Medication
Apr 25, 2022 · Several forms of rhizotomy are available to treat trigeminal neuralgia: Balloon compression works by injuring the insulation on nerves that are involved with the sensation of light touch on the face. The procedure is performed …
Procedures
Rhizotomy is a recommended surgical treatment for patients with trigeminal neuralgia resulting from multiple sclerosis (MS). It is minimally invasive and can be safely repeated, since the pain is more likely to come back due to the progression of MS. …
What is trigeminal neuralgia, and how is it treated?
Microvascular decompression (MVD), also known as the Jannetta procedure, is the most common surgical procedure for treating trigeminal neuralgia. In the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision behind the ear and drills a small hole in the skull. Using microscopic visualization, the trigeminal nerve is exposed.
Does trigeminal neuralgia ever go away on its own?
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in multiple sclerosis. The pharmacological treatment of TN in MS is similar to that of idiopathic TN. Randomized controlled treatment trials on this special subgroup of patients do not exist. Central nervous system (CNS) demyelination renders some patients with MS more sensitive to cognitive and motor side ...
Does trigeminal neuralgia go away or get better?
Jun 26, 2018 · If you are suffering from trigeminal neuralgia, give upper cervical chiropractic a try. A consultation with a practitioner near you may be your first step down the path to less face pain. to schedule a consultation today.
What is the best painkiller for trigeminal neuralgia?
Surgery may be an option for treating trigeminal neuralgia when the diagnosis is confirmed with an MRI scan or other neuro-imaging, and when less invasive options have been exhausted. The goal of surgery is to either stop a blood vessel from compressing the trigeminal nerve, or to sever the nerve that’s causing the pain.

Does trigeminal neuralgia ever go away?
How do you permanently treat trigeminal neuralgia?
Can trigeminal neuralgia start in the neck?
What is the most common treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
What is the best painkiller for neuralgia?
What foods should you avoid if you have trigeminal neuralgia?
...
Other foods and drinks to avoid include the following:
- spicy foods;
- high-sugar foods;
- caffeinated drinks;
- junk foods and highly processed foods.
Where is trigeminal nerve in neck?
Can you live a normal life with trigeminal neuralgia?
What is neck neuralgia?
What are the symptoms of neuralgia in the head and neck?
What is the most common cause of trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia usually occurs spontaneously, but is sometimes associated with facial trauma or dental procedures. The condition may be caused by a blood vessel pressing against the trigeminal nerve, also known as vascular compression.
What is the newest treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
Where is trigeminal neuralgia located?
Primary trigeminal neuralgia has been linked to the compression of the nerve, typically in the base of the head where the brain meets the spinal cord . This is usually due to contact between a healthy artery or vein and the trigeminal nerve at the base of the brain. This places pressure on the nerve as it enters the brain and causes ...
