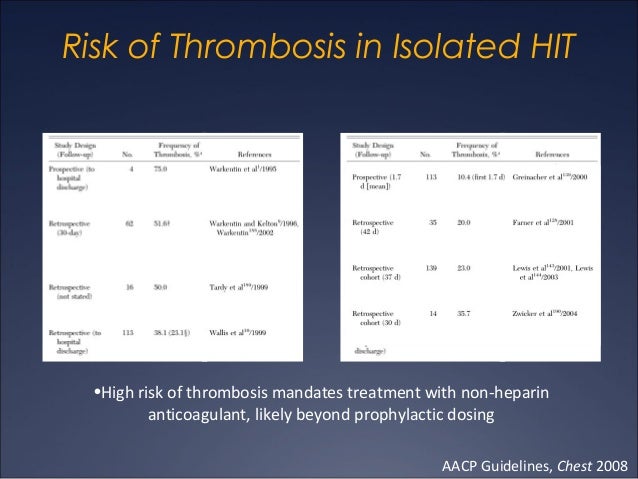
Treating high platelet counts starts with finding the underlying cause. In some cases, like if there are no symptoms, no treatment may be required. Treatment for essential thrombocythemia may include certain medications that slow down the production of platelets.
Full Answer
What are the causes of elevated PTT?
- PT evaluates clotting within the extrinsic and common coagulation pathways
- Causes of isolated prolonged PT ( Clin Lab Med 2009;29:253, Lab Med 2017;48:295 ) Deficiency of or inhibitor to factor VII Mild decrease in common pathway factor (s) Medications: warfarin ...
- aPTT evaluates clotting within the intrinsic and common coagulation pathways
What causes elevated PTT levels?
Elevated PTT results may be caused by malabsorption, a digestive problem that restricts the amount of nutrients that the body absorbs from food, according to the U.S. National Library of Medicine. Vitamin Deficiency. People with a vitamin K deficiency may notice that their blood takes longer to clot and they may have higher PTT test readings.
How to correct PTT?
- Factor assays should be run by using at least three dilutions. ...
- When performing the Bethesda assay to determine the specific factor inhibitor titer, this PTT-based test can also be affected by a strong LA
- Plasma containing FVIII specific inhibitors shows a time dependency for inhibition; this is not the case with other factor inhibitors or LA
What does it mean if PTT is high?
What does it mean when PTT is high? A prolonged PTT means that clotting is taking longer to occur than normal and may be due to a variety of causes. A prolonged PTT may be due to: Liver disease—most coagulation factors are produced by the liver, thus liver disease may cause prolonged PT and PTT .
How do you fix PTT?
In this guide, you'll learn 4 easy methods to fix Discord Push-To-Talk (PTT) not working....Try these fixes:Run as administrator.Reset your Discord settings and check your KeyBind Set.Update your audio driver.Uninstall newly installed programs.Repair system files.
What happens if PTT is high?
Your PTT test results will show how much time it took for your blood to clot. Results are usually given as a number of seconds. If your results show that your blood took a longer-than-normal time to clot, it may mean you have: A bleeding disorder, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease.
What is treatment for high aPTT?
Rivaroxaban (XareltoR) is a direct anti-Xa treatment. It increases the aPTT and the Prothrombin Time (PT) in a dose dependent fashion. At a therapeutic dose, the P/C ratio is between 1.30 and 1.70, which is variable according to the reagent used.
What is PTT medicine?
Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is a blood test that looks at how long it takes for blood to clot. It can help tell if you have a bleeding problem or if your blood does not clot properly.
What medications affect PTT?
AnswerDrugs that may prolong the test values, including antihistamines, ascorbic acid, chlorpromazine, heparin, and salicylates.Incorrect blood-to-citrate ratio.Hematocrit that is highly increased or decreased.Blood samples drawn from heparin lock or a heparinized catheter.
What causes prolonged PTT?
A prolonged PTT result may be due to: hemophilia A or B. deficiency of blood clotting factors. von Willebrand disease (a disorder that causes abnormal blood clotting)
How do you fix high INR?
Vitamin K is a safe and effective antidote to warfarin. Both oral and intravenous (IV) routes are effective in reducing a raised INR due to warfarin with a similar correction of INR by 24 hrs. IV has a more rapid response, within 6-8 hours. Anaphylaxis to IV vitamin K is rare.
What should PTT be on heparin?
While protocols vary from institution to institution, the therapeutic PTT range for heparin is 60 to 100 seconds, with lower intensity dosing in the range of 60 to 80 seconds.
What causes elevated PT and PTT?
Common causes of prolonged PT and/or APTT are the use of oral anticoagulants or heparin, vitamin K deficiency and liver disease. Other causes include coagulation factor deficiencies, coagulation factor inhibitors and diffuse intravascular coagulation.
