
How is water filtered at a water treatment plant?
Particle filtration and membrane filtration are the two primary types of filtration municipal water treatment systems. Particle Filtration. Particle filtration is a system using either mechanical or physical means to separate solids from liquids. For treatment of contaminated wastewater, particle filtration is commonly one of the first steps.
How much cost for water filteration plant?
Jan 25, 2009 · HIGH RATE WATER TREATMENT FILTERS. High rate water treatment filters, which operate at a rate two to three times that of rapid sand filters, use a combination of filter media, not just sand. The combination vary with the application, but generally they are sand and anthracite coal. Multimedia or mixed-media water treatment filters use three or four different …
What is the best residential water filtration system?
Jan 10, 2017 · In a water treatment facility, the coagulant is added to the water and it is rapidly mixed, so that the coagulant is circulated throughout the water. The coagulated water can either be filtered directly through a medium filter (such as sand and gravel), a microfiltration or ultrafiltration membrane, or it can be moved to a settling tank.
What is the best DIY water filter?
May 03, 2021 · Media filtration systems filter water through a prescribed filter medium, including: Sand filters; Granular activated carbon; Woven or nonwoven fabric; and; Metal screens. Pressure Pressure filters are contained in a steel pressure vessel. Perforated pipes or a steel plate with nozzles collect the filtered water and for distribution of the wash water and air scour.
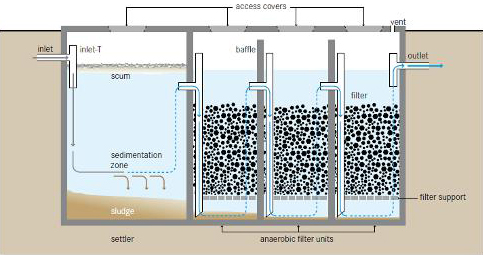
How do we filter water in water treatment plants?
Filtration. Finally, water goes through a filtration process using rapid gravity filters. Sand is commonly used in this type of filter and it removes any further sediment or particles in the water. During this final stage water is passed through a filter in a regulated manner.Jul 23, 2018
What is used to filter water in the treatment process?
Reverse osmosis is one of the most common physical water treatment methods employed in industrial water treatment. Reverse osmosis, also known as RO, filters contaminants out of water using applied pressure to force water through a semipermeable membrane.
What do most treatment plants use to filter water?
The majority of municipal water treatment plants use aluminum sulphate as the coagulation chemical. Generally, water treatment facilities have the coagulation process set up so that the coagulant chemicals are removed with the floc.Jan 23, 2017
What materials is used for filtering the water during water treatment?
Several natural materials are incorporated into modern water filtration systems to help remove potential contaminants so you can enjoy safer and tastier water.Carbon. Activated carbon, also known as charcoal, is a very porous type of carbon. ... Ceramic.Sand. ... Diatomaceous Earth.May 9, 2018
What is a filter for water?
Water filtering is a method used to filter out undesired chemical compounds, organic and inorganic materials, and biological contaminants from water. The purpose of water filtration is to provide clean drinking water.Feb 13, 2020
Where is water filtration used?
Filters cleanse water to different extents for purposes such as providing agricultural irrigation, accessible drinking water, public and private aquariums, and the safe use of ponds and swimming pools.
Which chemical is used for cleaning water?
chlorineThe most common disinfection method involves some form of chlorine or its compounds such as chloramine or chlorine dioxide. Chlorine is a strong oxidant that rapidly kills many harmful micro-organisms. Because chlorine is a toxic gas, there is a danger of a release associated with its use.
How do you filter river water?
0:147:32How to filter river water - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd be filtered out. And then what we're left with it's clear water you'd still have to boil it toMoreAnd be filtered out. And then what we're left with it's clear water you'd still have to boil it to kill any bacteria and viruses but at least it won't have any large debris in it.
What are the methods of water treatment?
When reverse osmosis is not available, there are 4 water purification methods that you can use to make your water safe for drinking.1 – Boiling. Boiling water is the cheapest and safest method of water purification. ... 2 – Filtration. ... 3 – Distillation. ... 4 – Chlorination.
