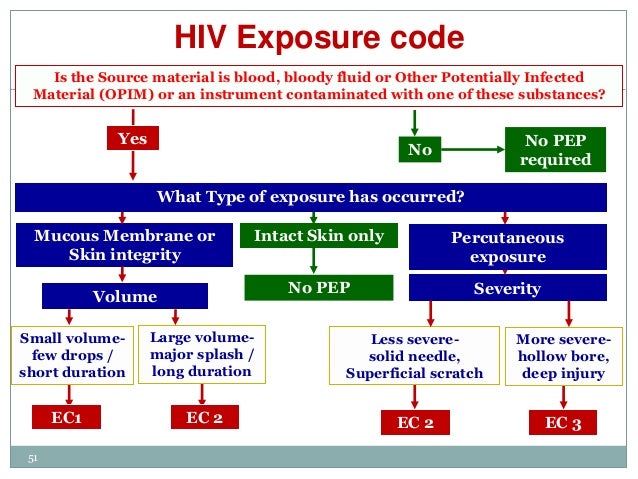
How PEP Is Prescribed
| Option | Recommended Treatment |
| Preferred Option 1 | Truvada (tenofovir + emtricitabine) once ... |
| Preferred Option 2 | Truvada (tenofovir + emtricitabine) once ... |
| Alternative Option | Truvada (tenofovir + emtricitabine) once ... |
What type of treatment is used when exposed with HIV?
The most effective treatment for HIV is antiretroviral therapy (ART). This is a combination of several medicines that aims to control the amount of virus in your body. Antiretroviral medicines slow the rate at which the virus grows. Taking these medicines can reduce the amount of virus in your body and help you stay healthy.
How do you prevent HIV after exposure?
- "French” or deep kissing (if the person with HIV has sores or bleeding in their mouth)
- vaginal sex with a condom and/or PrEP
- anal sex with a condom and/or PrEP
- oral sex without a condom or dental dam
How often to test for HIV after exposure?
There is no single correct answer to this question. One recommended strategy is to get tested 2-4 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months after a risky exposure. Using a sensitive antigen/antibody HIV test, of those who are infected, most will test positive at 1 month; almost all will test positive at 3 months; and the rest will test positive at 6 months.
Can We prevent infection with HIV after an exposure?
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) has been established to effectively prevent HIV infection in an exposed individual when initiated within 2 hours (ideal) and no later than 72 hours after an exposure. Rapid and effective response to a reported HIV exposure are key to the successful prevention of HIV infection.
What should you immediately do if you have been exposed to HIV?
If you are concerned that you have been exposed to HIV, immediately contact your local accident and emergency (A&E) department, GUM (genitourinary medicine) or sexual health clinic. The doctor or nurse there will ask you several questions to try to find out whether you could benefit from treatment.
What 2/3 actions can someone take if they may have been exposed to HIV?
Stay SafeBe honest. Let your partners know that you could have been exposed to HIV so that they can get tested, too.Safeguard your partner. Use a condom every time you have sex, including oral sex. ... Use only clean needles. ... Don't donate blood or semen. ... Protect your baby.
Can I take PEP after 5 days?
It can be used after the event if you've been at risk of HIV transmission. To work, PEP must be taken within 72 hours (three days), and ideally should be taken within 24 hours. PEP is not a 'morning after pill' for HIV, and it's not guaranteed to work.
What is a treatment option for someone who has HIV?
HIV treatment (antiretroviral therapy or ART) involves taking medicine as prescribed by a health care provider. HIV treatment reduces the amount of HIV in your body and helps you stay healthy. There is no cure for HIV, but you can control it with HIV treatment.
Does PEP work after 36 hours?
PEP is effective in preventing HIV infection when it is administered rapidly—ideally within 2 hours and not later than 72 hours—after a high-risk exposure.
How much is PEP medication?
A complete course of PEP can cost from $597 to $1,000 without insurance. However, most insurance providers will cover PEP. In some cases, an individual may not need to pay for PEP.