Does heparin affect INR or PTT?
Anticoagulant or anti-thrombotic drugs such as Heparin and Low Molecular Weight Heparin will cause the INR to be higher because they are affecting the coagulation cascade directly.
What are the anticoagulant drugs?
Warfarin and the newer alternatives are taken as tablets or capsules. There's also an anticoagulant called heparin that can be given by injection....Types of anticoagulantsrivaroxaban (Xarelto)dabigatran (Pradaxa)apixaban (Eliquis)edoxaban (Lixiana)
What happens if your INR is high?
If the INR is too high, you are at increased risk of bleeding. But the INR will usually come back down into the right range when you skip a couple doses of your medication. If you develop bleeding while your INR is too high, it can be life-threatening.
What is a PTT test?
A partial thromboplastin time (PTT) test is a blood test that helps doctors assess your body’s ability to form blood clots. Bleeding triggers a series of reactions known as the coagulation cascade. Coagulation is the process your body uses to stop bleeding. Cells called platelets create a plug to cover the damaged tissue.
Why do doctors order PTT?
Your doctor may order a PTT test to investigate the cause of prolonged or excessive bleeding. Symptoms that may prompt your doctor to order this test include: The PTT test can’t diagnose a specific condition. But it does helps your doctor learn whether your blood clotting factors are deficient.
How long does it take for a PTT to show up?
PTT test results are measured in seconds. Normal results are typically 25 to 35 seconds. This means that it took your blood sample 25 to 35 seconds to clot after adding the chemicals. The exact standards for normal results may vary depending on your doctor and lab, so ask your doctor if you have any concerns.
How to test blood clotting?
To test your body’s blood clotting abilities, the laboratory collects a sample of your blood in a vial and adds chemicals that will make your blood clot. The test measures how many seconds it takes for a clot to form. This test is sometimes called an activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) test.
What medications cause hypofibrinogenemia?
hypofibrinogenemia (deficiency of the blood clotting factor fibrinogen) certain medications, such as the blood thinners heparin and warfarin. nutritional issues, such as vitamin K deficiency and malabsorption. antibodies, including cardiolipin antibodies. lupus anticoagulants.
Can a PTT test diagnose a specific condition?
The PTT test can’t diagnose a specific condition. But it does helps your doctor learn whether your blood clotting factors are deficient. If your test results are abnormal, your doctor will probably need to order more tests to see which factor your body isn’t producing.
Can abnormal PTT be diagnosed?
Remember that an abnormal PTT result doesn’t diagnose any particular disease. It only provides insight about the time it takes for your blood to clot. Multiple diseases and conditions can cause abnormal PTT results.
What is the PTT test?
The PTT blood test is useful if you have frequent nose bleeding, heavy and prolonged menstruations, swollen joints that are painful, and easy bruising. Sometimes, this blood test is also recommended when you see blood in urine along with a UTI test.
Why do doctors order PTT blood tests?
Your doctor will order this PTT blood test if you have any bleeding or clotting disorder. This test is also done as a pre-surgical test, the PTT blood test helps your doctor determine the likelihood of excessive bleeding or clotting to determine risks during and/or after surgery.
What is the purpose of a prothrombin test?
The Prothrombin test is also ordered as a backup test while evaluating the functioning of the liver. Following are the medical conditions where a PTT blood test is ordered: Check the function of specific coagulation factors. (To monitor any bleeding disorders such as hemophilia) Any unexplained heavy bleeding.
How long does it take for a PTT to show up?
Normal PTT values are between 30 to 40 seconds. Abnormal levels don’t indicate any disease in particular, they provide insights only about the time taken for your blood to clot. If you take this PTT test because you’re taking heparin and monitor your health condition, your PTT results to be more like 120 to 140 seconds.
What are the factors that help stop blood clots?
There are coagulation factors that are in form of proteins are the core elements for the body to form blood clots to help stop bleeding. When you have too little or too much of any coagulation factor this may cause excessive bleeding/clotting.
Does PTT take insurance?
Our PTT blood testing providers do not accept any health insurance. But, on request, they can provide you with a receipt containing all the details like the name and code of the test, and CPT code which is necessary for insurance reimbursement purposes.
Does insurance cover PTT blood test?
Cost of PTT blood test cost with insurance. Many health insurance policies in the U.S. do not cover the cost of the PTT blood test. Also, the coverage offered by private health insurance policies and national health insurance programs varies widely. So we recommend you to check with your insurance company. Our PTT blood testing providers do not ...
What is a PTT test?