What materials do filters use?
Natural Materials Used for Water FiltrationSand. The use of sand for water filtration dates back 2,000 years. ... Oysters. Oysters naturally filter toxins when they feed. ... Plants. Plants are a natural choice for water filtration, especially in wetland areas. ... Charcoal. Charcoal is a slow, but effective, water filter. ... Coconut.Apr 24, 2017
What is the best filtration material?
Natural materials such as carbon, ceramic, and sand are some of the most efficient water filtration systems to protect against these deleterious effects.May 5, 2016
What material is used in filtration?
filtration materials (examples: soil, gravel, potting soil, cotton balls, scrap material, charcoal, sand, woodchips, Styrofoam packing, charcoal briquettes) screening. rubber bands.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
What is a CCR report?
Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water.
Why is surface water more contaminated than ground water?
Typically, surface water requires more treatment and filtration than ground water because lakes, rivers, and streams contain more sediment and pollutants and are more likely to be contaminated than ground water. Some water supplies may also contain disinfections by-products, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals, and radionuclides.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What are the materials used in water treatment filters?
Multimedia or mixed-media water treatment filters use three or four different materials, generally sand, anthracite coal, and garnet. The details of different types of media in the water treatments filter beds are shown below. In rapid sand water treatments filters, finer sand grains are at the top of the sand layer with larger grains farther down ...
Which layer of a water filter removes the larger particles?
In the coarse layer at the top, the larger suspended particles are removed first, followed by the finer materials. This allows for longer filter runs at higher rates of filtration than is possible with rapid sand water filters.
What chemicals are used to remove taste and odor from water?
Other chemicals used for oxidation include potassium permanganate, chlorine dioxid e, and ozone.
What is anthracite coal?
Anthracite coal is a very light (low density) coal which will settle slowly, ending up as the top layer of the filter.
What are the layers of a filter?
Typically, the layers (starting at the bottom of the filter above gravel and advancing upward) are sand and anthracite coal, or garnet, sand, and anthracite coal. The below Figure shows a cross-section through a dual media filter.
What happens when you use a rapid sand water treatment filter?
As a result, the water filter removes more suspended material in the first few cm thick of the filter. In the high rate filter, the media size decreases. The top layers consist of ...
How are media in a dual filter arranged?
The media in a dual or multimedia filter are arranged so that the water moves through media with progressively smaller pores. The largest particles are strained out by the anthracite. Then the sand and garnet trap the rest of the particulate matter though a combination of adhesion and straining.
What chemicals are used in water treatment plants?
Polyelectrolyte, ferrous sulfate, and aluminum sulfate are examples of chemicals used in the water treatment plant process to aid coagulation. Adding these coagulating agents during these water treatment plant steps requires careful administration by qualified engineers, as measurements of the chemicals need to be precise.
Why are water treatment plants important?
Water treatment plants are critical for a municipality so that clean water can be supplied to the local community. The process of water purification in water plants requires specialists to ensure safe and effective operation. The whole procedure occurs in stages and involves a combination of technical processes.
What is the process of coagulation of water?
These mix the chemicals and water together and enable the micro particles to form into larger pieces that are likely to stick together, making the sedimentation process in water treatment more effective. This process is known as flocculation.
What is added to water after it is clarified?
Once clarified water leaves the sedimentation basins in the treatment plant, chlorine is added during the disinfection water treatment stage. After the chlorine wastewater treatment occurs, ammonia follows which forms chloramine. This chloramine disinfected water passes through a further set of basins to complete the disinfection process.
Why is fluorosilicic acid added to water?
Once water exits the sedimentation basins, fluorosilicic acid is added in small quantities. This helps fluoridate the water supply to help in the prevention of dental decay.
What is the pH adjustment in water?
pH Adjustment. After the disinfection phase the water undergoes a pH treatment stage. Lime or calcium oxide makes water less acidic by adjusting the pH. It is also less corrosive to domestic water pipes. Polyphosphate solution is also added to the water at this stage to keep the lime dissolved.
