Medication
What patients and families should know about sepsis, and how hospice can help Patients are eligible for hospice care when a physician makes a clinical determination that life expectancy is six months or less if the condition or disease runs its expected course.
Therapy
- The patient's fundamental health � infants, the elderly and those with a weakened immune system are most vulnerable � will influence how well their body can combat and respond to ...
- The severity and duration of the sepsis attack
- The promptness with which their condition is recognised and treated
How long can a person live with untreated sepsis?
the actual acute illness may take anywhere from 3-10 days to resolve on average, but can also involve ICU ... Read More Long time: Sepsis is a systemic illness caused by an out of control infection. Usually the doctors are very good at killing the organism that causes the infecti...
What are the chances of Surviving Sepsis?
Molecular model of the broad-spectrum antibiotic fosfomycin (C3.H7.O4.P), also known as phosphomycin. This drug is used in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Credit: Science Photo Library/Alamy Stock A safe dose of fosfomycin, can be used to treat babies with neonatal sepsis, a paper published in Archives of Diseases in Childhood reports.
How long to cure sepsis?
How do you cure sepsis?

What is the main treatment for sepsis?
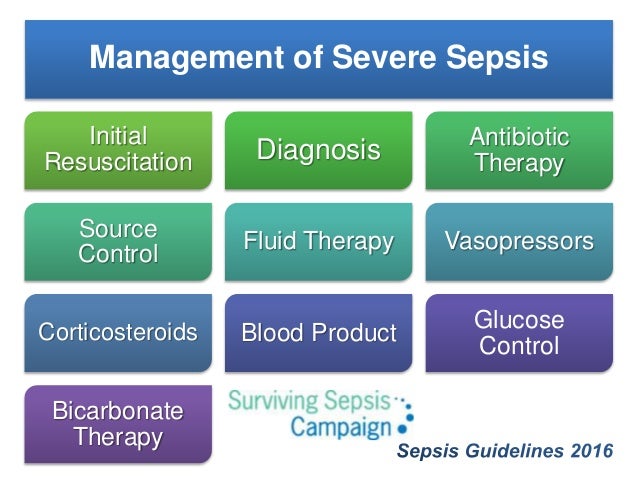
Doctors and nurses should treat sepsis with antibiotics as soon as possible. Antibiotics are critical tools for treating life-threatening infections, like those that can lead to sepsis.
What is sepsis and how is it cured?
Blood poisoning is an infection present in the blood, while sepsis refers to the body's response to any infection, wherever it is. Once a person is diagnosed with sepsis, she will be treated with antibiotics, IV fluids and support for failing organs, such as dialysis or mechanical ventilation.
What is the best antibiotic for sepsis?
The majority of broad-spectrum agents administered for sepsis have activity against Gram-positive organisms such as methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, or MSSA, and Streptococcal species. This includes the antibiotics piperacillin/tazobactam, ceftriaxone, cefepime, meropenem, and imipenem/cilastatin.
What is sepsis and is it treatable?
Sepsis needs treatment in hospital straight away because it can get worse quickly. You should get antibiotics within 1 hour of arriving at hospital. If sepsis is not treated early, it can turn into septic shock and cause your organs to fail.
How long is recovery from sepsis?
On average, the recovery period from this condition takes about three to ten days, depending on the appropriate treatment response, including medication.
What are the 5 signs of sepsis?
Sepsis SymptomsFever and chills.Very low body temperature.Peeing less than usual.Fast heartbeat.Nausea and vomiting.Diarrhea.Fatigue or weakness.Blotchy or discolored skin.More items...•
What is the first line treatment for sepsis?
Background: The Surviving Sepsis Campaign strongly recommends that intravenous antibiotic therapy should be started as early as possible, ideally within the first hour of recognition of severe sepsis or septic shock.
Can oral antibiotics cure sepsis?
Antibiotics alone won't treat sepsis; you also need fluids. The body needs extra fluids to help keep the blood pressure from dropping dangerously low, causing shock.
How quickly do antibiotics work for sepsis?
