Medication
These statistics are non-age-standardised which means they don't take into account the age of the people with cervical cancer. Around 95 out of 100 people (around 95%) will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis. Almost 70 out of 100 people (almost 70%) will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
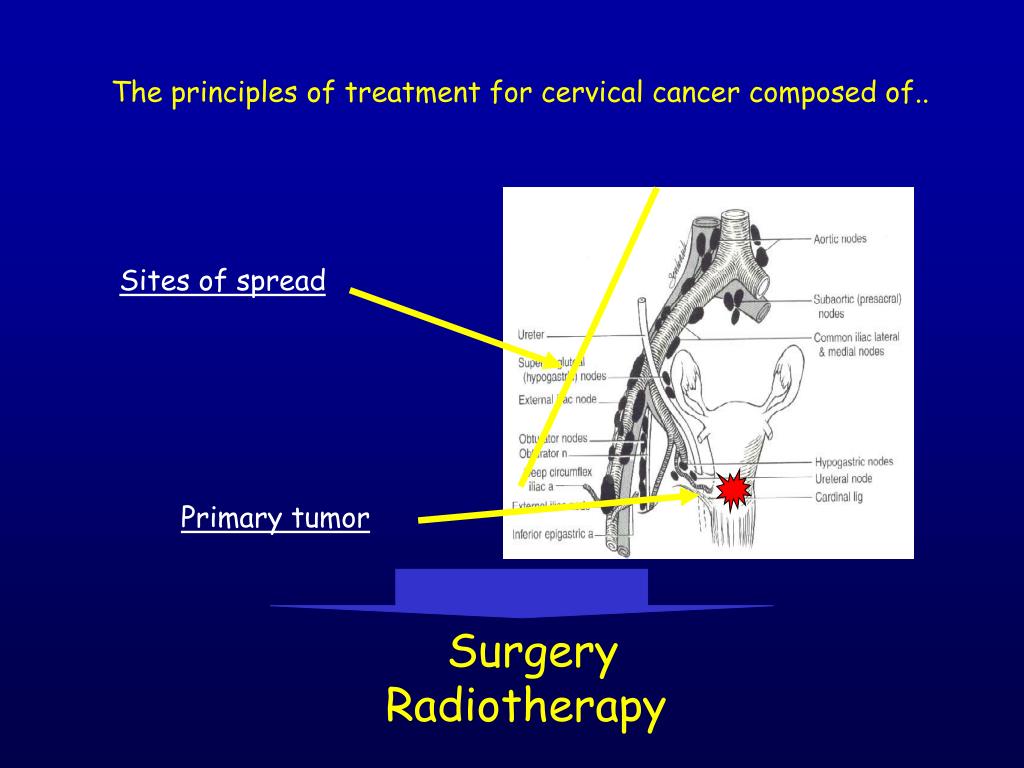
Procedures
- For surgery to remove precancerous growths, a portion of the cervix is generally enough. ...
- For more locally advanced cervical tumors where surgery can not achieve cure alone, radiation therapy is preferred. ...
- Chemotherapy is a cancer-fighting medication that not only sensitizes the cervical cancer cells to radiation and makes radiation work better. ...
Therapy
“This study provides a proof of concept of immunotherapeutic checkpoint inhibition in cervical cancer. If cemiplimab is approved, it will provide a second-line treatment option for women with recurrent cervical cancer,” Tewari said.
Nutrition
Understanding the numbers
- Women now being diagnosed with cervical cancer may have a better outlook than these numbers show. ...
- These numbers apply only to the stage of the cancer when it is first diagnosed. ...
- These numbers don’t take everything into account. ...
What is the life expectancy of someone with cervical cancer?
What is the best treatment for cervical cancer?
How do you cure cervical cancer?
What are survival rates for cervical cancer?

Is Stage 1 cervical cancer curable?
Stage I cervical cancer is curable for the majority of patients if surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy are appropriately used. A variety of factors ultimately influence a patient's decision to receive treatment of cancer.
What is the common treatment for early-stage cervical cancer?