What is the first step in water treatment?
Coagulation. When water enters a treatment plant, the first stage in the process is coagulation where chemicals are added to the water supply to enable microparticles and small solids to stick together. Polyelectrolyte, ferrous sulfate, and aluminum sulfate are examples of chemicals used in the water treatment plant process to aid coagulation.
What is the most widely used water treatment technology?
Many water treatment plants use a combination of coagulation, sedimentation, filtration and disinfection to provide clean, safe drinking water to the public. Worldwide, a combination of coagulation, sedimentation and filtration is the most widely applied water treatment technology, and has been used since the early 20th century.
Why are pathogens removed from water?
Usually, the pathogens that are removed from the water are removed because they are attached to the dissolved substances that are removed by coagulation. In the picture below, the coagulants have been added to the water, and the particles are starting to bind together and settle to the bottom.
Why is coagulation important in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is added to ferric chloride?
If ferric chloride is used, iron and chloride are added. And if aluminum sulphate is used, aluminum and sulphate are added. The majority of municipal water treatment plants use aluminum sulphate as the coagulation chemical. Generally, water treatment facilities have the coagulation process set up so that the coagulant chemicals are removed with ...
What is residual water?
Residuals are the by-products that remain in the water after substances are added and reactions occur within the water. The particular residuals depend on the coagulant that is used. If ferric sulphate is used, iron and sulphate are added to the water. If ferric chloride is used, iron and chloride are added.
What is the charge of ferric sulphate?
ferric sulphate, ferric chloride or polymers, to the water. These chemicals are called coagulants, and have a positive charge. The positive charge of the coagulant neutralizes the negative charge of dissolved and suspended particles in the water.
What is slow sand filtration?
that are used. Slow sand filtration removes bacteria, protozoa and viruses, and produces. essentially clean water, though it is still advisable to use a disinfectant as a precautionary. measure.
What is media filtration?
Media filtration systems promote the filtration of water through a prescribed filter medium, including: 1 Sand filters; 2 Granular activated carbon; 3 Woven or nonwoven fabric; and 4 Metal screens.
What is a pressure filter?
Pressure filters are contained in a steel pressure vessel. Perforated pipes or a steel plate with nozzles collect the filtered water and for distribution of the wash water and air scour.
What is the process of removing solid particles from a liquid?
Filtration is the process in which solid particles in a liquid or gaseous fluid are removed by the use of a filter medium that allows the fluid to pass through while retaining the solid particles. Filtration may mean the use of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or a biological process.
What are the requirements for filtration?
Basic requirements for filtration are: a filter medium (thin or thick barriers); a fluid with suspended solids; a driving force to cause the fluid to flow; and a the filter that holds the filter medium, contains the fluid, and permits the application of force.
What is clarified water?
In the water industry, clarified water is the goal of the filtration process. Filtration primarily is used for storm water, wastewater, and drinking water applications, but it also has uses in industrial manufacturing, power plants, food and beverage production facilities, mining and other heavy duty applications..
How is impure water purified?
These writings describe early water treatment as: “Impure water should be purified by being boiled over a fire, or heated in the sun or by dipping a heated iron into it and then allowed to cool, or it may be purified by filtration through sand and coarse gravel” (Jadhav, Aasawari, 2014).
What is the purpose of a straining cloth?
Straining is a very simple method of filtration in which water is poured through a piece of cloth , and can remove some of the suspended silt and solids, destroying some pathogens in the process.
What is the Cajon City water treatment plant?
The Cañon City Water Treatment Plant is a conventional surface water treatment plant that diverts water from the Arkansas River to produce drinkable (potable) water, which meets or exceeds all Environmental Protection Agency ( EPA) Safe Drinking Water Act and the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment Primary Drinking Water Standards.
What is the first chemical added to water?
