
The formula for ANOVA is F = variance caused by treatment/variance due to random chance. The ANOVA F value can tell you if there is a significant difference between the levels of the independent variable, when p <.05. So, a higher F value indicates that the treatment variables are significant.
Full Answer
What are the two sources of variation in an ANOVA?
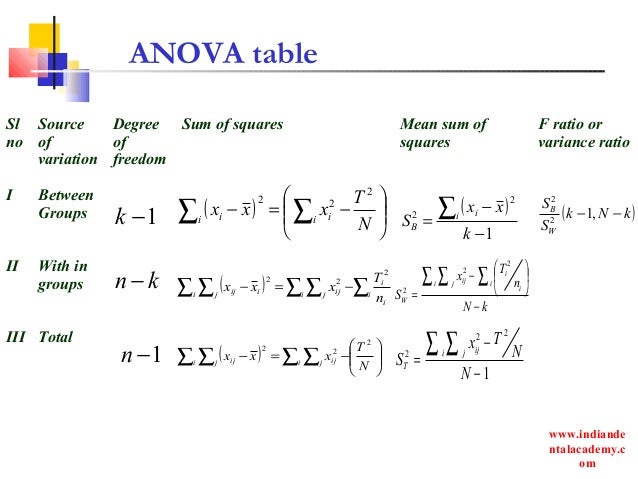
We can see that there are two different sources of variation that an ANOVA measures: Between Group Variation: The total variation between each group mean and the overall mean. Within-Group Variation: The total variation in the individual values in each group and their group mean.
What is the use of ANOVA?
ANOVA method is used to find out, if there is a difference between the mean values of the three groups. Like in all other Hypothesis Testing, the hypothesis of ANOVA is like:
What is analysis of variance (ANOVA)?
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a parametric statistical technique used to compare the data sets. This technique was invented by R.A. Fisher, hence it is also referred as Fisher’s ANOVA. It is similar techniques such as t-test and z-test, to compare means and also the relative variance between them.
What is the hypothesis of ANOVA?
ANOVA method is used to find out, if there is a difference between the mean values of the three groups. Like in all other Hypothesis Testing, the hypothesis of ANOVA is like: Null hypothesis: Mean of all the three methods are equal Alternate Hypothesis: There is a significant variation in mean in at least one of the methods

What is treatment variation?
The treatment variance is based on the deviations of treatment means from the grand mean, the result being multiplied by the number of observations in each treatment to account for the difference between the variance of observations and the variance of means.
What is the meaning of treatment in ANOVA?
In the context of an ANOVA, a treatment refers to a level of the independent variable included in the model.
What does between treatments variability signify in an ANOVA?
In ANOVA it is called the mean square between. For these data: Within-Treatment Variability: In addition to the between-treatments variability, there is variability within each treatment. The within treatments variability will provide a measure of the variability inside each treatment condition.
What is between treatment variability?
– Thus, the between-treatments variance simply measures how much difference exists between the di i treatment conditions. the differences have been caused by the treatment effects.
What is treatment and block in ANOVA?
Blocks are individuals who donated a blood sample. Treatments are different methods by which portions of each of the blood samples are processed.
What does treatment mean in statistics?
The term “statistical treatment” is a catch all term which means to apply any statistical method to your data. Treatments are divided into two groups: descriptive statistics, which summarize your data as a graph or summary statistic and inferential statistics, which make predictions and test hypotheses about your data.
What is number of treatments in ANOVA?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for comparing means of three or more variables. Background. If we have, say, 3 treatments to compare (A, B, C) then we would need 3 separate t-tests (comparing A with B, A with C, and B with C). If we had seven treatments we would need 21 separate t-tests.
What sources contribute to between treatments variance?
What sources of variability contribute to the within-treatment variability for a repeated-measures study? Variability (differences) within treatments is caused by individual differences and random, unsystematic differences.
What is good and bad variance in ANOVA?
