Medication
Apr 21, 2021 · Native valve endocarditis treatment typically requires 2 to 6 weeks of antibiotics. Initial antibiotic therapy for critically ill patients before cultures and sensitivities: [3] Ampicillin + gentamicin + flucloxacillin or oxacillin
Procedures
You can reduce the risk of bacterial endocarditis by practicing good oral hygiene habits every day. Good oral health is... Seeking professional dental care every six months Regularly brushing and flossing your teeth Making sure dentures fit properly …
Nutrition
Jun 26, 2015 · Endocarditis Medications Most cases of endocarditis are treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics are medicines to rid your body of the infection. They'll clear all the germs from your heart and heart...
What happens if endocarditis is not treated?
Jul 16, 2021 · Treatment of infective endocarditis. Infective endocarditis is a potentially lethal disease and requires prolonged antibiotic therapy. The aim of antibiotic therapy is to eradicate infection which includes sterilization of the vegetations. But there are certain challenges in the sterilization of vegetations.
How serious is endocarditis?
Nov 14, 2020 · You can take the following steps to help prevent endocarditis: Know the signs and symptoms of endocarditis. See your doctor immediately if you develop any signs or symptoms,... Take care of your teeth and gums. Brush and floss your teeth and gums often, and have regular dental checkups. Good... ...
Is endocarditis life threatening?
Aug 16, 2021 · When endocarditis is caused by a bacterial infection, it usually is treated with four to six weeks of antibiotics. The type of antibiotic and the length of therapy depend on the results of the blood cultures. Antibiotic treatment is given intravenously (through a vein). Treatment is almost always started while you are in the hospital.
How do you test for endocarditis?
May 15, 2012 · Antibiotic treatment of infectious endocarditis depends on whether the involved valve is native or prosthetic, as well as the causative microorganism and its antibiotic susceptibilities. Common...

What is the first line treatment for endocarditis?
Initial empiric therapy in patients with suspected endocarditis should include vancomycin or ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn) plus an aminoglycoside (plus rifampin in patients with prosthetic valves). Valve replacement should be considered in selected patients with infectious endocarditis.May 15, 2012
What IV antibiotics are used for endocarditis?
Native valve endocarditis (NVE) has often been treated with penicillin G and gentamicin for synergistic coverage of streptococci. Patients with a history of IV drug use have been treated with nafcillin and gentamicin to cover for methicillin-sensitive staphylococci.Jan 21, 2021
How long is antibiotic treatment for endocarditis?
The duration of treatment can range from 2 to 6 weeks. The American Heart Association 2015 Adult Infective Endocarditis guidelines and European Society of Cardiologists 2015 management of infective endocarditis guidelines serve as the basis for the following recommendation.Apr 21, 2021
Can endocarditis be treated with oral antibiotics?
Patients with endocarditis caused by common bacteria can be treated effectively and safely with oral antibiotics once they have been stabilized on an intravenous course of therapy, data from the POET trial suggest.Sep 4, 2018
Which antibiotic is best for endocarditis?
Treatment with aqueous penicillin or ceftriaxone is effective for most infections caused by streptococci. A combination of penicillin or ampicillin with gentamicin is appropriate for endocarditis caused by enterococci that are not highly resistant to penicillin.Mar 15, 2000
Can you fully recover from endocarditis?
In many cases of endocarditis, antibiotics alone can cure the infection. However, in about 25-30 percent of patients with IE, surgery is needed during the early acute phase of infection due to severe valve leakage or failure to control the infection with antibiotics.Jul 19, 2019
What happens if antibiotics don't work for endocarditis?
If germs or bacteria from other parts of your body, such as your mouth, spread through your blood and attach to this lining, it causes endocarditis. If the infection isn't treated with antibiotics or surgery, it can do permanent damage and can even be deadly.Aug 7, 2020
What is the most common cause of endocarditis?
