Treatment of Pes Cavus
| Severity of Deformity | Examination | Treatment |
| Mild | Flexible, painless | Heel cord stretching, eversion/dorsiflex ... |
| Mild | Progressive or symptomatic | Plantar release ± peroneus longus to bre ... |
| Varus because of peroneal weakness | Add tibialis anterior and/or posterior t ... | |
| Moderate | Rigid medial cavus | Dorsiflexion osteotomy of either first m ... |
What is the surgical treatment for pes cavus?
Surgical treatment of pes cavus by tarsal V-osteotomy. Preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968 Jul. 50 (5):927-44.
What are the treatment options for cavus foot?
There are multiple surgical procedures that can help improve the symptoms of cavus foot – and an orthopedic foot surgeon will determine which procedure or combination of procedures will be most successful.
Can pes cavus pain be eliminated?
While it is possible to eliminate pain, and pain is a common reason for seeking additional care, early intervention can prevent many of the consequences of pes cavus.
When should you seek consultation for pes cavus?
Although it is absolutely necessary to seek consultation if you have lost sensation in your feet, are experiencing severe pain, or have noticed a progression in the deformity of your foot, pes cavus can be intervened in its early stages.

Is pes cavus curable?
Can it be cured? Cavus foot can be straightened through surgery (see the part on treatment below), but this is only considered if it's causing severe symptoms.
What problems does pes cavus cause?
The spectrum of associated deformities observed with pes cavus includes clawing of the toes, posterior hindfoot deformity (described as an increased calcaneal angle), contracture of the plantar fascia, and cockup deformity of the great toe.
Is pes cavus progressive?
Pes cavus, characterized by high arches and hammer toes and the clawfoot deformity, are typical foot deformities in hereditary polyneuropathies with childhood onset. These deformities are a result of progressive weakness and atrophy of intrinsic foot muscles.
What causes pes cavus feet?
Pes cavus is a foot with an abnormally high plantar longitudinal arch. People who have this condition will place too much weight and stress on the ball and heel of the foot while standing and/or walking.
Is pes cavus normal?
Pes cavus is a common finding in the general population, with prevalence of approximately 10% [1]. Frequently, pes cavus may be a sign of an underlying neurological disorder, including spinal cord and peripheral nerve pathologies, such us spino-cerebellar ataxia and hereditary peripheral neuropathies.
Is pes cavus a disability?
At the most recent VA examination, the VA examiner changed the diagnosis for service-connected disability to pes cavus with chronic plantar fasciitis. Pes cavus disability is rated under its separate criteria under DC 5278, claw foot (pes cavus) acquired. 38 C.F.R.
What muscles cause pes cavus?
Forefoot driven pes cavus is most often caused by neurological diseases and is the result of muscular imbalances. A weak tibialis anterior, intrinsic foot muscles, and peroneus brevis are overpowered by a stronger peroneus longus and posterior tibialis.
Which arch is affected in pes cavus?
Pes cavus, also known as high arch, is a human foot type in which the sole of the foot is distinctly hollow when bearing weight. That is, there is a fixed plantar flexion of the foot....Pes cavusHigh arch in foot of a person with a hereditary neuropathySpecialtyMedical genetics, Podiatry2 more rows
Can pes cavus cause back pain?
The healthcare professional may also determine that the feet have too little motion (pes cavus or “high arches”) in either static or dynamic positions. In this case, you will most likely have an onset of low back pain due to the lack of shock absorption. This can lead to impact type injuries.
Can cavus feet get worse?
An accurate diagnosis is important because the underlying cause of cavus foot largely determines its future course. If the high arch is due to a neurologic disorder or other medical condition, it is likely to progressively worsen.
What are the symptoms of pes cavus?
Pes cavus is often due to an underlying neurological condition. Symptoms predominantly include a high arch of the foot resulting in pain and possible fractures, tripping, a loss of sensation in the lower leg, or dragging one's affected foot or feet.
How do I know if I have pes cavus?
Common Pes Cavus Symptoms Claw toes (toes clenched like a fist) Hammertoes (bent toes) Pain when walking or standing. Calluses on the ball, heel or side of the foot.
What is a cavus foot?
A cavus foot (also called pes cavus) is one that has a very high arch. The problem with having a high-arched foot is that it places too much weight on the ball and heel of the foot. This alteration in your foot’s weight-bearing surface can often lead to pain and instability. Cavus foot is often present at birth, although it can develop at any age.
Can you have surgery for hereditary cavus feet?
Whereas most hereditary cavus feet do fairly well with conservative treatment, in cases where an underlying neurologic condition exists, conservative therapy might fail to provide continued symptom relief as the disease progresses. Surgery is not uncommon and is an option when other treatments aren’t successful.
Can a cavus foot cause shin splints?