As was said previously, the point of ANOVA is to compare how many times greater the variance due to the treatment (=good) is than the variance due to uncontrolled effects (=bad), so the F ratio is the statistic that represents this quantity.
When comparing more than two treatment means Why should you use an analysis of variance instead of using multiple t tests?
when comparing more than two treatment means, why should you use an analysis of variance instead of using several t tests? using several t tests increases the risk of experiment-wise Type I error.
How do you interpret ANOVA results?
Interpret the key results for One-Way ANOVAStep 1: Determine whether the differences between group means are statistically significant.Step 2: Examine the group means.Step 3: Compare the group means.Step 4: Determine how well the model fits your data.More items...
How do you interpret F value in ANOVA?
The F-value in an ANOVA is calculated as: variation between sample means / variation within the samples. The higher the F-value in an ANOVA, the higher the variation between sample means relative to the variation within the samples. The higher the F-value, the lower the corresponding p-value.
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
The fundamental principle in ANOVA is to determine how many times greater the variability due to the treatment is than the variability that we cannot explain.
What is an ANOVA test?
An ANOVA tests the null hypothesis that there is no difference among the mean values for the different treatment groups. Although it is possible to conduct an ANOVA by hand, no one in their right mind having access to computer software would do so. Setting up an ANOVA using RStudio is quite easy.
What are differences caused by experimental treatment?
Differences caused by an experimental treatment can be thought of as just one part of the overall variability of measurements that originates from many sources. If we measured the strength of the response of cockroach retinas when stimulated by light, we would get a range of measurements. Some of the variability in measurements could be due to ...
When is ANOVA used?
The type of ANOVA test used depends on a number of factors. It is applied when data needs to be experimental. Analysis of variance is employed if there is no access to statistical software resulting in computing ANOVA by hand. It is simple to use and best suited for small samples.
What are the two types of ANOVA?
There are two main types of ANOVA: one-way (or unidirectional) and two-way. There also variations of ANOVA. For example, MANOVA (multivariate ANOVA) differs from ANOVA as the former tests for multiple dependent variables simultaneously while the latter assesses only one dependent variable at a time.
What is the ANOVA test?
The ANOVA test is the initial step in analyzing factors that affect a given data set. Once the test is finished, an analyst performs additional testing on the methodical factors that measurably contribute to the data set's inconsistency.
What is ANOVA in statistics?
What is Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)? Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is an analysis tool used in statistics that splits an observed aggregate variability found inside a data set into two parts: systematic factors and random factors.
What is the difference between a one way and a two way ANOVA?
A two-way ANOVA is an extension of the one-way ANOVA. With a one-way, you have one independent variable affecting a dependent variable.
How does ANOVA work?
ANOVA groups differences by comparing the means of each group and includes spreading out the variance into diverse sources. It is employed with subjects, test groups, between groups and within groups .
What is the F-ratio of an ANOVA?
If no true variance exists between the groups, the ANOVA's F-ratio should equal close to 1. 1:01.
What is the ANOVA method?
ANOVA method is used to find out, if there is a difference between the mean values of the three groups. Like in all other Hypothesis Testing, the hypothesis of ANOVA is like: Null hypothesis: Mean of all the three methods are equal. Alternate Hypothesis: There is a significant variation in mean in at least one of the methods.
What are the different types of ANOVA?
ANOVA has multiple uses and there are various types that can be used for different purposes: 1 One-way ANOVA: Used to compare means of groups/populations using one factor. 2 Two-way ANOVA: Used to compare means of groups/populations using two factors. 3 Two-way ANOVA (Repeated): Used to compare means of groups/populations using two factors with interactions among the factors 4 Nested ANOVA: Used to compare means of groups/populations that can be sub-grouped and the interactions happen only within the sub-groups and not with other factors.
What is nested ANOVA?
Nested ANOVA: Used to compare means of groups/populations that can be sub-grouped and the interactions happen only within the sub-groups and not with other factors. Thus ANOVA can be used for various purposes. This article is just an introduction to ANOVA.
