Healthline.com
1. Hot compress...
2. Tea tree oil...
3. Apple cider vinegar...
4. Aloe vera...
5. Castor oil...
6. Witch hazel...
7. Honey...
Learn More...Trueremedies.com
1. Breast Massage...
2. Enhance Iodine-Rich Foods...
3. The Choice Of Bra...
4. Hot Compresses...
5. Cabbage...
6. Cold Compresses...
7. Do Not Drink Tea And Caffeinated Beverages...
8. Frequently Eat Vegetables And Fruits...
Learn More...Homeremedyshop.com
1. Tea Tree Oil...
2. Aloe Vera...
3. Castor Oil...
4. Witch Hazel...
5. Lugol's Iodine...
6. Apple Cider Vinegar...
7. Black Bloodroot Drawing Salve...
8. Hot Compress...
Learn More...What is the most effective treatment for mucoid cysts?
To use
- Heat clean water to a warm or hot temperature, not boiling.
- Wait for the water to cool to a tolerable, but hot, temperature for skin contact.
- Dampen a clean cloth with the water and apply to the cyst for 20 to 30 minutes.
- Repeat a few times each day.
Is surgery necessary for treatment of renal sinus cyst?
When symptoms occur due to the cyst enlargement, treatment to shrink the cyst is required. The doctor may recommend you take surgery by injecting the cyst with some processed medical material that will be absorbed by lymphatic system.
What causes sinus retention cyst?
- difficulty breathing;
- headaches mainly localized in the forehead and the nose;
- the regular incidence of sinusitis;
- the pressure in the eye;
- a sharp pain that appears when strong changes of atmospheric pressure (e.g., flight, water immersion).
What are the symptoms of a sinus cyst?
rapid deterioration of vision; the feeling of stretching (pressure) in the sphenoid sinuses of the nose; nausea, vomiting, dizziness (especially when reading); headaches with localization in the occipital region. These sphenoid sinus cyst symptoms can be permanent or appear periodically.

What causes cysts on sinuses?
Nasal polyps are soft, painless, noncancerous growths on the lining of your nasal passages or sinuses. They hang down like teardrops or grapes. They result from chronic inflammation and are associated with asthma, recurring infection, allergies, drug sensitivity or certain immune disorders.
How common are cysts in sinuses?
Retention cysts in paranasal sinuses are common, incidental finding at radiographic examinations and are reported to occur in between 1.4% to 9.6% of the general population1.
What is a sinus cyst called?
Mucoceles are benign, locally expansile paranasal sinus masses. They are cyst-like structures lined by the mucoperiosteum of the involved sinus [1, 2]. Mucoceles are most commonly found in the frontal sinus, with the ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses involved less frequently.
How do you know if you have a cyst in your sinus?
pain when sitting or standing. swelling of the cyst. reddened, sore skin around the area. pus or blood draining from the abscess, causing a foul odor.
Is a sinus cyst serious?
Typically, a maxillary sinus retention cyst is not dangerous, although there have been cases where a cyst has ruptured after head trauma.
Are sinus cysts cancerous?
About nasal and sinus tumors Nasal and sinus tumors are benign or cancerous tumors that occur in the nose or sinuses. Cancerous nasal cavity or sinus tumors are rare, with only about 2,000 being diagnosed in the United States each year.
Can a sinus cyst burst?
Maxillary sinus retention cysts are common incidental findings on imaging and are usually of no clinical significance. Retention cysts that resolve on follow-up imaging are thought to spontaneously rupture, but there is rarely any clinical history or imaging to support this theory.
Can sinus cyst cause eye problems?
Patients with cysts of the maxillary sinus may present to the ophthalmologist with proptosis, enophthalmos, diplopia, ptosis, epiphora, and, rarely, decreased visual acuity.
How do they remove a cyst from a maxillary sinus?
Generally, treatment includes enucleation of the cyst and/or surgical excision, including endoscopic observation in some cases. Long-term multidisciplinary postoperative patient observation should be performed, especially in cases with high recurrence.
Is a sinus cyst the same as a polyp?
Polyps are the most common masses found in the nose. They are totally different in terms of ori- gin, as well as clinical significance, relative to “maxillary sinus polyps,” which really should be called mucous retention cysts. Nasal polyps carry an extremely low profile, but severely affect patients' quality-of-life.
