
What is a treatment in experiments?
Nov 04, 2015 · An experimental treatment is the intervention of the researcher to alter the conditions of an experiment. This is done by keeping all other factors constant and only manipulating the experimental treatment, it allows for the potential establishment of a cause-effect relationship.
What is the purpose of designing an experiment?
Dec 03, 2019 · An experimental group, also known as a treatment group, receives the treatment whose effect researchers wish to study, whereas a control group does not. They should be identical in all other ways. They should be identical in all other ways.
What are the types of experimental design?
Because the validity of a experiment is directly affected by its construction and execution, attention to experimental design is extremely important. Treatment In experiments, a treatment is something that researchers administer to experimental units. For example, a corn field is divided into four, each part is 'treated' with a different fertiliser to see which produces the most corn; a …
What is the design of drug testing experiment?
Experimental design is similar to sampling and inventory design in that information about forest variables is gathered and analyzed. However, experiments presuppose intervention through applying a treatment (an action or absence of an action) to a unit, called the experimental unit. The goal is to obtain results that indicate cause and effect.
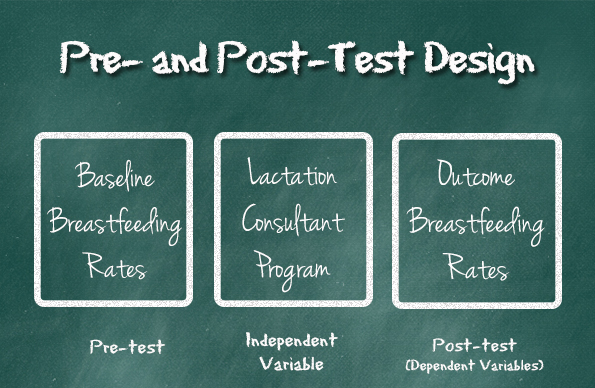
What is the treatment in an experiment?
The treatment is any independent variable manipulated by the experimenters, and its exact form depends on the type of research being performed. In a medical trial, it might be a new drug or therapy. In public policy studies, it could be a new social policy that some receive and not others.Jul 3, 2020
What is treatment in design?
A treatment design is the manner in which the levels of treatments are arranged in an experiment.
What is treatment in research design?
Treatment groups are the sets of participants in a research study that are exposed to some manipulation or intentional change in the independent variable of interest. They are an integral part of experimental research design that helps to measure effects as well as establish causality.Dec 19, 2018
What is treatment effect in experimental design?
A 'treatment effect' is the average causal effect of a binary (0–1) variable on an outcome variable of scientific or policy interest.
What is treatment in Anova analysis?
In the context of an ANOVA, a treatment refers to a level of the independent variable included in the model.
What is a treatment variable?
the independent variable, whose effect on a dependent variable is studied in a research project.
What is treatment structure?
◆ Treatment Structure. ⇨ Consists of the set of treatments, treatment. combinations or populations the experimenter has. selected to study and/or compare.
What is an experimental treatment in biology?
1. in research, the conditions applied to one or more groups that are expected to cause change in some outcome or dependent variable.
What is treatment of the data?
Statistical treatment of data is when you apply some form of statistical method to a data set to transform it from a group of meaningless numbers into meaningful output.
What does treatment mean in statistics?
In an experiment, the factor (also called an independent variable) is an explanatory variable manipulated by the experimenter. Each factor has two or more levels, i.e., different values of the factor. Combinations of factor levels are called treatments.
What is treatment effect model?
Standard treatment effects models include a treatment dummy as explanatory variable, assuming that the impact on the outcome variable can be represented as a simple intercept shift. In other words, a homogenous impact that is independent of farm and household characteristics is assumed.
What is a treatment effect in a study?
The term 'treatment effect' refers to the causal effect of a binary (0–1) variable on an outcome variable of scientific or policy interest.
What is experimental design?
Experimental design means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables . To design a controlled experiment, you ne...
What are independent and dependent variables?
You can think of independent and dependent variables in terms of cause and effect: an independent variable is the variable you think is the ca...
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable , also called a confounder or confounding factor, is a third variable in a study examining a potential cause-and-effect r...
What’s the difference between within-subjects and between-subjects designs?
In a between-subjects design , every participant experiences only one condition, and researchers assess group differences between participants in...
What is the difference between a control group and an experimental group?
An experimental group, also known as a treatment group, receives the treatment whose effect researchers wish to study, whereas a control group do...
What is the difference between internal and external validity?
I nternal validity is the degree of confidence that the causal relationship you are testing is not influenced by other factors or variables . Ext...
What’s the difference between reliability and validity?
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something: Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the r...
What is experimental design?
Experimental design means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables. To design a controlled experiment, you need: A testable hypothesis. At least one independent variable that can be precisely manipulated. At least one dependent variable that can be precisely measured.
What is the independent variable in an experiment?
For example, in an experiment about the effect of nutrients on crop growth: The independent variable is the amount of nutrients added to the crop field.