Endocarditis is usually caused by an infection. Bacteria, fungi or other germs from another part of your body, such as your mouth, spread through your bloodstream and attach to damaged areas in your heart. If it's not treated quickly, endocarditis can damage or destroy your heart valves.Nov 14, 2020
When does endocarditis require surgery?
Standard indications for surgery are severe heart failure, severe valve dysfunction, prosthetic valve infection, invasion beyond the valve leaflets, recurrent systemic embolization, large mobile vegetations, or persistent sepsis despite adequate antibiotic therapy for more than 5-7 days.
Is amoxicillin used for endocarditis?
There was 1 relapse of streptococcal prosthetic valve endocarditis 8 weeks after oral treatment, but this responded to conventional intravenous therapy. Oral amoxycillin is effective in uncomplicated streptococcal endocarditis, and should not be used with prosthetic valve infections.
How do doctors test for endocarditis?
Echocardiogram. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to produce images of your heart while it's beating. This test shows how your heart's chambers and valves are pumping blood through your heart. Your doctor may use two different types of echocardiograms to help diagnose endocarditis.Nov 14, 2020
Can azithromycin treat endocarditis?
Azithromycin is effective in preventing experimental streptococcal endocarditis, but against MRSA it is less effective than vancomycin. Azithromycin (AZM) differs from other macrolide antibiotics in that it has unusual pharmacokinetics characterized by rapid tissue penetration with simultaneous low levels in serum (5).
What does an echocardiogram show?
Echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) may show growths (vegetations on the valve), abscesses (holes), new regurgitation (leaking) or stenosis (narrowing), or an artificial heart valve that has begun to pull away from the heart tissue.
How long does it take for an IV antibiotic to work?
IV antibiotics is usually given for as long as 6 weeks to cure of the infection. Symptoms are monitored throughout therapy and blood cultures are repeated to determine the effectiveness of treatment. If heart valve and heart damage has occurred, surgery may be required to fix the heart valve and improve heart function.
What is a blood culture?
Blood cultures are blood tests taken over time that allow the laboratory to isolate the specific bacteria that is causing your infection. Blood cultures must be taken before antibiotics are started to secure the diagnosis.
Where can bacteria be found?
Normally, bacteria can be found in the mouth, on the skin, in the intestines, respiratory system, and in the urinary tract. Some of these bacteria may be able to get into the bloodstream when eating, during teeth brushing and when passing stools and cause endocarditis.
What is a dental procedure?
All dental procedures that involve manipulation of gingival tissue or the periapical region of teeth, or perforation of the oral mucosa. Procedures of the respiratory tract or infected skin, tissues just under the skin, or musculoskeletal tissue. Link to Prevention of Bacterial Endocarditis Wallet Card.
Can endocarditis be prevented?
Not all endocarditis can be prevented. Call your doctor if you have symptoms of an infection (See signs of infection listed above). Do not wait a few days until you have a major infection to seek treatment. Colds and the flu do not cause endocarditis.
Can antibiotics be used for bacterial endocarditis?
Only the people who have the highest risk for bacterial endocarditis will reasonably benefit from taking preventive antibiotics before certain procedures. The highest risk group for bacterial endocarditis includes those with: An artificial (prosthetic) heart valve, including bioprosthetic and homograft valves.
How to treat endocarditis?
Surgery for endocarditis is often suggested: 1 If small chunks of vegetation (blood clots caused by the infection) are breaking off and causing strokes 2 If the endocarditis is caused by a fungus, because fungal infections are harder to treat than bacterial infections 3 If the infection is not clearing with antibiotics, or if the bacteria causing the infection have become resistant to antibiotics 4 If the infection has damaged the heart valves 5 If you've developed congestive heart failure, which occurs when fluid builds up in and around the heart and lungs because blood doesn't pump properly though the heart (congestive heart failure may be due to damaged heart valves)
What is the treatment for infective endocarditis?
Treatment options for infective endocarditis generally include drugs and surgeries. Endocarditis, also called infective endocarditis, is a bacterial or fungal infection of the inner lining of the heart or heart valves. Endocarditis can be life threatening, but most people recover with prompt treatment. Infective endocarditis is generally treated ...