In addition, one or more of the following symptoms may occur: In severe cases, cavus foot deformity can lead to ankle arthritis, frequent tripping, and falling due to ankle instability, stress fractures around the ankle, shin splints, or Achilles tendon pain.
What is the treatment for a PES Cavus foot?
Treatment of a cavus foot deformity must be considered in the context of the underlying diagnosis. If the cause of the pes cavus foot deformity is treatable (such as a spinal cord tumor or tethered spinal cord) it should be the first focus of treatment even though the resultant foot deformity may still be progressive. The goal of treatment of a patient with a cavus foot deformity is to achieve a painfree, plantigrade, mobile foot with improved muscle balance.
Why is the Pes Cavus foot less effective?
This is so because more stress is placed on the section of the foot between the ankle and toes (metatarsals). Pes cavus foot is a less efficient shock absorber, while being placed under constant tension.
What are the indications for cavus foot surgery?
Indications for surgical intervention include progressive deformity, painful callosities and hindfoot or ankle instability. Many operative procedures have been described to correct the individual deformities and balance the muscle forces in a cavus foot (a full description of these is beyond the scope of this discussion). An important classification that should guide treatment is the flexibility of the segmental deformities. Soft tissue and plantar fascia releases may be used for a flexible deformity whereas an osteotomy or multiple osteotomies are required for a fixed deformity. Plantar fascia release is a standard component of cavus foot procedures. Open release rather than percutaneous release is preferable and should include release of the intrinsic muscles of the foot and the origin of the abductor hallucis. Muscle balancing procedures to help the first ray imbalance are typically considered next, including the peroneus longus to brevis transfer and the transfer of the extensor hallucis longus to the first metatarsal head with interphalangeal joint fusion of the great toe (Jones transfer). Lesser toe imbalance may be addressed by transfer of the extensor digitorum longus tendons to the metatarsal necks (Hibbs transfer) with proximal interphalangeal joint fusion, with or without flexor tenotomy. Correction of the claw toe deformities frequently requires dorsal capsulotomy of the metatarsophalangeal joint in addition to the described tendon transfers and interphalangeal joint fusion.
What causes a bilateral pes cavus foot deformity?
Bilateral pes cavus causes: Greater than two-thirds of cavus foot deformities are associated with an underlying neurological disorder causing a muscle imbalance 3). The most common underlying diagnosis is Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy).
Why does my pes cavus hurt?
Symptomatic or painful pes cavus (high arch feet) often present with the following: Pain along the lateral column of the foot due to joint degeneration, periostitis, capsulitis, tendonitis, bursitis, and neuritis. Ankle instability and the tendency to suffer ankle sprains.
Why are my pes cavus feet so painful?
Unlike pes planus (flat feet), pes cavus (highly arched feet) are often more rigid in structure and tend to be painful as the shock absorption function during gait is lost as a result of the inability of the hindfoot to assume a valgus alignment.
What is a pes cavus?
Pes cavus is high arch foot, which is an abnormal elevation of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot. The arch runs from your toes to the heel on the bottom of your foot. Pes cavus is the opposite of pes planus (flat feet). Unlike pes planus (flat feet), pes cavus (highly arched feet) are often more rigid in structure ...
What is the best treatment for a pes cavus?
Physical therapy may also be prescribed to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the lower leg. Tight calf muscles and weak muscles along the outside of the lower leg (peroneal muscles) are often present in pes cavus. While therapy cannot change the shape of the foot, it may be able to help with pain control and function.
What is a PES cavus?
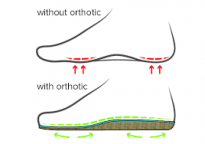
As opposed to pes planus (flat feet), which is often a flexible disorder of the foot that we try to correct with orthotics (i.e., push back into the correct position), pes cavus is usually a rigid deformity,meaning that the shape of the foot cannot be changed.
How to identify a PES Cavus?
Identifying pes cavus is a straightforward process. The high arched foot is noticeable to anyone, but an orthopedic surgeon should evaluate the individual in order to identify some of the nuances of the condition. Diagnosing which muscles are tight or weak and assessing their potential to be stretched or strengthened is important for initiating an effective treatment plan .
Why does my foot have a pes cavitus?
Pes Cavus is caused by muscle imbalances in the lower leg and foot that draws the front of the foot, or sometimes draws the heel downward , making the arch higher than normal.
Why is the cavus foot not able to flex?
In this case, the goal of orthotics is to accommodate the shape of the foot and to redistribute body weight over a larger area. Because of the rigidity, the cavus foot is not able to flex and absorb impact as the individual walks.
What is cavus foot?
Cavus foot is a condition in which the foot has an arch that is higher than normal. While cavus foot deformity varies in severity from a subtle and flexible to a severe and fixed deformity, careful assessment by an orthopedic foot surgeon or podiatrist is required to identify and prescribe the correct pes cavus treatment.
