What are the symptoms of polyps?
| Type of polyps | Location | Symptoms |
| colorectal (colon) | large intestine, colon, and rectum | blood in stool, abdominal pain, constipa ... |
| endometrial (uterine) | uterus, usually uterine lining | infertility, irregular menstrual bleedin ... |
| cervical | cervix, where the uterus connects to the ... | typically no symptoms, but can include b ... |
| gastric (stomach) | stomach and stomach lining | nausea, pain, tenderness, vomiting, blee ... |
How to remove polyps from uterus naturally?
- Inflammation – Chronic inflammation causes abnormal tissue growth. ...
- Estrogen – Imbalanced estrogen levels also cause abnormal growth of estrogen-sensitive tissues like the uterus.
- Progesterone deficiency. ...
- Ageing – As women age, ovulation occurs less often. ...
- Excess weight/obesity
- Unbalanced estrogen therapy
What is the recovery time after uterine polyp removal?
Recovery is generally quick. Minor side effects such as gassiness, bloating, and cramps usually resolve within 24 hours. With a more involved procedure, a full recovery can take up to two weeks.
How do they remove polyps from uterus?
These include:
- progestin drug
- medicated intrauterine device (IUD)
- endometrial ablation, a procedure that destroys the uterus lining
How do you remove a polyp from the uterus?
The options for removal include:
- Removal with forceps or a wire loop (polypectomy). If a polyp is too large to remove with this method, a liquid may be injected under it to lift and isolate ...
- Minimally invasive surgery. ...
- Colon and rectum removal (total proctocolectomy). ...
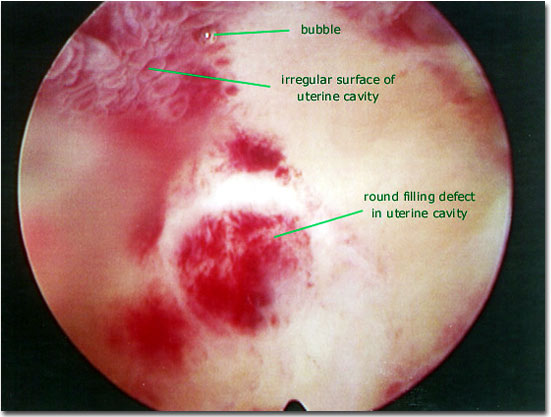
Do polyps in the uterus need to be removed?
Management and Treatment They should be removed if they cause problems during pregnancy, such as a miscarriage, or result in infertility in women who want to become pregnant. If a polyp is discovered after menopause, it should be removed.
Should I be worried about a uterine polyp?
ANSWER: It is rare for uterine polyps to be cancerous. If they aren't causing problems, monitoring the polyps over time is a reasonable approach. If you develop symptoms, such as abnormal bleeding, however, then the polyps should be removed and evaluated to confirm that there is no evidence of cancer.
What happens if you have a polyp in your uterus?
Uterine polyps attach to your uterus by a large base or a thin stalk and can grow to be several centimeters in size. Irregular menstrual bleeding, bleeding after menopause, excessively heavy menstrual flow or bleeding between periods could signal the presence of uterine polyps.
How do they remove a polyp from the uterus?
The gynecologist guides the hysteroscope into your vagina, through the cervix, and into the uterus. Gas or saline is released through the scope to inflate your uterus, allowing for better visualization. The physician will remove any polyps with special scissors, a laser, or another device that uses electricity.
Can uterine polyps be treated with medication?
Treatment of small polyps is unnecessary unless you're at risk of uterine cancer. Medication. Certain hormonal medications, including progestins and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, may lessen symptoms of the polyp.
Can uterine polyps be cured naturally?
You may not need treatment if you don't have any symptoms and the polyp isn't cancer. It might go away on its own. But if you're past menopause or at a higher risk for uterine cancer, your doctor will remove it. Medications.
Is uterine polyp removal painful?
