Medication
Sources of natural folate include:
- peanuts
- black-eyed peas
- kidney beans
- oranges
- orange juice
Procedures
- Search the American Society of Hematology “ Find a Hematologist ”
- Locate the largest teaching hospital near you and ask for a referral to the head of hematology or the specialist in non-malignant hematology
- Visit PDSA’s Discussion Group or Facebook Group for recommendations from others for doctors in your area Discussion Group Facebook Group
Self-care
platelets (Blood Component)
- Dosing & Uses. Typical dosing for an adult is a pool of 6 whole blood derived (sometimes referred to as random donor) platelets or one apheresis platelet.
- Adverse Effects
- Warnings. ...
- Pregnancy & Lactation. ...
- Pharmacology. ...
Nutrition
People with mild thrombocytopenia might not need treatment. For people who do need treatment for thrombocytopenia, treatment depends on its cause and how severe it is. If your thrombocytopenia is caused by an underlying condition or a medication, addressing that cause might cure it.
What are home remedies for thrombocytopenia?
What doctor treats thrombocytopenia?
How to correct thrombocytopenia?
Can thrombocytopenia be cured?

What are the main causes of thrombocytopenia?
What causes thrombocytopenia?Alcohol use disorder and alcoholism.Autoimmune disease which causes ITP. ... Bone marrow diseases, including aplastic anemia, leukemia, certain lymphomas and myelodysplastic syndromes.Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.More items...•
How long does it take to cure thrombocytopenia?
Key points about immune thrombocytopenic purpura ITP may be acute and resolve in less than 6 months, or chronic and last longer than 6 months. Treatment options include a variety of medications that can reduce the destruction of platelets or increase their production.
What are the risks of thrombocytopenia?
Risk Factors of ThrombocytopeniaHave certain types of cancer, aplastic anemia, or autoimmune diseases.Are exposed to certain toxic chemicals.Have a reaction to certain medicines.Have certain viruses.Have certain genetic conditions.
Which medicine is best for low platelet count?
Corticosteroids. Dexamethasone or prednisone is typically prescribed to raise your platelet count. You take it once a day in the form of a pill or tablet. An increased or normalized platelet count is generally seen within 2 weeks of therapy, particularly with high-dose dexamethasone.
What medication increases platelets?
Medications such as romiplostim (Nplate) and eltrombopag (Promacta) help your bone marrow produce more platelets. These types of drugs can increase your risk of blood clots.
What cancers cause low platelets?
Certain cancers such as leukemia or lymphoma can lower your platelet count. The abnormal cells in these cancers can crowd out healthy cells in the bone marrow, where platelets are made. Less common causes of a low platelet count include: Cancer that spreads to the bone.
Can thrombocytopenia cause stroke?
Abstract. Although the patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) have a very low platelet count, which usually causes hemorrhagic complications, they occasionally experience ischemic stroke.
How to prevent thrombocytopenia?
If you’re at risk for thrombocytopenia, these steps may help prevent it: Avoid medicines that thin blood and increase bleeding risk, such as aspirin, naprosyn and ibuprofen. Take care with contact sports and activities that can cause injuries, bruising and bleeding. Minimize contact with toxic chemicals.
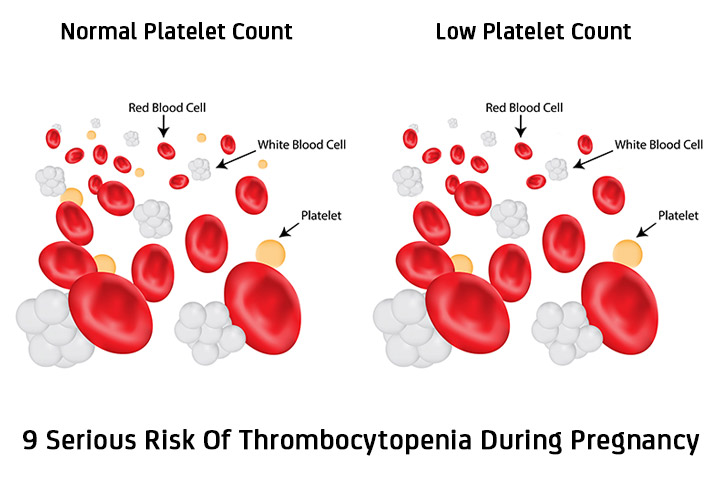
What is thrombocytopenia in blood?