What size is a large sinus cyst?
The mean cyst size was 1.56 cm (range, 0.5-4.44 cm), and cysts were most commonly located inferiorly within the sinus. The specific location of the maxillary sinus RCs was as follows: In only 1 case was the cyst itself found to be obstructing the maxillary infundibulum.
What is a sinus cyst?
Nasal cyst (sinus cyst): types of cysts and methods of treatment. Nasal cyst or nasal cyst is a pathological formation in the nasal cavity. It’s considered abnormal, but not malignant. A sinus cyst looks like a small container that is filled with a liquid substance. Typically, cyst formation occurs in the paranasal sinus.
How to treat cysts in the wall?
The most popular treatment for cysts is puncturing. The surgeon pierces the wall of the cyst with a thin needle and pumps out a purulent substance. However, this method has only a temporary effect. Puncturing a cyst for some time relieves a person from pain.
How do you know if you have a cyst in your nose?
As the pathological formation increases, the symptoms become more visible and obvious: A person begins to feel a foreign body in the nasal cavity; Difficult breathing through the nose.
How to remove cysts from a capsule?
The method is suitable for removing small formations (up to 4 mm). During the operation, the burning area is disinfected and sealed, which eliminates the risk of severe bleeding.
Why do cysts form in upper row?
Sometimes the formation of a cyst is affected by the roots of the teeth of the upper row, because they are close to the source of the disease; Non-anatomical structure of the nasopharynx. Congenital or acquired defects of the nasal septum causes an unusual anomaly: a different volume of air passes through each nostril.
How to treat a nasal cyst?
If the formation has a small size (up to 1 cm) and doesn’t emit liquid substances, then the attending physician usually prescribes standard treatment methods: regular examination, tablets, sprays, drops.
What is the bladder made of?
Bladder or sinus tank is filled with secretory fluid. Its walls are made up of epithelial cells. The appearance of cells is a consequence of mucosal edema due to inflammatory processes; False nasal cyst. It’s mainly formed due to adverse factors.
What is sinus cyst?
Prophylaxis of the sinus sinus cyst suggests fast and effective elimination of all kinds of rhinitis, sinusitis, as well as avoiding the development of polyps of the nose and paranasal cavities. It is these diseases that contribute to the congestion of the nasal mucosa, which leads to blockage of the mucus channels.
What is the cyst of the maxillary sinus?
The cyst of the maxillary sinus is a benign, spherical formation filled with fluid. The wall of the cyst is two-layer, the inner layer of which is represented by the epithelium, which produces mucus. [ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ], [ 6]
What is the most accurate way to diagnose sinus cysts?
One of the most accurate variants of diagnostics of the sinus sinus cyst is CT, magnetic resonance imaging of sinuses, endoscopy of maxillary sinuses. From the known methods of determining the cyst of the maxillary sinus, the contrast fluid is also introduced into the place of the presumed formation of the cyst - hymorography.
How to treat sinus cysts?
The most common method of treatment of the sinus sinus cyst is surgical surgical intervention, that is, removal of the cyst. If there is no need for such an intervention, and the disease itself does not create inconvenience to the person, then conservative non-surgical treatment is performed.
What is the most common retention cyst?
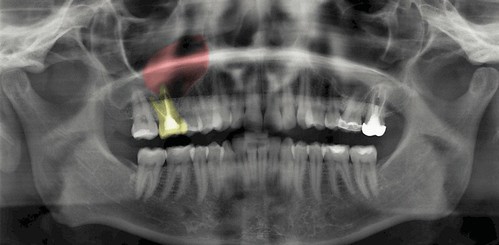
Retreatment cyst of the maxillary sinus. The most common is the retention cyst, the so-called true cyst. Her nature helps to clarify only the histological examination. A characteristic location is the maxillary sinus, namely its lower wall. It consists of a cylindrical epithelium and is clearly visible on X-rays.
What is the medical term for the mammary gland?
Diseases of the mammary glands (mammology) Diseases of the joints, muscles and connective tissue (rheumatology) Cancer (oncology) Diseases of the immune system (immunology) Diseases of the blood (hematology) Diseases of the heart and blood vessels (cardiology) Mental health (psychiatry) Injuries and poisonings.