A person may feel pressure or pulling during the procedure, but they should feel no pain. Depending on the location of the polyp and other factors, a doctor may give the person pain-blocking medication before, during, or after the procedure.
Are polyps in uterus painful?
Typically, polyps grow to be a few millimeters to a few centimeters. Pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile and can protrude from the uterus into the vagina. Women will typically only feel pain from uterine polyps when this happens.
Is a hysteroscopy painful?
Some women feel no or only mild pain during a hysteroscopy, but for others the pain can be severe. If you find it too uncomfortable, tell the doctor or nurse. They can stop the procedure at any time.
How long does uterus polyp surgery take?
The procedure generally takes from 5-10 minutes to perform and is called a hysteroscopic (or resectoscopic) polypectomy.
What is the recovery time for uterine polyp removal?
Many patients worry about uterine polyp removal recovery time, but recovery is quick; after a single polypectomy, patients can return to work the next day and expect a full recovery within two weeks.
What causes uterus polyps?
What causes uterine polyps? No definitive cause of endometrial polyps is known, but they appear to be affected by hormone levels and grow in response to estrogen circulating in the blood. Endometrial polyps are rare among women younger than 20 years of age.
What to do if you have a polyp after menopause?
If a polyp is discovered after menopause, it should be removed. Methods of treatment include the following: Medications: Drugs that help regulate the hormonal balance, such as progestins or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, may be used as a temporary treatment. These medications help to relieve symptoms.
What is the procedure to check for uterine polyps?
Hysteroscopy: this may be used to either diagnose or treat uterine polyps. During this procedure, a doctor inserts a long, thin tube with a lighted telescope (hysteroscope) through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. The hysteroscope allows the physician to examine the inside of the uterus.
How are polyps formed?
For that reason, they are sometimes called endometrial polyps. Uterine polyps are formed by the overgrowth of endometrial tissue. They are attached to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base and extend inward into the uterus. The polyps may be round or oval, and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) ...
How are polyps attached to the endometrium?
They are attached to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base and extend inward into the uterus. Uterine polyps are usually noncancerous, but they may cause problems with periods (menstruation) or fertility. Appointments 216.444.6601. Appointments & Locations. Have My Baby at Cleveland Clinic.
Why do polyps form in the uterus?
What causes uterine polyps? The exact reason that polyps form is unknown, but swings in hormone levels may be a factor. Estrogen, which plays a role in causing the endometrium to thicken each month, also appears to be linked to the growth of uterine polyps.
How big are uterine polyps?
The polyps may be round or oval, and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball), or larger. There may be one or several polyps present. Uterine polyps are usually benign (noncancerous), but they may cause problems with periods ( menstruation) or the ability to have children ...
How long does a polyp last?
Infertility. The most common symptom of uterine polyps is irregular or unpredictable menstrual periods. Most women have periods that last four to seven days. A woman's period usually occurs every 28 days, but normal menstrual cycles can range from 21 days to 35 days.
How to cure uterine polyps?
The majority of cases of uterine polyps are cured by thorough dilation and curettage. However, removal of polyps or other structural abnormalities may be missed by blind curettage, therefore, a surgical procedure may be needed. Hysteroscopy is a procedure that is performed minimally invasively at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
What is a polyp in the uterus called?
Uterine polyps, also called endometrial polyps , are excess outgrowths of the endometrium (innermost uterine layer) in the uterine cavity. The prevalence of polyps is estimated to be 10 percent to 24 percent of women undergoing hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) or localized endometrial biopsy. Uterine polyps are rare among women younger ...
What is hysteroscopy in women?
Hysteroscopy is a procedure that is performed minimally invasively at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Using a thin instrument with a lens, light source and camera attached to one end. This procedure enables surgeons to thoroughly examine the lining of the uterus and to remove the uterine polyps.
What is the division of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery?
The Division of Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery care team is committed to patients and their families. Each patient's diagnosis and treatment plan will be designed and tailored to their needs. Our team of highly skilled doctors, nurses, and other health care professionals work together to deliver the highest quality care to every patient. View our Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery Team.
