Options include:
- Excisional surgery
- Mohs surgery
- Cryosurgery
- Curettage and electrodesiccation (electrosurgery)
- Laser surgery
- Radiation
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT)
- Topical medications
What are the treatments for squamous cell carcinoma?
Options include: Excisional surgery Mohs surgery Cryosurgery Curettage and electrodesiccation (electrosurgery) Laser surgery Radiation Photodynamic therapy (PDT) Topical medications
What are the treatment options for atypical Pap smear results?
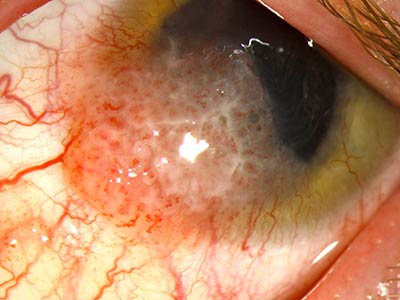
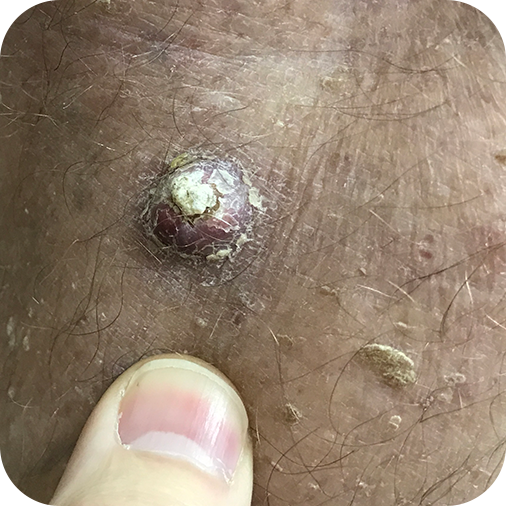
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma is a cancer of the keratin producing cells in the squamous epithelium (i.e., keratinocytes) within the stratum spinosum layer of the epidermis. It may be visible as skin growths that appear as a non-healing, ulcerated (i.e. crusted) nodule or erosion in the skin. Most commonly, it is found on sun-exposed areas ...
Do abnormal squamous cells in Pap smear mean cancer?
Based on the type and stage of the cancer and other factors, your treatment options may include: Surgery for Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancers. Local Treatments Other than Surgery for Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancers. Radiation Therapy for Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancers. Systemic Chemotherapy for Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancers. Targeted …
How does immunotherapy work for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pap Smear Naturally, effortlessly eliminate HPV virus and problems, such as atypical Pap smears and cervical dysplasia, ... Papillomavirus Treatment is a usually noted condition simply because it is of concern when considering Papillus Virus, Papiloma, and …
What is the best treatment for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix?
What is the most common treatment for squamous cell carcinoma?
- Mohs Surgery. Mohs surgery has the highest cure rate of all therapies for squamous cell carcinomas. ...
- Curettage and Electrodessication. This very common treatment for squamous cell carcinoma is most effective for low-risk tumors. ...
- Cryosurgery. ...
- Laser Surgery.
What is one option of treatment for squamous cell carcinoma?
Does squamous cell carcinoma need to be removed?
Do you need chemo for squamous cell carcinoma?
What is the survival rate for squamous cell carcinoma?
What happens if you don't remove squamous cell carcinoma?
What is considered early detection of squamous cell carcinoma?
How long can you live with squamous cell carcinoma?
How long does it take to recover from squamous cell carcinoma surgery?
What is Mohs surgery for squamous cell carcinoma?
How do I know if squamous cell carcinoma has spread?
- The tumor is thicker than 2 millimeters.
- The tumor has grown into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin.
- The tumor has grown into the nerves in the skin.
- The tumor is present on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip.
Which Treatments Are Used For Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancers?
Based on the type and stage of the cancer and other factors, your treatment options may include: 1. Surgery 2. Other forms of local therapy 3. Radi...
Which Doctors Treat Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancers?