Primary Outcome: Time to Antibiotic Administration The overall median time (and IQR) from onset to administration of antibiotics was 4.00 hours (IQR 1.80–6.45 h). Of the 100 patients, only 6% received antibiotics within 1 h of onset of severe sepsis or septic shock.
How long is a hospital stay with sepsis?
The average length of stay for severe sepsis hospitalizations decreased by approximately three days, from 14 days to 11 days (Figure 1). The median charge per day (unadjusted for inflation) for severe sepsis hospitalizations increased by 16.2 percent (Figure 1).
What are the chances of surviving sepsis?
Sepsis Survival Rates While most people recover from mild sepsis, the mortality rate for septic shock is approximately 40%. Additionally, a person who survives severe sepsis is at a higher risk of getting future infections.
Can you survive sepsis?
Sepsis may cause abnormal blood clotting that results in small clots or burst blood vessels that damage or destroy tissues. Most people recover from mild sepsis, but the mortality rate for septic shock is about 40%. Also, an episode of severe sepsis places you at higher risk of future infections.
How to treat sepsis?
It needs to be treated as such. In other words, sepsis should be treated as quickly and efficiently as possible as soon as it has been identified. Treatment includes rapid administration of antibiotics and fluids.
What is the best fluid for sepsis?
Several types of fluid. While there are several types of IV fluids, some are standard in treating sepsis. Normal saline is one commonly given fluid. It is a crystalloid fluid. These are fluids that contain minerals, such as sodium, and are water-soluble, or dissolve in water. These add fluid to the blood system.
What is the first line of antibiotics?
Physicians prescribe antibiotics (usually more than one type) based on the type of infection. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are the first-line medications. These antibiotics work against several of the more common bacteria. These are intravenous antibiotics so they can get into the blood system quickly and efficiently.
Why do you need a special cap on a blood line?
It allows blood draws directly from the line. The line and cap must be monitored closely because the pressure caused by the blood pumping from the heart can result serious bleeding if the line becomes undone.
Do corticosteroids help with sepsis?
Corticosteroids – Although doctors don’t know why corticosteroids work for some patients who have sepsis and not others, they can be helpful. Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation in the body and depress the immune system, making it less active.
Can septic shock cause hallucinations?
Patients with severe sepsis or septic shock who are treated in an intensive care unit (ICU) can experience issues related to the illness and medications, the lack of sleep, and the overstimulation of having people and noise around them 24 hours a day. This can result in agitation, confusion, even hallucinations.
What causes sepsis in the body?
Bacterial infections are the most common cause of sepsis. Sepsis can also be caused by fungal, parasitic, or viral infections. The source of the infection can be any of a number of places throughout the body. Common sites and types of infection that can lead to sepsis include: The abdomen: An infection of the appendix ( appendicitis ), ...
What is the most common cause of sepsis?
Bacterial infections are the most common cause of sepsis. Sepsis can be life-threatening. Overview. Symptoms and Causes. Diagnosis and Tests. Management and Treatment. Prevention. Resources. Sepsis.
What is the medical term for a person who has an infection and is a life threatening condition?
What is sepsis ? Sepsis is a medical emergency caused by the body's response to an infection and can be life-threatening. Sepsis is the consequence of widespread inflammation (swelling) in the body.
How do you know if you have sepsis?
Because of the many sites on the body from which sepsis can originate, there are a number of symptoms. The most prominent are: Fast heart rate. Fever or hypothermia (very low body temperature) Shaking or chills. Warm or clammy/sweaty skin.
Why do you need IV fluids?
IV (intravenous or in the vein) fluids are administered to prevent blood pressure from dropping too low. In some cases, the patient may need vasopressor medications (which tighten blood vessels) to reach an adequate blood pressure.
Can bacteria cause sepsis?
The skin: Bacteria can enter skin through wounds or skin inflammation, or through the openings made with intravenous (IV) catheters (tubes inserted into the body to give or drain fluids). Conditions such as cellulitis (inflammation of the skin's connective tissue) can also cause sepsis.
Can you get sepsis if you are 65?
Sepsis can affect anyone, but those at particular risk include: The very old ( older than 65 years old) or very young or pregnant women. People with pre-existing infections or medical conditions such as diabetes, lung disease, cancer and kidney disease. People with weakened immune systems.