What is the BWH Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology?
The faculty members and researchers at the BWH Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology are dedicated to doing everything possible to provide women and their families with the most advanced care available anywhere.
Why Choose Us for Uterine Polyps Care?
Uterine polyps, sometimes called endometrial polyps, are growths on the lining of the uterus (endometrium). Polyps can be small or large, and can cause irregular or excessive bleeding.
Find Doctors and Specialists
Find your gynecologic surgeon by browsing our provider profiles to ensure the best fit for you.
Locations
Our office at Cleveland Clinic's main campus is located in the A Building - Crile Building:
Make an Appointment
Learn more about how we care for women with uterine polyps at Cleveland Clinic. Call 216.444.6601 to request an appointment or to schedule a virtual visit.
Uterine Polyps Diagnosis at Cleveland Clinic
We diagnose uterine polyps with imaging techniques that help us see inside your uterus. Your doctor may choose:
Uterine Polyps Treatment at Cleveland Clinic
Before creating a treatment plan, our doctors talk with you about your symptoms, potential cancer risk and your future plans for pregnancy. We review treatment options with you to make sure you get the care that’s right for you.
Preserving Your Fertility
If pregnancy is among your future goals, we consider your wishes before creating a treatment plan for uterine polyps. Our experts work closely with Cleveland Clinic fertility center specialists, including reproductive endocrinology and infertility (REI) doctors.
How to get rid of polyps in uterus?
Instead of making a cut in your belly, they can insert a curette or other surgical tools through your vagina and cervix to take the polyps out. If your polyps have cancer cells, you may need surgery to take out your entire uterus, called a hysterectomy.
How do you know if you have uterine polyps?
Symptoms of Uterine Polyps. You may not have any symptoms, especially if you have small polyps or only one. Talk to your doctor if you notice: Irregular periods, when you can’t predict their timing, length, or heavi ness. Heavy periods. Bleeding or spotting between periods. Vaginal bleeding after menopause.
Why do women get polyps?
Experts don’t know exactly why women get uterine polyps. It may be linked to changes in hormone levels. Each month, your estrogen levels rise and fall , causing the lining of your uterus to thicken and then shed during your period. Polyps form when too much of that lining grows.
What is the procedure called when you put salt water in your uterus?
Hysterosonography or sonohysterography. Your doctor can use this procedure during a transvaginal ultrasound. They put a thin tube called a catheter inside your vagina and inject salt water into your uterus. The liquid expands your uterus to allow a clearer ultrasound.
What to take before cervix dilation?
Before the exam, you may need to take antibiotics, pain relievers, or medicines to dilate your cervix. Tests include: Transvaginal ultrasound. Your doctor puts a slender wand-like device inside your vagina. It gives off sound waves and sends them to a computer to create images of the inside of your uterus.
What is the name of the procedure that a doctor uses to see the inside of the uterus?
Hysteroscopy. Your doctor puts a thin, flexible, lighted telescope, called a hysteroscope, through your vagina and cervix and into your uterus. It lets them look at the tissue lining the inside. If they see polyps, they can use tools to remove them at the same time. Endometrial biopsy.
Where do polyps come from?
They come from the tissue that lines the uterus, called the endometrium. They can range in size from as small as a sesame seed to as big as a golf ball. You may have just one polyp or many of them at once.
What does it mean when you have a uterine polyp?
Irregular menstrual bleeding, bleeding after menopause, excessively heavy menstrual flow or bleeding between periods could signal the presence of uterine polyps. Uterine polyps are growths attached to the inner wall of the uterus that extend into the uterine cavity.
What is the term for the growth of uterine polyps?
Overgrowth of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) leads to the formation of uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps. These polyps are usually noncancerous (benign), although some can be cancerous or can eventually turn into cancer (precancerous polyps). Uterine polyps range in size from a few millimeters — no larger ...