The most common treatment for early-stage cervical cancers is radical hysterectomy (surgical removal of the cervix, uterus, and surrounding tissues called the parametrium). The alternative is radiation therapy (RT), which is usually given in combination with chemotherapy.
What is the survival rate for Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Stage I cervical cancer patients have a 5-year survival rate of 80% to 93%. Women with stage II cervical cancer have a 5-year survival rate of 58% to 63%. The survival rate for women with stage III cervical cancer is 32% to 35%.
How long can you live with Stage 1 cervical cancer?
What is the survival rate for stage 1 cervical cancer? Approximately 92% of women with localized cervical cancer are likely to be alive in 5 years. However, if there is pelvic lymph node involvement, the survival rate is lower.
Do you need chemo for Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Stage 1 cervical cancer is usually treated with: surgery. combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy (chemoradiotherapy)
What are the symptoms of Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Signs and symptoms of stage 1 cervical cancer can include:Watery or bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and can have a foul odor.Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between menstrual periods or after menopause.Menstrual periods may be heavier and last longer than normal.
Does a hysterectomy cure cervical cancer?
Nearly half of cervical cancers are diagnosed at an early stage, meaning the tumors are small and have not spread beyond the cervix. Although there are other treatment options, radical hysterectomy is the most common treatment for early-stage disease, and cure rates for the disease are around 80%.
How do they remove cervical cancer?
Two types of procedures can be used to treat pre-cancers of the cervix:Ablation destroys cervical tissue with cold temperatures or with a laser rather than removing it.Excisional surgery (conization) cuts out and removes the pre-cancer.
What if cervical biopsy shows cancer?
If the biopsy shows that cervical cancer is present, the doctor will refer you to a gynecologic oncologist, which is a doctor who specializes in treating cancers of the female reproductive system. Your doctor may suggest additional tests to see if the cancer has spread beyond the cervix.
Can cervical cancer be cured completely?
Cervical cancer is curable, but it is difficult for doctors to know for sure that it will never come back following treatment. Therefore, doctors often use the term “remission” to describe cancer that has gone away and is no longer causing symptoms.
What are the odds of beating cervical cancer?
Survival for all stages of cervical cancer more than 80 out of every 100 (more than 80%) will survive their cancer for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed. more than 60 out of every 100 (more than 60%) will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after diagnosis.
Is cervical cancer a death sentence?
It happens less often than it used to, but yes, it's possible to die from cervical cancer. The American Cancer Society (ACS) estimates that about 4,250 people in the United States will die from cervical cancer in 2019.
How to treat cervical cancer?
Stage IVB cervical cancer is not usually considered curable. Treatment options include radiation therapy with or without chemo to try to slow the growth of the cancer or help relieve symptoms . Most standard chemo regimens include a platinum drug (cisplatin or carboplatin) along with another drug such as paclitaxel (Taxol), gemcitabine (Gemzar), or topotecan. The targeted drug bevacizumab (Avastin) may be added to chemo or immunotherapy alone with pembrolizumab (Keytruda) may also be an option.
What is the best treatment for cancer after birth?
Surgery options after birth for early-stage cancers include a hysterectomy, radical trachelectomy, or a cone biopsy. If the cancer is stage IB or higher, then you and your doctor must decide whether to continue the pregnancy. If not, treatment would be radical hysterectomy and/or radiation. Sometimes chemotherapy can be given during ...
What is the treatment for a tumor that has grown into blood vessels?
If the cancer has grown into blood or lymph vessels, one treatment option is a cone biopsy (with negative margins) with removal of pelvic lymph nodes. Another option is a radical trachelectomy along with removal of the pelvic lymph nodes.
What is stage IA1?
Stage IA1. Treatment for this stage depends on whether or not you want to be able to have children (maintain fertility) and whether or not the cancer has grown into blood or lymph vessels (called lymphova scular invasion).
What is the goal of cancer treatment?
No matter which type of treatment your doctor recommends, it's important that you understand the goal of treatment (to try to cure the cancer, control its growth, or relieve symptoms ), as well as its possible side effects and limitations.