What causes cavus foot?
The most common cause of pes cavus is a nerve or muscle disease that develops slowly in children, typically by the age of 10. These diseases include:
Common Pes Cavus Symptoms
There are a few common cavus foot symptoms in addition to an unusually high arch, including:
How is cavus foot diagnosed?
An orthopedic foot surgeon or podiatrist will first review the patient’s family medical history for possible inherited disorders that cause pes cavus deformity and perform an exam to check for a high arch, hammertoes, claw toes and calluses.
Pes Cavus Treatment
Nonsurgical treatment methods are typically used to help relieve pain and improve stability for both children and adults with cavus foot deformity. These methods include orthotic devices such as cavus foot inserts, bracing to help keep the foot and ankle stable and specialty cavus foot shoes with a wider heel and high-top ankle.
What is the underlying cause of PES Cavus?
The underlying cause of pes cavus must be identified to determine whether the disorder is progressive. The goal of treatment is to produce a plantigrade foot that allows even distribution of weight and permits the patient to ambulate without symptoms (eg, pain). Failure to maintain an asymptomatic plantigrade foot is an indication for surgery.
What is the procedure for a hindfoot?
Patients with hindfoot involvement usually require a calcaneal osteotomy to correct the deformity. The osteotomy can include a closing wedge, a vertical displacement, or a combination (triplanar osteotomy). This procedure is usually combined with a plantar fascia release and, frequently, tendon transfer (s).
How deep is the talus in a medial incision?
From the medial incision, a segment of the plantar two thirds of the talus is resected to a depth of 1 cm; the dorsal one third of the talus is left intact. The dorsal aspect of the navicular is removed so that the navicular can be placed against the talus.
How long does casting last in ankle?
Casting is left in place for a total of 8 weeks, with weightbearing disallowed for the first 4 weeks.
Causas del pie hollow
The cavus is the standing plane and is a condition that may be caused by various factors, as explained below much less frequent foot anomaly.
Pes cavus symptoms
When you have cavus foot, you suffer from a dysfunction of the foot muscles, which is characterized specifically by an excessively raised plantar vault and an exaggerated convexity, which causes the foot support to be reduced to only two points, the metatarsal area, that is, the part under the toes, and the heel area.
Tests to diagnose pes cavus
It is important to say that two different types of cavus feet are observed: the posterior cavus foot , in which there is a greater drop in the heel area; and the anterior cavus foot , which, on the contrary, has a greater fall in the metatarsal area and claw toes are usually present.
Treatment of pes cavus
In general, cavus feet do not usually cause much discomfort, unless they are caused by a neurological disease. In any case, the treatment will largely depend on the type of pes cavus that is present, as well as the severity of the symptoms and the state in which the foot is.
In which cases is surgery necessary?
Surgical intervention may be necessary in severe cases of pes cavus, in which the pain becomes chronic, is not reduced and stability cannot be improved by carrying out the aforementioned treatments.
.jpg)
Health
Causes
Symptoms
- High arches can cause a number of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. Pain in the forefoot is a common occurrence due to increased weight bearing in this area. Excessive callus buildup at the ball of the foot behind the great toe as well as just behind the fifth toe is common, as these become high-pressure areas during standing and walking. Tightness in the calf muscles is ofte…
Diagnosis
- Identifying pes cavus is a straightforward process. The high arched foot is noticeable to anyone, but an orthopedic surgeon should evaluate the individual in order to identify some of the nuances of the condition. Diagnosing which muscles are tight or weak and assessing their potential to be stretched or strengthened is important for initiating an effective treatment plan.
Impact
- Also, the cavus foot causes increased body weight to be distributed through areas of the foot that are not designed for this purpose. Evaluation by the surgeon will aid in a proper prescription of orthotics, if deemed necessary.
Management
- Conservative intervention is generally the rule when starting to treat high arches. Often times if the feet have become painful, orthotic inserts are prescribed. As opposed to pes planus (flat feet), which is often a flexible disorder of the foot that we try to correct with orthotics (i.e., push back into the correct position), pes cavus is usually a rigid deformity,meaning that the shape of the fo…
Purpose
- In this case, the goal of orthotics is to accommodate the shape of the foot and to redistribute body weight over a larger area. Because of the rigidity, the cavus foot is not able to flex and absorb impact as the individual walks. For this reason, orthotics are usually constructed of softer materials to act as a shock absorber.
Treatment
- Physical therapy may also be prescribed to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the lower leg. Tight calf muscles and weak muscles along the outside of the lower leg (peroneal muscles) are often present in pes cavus. While therapy cannot change the shape of the foot, it may be able to help with pain control and function. Because the foot is usuall...