The first chemical added is chlorine dioxide and it is an oxidant used to break down naturally occurring organic matter such as decaying leaves and other plant material. A chemical coagulant known as aluminum sulfate is used as the primary coagulant. A polymer, a long chain of synthetic organic compounds, is also added to the water as a coagulant aid to help in strengthening the primary coagulant’s bonding chains. The coagulants are added at the rapid mix unit; this is a unit that creates turbulent mixing energies to help thoroughly disperse the chemical coagulants into the raw water and to begin the coagulation process. The coagulants that cause very fine particles to clump together into larger particles that can then be removed later in the treatment process by settling, skimming, draining or filtering.
What is the process of flocculation?
The flocculation process promotes contact between the floc particles and the particulates (sediment) in the water. Generally, these contacts or collisions between particles result from gentle stirring created by a mechanical or hydraulic means of mixing.
How does sedimentation work?
Sedimentation is accomplished by decreasing the velocity of the water being treated below the point where it can transport settleable suspended material, thus allowing gravitational forces to remove particles held in suspension. When water is almost still in sedimentation basins, settleable solids will move toward the bottom of the basin. This process of sedimentation removes almost ninety percent of the solids in the water. The clearer water on the surface is collected in the launder tubes that direct the water to the filter gallery to remove the remaining ten percent of solids.
How does the pre sedimentation process work?
The raw water is delivered to the headworks of the water treatment plant where the first of 5 major unit water treatment processes start the treatment to make the water safe to drink. The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
How is potable water run?
Potable water is run backwards through the filters releasing the entrapped particulates that are collected in drain troughs. The backwash water is sent to the Backwash Recovery Pond and, after a settling process, the backwash water is returned to the raw water settling pond for re-use.
What is a PLC in water treatment?
Devices known as programmable logic controllers ( PLCs) that are networked together with other PLCs control the water treatment plant and the treatment processes. The PLCs track over 1,500 signals or data points to ensure optimized treatment. The computer signals and data are collected by the Supervisory Collection and Data Acquisition ( SCADA) system and provide information to the Operator on shift whenever any item requires Operator intervention.
What is a water treatment plant?
Drinking water treatment plant could be classified into: –. Disinfection plant which is used for high-quality water source to ensure that water does not contain pathogens. –. Filtration plant : this is usually used to treat surface water. –. Softening plant which is used to treat groundwater.
What is make up water treatment?
Make up water treatment. Treated raw water is mixed with potable water and pumped to the boiler feedwater treatment system. The system is designed to remove 99% of the dissolved minerals and provide high-purity water to the boiler.
What is a WTP plant?
WTP including an effluent treatment plant: There are three different sections in a WTP: a pretreatment (PT) plant, a posttreatment or demineralized water (DM) plant, and a waste treatment or effluent treatment (ET) plant.
What is raw water pretreatment?
The raw water pretreatment plant is designed principally for solids removal from the incoming Hanover county sewage effluent (grey water), backwash water and wastewater from the oily water collection system. Raw water enters a coagulation/flocculation chamber followed by a clarifier and dual media depth filters. Backwash water from the filters is periodically returned to the clarifier. Clarifier sludge is dosed with polymer before being thickened and then sent to the filter press for dewatering. The cake is sent to landfill and the recovered water returned to the clarifier.
What is the water used in CMF-S?
Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals.
Can a chlorination plant be controlled by a PLC?
Again, a chlorination plant is almost an independent plant and may be controlled by a micro PLC.
What is the role of filtration in water?
The role of filtration is mainly to remove suspended or colloidal impurities in water, especially to remove tiny particles and bacteria that cannot be removed by precipitation technology. BOD5 and COD also have a certain degree of removal effect.
What is a multi media filter?
Multi-media filter, which uses more than two media as the media filter of the filter layer, is used to remove impurities and adsorb oil in sewage in industrial circulating water treatment system, so that the water quality meets the requirements of recycling.
What is quartz sand filter?
Quartz sand filter is a kind of filter that uses quartz sand as filter material. It can effectively remove suspended matter in water, and has obvious removal effect on colloid, iron, organic matter, pesticide, manganese, bacteria, virus and other pollutants in water. It has the advantages of low filtration resistance, large specific surface area, ...
What is make up water treatment?
Make up water treatment. Treated raw water is mixed with potable water and pumped to the boiler feedwater treatment system. The system is designed to remove 99% of the dissolved minerals and provide high-purity water to the boiler.