How to treat sepsis quickly?
Research shows that rapid, effective sepsis treatment includes: Giving appropriate treatment, including antibiotics . Maintaining blood flow to organs. Sometimes surgery is required to remove tissue damaged by the infection. Doctors and nurses should treat sepsis with antibiotics as soon as possible.
What are the symptoms of sepsis?
Fever. Low blood pressure. Increased heart rate. Difficulty breathing. Doctors also perform lab tests that check for signs of infection or organ damage. Doctors also perform specific tests to identify the germ that caused the infection that led to sepsis.
Can antibiotics help with sepsis?
Doctors and nurses should treat sepsis with antibiotics as soon as possible. Antibiotics are critical tools for treating life-threatening infections, like those that can lead to sepsis. However, as antibiotic resistance grows, infections are becoming more difficult to treat.
What is the best medicine for sepsis?
Broad-spectrum antibiotics may fight infections caused by bacteria early on. Once your doctor knows what’s causing your sepsis, they can give you medicine that targets that specific germ. Often, doctors prescribe vasopressors (which make your blood vessels narrow) to improve blood pressure.
What is the infection that causes sepsis?
An infection of the bone, called osteomyelitis, could lead to sepsis. In people who are hospitalized, bacteria may enter through IV lines, surgical wounds, urinary catheters, and bed sores. Sepsis is more common in people who:
What causes sepsis?
Sepsis Causes and Risk Factors. Bacterial infections are most often to blame for sepsis. But it can also happen because of other infections. It can begin anywhere bacteria, parasites, fungi, or viruses enter your body, even something as small as a hangnail.
What to do if you have a severe infection?
If your case is severe, you might need other types of treatment, like a breathing machine or kidney dialysis. Or you may need surgery to drain or clean out an infection.
Can sepsis cause a drop in blood pressure?
In severe cases, sepsis causes a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Doctors call this “ septic shock .”. It can quickly lead to organ failure, such as your lungs , kidneys, and liver. This can be deadly.
What is the best way to get care for a person with sepsis?
Get medical care IMMEDIATELY either in-person, or at minimum, through telehealth services.
What is the body's extreme response to an infection?
Act Fast. Sepsis is the body’s extreme response to an infection. It is a life-threatening medical emergency. Sepsis happens when an infection you already have triggers a chain reaction throughout your body.
Can you spread sepsis to other people?
You can’t spread sepsis to other people. However, an infection can lead to sepsis, and you can spread some infections to other people. Bacterial infections cause most cases of sepsis. Sepsis can also be a result of other infections, including viral infections, such as COVID-19 or influenza. Sepsis happens when….
When did sepsis become a global health priority?
On May 2017, the World Health Assembly (WHA) and World Health Organization (WHO) made sepsis a global health priority and adopted a resolution that urged the 194 United Nations Member States to improve the prevention, diagnosis, and management of sepsis5.
What is the World Health Assembly's resolution on sepsis?
To improve sepsis management and reduce its burden, in 2017, the World Health Assembly and World Health Organization adopted a resolution that urged governments and healthcare workers to implement appropriate measures to address sepsis.
Is sepsis a global health problem?
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by infection and represents a substantial global health burden. Recent epidemiological studies showed that sepsis mortality rates have decreased, but that the incidence has continued to increase.
Is lactate retained in sepsis?
First, lactate was not retained in the sepsis definition. Hence, by the Sepsis-3 definitions, patients with an increased lactate level but no hypotension (or compensated septic shock) can be missed.
Is lactate level a component of the definitions of septic shock?
That is, the lactate level is not a component of the definitions until the patient becomes hypotensive.
Does sepsis increase survival?
However, early detection of sepsis with timely, appropriate interventions increases the likelihood of survival for patients with sepsis. Also, performance improvement programs have been associated with a significant increase in compliance with the sepsis bundles and a reduction in mortality.

Antibiotics
IV Fluids
Several Types of Fluid
Additional Possible Treatments and Equipment
Specialist to consult
Extracorporeal Therapies
Special Types of Ivs
Medications
Equipment