
Why is adenosine contraindicated in WPW?
Why is adenosine contraindicated in WPW? Adenosine slows or blocks antegrade (atrial to ventricular) conduction through the AV node but doesn't affect accessory or bypass tracts like those seen in WPW syndrome. Because of this, adenosine can be dangerous when given to patients with atrial fibrillation, especially if they have a bypass track.
How to treat WPW?
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Treatments
- Medications. ...
- Follow-up Electrophysiology Study. ...
- Implantable Device (Pacemaker) All implantable devices or pacemakers work on "demand" and are used to treat slow heart rhythms. ...
- Catheter Ablation. ...
- Internal Cardioversion. ...
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. ...
- Biventricular Pace Maker. ...
Can adenosine be used in WPW?
In the presence of WPW, traditional treatments may be contraindicated. Any AV nodal slowing agent, including adenosine, diltiazem and amiodarone, may cause an adverse reaction in the presence of WPW. Of those three medications, AHA recommends amiodarone. It is important to keep WPW in mind when treating a tachycardia.
What is the prognosis of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome?
There is no definitive life expectancy for WPW Syndromes because if it is treated there would be a good prognosis as well as quality of life. However, if this disorder is left untreated sudden death may occur. WPW Syndrome is a congenital disorder which means it is already present at birth.

What is WPW and how is it treated?
Cardiac catheter ablation Treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome depends on the severity and frequency of symptoms and the type of heart rhythm problem (arrhythmia) causing the fast heart rate. The goals of treatment are to slow a fast heart rate when it occurs and to prevent future episodes.
What is the drug of choice for WPW?
The drug of choice for the treatment of regular supraventricular (reciprocating) tachycardia with narrow QRS complexes, which is the most common arrhythmia in the WPW syndrome, is propranolol.
Is WPW syndrome curable?
With treatment, the condition can normally be completely cured. For some people, their condition settles down without needing treatment. WPW syndrome can sometimes be life-threatening, particularly if it occurs alongside a type of irregular heartbeat called atrial fibrillation.
How do you fix WPW?
Your doctor threads a long, thin, flexible tube (catheter) through a vein in your groin to the heart. There, low-voltage, high-frequency electrical energy is used to destroy the abnormal connection. The treatment cures WPW about 85% to 95% of the time.
Can beta blockers be used in Wolff Parkinson White?
In particular, avoid adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, and other calcium-channel blockers and beta-blockers. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the heart's normal electrical pathway and facilitating antegrade conduction via the accessory pathway [2, 5].
What medication is contraindicated in atrial fibrillation with Wolff Parkinson White?
The use of digoxin or verapamil for long-term therapy appears to be contraindicated for many patients with WPW syndrome, because these medications may enhance antegrade conduction through the AP by increasing the refractory period in the AV node.
Does WPW shorten your life?
With appropriate referral, treatment, and patient education, patients with WPW syndrome can expect to have a normal life expectancy and good quality of life.
Does WPW get worse with age?
Therefore, the prevalence of a potentially malignant form of WPW syndrome in asymptomatic subjects does not decrease significantly with age.
Is Wolff-Parkinson-White Serious?
WPW is not a dangerous disease for most people. You can manage or correct the condition with treatment. The biggest risk is for sudden death from a heart attack, which tachycardia can cause. However, this is extremely rare, occurring in less than one-half of 1 percent of cases.
How serious is heart ablation surgery?
In general, cardiac (heart) catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure and risks and complications are rare. Catheter ablation may require an overnight stay in the hospital though most patients can return home the same day as the procedure.
What is the best treatment for irregular heartbeat?
Therapies to treat heart arrhythmias include vagal maneuvers and cardioversion to stop the irregular heartbeat.Vagal maneuvers. If you have a very fast heartbeat due to supraventricular tachycardia, your doctor may recommend this therapy. ... Cardioversion.
How long does it take to recover from WPW surgery?
You'll spend a day or two in intensive care, and you may be in the hospital for up to a week. At first, you'll feel very tired and have some chest pain. You can probably go back to work in about 3 months, but it may take 6 months to get back to normal.
What tests can be done to diagnose WPW syndrome?
Your doctor will likely recommend tests to diagnose WPW syndrome, such as: Electrocardiogram (ECG). Small sensors attached to your chest and arms record electrical signals as they travel through your heart. Your doctor can look for patterns among these signals that indicate an extra electrical pathway in your heart. Holter monitor.
What to do if you have WPW but don't have symptoms?
If you have the WPW pathway but don't have symptoms, you probably won't need treatment. If you do, the goal of treatment is to slow a fast heart rate when it occurs and to prevent future episodes. Treatment options include: Vagal maneuvers.
What is WPW in ventricular preexcitation?
It is the most common type of ventricular preexcitation (preexcitation: the impulses travel to the ventricle earlier than what you would expect them to if they traveled down the normal pathway through the AV node). WPW occurs randomly in the general population, occurring in about 1 to 3 per 1,000 persons.
What is WPW in heart?
WPW is an electrical abnormality in the heart that may be associated with supraventricular tachycardia ( fast heart rate originating above the ventricles).
How many people have WPW?
WPW occurs randomly in the general population, occurring in about 1 to 3 per 1,000 persons. In the general population, men have a higher incidence of WPW than women do, and there is a higher incidence of multiple accessory pathways in men. Some cases of WPW are inherited.
How do you know if you have WPW?
Symptoms of WPW may include one or more of the following: Heart palpitations – a sudden pounding, fluttering or. Racing feeling in your chest. Dizziness – feeling lightheaded or faint.