How big are uterine polyps?
Uterine polyps range in size from a few millimeters — no larger than a sesame seed — to several centimeters — golf-ball-size or larger. They attach to the uterine wall by a large base or a thin stalk. You can have one or many uterine polyps.
Can you have children with uterine polyps?
If you have uterine polyps and you're unable to have children, removal of the polyps might allow you to become pregnant, but the data are inconclusive. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What happens if you have a polyp in your uterus?
Spotting and bleeding in between your periods. Prolapse; this occurs if a uterine polyp protrudes through the cervix, out of the uterus. Vaginal bleeding after menopause. Irregular menstrual periods- you might be unable to predict the heaviness, length, and timing of your periods. Trouble conceiving.
Why are endometrial polyps important?
The endometrial polyps could prevent a fertilized egg from attaching on your uterus, thus preventing conception. The growths could also block the cervix and fallopian tubes. The removal of endometrial polyps could help improve the chance of conceiving.
What is the term for a small bump in the uterus?
Removal of Uterine Polyps. Uterine polyps are also known as endometrial polyps and refer to small growths in the inner lining of the uterus in women. The polyps resemble flat bumps or small mushrooms. You could have one of several polyps at a time. The polyps vary in size and could range from a few millimeters to six centimeters.
When do endometrial polyps develop?
As you age, you might become more prone to uterine polyps; most women develop polyps between the ages of 40 and 50 years. Before the onset of menopause, women experience changes in estrogen levels; this change could lead to the development of polyps.
Where do uterine polyps come from?
Uterine polyps come from the tissue that lines the walls of the uterus known as the endometrium. Gyn LA provides the best treatment for uterine polyps, and we invite you to connect with our experienced Los Angeles gynecologists to learn more about our services.
What instrument is used to remove polyps?
Curettage. While performing this procedure, a doctor uses a metal instrument, which contains a loop on one edge. The instrument comes in handy in removing a portion of polyp for testing. The instrument would also come in handy to remove polyps.
What is the procedure to examine the inner part of the uterus?
Hysteroscopy. This diagnosis procedure entails inserting a thin and flexible telescope into your uterus through the vagina and the cervix. This telescope, commonly known as a hysteroscopy, enables the doctor to examine the tissues lining the inner part of your uterus.
What is the treatment for small polyps?
Medication: Certain hormonal medications, including progestins and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, may lessen symptoms of the polyp.
What is endometrial polyp?
Sexual & Reproductive. An endometrial polyp is a usually noncancerous growth attached to the inner wall of the uterus, common for women undergoing or who have completed menopause.
What percentage of endometrial polyps are malignant?
Cancer: Approximately 5 percent of endometrial polyps are malignant. However, data shows that the incidence of polyps that were malignant was significantly higher in postmenopausal compared with premenopausal women, and higher in women who had symptoms of bleeding than in women who did not.
What are some examples of endometrial polyps?
Be suspicious of endometrial polyps if your vaginal bleeding is different from your regular pattern. For example, abnormal patterns of vaginal bleeding include bleeding that is: Lighter or heavier than normal. At an unexpected time.
Why do polyps grow in women?
Polyps are caused by overgrowth of the cells lining the uterus (also known as endometrial cells). These cells are very sensitive to the hormone estrogen and grow as a response to circulating levels of estrogen. Endometrial polyps are relatively common in women who [5]:
Where are endometrial polyps located?
Endometrial polyps are growths or masses that occur in the lining of the inner wall of the uterus and often grow large enough to extend into the uterine cavity. They attach to the uterine wall by a large base (these are called sessile polyps) or a thin stalk (these are called pedunculated polyps). Endometrial polyps can be asymptomatic ...
Can polyps cause cancer?
Treatment involves careful monitoring, as polyps can sometimes be malignant and lead to cancer or problems with fertility. Removal may be necessary as well as medication. You should speak with your primary care physician or OB/GYN about these symptoms.