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
ANOVA has multiple uses and there are various types that can be used for different purposes: One-way ANOVA: Used to compare means of groups/populations using one factor. Two-way ANOVA: Used to compare means of groups/populations using two factors.
Can ANOVA be used for more than two means?
It is an advanced version of t – test. While t-test is used to compare two means, ANOVA can be used for more than two means.
When to use one way ANOVA?
Use a one-way ANOVA when you have collected data about one categorical independent variable and one quantitative dependent variable. The independent variable should have at least three levels (i.e. at least three different groups or categories). ANOVA tells you if the dependent variable changes according to the level of the independent variable.
What is an ANOVA variable?
ANOVA tells you if the dependent variable changes according to the level of the independent variable. For example: Your independent variable is social media use, and you assign groups to low, medium, and high levels of social media use to find out if there is a difference in hours of sleep per night. Your independent variable is brand of soda, and ...
What are the assumptions of ANOVA?
The assumptions of the ANOVA test are the same as the general assumptions for any parametric test: 1 Independence of observations: the data were collected using statistically-valid methods, and there are no hidden relationships among observations. If your data fail to meet this assumption because you have a confounding variable that you need to control for statistically, use an ANOVA with blocking variables. 2 Normally-distributed response variable: The values of the dependent variable follow a normal distribution. 3 Homogeneity of variance: The variation within each group being compared is similar for every group. If the variances are different among the groups, then ANOVA probably isn’t the right fit for the data.
What is the difference between a one way and a two way ANOVA?
The only difference between one-way and two-way ANOVA is the number of independent variables. A one-way ANOVA has one independent variable, while a two-way ANOVA has two. One-way ANOVA: Testing the relationship between shoe brand (Nike, Adidas, Saucony, Hoka) and race finish times in a marathon.
What test is used in ANOVA?
ANOVA uses the F-test for statistical significance. This allows for comparison of multiple means at once, because the error is calculated for the whole set of comparisons rather than for each individual two-way comparison (which would happen with a t-test).
What is the null hypothesis in ANOVA?
The null hypothesis (H 0) of ANOVA is that there is no difference among group means. The alternate hypothesis (H a) is that at least one group differs significantly from the overall mean of the dependent variable. If you only want to compare two groups, use a t-test instead.
What command to use to run an ANOVA?
After loading the dataset into our R environment, we can use the command aov () to run an ANOVA. In this example we will model the differences in the mean of the response variable, crop yield, as a function of type of fertilizer.
What Is Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)?
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is an analysis tool used in statistics that splits an observed aggregate variability found inside a data set into two parts: systematic factors and random factors. The systematic factors have a statistical influence on the given data set, while the random factors do not. Analysts use the ANOVA test to determine the infl...
The Formula For Anova Is
- F=MSTMSEwhere:F=ANOVA coefficientMST=Mean sum of squares due to treatmentMSE=Mean…
What Does The Analysis of Variance Reveal?
- The ANOVA test is the initial step in analyzing factors that affect a given data set. Once the test is finished, an analyst performs additional testing on the methodical factors that measurably contribute to the data set's inconsistency. The analyst utilizes the ANOVA test results in an f-test to generate additional data that aligns with the proposed regressionmodels. The ANOVA test all…
Example of How to Use Anova
- A researcher might, for example, test students from multiple colleges to see if students from one of the colleges consistently outperform students from the other colleges. In a business application, an R&D researcher might test two different processes of creating a product to see if one process is better than the other in terms of cost efficiency. The type of ANOVA test used de…
One-Way Anova Versus Two-Way Anova
- There are two main types of ANOVA: one-way (or unidirectional) and two-way. There also variations of ANOVA. For example, MANOVA (multivariate ANOVA) differs from ANOVA as the former tests for multiple dependent variables simultaneously while the latter assesses only one dependent variable at a time. One-way or two-way refers to the number of independent variable…