What is the best treatment for pelvic cancer?
If the cancer has recurred in the center of the pelvis only, extensive surgery (s uch as pelvic exenteration) may be an option for some patients, and offers the best chance for possibly curing the cancer (although it can have major side effects). Radiation therapy (sometimes along with chemo) might be another option.
What is the procedure for a woman who wants to have children after cancer?
A cone biopsy is the preferred procedure for women who want to have children after the cancer is treated. If the edges of the cone don’t contain cancer cells (called negative margins), the woman can be watched closely without further treatment as long as the cancer doesn’t come back. If the edges of the cone biopsy have cancer cells (called ...
Surgery
Surgery is a main treatment for stage 1 cervical cancer. The type of surgery you are offered will depend on many factors, including your age, the stage and if you want to become pregnant.
Radiation therapy
You may be offered radiation therapy for stage 1 cervical cancer. It is used as the main treatment if you can’t have surgery or choose not to have surgery.
Chemoradiation
You may be offered chemoradiation for stage 1B1 cervical cancer. It is often a main treatment for stage 1B2 or higher cervical cancer. It is used if you can’t have surgery or choose not to have surgery.
Clinical trials
Talk to your doctor about clinical trials open to women with cervical cancer in Canada. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, find and treat cancer. Find out more about clinical trials.
What is the treatment for stage 1 cervical cancer?
other health conditions that you have. Stage 1 cervical cancer is usually treated with: surgery. combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy (chemoradiotherapy) Read more about how your doctor decides which treatment you need.
What is the stage of cervical cancer?
Stage 1. Stage 1 means that the cancer is only in the neck of the womb (cervix). The main treatment is surgery. You might also have combined radiotherapy and chemotherapy (chemoradiotherapy) if you have stage 1B cervical cancer.
How long does radiotherapy last for stage 1B cervical cancer?
With this treatment, you have chemotherapy during your course of radiotherapy. You have daily external radiotherapy for 5 days every week, for around 5 weeks.
How big is stage 1B1?
In stage 1B1 the cancer is deeper than 5mm but no more than 2cm in size. In stage 1B2 the cancer is at least 2cm but not bigger than 4cm in size. In stage 1B3 the cancer is at least 4cm but is still only in the cervix.
How often do you get chemo after a radiotherapy course?
During your course of radiotherapy, you also have chemotherapy once a week or once every 2 or 3 weeks.
What is stage 1A?
Stage 1A. In stage 1A the growth is so small that it can only be seen with a microscope or colposcope. It can be divided into 2 smaller groups: stage 1A1. stage 1A2. Stage 1A1 means the cancer has grown less than 3 millimetres (mm) into the tissues of the cervix.
Can you have a baby after cervical cancer surgery?
Surgery for early cervical cancer usually involves removing your cervix and womb (hysterectomy). For some very early cer vical cancers, it might be possible to just remove most of the cervix, but leave enough behind so that you might be able to become pregnant and have a baby afterwards .
What are the treatments for cervical cancer?
Common types of treatments for cervical cancer include: Surgery for Cervical Cancer. Radiation Therapy for Cervical Cancer. Chemotherapy for Cervical Cancer. Targeted Therapy for Cervical Cancer. Immunotherapy for Cervical Cancer.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What are the best doctors for cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: 1 A gynecologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the female reproductive system 2 A gynecologic oncologist: a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system who can perform surgery and prescribe chemotherapy and other medicines 3 A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer 4 A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer
Why is communicating with your cancer team important?
Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life. Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, ...
What kind of doctor treats cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team may include: A gynecologist: a doctor who treats diseases of the female reproductive system. A gynecologic on cologist: a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system who can perform surgery and prescribe chemotherapy and other medicines. A radiation on cologist: a doctor who uses radiation ...
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
Who are the specialists involved in cancer care?
Many other specialists may be involved in your care as well, including nurse practitioners, nurses, psychologists, social workers, rehabilitation specialists, and other health professionals. Health Professionals Associated with Cancer Care.