Can I get PEP at pharmacy?
You can buy the emergency contraceptive pill from chemists, and it is usually also available from GPs, sexual health clinics and A&E departments.
Is PEP same as ARVs?
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is the short-term use of antiretrovirals (ARVs) to reduce the probability of contracting HIV after potential exposure, either occupational (through a work-related accident) or non-occupational (for example, during unprotected sex, rape, or the use of contaminated injection supplies).
Can I use Atroiza as PEP?
When using Atroiza or any other ARV regimen as post exposure prophylaxis (to prevent HIV transmission after contact to possibly infected body fluids), time is of the essence. Unfortunately as far as I know, there is no evidence that starting these drugs after 72 hours post exposure, will prevent HIV transmission.
I Think I've been Exposed to HIV. Can I Still Prevent HIV Infection?
There may be times when you have a high-risk exposure to HIV (this means the chances of passing HIV are great) and you cannot or did not protect yo...
What Should I Know Before I Start Pep?
When you go to the hospital or clinic, you will be asked to have an HIV test. Taking an HIV test at this time will let you know if you already have...
What Should I Do After I Start Pep?
You need to see a doctor during the four weeks you are on PEP and again at the end of the four weeks when you are done with the PEP medicines. You...
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is n...
When should I start treatment?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the vir...
What if I delay treatment?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infecti...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Treatment Reduces the Amount of HIV in the Blood The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load. Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will h...
Does HIV medicine cause side effects?
HIV medicine can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vom...
Will HIV treatment interfere with my hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy. Talk to your health care provider if you are worried about taking HI...
What if my treatment is not working?
Your health care provider may change your prescription. A change is not unusual because the same treatment does not affect everyone in the same way.
Sticking to my treatment plan is hard. How can I deal with the challenges?
Tell your health care provider right away if you’re having trouble sticking to your plan. Together you can identify the reasons you’re skipping med...
What are some examples of HIV?
For example: The condom slipped or broke during use. Your partner has HIV and you usually use condoms, but didn't the last time you had sex. Rape or a sexual assault. You shared a needle to shoot drugs with someone and you are not sure if he or she has HIV.
How long after exposure to HIV should I start PEP?
When do I start PEP? If you have been exposed to HIV, go to a hospital or clinic. You should start PEP within 2 hours of your exposure and generally no later than 36 hours after your exposure.
How to protect yourself while on PEP?
Ask your health care provider for a number to call with questions about your PEP treatment. While you are on PEP, and after you are done, be sure to protect yourself and others from HIV infection. Avoid sex or use condoms each time you have sex. Do not shoot drugs. If you do, do not share needles or syringes.
What to do after starting PEP?
What should I do after I start PEP? You need to see a doctor during the four weeks you are on PEP and again at the end of the four weeks when you are done with the PEP medicines. You will be tested for HIV again after the four weeks .
Can you take PEP for HIV?
In these cases, if you seek medical care right away, you may be able to take medicines that may help you from getting infected with HIV. This is called. PEP has been used for people who come in contact with HIV by accident - like a nurse getting stuck by a used needle. Now, PEP can be used for more than just on-the-job accidents.
Does PEP cover HIV?
Taking an HIV test at this time will let you know if you already have HIV or not. It is your choice whether or not to take the HIV test. There may be a cost for PEP and it may be covered by your health insurance. Ask your provider about costs for PEP before starting it.
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV medication consistently, as prescribed, helps prevent drug resistance. Drug resistance develops when people with HIV are inconsistent with taking their HIV medication as prescribed. The virus can change (mutate) and will no longer respond to certain HIV medication. If you develop drug resistance, it will limit your options ...
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission ...
What does it mean when your HIV is suppressed?
Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood. HIV medicine can make the viral load so low that a test can’t detect it (called an undetectable viral load ). If your viral load goes down after starting HIV treatment, that means treatment is working.