How long does it take for endocarditis to clear?
They'll clear all the germs from your heart and heart valves. You'll get antibiotics for two to six weeks through an intravenous (IV) tube inserted into a vein.
Can antibiotics cause endocarditis?
Starting antibiotic treatment early can reduce the risk of complications from endocarditis. Even with antibiotics, endocarditis can cause damage to the heart or heart valves. Surgery may be required to repair the damage. Your doctors may also recommend surgery to clear up the infection or to replace heart valves that were badly damaged by ...
Can endocarditis be treated with antibiotics?
Endocarditis can be life threatening, but most people recover with prompt treatment. Infective endocarditis is generally treated with antibiotics, but some people with endocarditis may also need heart surgery. You'll likely have a team of doctors monitoring you're progress, including: A cardiologist (heart doctor) A heart surgeon.
What causes endocarditis?
Causes of Endocarditis. The bacteria that live in your mouth, throat or other parts of your body, such as your skin or your gut, can sometimes cause serious infections like endocarditis. However, other conditions, traits or habits may also raise your risk for the disease.
How do you know if you have endocarditis?
Endocarditis may develop slowly or rapidly depending on what germs are causing the infection, your immunity, and whether you have any underlying heart problems. Endocarditis signs and symptoms can vary from person to person. Common symptoms include: Fatigue. Flu-like symptoms. Blood in your urine. Chest pain.
What is the inner lining of the heart called?
The endocardium is the inner lining of the heart. Endocarditis is an infection of this inner lining. Endocarditis generally occurs when bacteria, fungi or other germs from the environment or another part of your body, such as your mouth, spread through your bloodstream and attach to heart valves. If not treated quickly, endocarditis can ...
What is the name of the disease that causes a person to have a heart valve?
Infectious (bac terial) endocarditis: This type of endocarditis is characterized by an infection caused by bacteria or fungi that enter the bloodstream and settle in the heart lining, a heart valve or a blood vessel. This type of endocarditis is uncommon, but people with some heart conditions have a greater risk of developing it.
What causes inflammation in the digestive tract?
Infections such as skin sores and sexually transmitted diseases. Inflammatory bowel disease: a group of disorders that cause chronic inflammation of your digestive tract. Any type of catheters, including those that stay in your body for a longer period of time such as urinary catheters.
How to get rid of a swollen ear?
Avoid smoking. Decrease your alcohol or caffeinated beverage consumption. Eat a heart-healthy diet. Exercise under the directions of your doctor. Fluid restriction. Make and keep appointments to see your doctor for routine check-ups and follow-up tests.
What are non-modifiable risk factors?
Non-modifiable risk factors: These factors are irreversible and cannot be changed. The more of these risk factors you have, the greater your chance of developing endocarditis. Family history/Genetics. Modifiable risk factors: These factors can be modified, treated or controlled through medications or lifestyle changes.
What is the treatment for infective endocarditis?
Treatment of infective endocarditis. Infective endocarditis is a potentially lethal disease and requires prolonged antibiotic therapy. The aim of antibiotic therapy is to eradicate infection which includes sterilization of the vegetations. But there are certain challenges in the sterilization of vegetations.
How long does it take to cure prosthetic valve endocarditis?
Prosthetic valve endocarditis. Duration of treatment for prosthetic valve endocarditis is 6 weeks or more. Rifampicin is an important drug in this situation. For oxacillin-susceptible strains of staphylococci, rifampicin and oxacillin for a minimum of 6 weeks along with gentamicin for initial 2 weeks are recommended.
How long does ceftriaxone last?
In the presence of a prosthetic valve or prosthetic valve material, duration of therapy is 6 weeks. Staphylococcus aureus is now the most common causative organism for infective endocarditis in most of the industrialized nations [1]. This has been primarily attributed ...
Can you take penicillin with gentamicin?