How does soil moisture affect respiration?
Soil moisture also affects respiration, and moisture can decrease with increasing temperature. Control experimentally: monitor soil moisture and add water to make sure that soil moisture is consistent across all treatment plots. Finally, put these variables together into a diagram.
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable, also called a confounder or confounding factor, is a third variable in a study examining a potential cause-and-effect relationship. A confounding variable is related to both the supposed cause and the supposed effect of the study.
What is the difference between reliability and validity?
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something: Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure ( whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions). Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
Does phone use affect sleep?
Phone use before sleep does not correlate with the amount of sleep a person gets. Increasing phone use before sleep leads to a decrease in sleep. Temperature and soil respiration. Air temperature does not correlate with soil respiration. Increased air temperature leads to increased soil respiration.
What is experimental design?
Experimental design is the process of carrying out research in an objective and controlled fashion so that precision is maximized and specific conclusions can be drawn regarding a hypothesis statement. Generally, the purpose is to establish the effect that a factor or independent variable has on a dependent variable.
What are the two main applications of experimental design?
The two main applications of experimental design are screening, in which the factors that influence the experiment are identified, and optimization , in which the optimal settings or conditions for an experiment are found.
Why is experimental design important?
Through accurate and precise empirical measurement and control an experimental design increases a researcher’s ability to determine causal relationships and state causal conclusions. Experimental design as a subset of scientific investigation is a popular and widely used research approach.
What is OED in statistics?
OED, often also referred as statistical experimental design, can be considered as the optimization of an inversion problem. Eqs. (1)– (4) indicate that the inverse problem estimates an optimal set of model parameters using data constraints. In contrast, OED seeks an optimized experimental layout (i.e., data set) that constrains the model parameter in an optimal fashion.
What is environmental metabolomics?
The experimental design of environmental metabolomics projects involves the selection of an environmental stressor and the target organism. Environmental metabolomics studies are done on a variety of organisms which span from microorganisms to plants and animals (Sivaram et al., 2019; Tian et al., 2017; Tomonaga et al., 2018 ). Microorganisms have been exposed to environmental contaminants, for instance, the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been exposed to copper ( Farrés et al., 2016) and tetrachlorobisphenol A ( Tian et al., 2017 ). Plant metabolomics has investigated the exposure to nanoparticles ( Zhang et al., 2018a ), how plants respond to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons or metals from remediation efforts ( Pidatala et al., 2016; Sivaram et al., 2019 ), the impact of mineral deficiency ( Sung et al., 2015 ), UV-B radiation ( Zhang et al., 2018b ), and drought ( Khan et al., 2019 ). Common terrestrial organisms used in environmental metabolomics studies include nematodes ( Ratnasekhar et al., 2015 ), earthworms ( Tang et al., 2017 ), flies ( Cox et al., 2017 ), and mice ( Wang et al., 2018a ). The choice of organism should reflect the environmental compartment under consideration, for instance, earthworms are commonly used to assess soil contamination in metabolomics studies due to their occurrence in a variety of soils worldwide ( He et al., 2018; Tang et al., 2017 ). Aquatic organisms frequently used in environmental metabolomics studies include crustaceans ( Garreta-Lara et al., 2016; Gómez-Canela et al., 2016) and fish such as medaka, rainbow trout, salmon, and fathead minnow ( Kaneko et al., 2019 ). The studied aquatic organism should also reflect the research question, for instance, bivalves have a sessile lifestyle and can accumulate contaminants, and therefore an analysis of the metabolic profile of bivalves may reflect the contamination at the site of collection ( Watanabe et al., 2015 ). Metabolomics studies may also be performed on a targeted selection of organisms that serve as research models. Model organisms may be represented by the rat and mouse for mammals, zebrafish Danio rerio for aquatic vertebrates, the water flea Daphnia magna for aquatic invertebrates, Arabidopsis thaliana for plants, the yeast S. cerevisiae for eukaryotes, and Escherichia coli for prokaryotes ( Kim et al., 2015; Reed et al., 2017 ).
What are the two types of factors?
In general, the following types of factors can be distinguished: (1) continuous, e.g., temperature; and (2) discrete, e.g., experimenters. Factors are considered to be independent if there is no relationship between them and dependent if a relationship exists.
Why is sulfuric acid important?
As sulfuric acid is an active material in the cell, it is important that the separator and plate active materials absorb as much electrolyte as possible while maintaining enough separator porosity to allow diffusion of oxygen from the positive to the negative plate. The fact that the oxygen transport process is diffusion and can proceed at high degrees of saturation has been demonstrated experimentally.
What is the design of an experiment?
Design of experiment means how to design an experiment in the sense that how the observations or measurements should be obtained to answer a query in a valid, efficient and economical way. The designing of the experiment and the analysis of obtained data are inseparable. If the experiment is designed properly keeping in mind the question, then the data generated is valid and proper analysis of data provides the valid statistical inferences. If the experiment is not well designed, the validity of the statistical inferences is questionable and may be invalid.
