Nutrition
5 rows · The 4-month rifapentine-moxifloxacin TB treatment regimen is as effective as (noninferior to) ...
What medications are used to treat TB?
Nov 25, 2021 · Anti-tubercular medications: rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol are FDA-approved for the treatment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. The combination and duration on which medications to use for therapy rely on whether the patient has active or latent disease. A feared complication of tuberculosis therapy is multi-drug-resistant …
What antibiotic is used for TB treatment?
This includes people you live, work, or come in close contact with. You need to take many medicines for TB for at least 6 months to rid your body of the TB bacteria. You should begin to feel better within a month of starting the medicines. For the first 2 to 4 weeks after starting the medicines, you may need to stay home to avoid spreading TB ...
What are the most common TB medications?
Tuberculosis Drugs and Mechanisms of Action First-Line Treatment of TB for Drug-Sensitive TB. Shown here are the four drugs in the standard regimen of first-line... Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR TB) and Second-Line Treatments. MDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis... Extensively ...
What meds treat TB?
Apr 03, 2021 · The most common medications used to treat tuberculosis include: Isoniazid; Rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane) Ethambutol (Myambutol) Pyrazinamide; If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB …
What does TB treatment include?
What happens after taking TB medication?
Why is TB treated with 4 drugs?
When does TB treatment start?
How do you know TB treatment is working?
- A reduction in symptoms, such as less coughing.
- Overall improvement in the way one feels.
- Weight gain.
- Increased appetite.
- Improvement in strength and stamina.
Is TB curable today?
What are the 3 types of tuberculosis?
What are 3 drugs for TB?
- Rifampin (RIF),
- Isoniazid (INH),
- Pyrazinamide (PZA), and.
- Ethambutol (EMB)
Is there a vaccine for tuberculosis?
Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) disease. This vaccine is not widely used in the United States, but it is often given to infants and small children in other countries where TB is common. BCG does not always protect people from getting TB.
What is the fastest way to cure TB?
- 2 antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampicin) for 6 months.
- 2 additional antibiotics (pyrazinamide and ethambutol) for the first 2 months of the 6-month treatment period.
How do u know if u have TB?
What is the gold treatment for TB?
Is TB contagious?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs, but may spread to other organs. The goal of treatment is to cure the infection with medicines that fight the TB bacteria.
What is latent TB?
This means the TB bacteria remain inactive (dormant) in a small area of your lungs. This type of infection may be present for years and is called latent TB. With latent TB:
Can TB be active?
You may have a TB infection but no active disease or symptoms. This means the TB bacteria remain inactive (dormant) in a small area of your lungs. This type of infection may be present for years and is called latent TB. With latent TB:
Can you spread TB to other people?
You cannot spread TB to other people. In some people, the bacteria can become active. If this happens, you may become sick, and you can pass the TB germs to someone else. Even though you do not feel sick, you need to take medicines to treat latent TB for 6 to 9 months.
How long does it take to get rid of latent TB?
Even though you do not feel sick, you need to take medicines to treat latent TB for 6 to 9 months. This is the only way to make sure all of the TB bacteria in your body are killed and you do not develop active infection in the future.
How long after taking TB medicine can you stay home?
For the first 2 to 4 weeks after starting the medicines, you may need to stay home to avoid spreading TB to others. Ask your health care provider when it is OK to be around other people. Your provider is required by law to report your TB to the local public health department.
How long do you have to take TB pills?
You need to take several different pills at different times of the day for 6 months or longer. The only way to get rid of the germs is to take your TB medicines the way your provider has instructed. This means taking all of your medicines every day.
How to cure MDR TB?
To cure MDR TB, healthcare providers must turn to a combination of second-line drugs, several of which are shown here. Second-line drugs may have more side effects, the treatment may last much longer, and the cost may be up to 100 times more than first-line therapy. MDR TB strains can also grow resistant to second-line drugs, ...
Is second line TB treatment more expensive than first line?
Second-line drugs may have more side effects, the treatment may last much longer, and the cost may be up to 100 times more than first-line therapy. MDR TB strains can also grow resistant to second-line drugs, further complicating treatment. Credit.
What is the new drug for TB?
Bedaquiline and Delamanid are new drugs. Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide, Thioamides, Cycloserine, Para-aminosalicylic acid, Streptomycin, and Clofazimine are possibly effective. Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, ...
Is kanamycin a second line drug?
Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above.
Is XDR TB resistant to isoniazid?
NIAID. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above. XDR TB strains may also be resistant to additional drugs, ...
What is XDR TB?
XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above.
What drugs target DNA?