When the streptococci are not highly sensitive, penicillin for 4 weeks is combined with gentamicin for 2 weeks. Vancomycin for 4 weeks is the alternative option.
What happens if you don't treat endocarditis?
If it's not treated quickly, endocarditis can damage or destroy your heart valves. Treatments for endocarditis include medications and, sometimes, surgery. People at greatest risk of endocarditis usually have damaged heart valves, artificial heart valves or other heart defects.
What are the symptoms of endocarditis?
A new or changed heart murmur, which is the heart sound made by blood rushing through your heart. Less common signs and symptoms of endocarditis can include: Unexplained weight loss.
What causes a heart valve to leak?
Abnormal growths (vegetations) that contain collections of bacteria may form in your heart at the site of the infection and damage the heart valves, which can cause them to leak. Endocarditis is a life-threatening inflammation of the inner lining of your heart's chambers and valves (endocardium). Endocarditis is usually caused by an infection.
How do you know if you have endocarditis?
Endocarditis may develop slowly or suddenly, depending on what germs are causing the infection and whether you have any underlying heart problems. Signs and symptoms of endocarditis can vary from person to person. Common signs and symptoms of endocarditis include: Aching joints and muscles. Chest pain when you breathe.
What are the symptoms of antibiotics?
Headaches. Joint pain. Shortness of breath. If you're being treated with antibiotics for endocarditis, tell your doctor if you develop diarrhea, a rash, itching or joint pain. These signs and symptoms may mean you're having a reaction to your prescribed antibiotic.
Why is flossing important?
Proper toothbrushing and flossing helps prevent gum disease. If you don't take good care of your teeth and gums, brushing could cause unhealthy gums to bleed, giving bacteria a chance to enter your bloodstream. Some dental procedures that can cut your gums also may allow bacteria to enter your bloodstream. Catheters.
How many chambers does the heart have?
Chambers and valves of the heart. A normal heart has two upper and two lower chambers. The upper chambers — the right and left atria — receive incoming blood. The lower chambers — the right and left ventricles — pump blood out of your heart.
What to do if you have endocarditis?
To prevent endocarditis, your doctor and dentist may prescribe antibiotics before you have any medical or dental procedure in which bacteria have a chance of entering your blood.
How long does it take to treat endocarditis?
When endocarditis is caused by a bacterial infection, it usually is treated with four to six weeks of antibiotics. The type of antibiotic and the length of therapy depend on the results of the blood cultures. Antibiotic treatment is given intravenously (through a vein).
What are the symptoms of endocarditis?
Symptoms of acute endocarditis include: Symptoms of subacute endocarditis include: Tiny broken blood vessels on the whites of the eyes, the palate, inside the cheeks, on the chest, or on the fingers and toes.
How long does it take for endocarditis to be fatal?
If untreated, this form of endocarditis can be fatal in less than six weeks. Subacute endocarditis - This form of endocarditis most often is caused by one of the viridans group of streptococci ( Streptococcus sanguis, mutans, mitis or milleri) that normally live in the mouth and throat.
How long before dental procedure should antibiotics be given?
In general, antibiotics are given one to two hours before a high-risk procedure, and up to eight hours afterward. Before a dental procedure, an antiseptic mouth rinse also can be used, especially one containing chlorhexidine or povidone-iodine. You also can help to prevent endocarditis by avoiding IV drug use.
What are the indications for surgery?
Indications for surgery may include: Damage to a heart valve that is severe enough to cause heart failure unresponsive to medical therapy. Backflow of blood through the aortic or mitral valve (regurgitation) that is severe and unresponsive to medical therapy. Formation of an abscess around a heart valve.
Do you need antibiotics for mitral valve prolapse?
Most people with mitral valve prolapse and other minor abnormalities of heart structure do not need antibiotics before medical or dental procedures.
What are the risk factors for endocarditis?
Risk factors include the presence of a prosthetic heart valve, structural or congenital heart disease, intravenous drug use, and a recent history of invasive procedures.