What tests are done to determine if you have cervical cancer?
Your cancer's stage is a key factor in deciding on your treatment. Staging exams include: Imaging tests.
What is the test for cervical cancer?
A Pap test can detect abnormal cells in the cervix, including cancer cells and cells that show changes that increase the risk of cervical cancer. HPV DNA test.
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care.
What tests can be done to check if you have cancer?
Tests such as X-ray, CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET) help your doctor determine whether your cancer has spread beyond your cervix. Visual examination of your bladder and rectum. Your doctor may use special scopes to see inside your bladder and rectum.
Can you remove cancer from a small cervix?
Surgery to cut away the cancer only. For a very small cervical cancer, it might be possible to remove the cancer entirely with a cone biopsy. This procedure involves cutting away a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue, but leaving the rest of the cervix intact.
Can you use chemotherapy for cervical cancer?
Sometimes both methods are used. For locally advanced cervical cancer, low doses of chemotherapy are often combined with radiation therapy, since chemotherapy may enhance the effects of the radiation . Higher doses of chemotherapy might be recommended to help control symptoms of very advanced cancer.
Can you be prepared for cancer?
No one can be prepared for a cancer diagnosis. You can, however, try to manage the shock and fear you're feeling by taking steps to control what you can about your situation.
What is the treatment for cervical cancer?
Radiotherapy is a treatment method that prevents the growth of cancer cells by using high energy X-rays. External radiotherapy is applied in cervical cancer. With this method, treatment is provided without disrupting the body integrity or touching the body. Another radiotherapy method is called brachytherapy.
How is stage 1B cervical cancer determined?
Stage 1B cervical cancer treatment is determined by your doctor according to factors such as the type of cell, its location, and the person’s health. Surgery combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy can be applied for Stage 1B treatment.
What is the 1B stage of cancer?
Cervical cancer in the 1B stage consists of larger cancer cells than the previous stage. It can often be seen without a microscope. It has two phases, 1B1 and 1B2. In the 1B1 stage, cancer cells have not reached 4cm yet. In 1B2 phase, cancer cells have reached 4cm. At this stage, cancer cells have not yet metastasized and spread.
How many stages of cervical cancer are there?
Cervical cancer is classified in 4 stages. Diagnosis of the disease in early Stage 1 is very important to get rid of this disease. In early cervical cancer the 5 yr. survival is 90%. It is important for cervical cancer stage 1b1 treatment that it has not yet been metastasized and is still operable.
What is stage 1b1?
What is cervical cancer stage 1b1 treatment and how is the disease diagnosed? Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that can be treated and potentially cured when detected in early stages. Typically caused by the HPV virus, it is a slowly developing cancer.
What is stage 1B surgery?
Stage 1B Cervical Cancer Surgery. For early-stage cervical cancer, surgery is performed to remove the cervix and the uterus. Another early stage surgery method is when a part of the cervical canal called “cervical conization” is performed. With this method, fertility is not lost.
What is the treatment for cancer in the vagina?
In this treatment, a device placed inside the vagina aims to destroy the cancer cells by sending X-rays directly. Chemotherapy is the most widely known treatment method in cancer treatment. Drugs that directly affect cancer cells are used to stop their growth.
What is the most local stage of cervical cancer?
Stage 1 cervical cancer is the most local stage of cervical cancer. In stage 1, cancer cells: Grow from the surface of the cervix into deeper tissues of the cervix. Have not spread to nearby lymph nodes. Have not spread to distant sites. Stage 1 is split into A and B, which are further divided.
How to stay healthy with cervical cancer?
The best way to stay healthy is to see your healthcare provider regularly for routine screening. Many of the symptoms of cervical cancer can also be caused by other conditions. If you experience any signs and symptoms of cervical cancer, see a healthcare professional right away.
How many women will have cervical cancer in 2020?
Cervical cancer is one of the most common forms of gynecologic cancers, with 6 in 1,000 women receiving a cervical cancer diagnosis at some point in their lifetime. In 2020, American Cancer Society’s estimates there were an estimated 14,000 new cases of invasive cervical cancer diagnosed in the United States.