How many people are diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia every year?
Prevalence and Incidence. It is reported that 150,000 people are diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) every year. While the disorder can occur at any age, it is most common in people over the age of 50.
What is the pain in the lower jaw called?
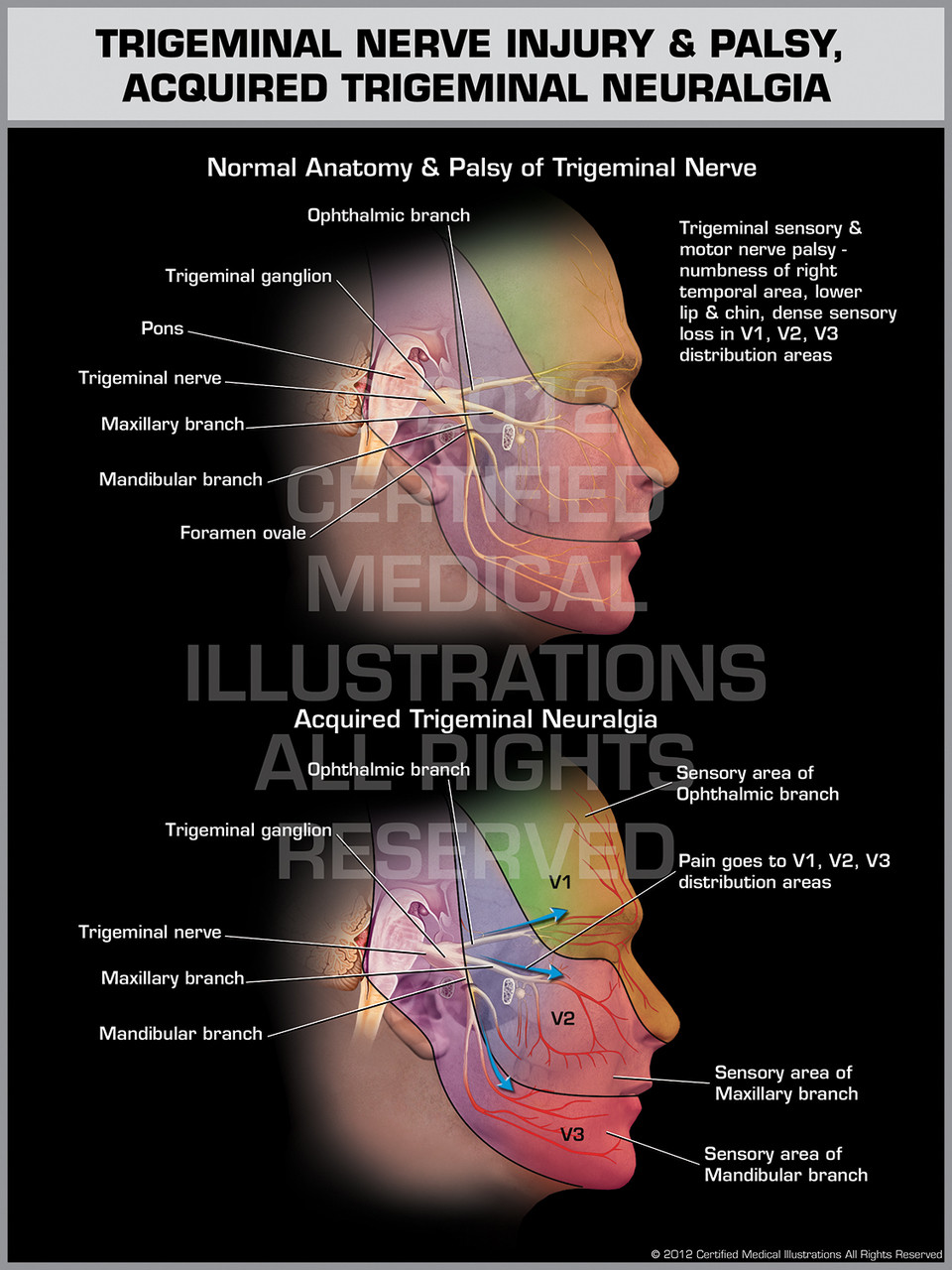
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN), also known as tic douloureux, is sometimes described as the most excruciating pain known to humanity. The pain typically involves the lower face and jaw, although sometimes it affects the area around the nose and above the eye.
How many branches does the trigeminal nerve have?
Each of these nerves has three distinct branches. "Trigeminal" derives from the Latin word "tria," which means three, and "geminus," which means twin. After the trigeminal nerve leaves the brain and travels inside the skull, it divides into three smaller branches, controlling sensations throughout the face:
What nerves are responsible for the face?
The trigeminal nerve is one set of the cranial nerves in the head. It is the nerve responsible for providing sensation to the face. One trigeminal nerve runs to the right side of the head, while the other runs to the left. Each of these nerves has three distinct branches. "Trigeminal" derives from the Latin word "tria," which means three, and "geminus," which means twin. After the trigeminal nerve leaves the brain and travels inside the skull, it divides into three smaller branches, controlling sensations throughout the face:
How to diagnose TN?
Newer scanning techniques can show if a vessel is pressing on the nerve and may even show the degree of compression. Compression due to veins is not as easily identified on these scans. Tests can help rule out other causes of facial disorders. TN usually is diagnosed based on the description of the symptoms provided by the patient, detailed patient history and clinical evaluation. There are no specific diagnostic tests for TN, so physicians must rely heavily on symptoms and history. Physicians base their diagnosis on the type pain (sudden, quick and shock-like), the location of the pain and things that trigger the pain. Physical and neurological examinations may also be done in which the doctor will touch and examine parts of your face to better understand where the pain is located.
What is the pain of TN1?
TN1 is characterized by intensely sharp, throbbing, sporadic, burning or shock-like pain around the eyes, lips, nose, jaw, forehead and scalp. TN1 can get worse resulting in more pain spells that last longer.
What causes trigeminal neuralgia?
The condition may be caused by a blood vessel pressing against the trigeminal nerve , also known as vascular compression.
Where is the pain of trigeminal neuralgia felt?
Depending on which branch and which part of the nerve is irritated, trigeminal neuralgia pain can be felt anywhere in the face. Most commonly, it is felt in the lower part of the face. The intensity of the pain is exceptional: Some people report it to be more severe than experiencing a heart attack, passing a kidney stone or even giving birth.
