 founding of the Betty Ford Center, the Foundation today also encompasses a graduate school of addiction studies, a publishing division, an addiction research center, recovery advocacy and thought leadership, professional and medical education programs, school-based prevention resources and a specialized program for children who grow up in families with addiction.
What is the purpose of medication?
Medications are primarily used to treat substance use disorders related to opioids and alcohol, helping to ease withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. Our use of medication-assisted treatment for opioid dependence with naltrexone and buprenorphine/naloxone is supported by scientific research and recommended by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), Washington Circle (a policy group devoted to improving care) and the Veterans Administration. At Hazelden Betty Ford, medication-assisted therapy is always used in conjunction with other behavioral therapies, with abstinence as the end goal.
Where was Betty Ford's model?
What Is the Hazelden Betty Ford Model? Beginning in 1949, at a quiet lakeside retreat in rural Center City, Minnesota, Hazelden Betty Ford’s earliest clinicians developed the holistic approach to addiction care most widely emulated in the world today, known originally as the Minnesota Model.
Who is Betty Ford?
As a national nonprofit organization founded in 1949, Hazelden Betty Ford leads the field in providing the most-effective, evidence-based practices to treat addiction and co-occurring disorders.
What is CBT model?
According to the CBT model, dysfunctional or inaccurate thoughts often underlie chronic and severe emotional and behavioral problems. Through various techniques, thoughts and behaviors are examined and modified. With practice, you learn these techniques so that you can effectively deal with your challenges on your own.
What is FIT therapy?
Feedback Informed Treatment – FIT (also known as Client Directed Outcome Informed Therapy – CDOI).#N#FIT was born out of therapy outcome research in which researchers examined what really works in therapy. Therapy outcome research reveals that the alliance between you and your therapist is more important to a positive therapy outcome than any particular kind of therapy. There are many different models, techniques and approaches to therapy such as Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT), reality therapy, and interpersonal therapy. FIT (or CDOI) encompasses many different kinds of therapy within one overarching philosophy. FIT allows your therapist to modify his/her approach to therapy as directed by you. If your therapist is out of sync with you (or worse, is annoying, patronizing, etc.) then there’s little chance that he/she can help. You probably won’t even come back after a session or two! Keeping an open dialogue about what does and does not help, informs your therapist about how best to help you.Scientifically validated, FIT maintains that you are the best judge of whether your therapy is effective and helpful. ApaCenter therapists embrace this idea. Think of it this way – If you go to a fine restaurant, does the chef tell you what you must order? Does he get to tell you how much you liked it? Of course not! Similarly, research shows that you benefit most from an on-going dialogue with your therapist (chef) about what is or is not helpful (tasty). Like having your own personal chef, an ApaCenter therapist actually checks in with you every session to get your input on how things are progressing. Your ideas and preferences are used to modify and enhance our approaches and techniques. This allows you to take an active role in your therapy because you are central to your own process of change. So, with FIT, one or more therapy models (described below) could be used in your sessions – depending on what works best for you.
What is cognitive behavioral therapy?
Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) CBT is a form of therapy that has gained much attention within the last few decades. According to the cognitive behavioral therapy model, your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are inextricably linked.
What is solution focused therapy?
The obstacles that brought you to therapy will seem less like obstacles and more like surmountable challenges. Solution-Focused therapy is primari ly present and future focused.
What is the goal of a family therapist?
Your therapist’s goal is to find the sources of tension and conflict within your family system and assist you in resolving that tension by engaging in new, more positive interaction patterns. Also, your therapist will highlight past and present positive family interaction patterns to build upon. Play Therapy.
How many sessions are there in a brief therapy session?
Because it is usually short-term, perhaps 3-10 sessions, it is often referred to as, “Solution Oriented Brief Therapy” or simply, “Brief Therapy.”. Choice Theory / Reality Therapy. Choice Theory, as formulated by psychiatrist Dr. William Glasser, posits that all humans have 5 basic needs.
What are the other 4 needs?
The other four needs are psychological. They include freedom, fun, power, and love/belonging. We attempt to satisfy our 5 needs through our behavioral choices. According to choice theory, almost all behavior is chosen, and we are all ultimately responsible for our own behavioral choices.
What is matrix model therapy?
Matrix Model therapists adopt a positive, encouraging relationship with their patients. Establish a positive and collaborative relationship between the therapist and the recovering user. The therapist treats the person with empathy and respect instead of confrontation. They set goals together and work as a team.
Why do matrix models do drug tests?
Matrix Model programs also perform drug tests randomly on a weekly basis. Drug testing is used to keep users accountable and reward sobriety. It is not used to punish users. A positive drug test may indicate a need for increased structure in the program. 2.
What is matrix model?
The Matrix Model is a treatment approach that is administered over the course of a structured, 16-week period. Used most often with people who are addicted to stimulants (mainly cocaine and methamphetamine), the program is highly structured and is largely made up of group therapy sessions. Users learn about the addiction ...
How many sessions are there in a relapse prevention program?
Treatment consists mainly of groups, with 3 to 10 individual sessions over the duration of the program. Patients attend 2 relapse prevention groups and 1 family/education group per week. During the first 4 weeks, they also attend 2 early recovery skills groups per week.
How does matrix model work?
Monitor drug use through urine tests. Matrix Model programs use drug testing to monitor patients and provide feedback, such as rewards when they submit a negative test or discussion about a positive test. Matrix Model therapists adopt a positive, encouraging relationship with their patients.
When was the MM model developed?
The model was developed during the cocaine epidemic in Southern California in the 1980s.
Why is weekly drug testing important?
Weekly drug testing is another important component of programs that utilize the Matrix Model and is conducted to assess recovery progress and encourage program compliance.
What is a treatment plan?
In both mental and general healthcare settings, a treatment plan is a documented guide or outline for a patient’s therapeutic treatment. Treatment plans are used by professionals such as psychologists, psychiatrists, behavioral health professionals, and other healthcare practitioners as a way to: Design. Blueprint. Evaluate, and.
What is a treatment plan in healthcare?
Treatment plans are a crucial part of any mental healthcare solution and feature regularly in practitioners’ day-to-day work with patients.
Why is it important to involve patients in the treatment planning process?
Involving patients in the treatment planning process, and especially in the goal-setting stage, is often a great way for therapists and psychologists to build patient health engagement for optimal involvement and motivation.
What is therapeutic objective?
Therapeutic objectives or goals: Both over the longer term, and broken down into shorter-term subgoals. Treatment modalities: For example, the behavioral, social, or psychological treatments that will be targeted. Interventions/Methods: A description of the techniques and approaches to be implemented.
What type of therapy does a therapist use?
Therapists may use cognitive behavioral therapy , contingency management, and motivational interviewing throughout the treatment process. They may also be conjoint sessions (with a loved one in the room) to set the treatment plan.
What is matrix treatment?
The matrix model is a highly structured treatment framework used in intensive outpatient treatment programs developed in the 1980s in Los Angeles. It is an effective substance abuse treatment model for patients with substance use disorders involving stimulant substances such as cocaine, crystal meth, and methamphetamine-based prescription drugs.
What are the eight central therapeutic constructs?
Therapists using the matrix model use eight central therapeutic constructs: Create a positive and collaborative connection with the patient. Establish an explicit treatment structure and clear expectations. Educating the patient on brain chemistry and other clinically relevant knowledge (psychoeducation)
How effective is matrix model?
One study found that the matrix model was effective in treating people addicted to stimulant drugs, particularly cocaine, eight months after treatment. Another study examined methamphetamine users who were treated using the Matrix Model.
What is the disease model of addiction?
The disease model of addiction is currently the most widely accepted school of thought when it comes to how we understand addiction. More importantly, the disease model informs how we approach recovery and treatment. So to make sure you’re up to speed, let’s have a discussion about the disease model of addiction. In particular….
What were the first treatment centers?
The earliest treatment centers were actually churches, convents, and other religious centers. People who were chemically dependent were brought to these kinds of locations to give them a safe space to detox. From there, they were encouraged to join support groups and recovery fellowships.
What is the purpose of cognitive behavioral therapy?
It’s also used to identify a person’s triggers and teach strategies for avoiding or nullifying those triggers to safeguard sobriety.

Programs
Results
- As you begin your decision making process, it's helpful to understand what's involved in rehab programs. There are medical and physical aspects of care to consider as well as issues related to mental, emotional and spiritual health. Look for centers that use evidence-based addiction treatment and for facilities that are licensed. A holistic approach to healing that addresses all as…
Treatment
- Ideally, treatment involves a team made up of licensed professionals including chemical dependency counselors, mental health staff, wellness specialists and spiritual care counselors. The team works together to map out a care plan unique to the individual client or patient. During the course of rehab and based on a number of different indicators, o...
Management
- Most people who struggle with addiction face mental health challenges as well. A quality provider will have licensed psychologists or therapists working in tandem with addiction counselors to address problems such as anxiety, depression, trauma, bi-polar disorder and other conditions.
Significance
- In-network status with insurance companies is another sign of a quality provider. Programs that are in-network with health insurance companies have completed important credentialing requirements in order to be deemed a provider.
Prognosis
- No. Addiction is a chronic disease, much like diabetes or hypertension. People with drug or alcohol addiction need to actively manage the condition over their lifetime. A quality rehab program helps patients learn to manage their symptoms, first within the structure and support of a treatment setting and eventually in their home environment where they are in charge of their s…
History
- Beginning in 1949, at a quiet lakeside retreat in Center City, Minnesota, Hazelden Betty Ford's earliest clinicians developed the addiction treatment approach most widely used in the world today, known originally as the Minnesota Model. Combining a medical model of care with emerging Twelve Step principles and practices, treatment was provided with an abiding respect …
Mission
- Our pioneering model of addiction services has continued to evolve to integrate the latest in biological, behavioral, genetic and other scientific findings and to address the disease holistically mind, body and spirit. Today, our protocols include science-based assessments, medication-assisted treatment and evidence-based practices, delivered with the same patient-centered focu…
Overview
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a treatment approach that emphasizes balancing behavioral change, problem-solving and emotional regulation with validation, mindfulness and acceptance.
Services
- More often than not, addiction comes with complicating factors such as depression, anxiety or trauma, also known as co-occurring disorders. With such complex conditions, the most effective approach to care integrates treatment for addiction and mental health so that both issues are addressed at the same time. Our services are provided by psychiatrists, psychologists, marriage …
Prevention
- Contingency management (CM) involves incentive-based interventions. Studies show that tangible rewards reinforce positive behaviors and are highly effective in increasing treatment retention and promoting abstinence from drug use. Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) is used to help prevent depression relapse. This approach works especially well for those with m…
Goals
- Solution Focused Therapy focuses on a person's present and future, rather than past. This is considered goal-oriented therapy. The symptoms or issues that brought a person to their current situation are usually not the target in this therapy setting.
Mechanism of action
- This specific type of group therapy focuses on educating people about disorders and developing coping strategies.
Purpose
- Twelve Step Facilitation was originally designed as an approach to actively engage patients in abstinence-based Twelve Step groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous. Today, the interventions are more widely utilized to help patients achieve and sustain recovery from both substance use disorders and mental health issues that affect the mind, body and spirit.