Is maxillary sinus cyst a tumor?
It should be noted that the cyst of the maxillary sinus is a rather "harmless" disease. This is not an oncology, not a tumor, but just a fluid accumulation in the bladder.
What is incidental finding?
An incidental finding means that the imaging test was ordered for another clinical purpose and the retention cyst was discovered by chance. Even though maxillary sinus retention cysts are relatively common, many people don’t know they have them.
What is a retention cyst?
A maxillary sinus retention cyst is a lesion that develops on the inside of the wall of the maxillary sinus. They are often dome-shaped, soft masses that usually develop on the bottom of the maxillary sinus. Fortunately, a retention cyst of the maxillary sinus is a benign lesion, or non-cancerous. Still, if you have a maxillary sinus retention ...
Why are paranasal sinuses called that?
They are known as “paranasal sinuses” because they are all located around the nose and connected to the nasal cavity. The different pairs of paranasal sinuses are named for the bones where they are located. The largest pair of sinuses are the maxillary sinuses on either side of the nose, near the cheekbones. The other pairs of sinuses are the:
How to remove cysts from sinuses?
Then, the cyst may be removed through a minor endoscopic sinus surgery that includes either enucleation, which is removing the entire lesion without rupturing it, or using curettage, which removes the cyst with a special loop-shaped instrument.
How many ethmoid sinuses are there?
They are small and there are six ethmoid sinuses in total. Frontal sinuses: These are near the forehead above the eyes. Sphenoid sinuses: These are deeper in the skull than the other pairs of sinuses, located behind the eyes.
What are the symptoms of sinus pressure in the back of the teeth?
Symptoms may include: Facial pain, especially over the cheek and upper teeth. Tenderness or pain in the back teeth. Headache.
Can sinus retention cysts be recurring?
Sometimes, recurring or chronic sinus infections, or sinusitis of the maxillary sinuses, are related to the development of maxillary sinus retention cysts, although you can develop lesions without sinusitis.
What is the paranasal sinus?
The paranasal sinuses are air-filled cavities covered by a thin mucous membrane that adhere to the periosteum. Retention cysts in paranasal sinuses are common, incidental finding at radiographic examinations and are reported to occur in between 1.4% to 9.6% of the general population1.
Is mucous retention cyst asymptomatic?
Most mucous retention cysts (MRC) are asymptomatic2; however, when they cause symptoms like headache, periorbital or facial pain, repeated infections of the paranasal sinuses, and/or nasal obstruction, surgical treatment may be necessary3. In the literature, retention cysts have only been reported in the maxillary sinuses (MS).
What to do if your sinuses are swollen?
Your doctor may prescribe drugs to treat conditions that contribute to long-term swelling in your sinuses or nasal passages. These may include antihistamines to treat allergies and antibiotics to treat a chronic or recurring infection.
What is the procedure to remove polyps from the sinuses?
Your surgeon may also enlarge the openings leading from your sinuses to your nasal passages. Endoscopic surgery is usually performed as an outpatient procedure.
How to treat a large nasal polyp?
Drug treatments may include: Nasal corticosteroids. Your doctor is likely to prescribe a corticosteroid nasal spray to reduce swelling and irritation. This treatment may shrink the polyps or eliminate them completely.
What is the best treatment for nasal polyps?
If you have nasal polyps and chronic sinusitis, your doctor may give you an injection of a medication called dupilumab (Dupixent) to treat your condition. This medication may reduce the size of the nasal polyps ...
What is CT scan for sinuses?
Images obtained with computerized tomography (CT) can help your doctor pinpoint the size and location of polyps in deeper areas of your sinuses and evaluate the extent of swelling and irritation (inflammation). These studies may also help your doctor rule out other possible blockages in your nasal cavity, such as structural abnormalities ...
What is the test for nasal polyps?
The standard diagnostic test for cystic fibrosis is a noninvasive sweat test, which determines whether your child's perspiration is saltier ...
What is the best test for cystic fibrosis?
The standard diagnostic test for cystic fibrosis is a noninvasive sweat test, which determines whether your child's perspiration is saltier than most people's sweat is. Blood test. Your doctor may test your blood for low levels of vitamin D, which are associated with nasal polyps.