What nerve is irritated in the face?
Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain. The trigeminal nerve splits off into three branches: ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular. Each branch provides sensation to different areas of the face. Depending on which branch and which part of the nerve is irritated, trigeminal neuralgia pain can be felt anywhere in the face.
How does a rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia work?
The surgeon inserts a long needle through the cheek on the affected side of the face and uses an electrical current (heat) or a chemical (glycerin or glycerol) to deaden the pain fibers of the trigeminal nerve. For those undergoing trigeminal neuralgia rhizotomy for the first time, the chemical approach is typically recommended. Those who have the procedure repeated often benefit from both the chemical and the heat treatment delivered in the same session.
How long does a trig neuralgia pain last?
The pain travels through the face in a matter of seconds, but as the condition progresses, the pain can last minutes and even longer. Trigeminal neuralgia is sometimes known as tic douloureux, ...
What causes facial pain?
Trigeminal neuralgia is the most common cause of facial pain and is diagnosed in approximately 15,000 people per year in the United States. Trigeminal neuralgia pain is exceptionally severe. Although the condition is not life-threatening, the intensity of the pain can be debilitating. Trigeminal neuralgia relief is possible: Medical ...
Can triceminal neuralgia be treated?
Trigeminal neuralgia relief is possible: Medical and surgical treatments can bring the pain under control, especially when managed by an expert physician and surgeon.
How to treat trigeminal neuralgia?
Microvascular decompression (MVD), also known as the Jannetta procedure, is the most common surgical procedure for treating trigeminal neuralgia. In the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision behind the ear and drills a small hole in the skull. Using microscopic visualization, the trigeminal nerve is exposed. In most cases, there is a blood vessel — typically an artery, but sometimes a vein — compressing the trigeminal nerve. By moving this blood vessel away from the nerve and interposing a padding made of Teflon felt, the pain is nearly always relieved.
What is the best anti-convulsant for trigeminal neuralgia?
The anti-convulsant drug most commonly prescribed for trigeminal neuralgia is carbamazepine (Tegretol), which can provide at least partial pain relief for up to 80 to 90 percent of patients. Other anti-convulsants prescribed frequently for trigeminal neuralgia include: 1 Phenytoin (Dilantin) 2 Gabapentin (Neurontin) 3 Lamotrigine (Lamictal) 4 Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) 5 Topiramate (Topamax)
How long does it take for trigeminal neuralgia to respond to treatment?
Patients usually begin to respond to the treatment within four to 12 weeks post-treatment, but some patients require as much as six to 12 months for the full response. Most patients remain on full doses of their trigeminal neuralgia medication for at least three to six months after treatment.
What is the trigeminal nerve exposed to?
Using microscopic visualization, the trigeminal nerve is exposed. In most cases, there is a blood vessel — typically an artery, but sometimes a vein — compressing the trigeminal nerve. By moving this blood vessel away from the nerve and interposing a padding made of Teflon felt, the pain is nearly always relieved.
Can you have trigeminal neuralgia surgery?
Surgery for trigeminal neuralgia is rarely attempted on patients with non-trigeminal neural gia face pain or on atypical trigeminal neuralgia, since operations for these conditions have much lower success rates and, in many cases, can make the pain worse and/or cause additional medical problems.
Is gamma knife surgery?
Gamma Knife is the least invasive surgical option for trigeminal neuralgia. In fact, it is technically not surgery at all. The Gamma Knife is a device that delivers precise, controlled beams of radiation to targets inside the skull, including the brain and associated nerves. For trigeminal neuralgia treatment, the radiation beams are aimed at the trigeminal nerve where it enters the brainstem.
Is MVD the best treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
While MVD is considered to be the most invasive surgery for trigeminal neuralgia, it is also the best procedure for fixing the underlying problem: vascular compression. MVD also causes the least damage to the trigeminal nerve and provides, on average, the longest pain-free periods and the best chance for the patient to be permanently off medication. MVD has a long-term success rate of approximately 80 percent as a stand-alone treatment. The procedure requires an average hospital stay of two to three days, and four to six weeks to return to normal daily activities.