What is factor in science?
factor is a variable defining a categorization. A factor can be fixed or random in nature. A factor is termed as a fixed factor if all the levels of interest are included in the experiment.
What is experimental design?
Experimental design means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables. To design a controlled experiment, you need: A testable hypothesis. At least one independent variable that can be precisely manipulated. At least one dependent variable that can be precisely measured.
How to design an experiment?
When designing the experiment, you decide: 1 How you will manipulate the variable (s) 2 How you will control for any potential confounding variables 3 How many subjects or samples will be included in the study 4 How subjects will be assigned to treatment levels
Why is random assignment important?
In this research design, there’s usually a control group and one or more experimental groups. Random assignment helps ensure that the groups are comparable.
What is a method in science?
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys, and statistical tests ). In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section.
What is the independent variable of a crop?
The independent variable is the amount of nutrients added to the crop field. The dependent variable is the biomass of the crops at harvest time. Defining your variables, and deciding how you will manipulate and measure them, is an important part of experimental design.
What is longitudinal study?
Longitudinal studies and cross-sectional studies are two different types of research design. In a cross-sectional study you collect data from a population at a specific point in time; in a longitudinal study you repeatedly collect data from the same sample over an extended period of time. Longitudinal study. Cross-sectional study.
What is a true experiment?
A true experiment (a.k.a. a controlled experiment) always includes at least one control group that doesn’t receive the experimental treatment. However, some experiments use a within-subjects design to test treatments without a control group.
What is experimental design?
In Statistics, the experimental design or the design of experiment (DOE) is defined as the design of an information-gathering experiment in which a variation is present or not, and it should be performed under the full control of the researcher. This term is generally used for controlled experiments.
What is the simplest type of experimental design?
Of all the types, the simplest type of experimental design is the completely randomized design, in which the participants are randomly assigned to the treatment groups. The main advantage of using this method is that it avoids bias and controls the role of chance. This method provides a solid foundation for the Statistical analysis as it allows the use of probability theory.
Why is randomised block design preferred?
The randomised block design is preferred in the case when the researcher is clear about the distinct difference among the group of objects. In this design, the experimental units are classified into subgroups of similar categories. Those groups are randomly assigned to the group of treatment. The blocks are classified in such a way in which the variability within each block should be less than the variability among the blocks. This block design is quite efficient as it reduces the variability and produces a better estimation.
What is statistical research?
Statistics deals with the study of gathering, observing, calculating, and interpreting the numerical data. It is full of experiments and research. A statistical experiment is defined as an ordered procedure which is performed with the objective of verifying, determining the validity of the hypothesis. Before performing any experiment, some specific questions for which the experiment is intended should be clearly identified. To minimise the variability effect on the result of interest, the experiment has to be designed. So, the researcher will design the experiments for the purpose of improvement of precision. It is called experimental designs or the design of experiments (DOE). In this article, let us discuss the definition and example of experimental design in detail.
What is an experimental unit?
An experimental unit is the smallest unit of experimental material to which a treatment can be assigned. Example: In a study of two retirement systems involving the 10 UC schools, we could ask if the basic unit should be an individual employee, a department, or a University.
What is the goal of a study?
Usually the goal of a study is to find out the relationships between certain explanatory factors and the response variables. The design of a study thus consists of making decisions on the following:
What is sample size in a study?
For many designed studies, the sample size is an integer multiple of the total number of treatments. This integer is the number of times each treatment being repeated and one complete repitition of all treatments (under similar experimental conditions) is called a complete replicate of the experiment.
What are factors in a study?
1.2 Factors. Factors are explanatory variables to be studied in an investigation. Examples: 1. In a study of the effects of colors and prices on sales of cars, the factors being studied are color (qualitative variable) and price (quantitative variable). 2.
What is representativeness in a study?
Representativeness: the experimental units should be representative of the population about which a conclusion is going to be drawn. Example: A study conducted surveys among 5,000 US college students, and found out that about 20% of them had uses marijuana at least once.
What are the two types of factors?
Types of factors. Experimental factors: levels of the factor are assigned at random to the experimental units. Observational factors: levels of the factor are characteristic of the experimental units and is not under the control of the investigators. There could be observational factors in an experimental study.
What is experimental design?
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to the different conditions (or IV levels) in an experiment. There are three types: 1. Independent measures / between-groups: Different participants are used in each condition of the independent variable. 2.
What are the three types of experimental designs?
Three types of experimental designs are commonly used: 1. Independent Measures: 1. Independent Measures: Independent measures design, also known as between-groups, is an experimental design where different participants are used in each condition of the independent variable. This means that each condition of the experiment includes ...
What is matched pairs design?
A matched pairs design is an experimentl design where pairs of participants are matched in terms of key variables, such as age or socioeconomic status. One member of each pair is then placed into the experimental group and the other member into the control group.