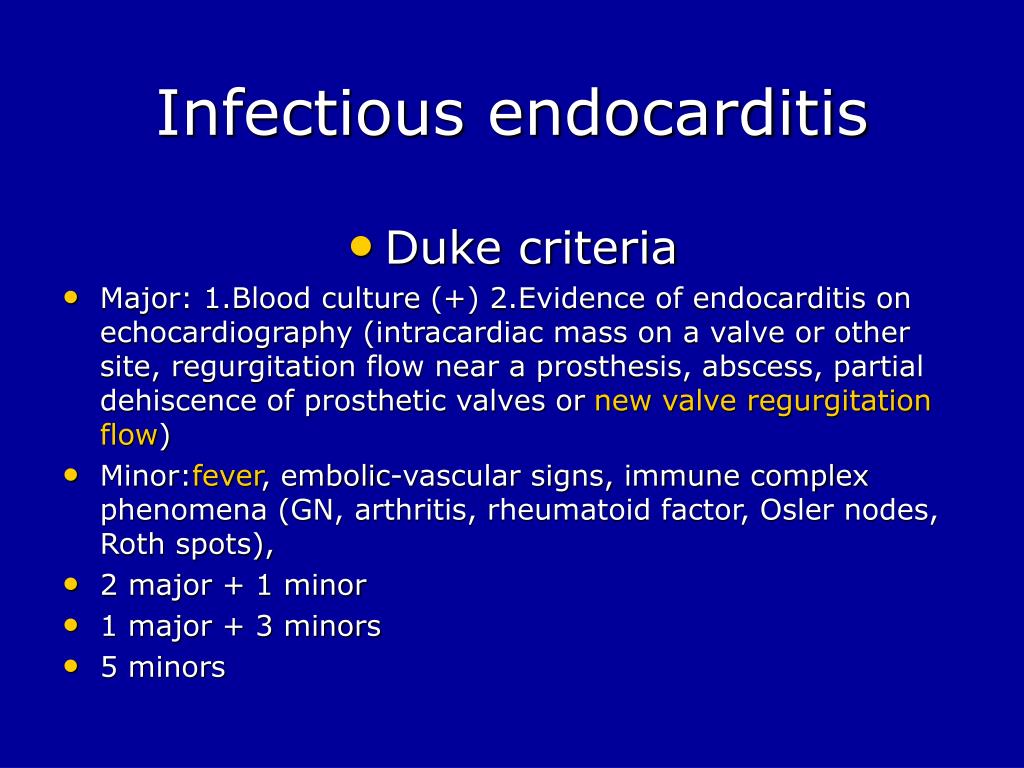
What is the Duke criteria for endocarditis?
Diagnosis is made using the Duke criteria, which include clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic findings.
When should anticoagulation be discontinued?
In general, anticoagulation should be discontinued for at least the first two weeks of antibiotic therapy in patients with Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic valve endocarditis who have experienced a recent central nervous system embolic event. 3
Should intravenous catheters be removed after antibiotics?
Intravenous catheters should be removed promptly after antibiotic therapy is complete. Transthoracic echocardiography should be performed to establish a new baseline. In patients with a history of infectious endocarditis, three sets of blood cultures should be obtained from separate sites before antibiotics are initiated for febrile illness.
What bacteria are in a blood culture positive for?
Two separate blood cultures positive for microorganism consistent with infectious endocarditis (viridans Streptococcus, Streptococcus bovis, gram-negative HACEK bacilli, Staphylococcus aureus, or community-acquired enterococci in the absence of a primary focus)
Can you have endocarditis with night sweats?
Endocarditis should be suspected in any patient with unexplained fe vers, night sweats, or signs of systemic illness, particularly if any of the following risk factors are present 1: a prosthetic heart valve, structural or congenital heart disease, intravenous drug use, and a recent history of invasive procedures (e.g., wound care, hemodialysis). Clinical history consistent with infectious endocarditis includes the combination of a prior cardiac lesion and evidence of a recent source of bacteremia.