What is the amount of HIV in the blood called?
The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load . Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will help keep your viral load low and your CD4 cell count high. HIV medicine can make the viral load very low (called viral suppression ). Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
How long does it take for a mother to give her baby HIV?
If a mother with HIV takes HIV medicine as prescribed throughout pregnancy, labor, and delivery and gives HIV medicine to her baby for 4 to 6 weeks after birth, the risk of transmitting HIV to her baby can be 1% or less.
What to do if substance use is interfering with your ability to keep yourself healthy?
If substance use is interfering with your ability to keep yourself healthy, it may be time to quit or better manage it. If you need help finding substance use disorder treatment or mental health services, use SAMHSA’s Treatment Locator. external icon. .
Does HIV harm the immune system?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infections. This will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your sexual and injection partners.
What is the treatment for HIV?
However, there are many medications that can control HIV and prevent complications. These medications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART). Everyone diagnosed with HIV should be started on ART, regardless of their stage of infection or complications.
What to do if you think you have HIV?
If you think you might have HIV infection, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist — who additionally specializes in treating HIV / AIDS.
What test can help determine if you have HIV?
If you receive a diagnosis of HIV / AIDS, several tests can help your doctor determine the stage of your disease and the best treatment, including: CD4 T cell count. CD4 T cells are white blood cells that are specifically targeted and destroyed by HIV. Even if you have no symptoms, HIV infection progresses to AIDS when your CD4 T cell count dips ...
What is HIV RNA?
Viral load (HIV RNA). This test measures the amount of virus in your blood. After starting HIV treatment the goal is to have an undetectable viral load. This significantly reduces your chances of opportunistic infection and other HIV -related complications.
How long does it take to get tested for HIV?
Most rapid HIV tests, including self-tests done at home, are antibody tests. Antibody tests can take three to 12 weeks after you're exposed to become positive. Nucleic acid tests (NATs). These tests look for the actual virus in your blood (viral load). They also involve blood drawn from a vein.
What are some examples of anti-HIV drugs?
Examples include efavirenz (Sustiva), rilpivirine (Edurant) and doravirine (Pifeltro).
How to diagnose HIV?
Diagnosis. HIV can be diagnosed through blood or saliva testing. Available tests include: Antigen/antibody tests. These tests usually involve drawing blood from a vein. Antigens are substances on the HIV virus itself and are usually detectable — a positive test — in the blood within a few weeks after exposure to HIV.
What does it mean if you have HIV?
If you are HIV-positive, it means that you have HIV. A second test will then be given to confirm the results, after which a trained healthcare worker will discuss your results and explain how HIV is diagnosed and treated. If you are HIV-negative, it means there is no evidence of the virus in your blood. The healthcare worker will explain ...
How much does PEP reduce HIV?
With respect to PEP in healthcare settings, an early study published in the New England Journal of Medicine concluded that PEP administered after a percutaneous (needle puncture) wound reduced the risk of HIV by 81%. 2 Subsequent studies suggest the results today may be closer to 90% or greater. 3.
What is PEP treatment?
Before Treatment. How PEP Is Prescribed. Effectiveness. If you think that you've been accidentally exposed to HIV, either through sex or other high-risk modes of transmission, there are medications you can take—called post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)—that can significantly reduce your risk of infection if started in a timely manner.
How long does it take to get a follow up HIV test?
A follow-up HIV test would then be scheduled, usually within four to six weeks of the completion of PEP. If the test is negative, you will be counseled on how to reduce your risk of HIV moving forward. Once started, you need to complete the entire 28-day course of treatment.
Can you take PEP if you have HIV?
This can help you avoid taking drugs you don't actually need. On the other hand, PEP may not be viable if you have waited too long to seek treatment. If it is determined that you are at substantial risk of infection, you will be given a rapid HIV test to determine whether you are HIV-positive or HIV-negative .
Can you get HIV with PEP?