What is trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is defined by the International Headache Society (IHS) as “unilateral disorder characterized by brief electric shock-like pains, abrupt in onset and termination, and limited to the distribution of one or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve” [International Headache Society, 2004]. The IHS suggests a classification of TN as either classic (essential or idiopathic) TN (CTN) or symptomatic TN (STN; pain indistinguishable from that of CTN, but caused by a demonstrable structural lesion other than vascular compression). The diagnosis of CTN requires the absence of a clinically evident neurological deficit. CTN starts in the second or third divisions, affecting the cheek or the chin [International Headache Society, 2004]. The ophthalmic division alone is involved in less than 5% of cases [De Simone et al.2005]. The single attack generally lasts from less than a second to a few seconds, but it may present in clusters of variable intensity with up to 2 minutes duration. In many cases it is followed by a brief refractory period during which a new stimulation is not able to evoke another attack. Between paroxysms the patient is usually pain free, but a dull background pain may persist in some cases [International Headache Society, 2004]. Growing neurosurgical data advocate the distinction of these two subtypes of TN into type 1 as defined as >50% episodic onset of TN pain and type 2 defined by >50% constant pain [Tatli et al.2008; Limonadi et al.2006]. The mechanisms associated with the development of this persistent pain are not well understood but concomitant background pain is associated with poor medical and surgical outcome [Obermann et al.2008; Sandell and Eide, 2008; Szapiro et al.1985]. Recent investigations focused on the suspected central component in the pathophysiology of TN, which could involve central allodynic mechanisms that may also engage the nociceptive neurons at thalamic and cortical level [Obermann et al.2007].
What is the name of the drug that is used for neuralgia?
Killian J.M., Fromm G.H. (1968) Carbamazepine in the treatment of neuralgia. Use of side effects. Arch Neurol19: 129–136 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
What is repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation?
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is an emerging technology that introduces the possibility of assessing whether patients with trigeminal neuropathic pain will respond to direct epidural cortical stimulation by first measuring their response to a trial of non-invasive cortical stimulation. In a study of 24 TN patients given rTMS to the motor cortex at 20 Hz daily for 5 days, pain ratings decreased by approximately 45% for 2 weeks [Khedr et al.2005]. In a different study of 12 patients with chronic intractable TN who had failed surgical treatment, 58% experienced a greater than 30% reduction in pain after receiving repetitive TMS [Lefaucheur et al.2004].
How effective is phenytoin for neuralgia?
Phenytoin has proven effective in managing neuralgia crisis in a small case series. A loading dose of 14 mg/kg applied intravenously was required to relieve the pain for 1–2 days, which is long enough for alternative oral drug therapy to kick in when initiated simultaneously [Cheshire, 2001]. Intranasal administered lidocaine 8% was effective in temporarily relieving second-division neuralgic pain [Kanai et al.2006b]. Subcutaneous sumatriptan 3 mg was shown to be superior to placebo in providing prompt and marked analgesia in 80% of patients in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 24 patients with refractory TN. The median duration of pain relief was 8 h [Kanai et al.2006a]. A different approach could be ganglionic local opioid analgesia (GLOA) at the superior cervical ganglion, which was evaluated retrospectively in 74 patients with neuropathic facial pain. A clinically relevant pain reduction was observed in 73% of the patients. The proportion of responders (pain reduction ≥50%) was 59% after the first blockade [Elsner et al.2006].
How to treat TN?
The general recommendation is to start with medical therapy and consider surgical procedures in patients who are refractory to medical treatment (Figure 1). Studies that compare medical and surgical treatment directly are still missing. Active participation in support groups may help many patients in dealing better with their disease and with suggested therapy [Zakrzewska et al.2009].
Is tizanidine an alpha agonist?
Tizanidine is a centrally acting alpha-adrenergic agonist and has proven efficacy in a double-blind crossover study in 8 out of 10 patients with TN. All patients that were followed-up after 1–3 months experienced recurrence of pain [Fromm et al.1993]. Tizanidine is less efficacious than CBZ [Vilming et al.1986].
How to tell if you have trigeminal neuralgia?
The primary symptom of trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is pain in the face. This pain can be excruciating and debilitating, but it doesn’t last long. The pain of TN lasts less than 2 minutes at a time and may only last seconds sometimes. The incapacitating effects are that the pain may recur rapidly. The simplest things can be the trigger that sets it off. TN patients often experience pain from: 1 Smiling 2 Chewing 3 Brushing 4 Laying the face on a pillow
What is the branch of migraine?
One branch goes above the eye, one extends below the eye and to the upper cheek, and the third extends along the jawline. The length of time the pain lasts is an important factor in diagnosis. For example, longer lasting face pain can be an atypical symptom of migraines.
What is upper cervical chiropractic?
The Upper Cervical Chiropractic Difference. Upper cervical practitioners focus on the top two bones in the neck. These bones are most likely to affect the trigeminal nerve, blood flow to the head, and the brainstem. They use diagnostic imaging to take precise measurements of the misalignment.
How long does TN pain last?