A partial thromboplastin time (PTT) test measures the time it takes for a blood clot to form. Normally, when you get a cut or injury that causes bleeding, proteins in your blood called coagulation factors work together to form a blood clot. The clot stops you from losing too much blood. You have several coagulation factors in your blood.
What does it mean when your PTT results show you have a clot?
If your results show that your blood took a longer-than-normal time to clot, it may mean you have: A bleeding disorder, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease.
Is there a cure for bleeding disorders?
While there is no cure for most bleeding disorders, there are treatments available that can help manage your condition. Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
Differential Diagnosis of Prolonged PTT with a Normal PT
Heparin in the specimen, which may be a result of heparin treatment of the patient
Suggested Additional Lab Testing
If heparin contamination in the sample is a possibility, ask for a repeat PTT or, if necessary, get a heparin measurement.
What is a partial thromboplastin time test?
The partial thromboplastin time (PTT) test is performed primarily to determine if heparin therapy is effective 5 and it can also detect a clotting/bleeding disorder. However, it can't be used to monitor the effect of drugs such as Lovenox, which are used to prevent and treat blood clots in the legs and complications of heart disease. 6
What is the INR in PT?
The international normalized ratio (INR) is used to make sure the results from a PT test are the same from one lab to another. In the 1980s, the World Health Organization determined that people undergoing surgery may be at risk of excessive bleeding because different labs had different standardized values than other labs. 9
What is a coagulation test?
Tests that assess blood clotting, known as coagulation studies, include prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and international normalized ratio (INR). You may need one or more of these tests to monitor an illness, follow the effects of blood thinner therapy, or as part of pre-surgical blood testing .
What to do if you are not taking blood clotting medication?
If you are not currently taking any medication that affects blood clotting factors, you may need to start taking one to normalize your levels. 13. If you are taking a medication that affects clotting, your dosage may require an adjustment if your PT is not in the target range.
Can you stop taking medications before a PTT?
Several conditions and medications can impact your PTT test results, including: Your doctor might ask you to stop taking certain drugs before your coagulation study. Do not stop taking any of your medications without your doctor's advice. 8.
What is PTT in blood work?
Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is the time it takes for a patient's blood to form a clot as measured in seconds. It is used to measure the activity of the intrinsic pathway of the clotting cascade.
What is PTT in coagulation?
PTT is usually measured as part of a panel of coagulation studies including international normalizing ratio (INR) and prothrombin time ( PT). INR and PT both measure the activity of the extrinsic clotting cascade.
Why is PTT elevated in liver disease?
With more severe disease, both the PT and PTT will be elevated due to decreased synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors which include factor II, factor VII, factor IX, and factor X. Correct with fresh frozen plasma (FFP), not vitamin K. .
How often is blood drawn for PTT?
For patients on continuous unfractionated heparin, infusion blood is drawn every 6 hours to facilitate dosing adjustments. Procedures. The PTT test uses decalcified blood to prevent clotting in the tube before the test begins. In the lab, plasma is separated from cellular components by centrifuge.
How many seconds does a normal PTT measure?
Measured in seconds to clot formation, normal PTT can vary based on laboratory or institution; however, normal PTT is between 25 to 35.
Why is prothrombin time so long?
Blood clotting : Defective. Prolonged prothrombin time can be due to deficiency of a number of coagulation factors. A common cause it treatment with warfarin/coumdain. Liver disease is an other common reason for prolonged pt. Depending on the prolongation, the person may be at risk of bleeding.
Is HealthTap a board certified doctor?
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video. Video chat with a U.S. board-certified doctor 24/7 in less than one minute for common issues such as: colds and coughs, stomach symptoms, bladder infections, rashes, and more.
Is prothrombin time higher than normal?
Dr. Gurmukh Singh answered. Yes.: Prothrombin times about three times higher than normal for the particular lab may be a risk for abnormal bleeding. Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers — it's anonymous and free!
Why are my platelets elevated?
Though these may seem like significant numbers, it is important to remember that the majority of elevated platelet counts are caused by a reactive process, such as infection or inflammation. Once the cause of the reactive process resolves, platelet counts generally return to normal levels.
What is the term for a disease that causes too many platelets to be made?
The myeloproliferative disorder that causes too many platelets to be made is called essential thrombocythemia, introduced above.
Can high platelet count cause blood clots?
It is possible, however, that having high platelet counts can lead to the development of blood clots. Blood clots can potentially form in any blood vessel, but most commonly form in the blood vessels in the arms and legs, or in the blood vessels in the brain. These clots can prevent blood from flowing properly through these vessels, ...
Is a high platelet count dangerous?
High Platelet Count Isn’ t Always Serious. Many times, a high platelet count doesn’t cause any symptoms but may be found on routine bloodwork. Although the cause for the high levels should be investigated, the possible cause is not always from something dangerous or serious.