Emergency contraception may also be prescribed in cases of rape or sexual assault. PEP is not recommended if you delay for more than 72 hours from the time of the exposure. This does not mean you will get HIV—only that the potential benefits of PEP will have been lost. 1 . What to Expect With an HIV Test.
What to do if you are taking PEP?
If you are taking PEP, talk to your health care provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. PEP medicines may also interact with other medicines that a person is taking (called a drug interaction).
Is PEP effective for HIV?
PEP is effective in preventing HIV infection when it’s taken correctly, but it’s not 100% effective. The sooner you start PEP after a possible HIV exposure, the better. While taking PEP, it’s important to use other HIV prevention methods, such as using condoms the right way, every time you have sex and using only new, ...
Is PEP right for HIV?
PEP may be right for you if you are HIV-negative or don’t know your HIV status, and you think you may have been exposed to HIV in the last 72 hours: During sex (for example, you had a condom break with a partner of unknown HIV status or a partner with HIV who is not virally suppressed)
Can you get PEP after HIV exposure?
In addition, if you are a health care worker, you may be prescribed PEP after a possible exposure to HIV at work , such as from a needlestick injury.
Can you use PEP for HIV?
No. PEP should be used only in emergency situations. It is not intended to replace regular use of other HIV prevention methods. If you feel that you might exposed to HIV frequently, talk to your health care professional about PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis).
Can you get PEP after a sexual assault?
If you’re prescribed PEP after a sexual assault —You may qualify for partial or total reimbursement for medicines and clinical care costs through the Office for Victims of Crime, funded by the U.S. Department of Justice (see the contact information for each state ).
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV Medication to Stay Healthy and Prevent Transmission. If you have HIV, it is important to start treatment with HIV medication (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) as soon as possible after your diagnosis. If taken every day, exactly as prescribed, HIV medication can reduce the amount of HIV in your blood (also called the viral load) ...
How long does it take for HIV to be undetectable?
Almost everyone who takes HIV medication daily as prescribed can achieve an undetectable viral load, usually within 6 months after starting treatment. There are important health benefits to getting the viral load as low as possible. People living with HIV who know their status, take HIV medication daily as prescribed, ...
Why is it called viral suppression?
It is called viral suppression because HIV medication prevents the virus from growing in your body and keeps the virus very low or “suppressed.”. Viral suppression helps keep you healthy and prevents illness.
Can HIV go back up?
So, you need to keep taking your HIV medication daily as prescribed. When your viral load stays undetectable, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. If you stop taking HIV medication, your viral load will quickly go back up.
Can HIV be transmitted to HIV-negative people?
People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners.
Does TasP work for HIV?
People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners. TasP works when a person living with HIV takes HIV medication exactly as prescribed and has regular follow-up care, ...
Can HIV be transmitted through breastfeeding?
Scientists don’t know if a woman living with HIV who has her HIV under control can transmit HIV to her baby through breastfeeding . While it isn’t known if or how much being undetectable or virally suppressed prevents some ways that HIV is transmitted, it is reasonable to assume that it provides some risk reduction.
How to protect yourself from HIV?
Stay Safe. Until you know for sure that you don’t have the virus, or if you know that you're HIV-positive, take care to protect others. Be honest. Let your partners know that you could have been exposed to HIV so that they can get tested, too. Safeguard your partner.
What to do if you test positive for HIV?
If you test positive for HIV, see a doctor right away so you can start taking medication (called antiretroviral therapy, or ART) as soon as possible. If you take it every day exactly as your doctor prescribes, it can lower the amount of the virus in your blood to a point where it doesn’t show up on a lab test.
How to get HIV?
Get Tested. Start PEP Quickly. Symptoms of HIV. Stay Safe. You can get HIV from unprotected sex, an accidental needle stick, or using a dirty needle to inject drugs. If that happened to you, there’s a chance that you’ve been exposed to the virus that causes AIDS. Exposure doesn’t automatically mean infection.