What happens when cervix cancer grows?
Cervical cancer occurs when previously healthy cells in the cervix become abnormal. As they grow, they crowd healthy cells. If the abnormal cells spread to other areas of the body, it makes it harder for the body to function correctly. Cervical cancer used to be one of the most common causes of cancer death for American women.
What is stage 2 cancer?
Stage 2 is split into A and B, but 2A is additionally divided. 2A: Cancer has grown beyond the cervix and uterus, but not into the parametrium. 2A1: The cancer is smaller than 4 cm (1 ⅗ inch). 2A2: The cancer is larger than 4 cm. 2B: The cancer extends beyond the cervix and uterus and has spread into the parametrium.
What is a radical hysterectomy?
A radical hysterectomy is a total hysterectomy, however, it includes the uppermost part of the vagina near the cervix (parametrium) and the pelvic ligaments that support the uterus.
Where does stage 2 cervical cancer spread?
Stage 2 cancer spreads to the parametrium and past the uterus to the upper vagina. Because the tumor is growing into nearby tissue, noticeable symptoms are more likely to occur at this stage. Symptoms of stage 2 cervical cancer include: Abnormal uterine bleeding.
What Are Symptoms of Cervical Cancer?
Early cervical cancer and pre-cancer usually do not have any symptoms. Symptoms of cervical cancer often do not start until the cancer grows and spreads into nearby tissue. When symptoms of cervical cancer occur, they may include:
What Causes Cervical Cancer?
The cause of cervical cancer is not always known though it may be due to genetic changes (mutations).
What Is the Treatment for Cervical Cancer?
Treatments for cervical cancer may include one or more of the following:
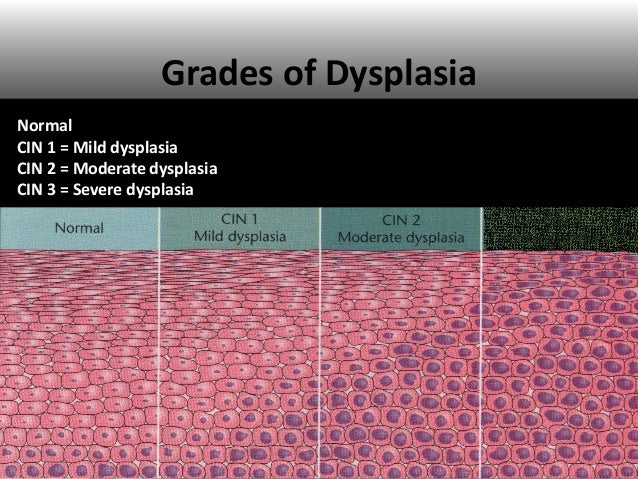
What Is Stage 1 Cervical Cancer?
Stage 1A
Stage 1B
Treatment
Specialist to consult
Surgery
- The stage of a cancer tells you how big it is and whether it has spread. It helps your doctor decide which treatment you need. Doctors use the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging system for cervical cancer. There are 4 stages, numbered 1 to 4. Stage 1 means that your cancer is within the neck of the womb (cervix). It hasn’t spread to nearby tissues or oth…
Combined Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
- In stage 1A the growth is so small that it can only be seen with a microscope or colposcope. It can be divided into 2 smaller groups: 1. stage 1A1 2. stage 1A2 Stage 1A1 means the cancer has grown less than 3 millimetres (mm) into the tissues of the cervix. Stage 1A2 means the cancer has grown between 3 and 5 mm into the cervical tissues.
Other Stages
- In stage 1B the cancerous areas are larger, but the cancer is still only in the tissues of the cervix and has not spread. It can usually be seen without a microscope, but not always. It can be divided into 3 groups: 1. stage 1B1 2. stage 1B2 3. stage 1B3 In stage 1B1 the cancer is deeper than 5mm but no more than 2cm in size. In stage 1B2 the cancer is at least 2cm but not bigger than 4cm i…