What is thrombocytopenia? Thrombocytopenia (THROM-bo-sigh-toe-PEE-ne-ah) occurs when your blood platelet count is low. Platelets are also called thrombocytes. This type of blood cell clumps together to form blood clots to help stop bleeding at the site of a cut or wound. Another name for a blood clot is thrombus.
What are the three main classes of thrombocytopenia?
The three main classes of thrombocytopenia are: Platelet destruction such as with an auto-antibody that attaches to the platelet surface. Platelet sequestration such as in someone with a large spleen or with liver disease. Decreased platelet production as occurs in certain bone marrow diseases.
How long does a platelet last in blood?
Platelets are transfused only if the platelet count is extremely low. (Transfused platelets only last about three days in the circulation.) Splenectomy or removal of the spleen.
How to tell if your platelet count is low?
Often, one of the first signs is a cut or nosebleed that won’t stop bleeding. Other signs of low platelet count include: Bleeding gums. Blood in stool (black, tarry-looking), urine (hematuria) or vomit. Heavy menstrual periods. Petechiae (tiny red or purple dots on the lower legs that resemble a rash).
What is the name of the tissue that makes blood clots?
Another name for a blood clot is thrombus. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue inside bones that makes all blood cells including platelets. People who have thrombocytopenia don’t have enough platelets to form a blood clot. If you get a cut or other injury, you may bleed too much and the bleeding can be hard to stop.
What causes ITP?
Autoimmune disease which causes ITP. ITP is sometimes associated with other autoimmune conditions such as lupus. Bone marrow diseases , including aplastic anemia, leukemia, certain lymphomas and myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
What is the treatment for thrombocytopenia?
Treatment for thrombocytopenia depends on its cause and severity. The main goal of treatment is to prevent death and disability caused by bleeding. If your condition is mild, you may not need treatment. A fully normal platelet count isn't necessary to prevent bleeding, even with severe cuts or accidents.
What is a blood transfusion?
Blood or platelet transfusions are used to treat people who have active bleeding or are at a high risk of bleeding. During this procedure, a needle is used to insert an intravenous (IV) line into one of your blood vessels. Through this line, you receive healthy blood or platelets.
Is it normal to have a low platelet count?
A fully normal platelet count isn't necessary to prevent bleeding , even with severe cuts or accidents. Thrombocytopenia often improves when its underlying cause is treated. People who inherit the condition usually don't need treatment. If a reaction to a medicine is causing a low platelet count, your doctor may prescribe another medicine.
Can you take another medicine for low platelet count?
If a reaction to a medicine is causing a low platelet count, your doctor may prescribe another medicine. Most people recover after the initial medicine has been stopped. For heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), stopping the heparin isn't enough. Often, you'll need another medicine to prevent blood clotting.
Can steroids slow platelet destruction?
Steroids may slow platelet destruction. These medicines can be given through a vein or by mouth. One example of this type of medicine is prednisone. The steroids used to treat thrombocytopenia are different from illegal steroids taken by some athletes to enhance performance.
Why does thrombocytopenia occur?
In general, thrombocytopenia develops for one or more of the following reasons: The body's bone marrow fails to produce enough platelets. This can happen because: A cancer gets into the bone marrow and destroys megakaryocytes. These are the cells that produce platelets. Aplastic anemia affects platelet production.
When to call a doctor for thrombocytopenia?
Be sure to call if you notice abnormal bruises or if you experience significant bleeding from your nose, mouth, vagina, rectum or urinary tract.
What is a TTP?
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). This is a rare disease. Blood clots form in the smallest arteries throughout the body. Platelets are consumed by this process. People with TTP also have anemia (low red blood cell count), fever, kidney malfunction and neurological symptoms.
What is the best treatment for persistent ITP?
For persistent ITP, your doctor may recommend periodic injections of the monoclonal antibody rituximab ( Rituxan ). Splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen). This may be necessary if ITP that has not improved with other treatment. If the spleen is removed, thrombocytopenia goes away in more than half of ITP patients.
How long does it take for thrombocytopenia to heal?
This is often the standard strategy in children with acute ITP. Most children recover without treatment within 6 weeks.
What are the symptoms of thrombocytopenia?
People with severe thrombocytopenia may have abnormal bleeding almost anywhere in the body. Symptoms can include: Reddish or purplish spots in the skin (called petechiae), often concentrated in the lower legs. Excessive bruising, even from minor trauma. Blood in the urine or stool.
What is the procedure to remove a small piece of bone marrow?