You might have different types of doctors on your treatment team. Most basal and squamous cell cancers (as well as pre-cancers) are treated by derm...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Clinic- or hos...
When is immunotherapy considered for squamous cell carcinoma?
For squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, immunotherapy might be considered when the cancer is advanced and other treatments aren't an option. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
How to test for squamous cell carcinoma?
To confirm a squamous cell carcinoma of the skin diagnosis, your doctor will use a tool to cut away some or all of the suspicious skin lesion (biopsy). What type of skin biopsy you undergo depends on your particular situation. The tissue is sent to a laboratory for examination.
What is photodynamic therapy?
During photodynamic therapy, a liquid drug that makes the cancer cells sensitive to light is applied to the skin. Later, a light that destroys the skin cancer cells is shined on the area.
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is sometimes used after surgery when there is an increased risk that the cancer will return. It might also be an option for people who can't undergo surgery.
How to minimize scarring on face?
To minimize scarring, especially on your face, consult a doctor skilled in skin reconstruction. Mohs surgery. During Mohs surgery, your doctor removes the cancer layer by layer, examining each layer under the microscope until no abnormal cells remain.
How to treat skin cancer?
It may be an option for treating superficial skin lesions. Freezing might be done after using a scraping instrument (curet) to remove the surface of the skin cancer.
What is laser treatment for skin lesions?
Laser treatment may be an option for very superficial skin lesions. Freezing. This treatment involves freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen (cryosurgery).
What is the most effective technique for removing SCCs?
When it’s used. Mohs surgery is the most effective technique for removing SCCs, sparing the greatest amount of healthy tissue while achieving the highest possible cure rate – up to 97 percent for tumors treated for the first time.
Where does the excised tumor go after surgery?
Typically, the patient goes home after the surgery, and the excised tumor goes to the lab. If the lab finds cancer cells beyond the margins, the patient may need to return for more surgery until margins are cancer-free.
What to do if SCC has not spread?
If you’ve been diagnosed with an SCC that has not spread, there are several effective treatments that can usually be performed on an outpatient basis. The choices available to you depend on the tumor type, size, location and depth, as well as your age and overall health. Options include: Excisional surgery. Mohs surgery.
How is Mohs surgery performed?
Mohs surgery is performed during a single visit, in stages. The surgeon removes the visible tumor and a very small margin of tissue around and beneath the tumor site. The surgeon color-codes the tissue and draws a map correlated to the patient’s surgical site.
How does scalpel surgery work?
Using a scalpel, the surgeon removes the entire tumor along with a “safety margin” of surrounding normal tissue. The margin of normal skin removed depends on the thickness and location of the tumor. Typically, the patient goes home after the surgery, and the excised tumor goes to the lab. If the lab finds cancer cells ...
What is the purpose of a laser on a tumor?
The physician applies a light-sensitizing topical agent and, after allowing a period of time for absorption, directs a strong blue or red light or laser at the tumor to activate the topical agent, killing cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue.
What to ask your dermatologist about treatment options?
Ask your dermatologist to clearly explain the options that might work best for you, including details about the risks and benefits. Check our treatment glossary for more detailed information.
What kind of doctor treats basal cell cancer?
Most basal and squamous cell cancers (as well as pre-cancers) are treated by dermatologists – doctors who specialize in treating skin diseases. If the cancer is more advanced, you may be treated by another type of doctor, such as: A surgical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer with surgery. A medical oncologist: a doctor who treats cancer ...
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Why is it important to communicate with your cancer care team?
Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
What is the number to call for cancer treatment?
Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists. Palliative Care. Find Support Programs and Services in Your Area.
What to talk to your cancer care team about?
Be sure to talk to your cancer care team about any method you are thinking about using. They can help you learn what is known (or not known) about the method, which can help you make an informed decision.
Why is it important to discuss all of your treatment options with your doctor?
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider include:
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
What tests are recommended after atypical Pap?
Additional tests, such as cervical biospies, endocervical sampling exams and colposcopies may also be recommended after an atypical Pap result. If cancerous squamous cells are detected during a Pap smear, prompt treatment is advised.