When was the first potable water treatment plant?
Already in 2001, the first potable water treatment plant using a MIEX® -DOC process was launched in Australia. In this plant, the MIEX ® -DOC step was introduced prior to conventional treatment, and a significant improvement in water quality was observed.
What is centralized water treatment?
Centralized water treatment plants are based on coagulation, flocculation and disinfection processes and found to be most cost-effective in treating large quantities of water.
What is the water district in Orange County?
Orange County Water District (OCWD). OCWD located between Los Angeles and San Diego counties in southern California manages the groundwater basin that supplies about 3.0 × 10 8 m 3 per year potable water to a population of more than 2 million.
What is the water used in CMF-S?
Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals.
What is the Bendigo water treatment plant?
I. Bendigo water treatment plant (BWTP). The 12.54 × 10 4 m 3/day (33 MGD) BWTP has been producing drinking water for nearly 1 million people in central Victoria, Australia since 2002. It is one of the largest if not the largest MF plant in the world. The plant combines submerged microfiltration (CMF-S), ozonation and biological activated carbon (BAC) to treat a variable and difficult raw water. Raw (surface) water is pre-screened, and dosed with lime and carbon dioxide in a contact reactor to control alkalinity and corrosion. Next, water is dosed with a coagulant, liquid aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) prior to entering the CMF-S plant to remove colour, some organic content, and dissolved metals. The coagulant dosage is typically 5–6 mg/l. The coagulant precipitate is removed by MF. The coagulant/CMF-S process removes up to 15% of the dissolved organic carbon.64
What is water treatment automation?
Automation of water treatment plant involves the control system opening and closing valves and starting and stopping equipment in predefined sequences to complete specific tasks or to provide the desired process plant output. To achieve these results the automation system relies on signals from correctly selected and placed instruments, devices such as actuators and motor control circuits and reliable control logic. The degree of automation to be used is fundamental to developing an automation system.

Community Water Treatment
Water Fluoridation
- Community water fluoridation prevents tooth decay safely and effectively. Water fluoridation has been named one of 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century 1. For more information on the fluoridation process and to find details on your water system’s fluoridation, visit CDC’s Community Water Fluoridationpage. Top of Page
Consumer Confidence Reports
- Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water. 1. View the CDC’s guide to Understandi…
Household Water Treatment
- Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1. Remove specific contaminants 2. Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3. Improve the taste of drinking water Household water treatment systems are composed of two categories: point-of-us…
Coagulation
Flocculation
- Once water has been treated with the coagulation chemicals it enters a tank with giant paddles. These mix the chemicals and water together and enable the micro particles to form into larger pieces that are likely to stick together, making the sedimentation process in water treatmentmore effective. This process is known as flocculation.
Sedimentation
- Once the flocculation process is complete the water enters the sedimentation phase. Once the water is in the primary settling basins the large particles formed during the coagulation and flocculation stage separate and settle. This leaves cleaner water for further processing in the treatment plant. The solids form a sludge layer which forms on the bottom of the tank and is lat…
Disinfection
- Once clarified water leaves the sedimentation basins in the treatment plant, chlorine is added during the disinfection water treatment stage. After the chlorine wastewater treatment occurs, ammonia follows which forms chloramine. This chloramine disinfected water passes through a further set of basins to complete the disinfection process.
Ph Adjustment
- After the disinfection phase the water undergoes a pH treatment stage. Lime or calcium oxide makes water less acidic by adjusting the pH. It is also less corrosive to domestic water pipes. Polyphosphate solution is also added to the water at this stage to keep the lime dissolved.
Fluoridation
- Once water exits the sedimentation basins, fluorosilicic acid is added in small quantities. This helps fluoridate the water supply to help in the prevention of dental decay.
Filtration
- Finally, water goes through a filtration process using rapid gravity filters. Sand is commonly used in this type of filter and it removes any further sediment or particles in the water. During this final stage water is passed through a filter in a regulated manner. Any particles stick to the filter, leaving clean water to be piped into the municipa...