If that happens, you have drug-induced thrombocytopenia. Your doctor may recommend a bone marrow biopsy. In this procedure, a long needle is used to remove a small piece of bone marrow. The marrow is examined in a laboratory.
What to do if you have thrombocytopenia?
If you have immune thrombocytopenia, try to: Avoid contact sports. Depending on your risk of bleeding, head impacts during sports like boxing, martial arts and football could cause bleeding in your brain. Talk to your doctor about what activities are safe for you. Watch for signs of infection.
What is the diagnosis of immune thrombocytopenia?
To diagnose immune thrombocytopenia, your doctor will try to exclude other possible causes of bleeding and a low platelet count, such as an underlying illness or medications you or your child may be taking.
How to treat ITP?
Medications to treat ITP may include: 1 Steroids. Your doctor will likely start you on an oral corticosteroid, such as prednisone. Once your platelet count is back to a safe level, you can gradually discontinue taking the drug under the direction of your doctor. Long-term use of these medications isn't recommended because they can increase your risk of infections, high blood sugar and osteoporosis. 2 Immune globulin. If corticosteroids don't help, your doctor may give you an injection of immune globulin. This drug may also be used if you have critical bleeding or need to quickly increase your blood count before surgery. The effect usually wears off in a couple of weeks. 3 Drugs that boost platelet production. Medications such as romiplostim (Nplate) and eltrombopag (Promacta) help your bone marrow produce more platelets. These types of drugs can increase your risk of blood clots. 4 Other drugs. Rituximab (Rituxan, Truxima) helps increase your platelet count by reducing the immune system response that's damaging your platelets. But this drug also can reduce the effectiveness of vaccinations, which may be needed if you later choose surgery to remove your spleen.
What are some medications that can help with platelet function?
Examples include aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and ginkgo biloba. Medications to treat ITP may include: Steroids.
What is the best treatment for ITP?
Medications to treat ITP may include: Steroids. Your doctor will likely start you on an oral corticosteroid, such as prednisone. Once your platelet count is back to a safe level, you can gradually discontinue taking the drug under the direction of your doctor.
How long does it take for a platelet to wear off?
The effect usually wears off in a couple of weeks. Drugs that boost platelet production. Medications such as romiplostim (Nplate) and eltrombopag (Promacta) help your bone marrow produce more platelets. These types of drugs can increase your risk of blood clots. Other drugs.
What to do if you have a spleen removed?
Watch for signs of infection. If you've had your spleen removed, be alert for any signs of infection, including fever, and seek prompt treatment. Infections can be more serious in people without spleens. Use caution with over-the-counter medications.
Drugs used to treat Thrombocytopenia
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
How to treat thrombocytopenia?
If you don’t like to crunch on carrots, try drinking carrot juice instead .
What is the best home remedy for thrombocytopenia?
Ginseng is another useful home remedy for thrombocytopenia. It is most effective when used in combination with other herbal remedies and more research is needed into the effectiveness of ginseng alone.
Why does my platelet count drop?
A lack of exercise can lead to cause your platelet level to drop as it can cause your body to start shutting down. This can leave you feeling fatigued and despondent, which will make you feel even less motivated to exercise. This creates a dangerous cycle so it’s important to maintain a regularly active lifestyle.
What is it called when you have thrombocytopenia?
This condition is known as thrombocytopenia . If you’re diagnosed with thrombocytopenia , you should speak to your doctor to figure out what’s causing it and how you can combat it. Only a doctor can properly diagnose thrombocytopenia, but home remedies can help to treat the symptoms.
How long does it take for cortisone to increase platelet count?
Cortisone can help to increase your platelet count in just a matter of weeks or months. This makes it an extremely effective home remedy for thrombocytopenia. Plus, it’s usually easy to purchase in stores.
How to reduce platelet count?
So, by reducing the stress in your life, you’re less vulnerable to a drop in your platelet count. To help manage your stress you could try taking up yoga, meditation or other soothing activities.
Does papaya help with thrombocytopenia?
Both the papaya fruit and its leaves can help to increase your platelet count which will combat your thrombocytopenia. You can consume ripe papaya or drink juice made from its leaves every day to help restore your platelet levels.

What Is Thrombocytopenia?
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Expected Duration
Specialist to consult
Prevention
- The following can be used to determine whether you have thrombocytopenia: 1. Blood test.A complete blood count determines the number of blood cells, including platelets, in a sample of your blood. 2. Physical exam, including a complete medical history.Your doctor will look for sign…
Treatment
When to Call A Professional
Prognosis
Further Information