Why is a squamous cell re-analyzed?
Usually, when atypical squamous cells are found, the cell sample is re-analyzed to check for the presence of certain viruses, such as HPV.
What does a Pap smear show?
When a Pap smear detects atypical squamous cells, follow-up testing is required to determine the underlying cause. In most cases, the presence of abnormal squamous cells does not indicate the presence of cervical cancer.
What is the number to call for a Pap smear?
If you’ve recently received abnormal Pap smear results involving the presence of atypical squamous cells, call 1-888-663-3488 or submit a new patient registration form online to request an appointment with one of Moffitt’s gynecologic oncologists.
How often should you follow up on a Pap smear?
Your particular schedule of follow up will depend on results of any biopsies you had and treatments you have chosen, but is usually at least annually for a few years.
What is abnormal Pap smear?
An abnormal Pap smear result of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) means that cells of the cervix (the narrow neck of a woman's uterus) look somewhat to very abnormal when examined under a microscope. 1 . Before cervical cancer forms, the cells of the cervix undergo abnormal changes called cervical dysplasia.
What does HSIL Pap smear mean?
An HSIL Pap smear result indicates that more defined changes in the size and shape of cervical cells have been detected, which indicates there is likely moderate-to-severe cervical dysplasia.
What is a colposcopy exam?
A colposcopy exam is an in-office procedure that allows a doctor to visually examine the cervix with a lighted instrument called a colposcope. 4 During the exam, the colposcope remains outside of the vagina. It acts like a microscope, allowing an in-depth view of the cervix.
What is the first step in colposcopy?
If the risk of CIN 3 is not very high, waiting for the results of biopsies done during a colposcopy is often the first step.
What is AIS in cervical biopsies?
Cervical biopsies can sometimes reveal adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), which means there are abnormal glandular cells that have not spread beyond where they formed. AIS is sometimes referred to as stage 0 cancer. When AIS if found or cervical cancer is caught at an early stage, it's easier to treat and the survival rates are highest. 6 Treatments for AIS are often similar to those for severe dysplasia.
What is the purpose of a biopsy result?
A biopsy result obtained during a colposcopy allows a pathologist to see the actual changes in cells and their relation to each other within the tissue. This is needed to confirm whether or not precancerous changes or cancer are present.
What is the only method of cervical cancer screening?
For many years, cytology -based screening, known as the Pap test or Pap smear, was the only method of screening. Its use reduced cervical cancer incidence and deaths in countries where screening is common.
What is a low grade squamous intraepithelial lesions?
Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) are considered mild abnormalities caused by HPV infection. LSILs often return to normal as the immune system controls the infection, especially in younger women.
Why do we need to screen for cervical cancer?
The primary goal of screening is to identify precancerous lesions caused by HPV so they can be removed to prevent invasive cancers from developing. A secondary goal is to find cervical cancers at an early stage, when they can usually be treated successfully.
What is the best test for HPV?
Several new tests are currently in development that can improve the evaluation of HPV-positive women. One test that is undergoing regulatory evaluation but is not yet clinically available is based on detection of two proteins that indicate an active HPV infection—p16 and Ki-67. P16/Ki-67 dual staining was found to be more accurate than Pap testing (the current standard for follow-up testing of HPV-positive women) at predicting whether an HPV-positive woman would go on to develop cervical precancer within 5 years. If positive for p16/Ki-67, she may be referred for colposcopy and biopsy.
Why is cervical cancer screening important?
The primary goal of screening is to identify precancerous lesions caused by HPV so they can be removed ...
How long does it take for HPV to be controlled?
Although HPV infection of the cervix is very common, most infections will be controlled by the immune system over the course of 1 to 2 years.
What is the purpose of a colposcopy?
During a colposcopy, the provider inserts a speculum into the vagina to widen it and may apply a dilute vinegar solution to the cervix, which causes areas of HPV infection, inflammation, precancer, or other cell changes to turn white. The provider then uses the colposcope (which remains outside the body) to examine the cervix.