How long does it take for HIV to show up on a test?
Many health insurance plans cover the cost of HIV tests. If you don't have insurance, some clinics offer free tests. It can take up to 3 months for HIV to show up on tests. So if you got tested soon after your exposure and the test was negative, get tested again after 3 months.
How long does it take to get HIV test results?
A rapid test can show if you're HIV positive in 30 minutes. You also can buy home tests in stores or online for more privacy. Some use your saliva and give you results in minutes.
How long does it take to get tested for HIV?
A rapid test can show if you're HIV positive in 30 minutes.
Can you breastfeed if you have HIV?
If the test is positive, you can take medicine so you won’t pass the virus to your baby. If you’re a new mother, don't breastfeed for at least 3 months or until your doctor confirms you're HIV-free. The virus and your medication can pass through your breast milk to your newborn.
Sharing needles
Needles can transmit small amounts of blood from person to person, even if no blood is visible on the syringe. Sharing syringes also increases your risk of developing other diseases such as hepatitis B or C.
HIV and pregnancy
HIV can be transmitted from parent to child during pregnancy, during delivery, or through breast milk. Parent-to-child transmission is the most common way children get HIV.
Viral load
Viral load is a measure of how much of a virus is in a person’s blood. The higher somebody’s viral load, the higher their chances of passing HIV to another person. People taking HIV medication can suppress HIV to the point that it’s undetectable after 7 to 12 months and therefore untransmittable.
Multiple exposures
Having multiple exposures to HIV increases your risk of infection. For example, if you engage in sex without a condom or other barrier method with an HIV-positive person multiple times, your risk of contracting HIV increases.
Multiple sexual partners
Having multiple sexual partners increases the odds that one of your partners will have HIV.
Having an STI
You’re more likely to transmit HIV when you have genital ulcers or urethritis.
People unaware of having HIV
It’s estimated that about 1 in 7 people living with HIV in the United States don’t know they have the virus.

Treatment After Exposure to HIV
Who Should Use Pep?
- PEP has been standard procedure since 1996 for healthcare workers exposed to HIV. Workers start taking medications within a few hours of exposure. Usually the exposure is from a “needle stick,” when a health care worker accidentally gets jabbed with a needle containing HIV-infected blood. PEP reduced the rate of HIV infection from workplace exposures by 79%. However, some …
Should Pep Be Used For Non-Occupational Exposure?
- HIV exposure at work is usually a one-time accident. Other HIV exposures may be due to unsafe behaviors that can occur many times. Some people think that PEP might encourage this unsafe behavior if people think that PEP is an easy way to avoid HIV infection. There are other reasons why PEP might not be a good idea for non-occupational exposure: 1. There is no research to sho…
How Is Pep taken?
- PEP should be started as soon as possible after exposure to HIV. The medications used in PEP depend on the exposure to HIV. The following situations are considered serious exposure: 1. Exposure to a large amount of blood. 2. Blood came in contact with cuts or open sores on the skin. 3. Blood was visible on a needle that stuck someone. 4. Exposure to blood from someone …
What Are The Side Effects?
- The most common side effects from PEP medications are nausea and generally not feeling well. Other possible side effects include headaches, fatigue, vomiting and diarrhea. For more information, see the fact sheets on individual ARVs.
The Bottom Line
- Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is the use of ARVs as soon as possible after exposure to HIV, to prevent HIV infection. PEP can reduce the rate of infection in health care workers exposed to HIV by 79%. The benefits of PEP for non-occupational exposure have not been proven. This use of PEP is controversial because some people fear it will encourage unsafe behaviors. PEP is a fou…
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
- People who are infected with HIV sometimes try dietary supplements that claim to boost the immune system or counteract side effects of anti-HIVdrugs. However, there is no scientific evidence that any nutritional supplement improves immunity, and many may interfere with other medications you're taking. Always check with your doctor before taking any...
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment