Prevention of Occiput Posterior
- Postures – avoid reclining positions and sit with the pelvis tilted. Use a birth ball to maintain this posture. Sleep...
- Exercises – perform exercises that involve pelvic rocking, walking, and swimming. Here is what can be done – 1. During...
- Therapies – chiropractic and acupuncture techniques help fix the improper alignment of the body...
What is occiput posterior (op)?
A baby is usually in the head-down (vertex) position, with the head facing your back. However, it is not the only position. The fetus might be in various other positions, including occiput posterior (OP). MomJunction tells you about this fetal position, its causes, and complications.
How is occipital neuralgia (PN) treated?
Treatment of occipital neuralgia aims to alleviate the pain; however, it is not a cure. Interventions can be surgical or non-surgical. Heat: patients often feel relief when heating pads or devices are placed in the location of the pain. Such heating pads can be bought over-the-counter or online.
How can I strengthen my occipital muscles?
Do occipital strengthening exercises. Place your fingertips on the front of your chin, keeping your mouth closed. Maintaining a straight neck, exhale and gently press your chin backward. Allow your head to move under the pressure until you feel the pull of your occipitals at the base of your skull.
What causes occiput posterior?
Here are some reasons for occiput posterior: The shape of the pelvis: Anthropoid and android-shaped pelvises could lead to OP. Women with heart-shaped pelvis (android) can have the baby in this position because of the narrower front.

How can we stop occiput posterior?
Preventing Posterior LaborAvoid all reclining positions. ... Keep knees below your pelvis at all times, back straight. ... Keep active, walk as much as possible.More items...
Is right occiput posterior normal?
In Right Occiput Posterior (ROP), baby is head down and the back is to the side- the right side. ROP is the most common of the four posterior positions. Attention: The ROP baby may need a longer time for fetal rotation in labor.
What are the complications of Occipito posterior position?
Complications of the occiput posterior position The OP position is associated with more frequent induction and augmentation of labour and prolonged first and second stage of [3,17,18,21], chorioamnionitis, post-partum haemorrhage, third and fourth degree perineal tears, wound infection and endometritis [22,23].
What causes occiput posterior position?
The occipitoposterior position in the main is caused by the adaptation of the head to a pelvis having a narrow fore pelvis and an ample anteroposterior diameter and therefore may be considered “physiologic.”
Can you deliver posterior baby?
How can a posterior position baby affect the birth? A posterior labour will generally progress just as efficiently as an anterior labour, especially if the mother has good contractions and assumes forward-leaning, active birth positions. Around 90 percent of posterior babies will turn during the course of labour.
How can I change my baby's posterior position?
Scrub the floor on your hands and knees. Crawling around in this position is great. Do pelvic rocks 10 times in a row 2-5 times a day. Go on your hands and knees and rock your pelvis up and down (alternately arching your back by tucking your pelvis under and then straightening, like the mad cat pose in yoga).
How can I make my baby face down?
Natural methodsBreech tilt, or pelvic tilt: Lie on the floor with your legs bent and your feet flat on the ground. ... Inversion: There are a few moves you can do that use gravity to turn the baby. ... Music: Certain sounds may appeal to your baby. ... Temperature: Like music, your baby may respond to temperature.More items...•
How do I know if my baby is occiput posterior?
Right or Left Occiput Posterior When facing forward, the baby is in the occiput posterior position. If the baby is facing forward and slightly to the left (looking toward the mother's right thigh) it is in the left occiput posterior (LOP) position.
How can I turn my baby from back to back?
2:4711:29Module 1: Back To Back Babies (OP Position ) - How to Get Them to TurnYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHead is angled towards the cervix. So they're putting really good pressure they're well applied toMoreHead is angled towards the cervix. So they're putting really good pressure they're well applied to the cervix. So that when you're in labor.
Can a posterior baby delay labor?
The Short Answer: You can't prevent a posterior baby and start and stop labor is not because baby is OP. Many babies need to be and are OP during labor as part of their natural rotation process.
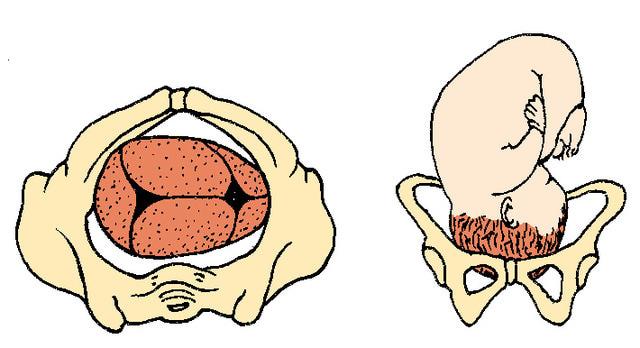
What does occiput posterior mean?
Occiput Posterior (OP) In occiput posterior position, your baby's head is down, but it is facing the mother's front instead of her back. It is safe to deliver a baby facing this way. But it is harder for the baby to get through the pelvis.
What causes a baby to be born face up?
The posterior position, also known as the occiput posterior (OP) position or the “sunny side up” position, occurs when the baby is in a head-first, forward facing position. Babies in the posterior position will be face up when they're delivered. Posterior position can cause labor dystocia and resultant birth injuries.
Where does a baby kick in occiput posterior position?
In occiput posterior position usually means the baby kicks right at the front of the tummy, generally around the middle. Also, the tummy looks as though it’s flattened out, rather than being a rounded shape.
How to help a baby move back to the right position?
3. During the pushing stage – doing double hip squeeze during the contractions can help the pelvis spread, providing more room for the baby to move back to the right position. Therapies – chiropractic and acupuncture techniques help fix the improper alignment of the body and turn the baby to the occiput anterior position.
What is Occiput Posterior?
An Occiput Posterior is a common fetal malposition. In this position, the baby’s head faces downwards, but it faces the mother’s front instead of her back. Although it is easy to deliver a baby in this position, but it gets harder for the baby to come out from the pelvis.
Left Occiput Posterior
By now we know that when the baby is facing forward, it is in an occiput posterior position. If the position of the fetus is facing forward and slightly to the left (looking towards the mom’s right thigh) it is in the left occiput posterior position.
Right Occiput Posterior
In the right occiput posterior presentation, the baby is usually seen to be facing forwards and a little to the right (looking towards the mom’s left thigh). In this kind of a presentation, the process of labor maybe slower and may cause more pain.
What is the right occput posterior?
In Right Occiput Posterior (ROP), baby is head down and the back is to the side- the right side. ROP is the most common of the four posterior positions. Attention: The ROP baby may need a longer time for fetal rotation in labor. The right-sided baby is posterior if the forehead favors the front, even if the baby is looking diagonally, ...
What is the biggest challenge of any posterior baby who has that posture?
Extension is the biggest challenge of any posterior baby who has that posture. The midwife will feel that the head is narrow and may think it is the nape of the neck. The difference is that the baby won’t play with the hands behind his or her back.
How to tell if a baby is posterior?
The easiest clue for pregnant women to feel is whether the baby has limb movements on both sides of her abdomen, right and left. If the hands and knees are on either side of her navel ( below and beside it, usually), it’s a good bet the baby is posterior.
What is the best treatment for occipital neuralgia?
Anticonvulsant medications. Percutaneous nerve blocks: these injections can be used both to diagnose and treat occipital neuralgia. Botulinum Toxin (Bot ox) Injections: Botox injections can be used to decrease inflammation of the nerve.
Why is occcipital neuralgia so hard to diagnose?
Occipital neuralgia can be very difficult to diagnose because of its similarities with migraines and other headache disorders. Therefore, it is important to seek medical care when you begin feeling unusual, sharp pain in the neck or scalp and the pain is not accompanied by nausea or light sensitivity.
Can occipital neuralgia be caused by neck pain?
It can also be caused by a head or neck injury. Occipital neuralgia can either be primary or secondary. A secondary condition is associated with an underlying disease. Although any of the following may be causes of occipital neuralgia, many cases can be attributed to chronic neck tension or unknown origins. Osteoarthritis of the upper cervical ...
Is occipital nerve stimulation the same as spinal cord stimulation?
Occipital Nerve Stimulation: This surgical treatment involves the placement of electrodes under the skin near the occipital nerves. The procedure works the same way as spinal cord stimulation and uses the same device. The procedure is minimally invasive and surrounding nerves and structures are not damaged by the stimulation. It is an off-label indication for an FDA-approved device.
What does occiput posterior mean?
So, good! we can assume that the occiput in “occiput posterior” means the back of the skull. Probably the baby’s skull, since you haven’t ever found much need for a medical term to refer to the back of your own head. And then there’s posterior: posterior refers to the back end of something.
What does persistent occiput posterior position mean?
Really, persistent occiput posterior position just means occiput posterior positioning that LASTS. Babies can often get themselves swirled around into this position throughout pregnancy. Even if this positioning is noticed early during labor, babies often resolve their position as labor progresses.
How to tell if baby is in occiput posterior position?
Your nurse can use a digital vaginal exam (with fingers) to tell if the baby is in occiput posterior position– If you are far enough along, sure, you can probably start feeling for features, but it’d be pretty late in the birth game. ( source)
Is it safe to have a baby in occiput?
Labor is still possible and potentially 100% safe with a baby in occiput posterior positioning. Even if this isn’t considered “optimal” positioning. It DOES mean that your little one will have a harder time getting through your pelvis.
Where is the occiput located?
Occiput: the back of the baby’s head. Posterior: located generally at or toward the back half of your body. Plain and simple: The back of baby’s head is pointed toward the BACK END of your body.
Is occiput posterior positioning scary?
Occiput posterior positioning can be a significant source of complication, so be sure to ask your provider questions WELL in advance of the L&D unit. Occiput posterior positioning can be scary, but if you have all the knowledge, you’ll come through this swinging. Happy Baby Birthing, mama.
How to turn a baby posterior?
Some practitioners may attempt to turn a posterior baby by manual rotation. Once you're fully dilated, the practitioner reaches into your vagina, puts his hand or fingers on your baby's head, and tries to rotate it. (Sometimes this is done while using ultrasound.)
What does it mean when a baby is in the posterior position?
What does it mean for a baby to be in the posterior position? A baby that is head-down but facing your abdomen is said to be in the posterior position. A small percentage of babies end up in this position at birth. If your baby is in the posterior position, you may be in for a more complicated delivery. The technical term is occiput posterior (OP) ...
What is the OP position for a baby?
The technical term is occiput posterior (OP) position. This term refers to the fact that the back of your baby's skull (the occipital bone) is in the back (or posterior) of your pelvis. You may also hear this position referred to as "face-up" ...
What percentage of babies are posterior?
While as many as 34 percent of babies are posterior when labor starts, only 5 to 8 percent of them are posterior at birth. It's common for a baby's position to change during labor, often more than once. Most babies rotate on their own to the face-down position before birth.

Cause
- Occipital neuralgia is a common cause of headache. It involves the occipital nerves two pairs of nerves that originate near the second and third vertebrae of the neck. The pain typically starts at the base of the skull by the nape of the neck and may spread to the area behind the eyes and to the back, front and side of the head. Occipital neuralgia is a headache syndrome that can be eith…
Signs and symptoms
- Symptoms include continuous aching, burning and throbbing, with intermittent shocking or shooting pain. The pain often is described as migraine-like and some patients experience other symptoms common to migraines and cluster headaches. The pain usually originates at the base of the skull and radiates near the back or along the side of the scalp. Some patients experience …
Diagnosis
- It can be difficult to distinguish occipital neuralgia from other types of headaches thus, diagnosis may be challenging. A thorough evaluation will include a medical history, physical examination and diagnostic tests. A doctor can document symptoms and determine the extent to which these symptoms affect a patient's daily living. If there are abnormal findings on a neurological exam, t…
Treatment
- The goal of treatment is to alleviate the pain. Often, symptoms will improve or disappear with heat, rest and/or physical therapy, including massage, anti-inflammatory medications and muscle relaxants. Oral anticonvulsant medications such as carbamazepine and gabapentin also may help alleviate pain. Percutaneous nerve blocks not only may be helpful...
Mechanism of action
- Occipital nerve stimulation uses a neuro-stimulator to deliver electrical impulses via insulated lead wires tunneled under the skin near the occipital nerves at the base of the head. The electrical impulses can help block pain messages to the brain. The benefit of this procedure is that it is minimally invasive, and the nerves and other surrounding structures are not permanently damag…
Resources
- The following websites offers additional helpful information on trigeminal neuralgia and its causes, treatment options, support and more. (Note: These sites are not under the auspices of AANS, and their listing here should not be seen as an endorsement of the sites or their content.)