Why do you need to ablate a WPW?
How often and at what times to take them. Ablation - In people with WPW and symptoms of palpitations or syncope, an ablation procedure is recommended for two reasons: 1) to prevent symptom recurrence and 2) to prevent sudden cardiac death.
Can WPW cause ventricular fibrillation?
Although rare, the greatest concern for people with WPW is the possibility of having atrial fibrillation with a fast ventricular response that worsens to ventricular fibrillation, a life-threatening arrhythmia.
What is the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
The term Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is used to refer to the combination of supraventricular arrhythmias and an electrocardiographic pattern of preexcitation. This syndrome was first described in 1930 in an article by Louis Wolff, Sir John Parkinson, and Paul Dudley White.
What causes APs in the atria?
APs result from failure of fibrous separation between the atria and the ventricles during the embryological development. These muscle bundles typically connect the epicardial surfaces of the atria and the ventricles along the AV groove outside of the regular atrioventricular conduction system.
Is EPS a good prognosis?
Most patients with asymptomatic preexcitation have a good prognosis. Because of the small but real risks associated with invasive procedures, EPS is not mandated for risk stratification or ablative therapy. The ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for Management of Patients with Supraventricular Arrhythmias gives catheter ablation a 2A classification for treatment of patients with asymptomatic preexcitation. A 2A designation means that it is reasonable to offer EPS with or without ablation in selected patients after a thorough discussion about the risks and benefits of the procedure.
What are the symptoms of WPW syndrome?
Common symptoms of WPW syndrome include: A rapid, fluttering or pounding heartbeat (palpitations) Dizziness or lightheadedness. Shortness of breath.
What is the most common arrhythmia associated with WPW syndrome?
The most common arrhythmia associated with WPW syndrome is called paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
Can WPW cause heart problems?
For many people, WPW syndrome doesn't cause serious problems. But complications can occur. It's not always possible to know your risk of serious heart-related events. If WPW syndrome is untreated — particularly if you have other heart conditions — you might have:
How to treat WPW?
Here are helpful lifestyle suggestions: 1 Don’t smoke. 2 Work with your doctor to keep conditions such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure under control. 3 Eat a heart-healthy diet. 4 Maintain a healthy weight. 5 Exercise regularly. 6 Tell your doctor right away if you have symptoms of WPW.
How does WPW affect the heart?
WPW affects one to three of every 1,000 people worldwide. Electrical signals going through your heart in an organized way control your heartbeat. This allows blood to pass from the upper chambers (the atria) to the lower chambers (the ventricles), and then to travel throughout your body. Normally, a structure in your heart called ...
Why is WPW a common cause of tachycardia?
WPW is a common cause of tachycardia in China, and you may be at increased risk if you are of Chinese descent.
How do you know if you have tachycardia with WPW?
Symptoms may also start and stop suddenly and occur at any age. Typical symptoms include: shortness of breath. a pounding in your chest. dizziness. passing out.
Is WPW dangerous?
WPW is not a dangerous disease for most people. You can manage or correct the condition with treatment. The biggest risk is for sudden death from a heart attack, which tachycardia can cause. However, this is extremely rare, occurring in less than one-half of 1 percent of cases.
What is the treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
The treatment of choice for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is direct-current cardioversion . The usual rate-slowing drugs used in atrial fibrillation are not effective, and digoxin and the nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (eg, verapamil, diltiazem) are contraindicated because they may increase the ventricular rate ...
Can you give digoxin to a patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
Do not give digoxin or nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (eg, verapamil, diltiazem) to patients with atrial fibrillation and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome because these drugs may trigger ventricular fibrillation.
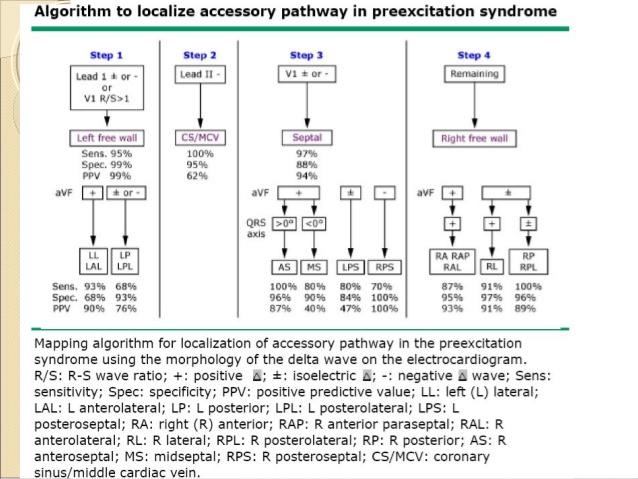
Definition
Variations
- Treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome depends on the severity and frequency of symptoms and the type of heart rhythm problem (arrhythmia) causing the fast heart rate. The goals of treatment are to slow a fast heart rate when it occurs and to prevent future episodes. Treatment options for a fast heart rate include: 1. Vagal maneuvers.Si...
Classification
Types
Clinical significance
Mechanism
Cause
Epidemiology
Prognosis
Signs and symptoms
Pathophysiology
Significance
Locations
Advantages
Diagnosis
Treatment
Research
Risks
Symptoms
- Management of patients with AP can vary depending on the symptoms, prognosis, and patients preference. While observation and close follow-up can be an option, particularly in the asymptomatic patient, most patients with WPW syndrome and/or PSVT involving an AP prefer curative treatment with catheter ablation.
Assessment