This pain can be excruciating and debilitating, but it doesn’t last long. The pain of TN lasts less than 2 minutes at a time and may only last seconds sometimes. The incapacitating effects are that the pain may recur rapidly.
Can you take anticonvulsants with TN?
In the meantime, you may be dealing with some of the common treatments for TN which primarily includes a concoction of anticonvul sants. These are powerful drugs that can produce many and varied side effects, especially if there is not proper regulation of the dosage.
Is it a good idea to see an upper cervical chiropractor?
As you can see from these cases, there is a link between the alignment of the top bones in the neck and the way the trigeminal nerve functions. Therefore, it makes sense to see an upper cervical chiropractor if you are suffering from TN. What makes upper cervical different?
What is the best treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
Surgery may be an option for treating trigeminal neuralgia when the diagnosis is confirmed with an MRI scan or other neuro-imaging, and when less invasive options have been exhausted. The goal of surgery is to either stop a blood vessel from compressing the trigeminal nerve, or to sever the nerve that’s causing the pain.
What is the choice of surgical treatment?
The choice of surgical treatment depends on the individual patient — the neurosurgeon will evaluate each case carefully before recommending a treatment option.
How does neurostimulation work?
Neurostimulation is a minimally invasive procedure in which a neurosurgeon places a small wire under the skin touching one or more branches of the nerve in the painful part of the face. The patient controls a device that can turn on a current to the wire. The device is tested for several days; the patient turns the stimulator device on to generate a buzzing or massage-type sensation, which is often pleasant and blocks the pain signal from getting to the brain. If a patient experiences good results from the test, the neurosurgeon can implant a permanent stimulator with a battery pack under the skin. The patient can control the device wirelessly, turning it on or off and changing the intensity of stimulation.
Why does trigeminal neuralgia cause pain?
In the first part of this article, we established that trigeminal neuralgia could be due to pressure on the trigeminal nerve. When pressed, the trigeminal nerve sends signals which the brain interprets as pain. Any movement that affects the trigeminal nerve triggers this transmission.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
It is the one responsible for transmitting facial stimuli to your brain. The trigeminal nerve is also responsible for breaking food into smaller pieces when you chew.
What does an upper cervical chiropractor do?
No matter how small the discrepancy, upper cervical chiropractors believe that restoring the cervical alignment will great ly alleviate trigeminal neuralgia.
How old is too old to have a trigeminal neuralgia?
This condition generally affects women over 50 years old. The initial outbursts can be short and mild, but the episodes will become more painful and last longer. Trigeminal neuralgia makes the most mundane activities excruciating.
What nerve breaks food into smaller pieces?
The trigeminal nerve is also responsible for breaking food into smaller pieces when you chew. This condition generally affects women over 50 years old. The initial outbursts can be short and mild, but the episodes will become more painful and last longer.
Why is the neck prone to imbalance?
The neck’s topmost bones are incredibly prone to imbalance because of their delicate structure and primary location. They are first in line to take on the weight of the head. They also precede the other bones in absorbing any impact to the head. Head and neck injury can affect the nerve pathways and blood flow, especially in the atlas and axis. When this happens, trigeminal neuralgia comes into play.
Does triceminal neuralgia hurt?
Trigeminal neuralgia hurts like no other. No matter how slight your movement is, your face hurts. It is not surprising that many people look for the ultimate painkillers to ease the pain. If you are looking for natural options, upper cervical chiropractors believe that an atlas bone adjustment can help address the pain.
How to relieve trigeminal neuralgia?
Taking a hot shower or bath may relieve you of the symptoms. Cold applications like cold water or ice water application may also help you obtain relief. Applying pressure with the entire hand to the affected area can help relieve you of the discomforting symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia.
What vitamins help with trigeminal neuralgia?
Certain vitamins, such as vitamin B12, minerals, etc. can help alleviate the discomforting trigeminal neuralgia symptoms. They lower the inflammatory responses and may help to form a stronger immune system.
What nerve is responsible for the pain in the jaw?
Pain is experienced in areas which are supplied by the trigeminal nerve that include jaw, lips, cheek, gums, teeth, or less often your eye and forehead.
How to stop pain from mind?
Slowing down this speed of the mind helps alleviate the pain. This can be achieved through deep slow breathing.
Does trigeminal neuralgia turn more frequent over time?
Trigeminal neuralgia attacks tend to turn more frequent and intense over time.

Treatment
Introduction
Epidemiology
Pathophysiology
Specialist to consult
Causes
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms
Diagnosis
Risks
Mechanism of action
Operation
Clinical significance
Resources