Rifamycins, Oxazolidinones and Macrolides act on DNA. Tuberculosis drugs target various aspects of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biology, including inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or nucleic acid synthesis. For some drugs, the mechanisms of action have not been fully identified.
What test is used to test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just ...
What to do if chest X-ray shows tuberculosis?
If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria.
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
Can a TB test be wrong?
Results can be wrong. The TB skin test isn't perfect. Sometimes, it suggests that people have TB when they don't. It can also indicate that people don't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Can you have TB if you don't have it?
Sometimes, it suggests that people have T B when they don't. It can also indicate that people don 't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
What to do if you have a positive skin test?
If you've had a positive skin test, your doctor is likely to order a chest X-ray or a CT scan. This might show white spots in your lungs where your immune system has walled off TB bacteria, or it might reveal changes in your lungs caused by active tuberculosis.
How long does ethambutol last?
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
What is acebrophylline used for?
Acebrophylline is prescribed to reduce the irritation, swelling, and narrowing of the bronchial tubes in patients with asthma, severe or chronic bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)and tightness of the chest.
What is the drug used for tuberculosis?
Delamanid. Delamanid is an anti-tubercular drug prescribed in combination with bedaquiline for treating active multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in adults when other treatments fail or show no response.
What is terizidone used for?
Terizidone. Terizidone is a second-line antitubercular drug which is prescribed for the treatment of both pulmonary and extra pulmonary tuberculosis caused by resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis or M. Trade Names :
How many people are affected by TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, affects about one third (more than 12 million) of all people worldwide. In South Africa, the World Health Organization says TB has reached epidemic proportions. This chronic infectious disease, explains Dr Andries W Dreyer, Pathologist at the National Institute for Communicable ...
Where does TB manifest?
This chronic infectious disease, explains Dr Andries W Dreyer, Pathologist at the National Institute for Communicable Diseases’ Centre for Tuberculosis, usually manifests in the lungs (pulmonary TB).
How is TB spread?
TB is spread mainly through the air via droplets (aerosols) when infectious people talk, laugh, spit, sneeze or cough. “People nearby may inhale the sprayed droplets that contain millions of bacteria and become infected. It only takes one to ten bacteria to establish TB infection,” remarks Dr Dreyer. TB bacteria have stealthy ways of hiding inside ...
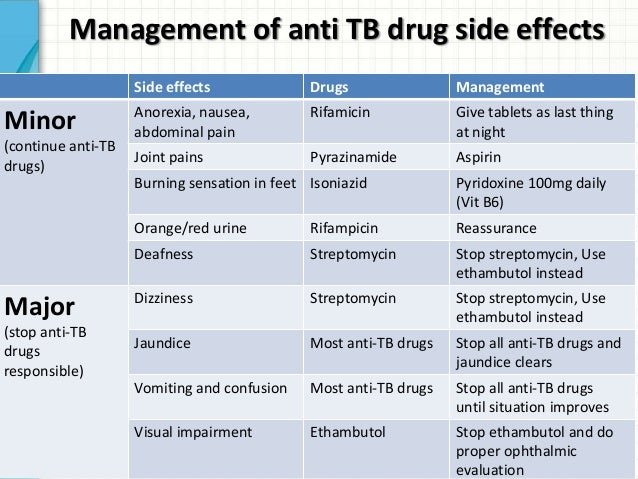
Can TB be treated with drugs?
Treating these resistant forms of TB is much more difficult; they don’t respond to treatment with the usual TB drugs. Doctors then have to resort to less effective medications that often cause severe side effects.
What is the first line of TB treatment?
Most commonly used TB drugs (known as first-line drugs) are Isoniazid (INH) and Rifampin (RIF). They are also combined in a specific treatment regimen with other drugs such as Pyrazinamide (PZN), Ethambutol (EMB) and Streptomycin (STR).
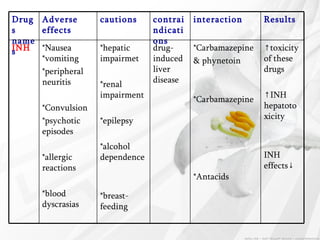
Can TB drugs cause weight loss?
Side effects of TB drugs. TB drugs unfortunately have side effects, some more serious than others. Irene Labuschagne, Dietitian at Stellenbosch University’s Nutrition Information Centre (NICUS), is mostly concerned about gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting and weight loss due to decreased appetite, ...
Does TB cause weight loss?
TB drugs unfortunately have side effects, some more serious than others. Irene Labuschagne, Dietitian at Stellenbosch University’s Nutrition Information Centre (NICUS), is mostly concerned about gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting and weight loss due to decreased appetite, although a dry mouth and sore throat are also often reported.