What is MRSA and how dangerous is it?
Dec 12, 2016 · Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Abstract. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a significant cause of health care-associated infections. Introduction. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a common cause of serious nosocomial ...
What is the best medicine for MRSA?
9 rows · Oct 05, 2020 · Common antibiotics for treatment of MRSA include sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim, ...
What's the difference between treating staph vs MRSA?
Feb 05, 2019 · Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a cause of staph infection that is difficult to treat because of resistance to some antibiotics.. Staph infections—including those caused by MRSA—can spread in hospitals, other healthcare facilities, and in the community where you live, work, and go to school.
Can MRSA kill you?
What should I know about MRSA treatments? Milder infections can be treated with oral antibiotics (antibiotic pills). More severe infections may require intravenous antibiotic treatment. It is very important to take all of the antibiotics exactly as your healthcare provider prescribes.
What is the best antibiotic to treat MRSA?
Vancomycin or daptomycin are the agents of choice for treatment of invasive MRSA infections [1]. Alternative agents that may be used for second-line or salvage therapy include telavancin, ceftaroline, and linezolid.Dec 12, 2016
How is MRSA treated?
If you get an MRSA infection, you'll usually be treated with antibiotics that work against MRSA. These may be taken as tablets or given as injections. Treatment can last a few days to a few weeks.
Can you ever get rid of MRSA?
MRSA is resistant to many antibiotics so it can be difficult to treat. However, there are antibiotics that can treat MRSA and make the infection go away. Your doctor may culture your infection and have the lab test the bacteria to find out which antibiotic is best for you.
What is the drug of choice for MRSA?
Vancomycin has been the drug of choice for treatment of MRSA in the critical care setting.
What are the first signs of MRSA?
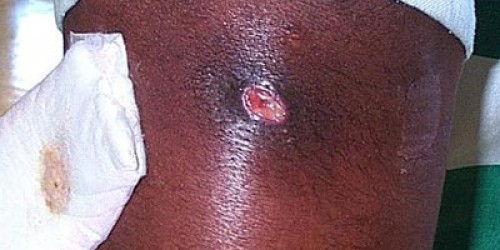
MRSA infections start out as small red bumps that can quickly turn into deep, painful abscesses. Staph skin infections, including MRSA , generally start as swollen, painful red bumps that might look like pimples or spider bites. The affected area might be: Warm to the touch.Dec 1, 2020
What is the main cause of MRSA infection?
MRSA is usually spread in the community by contact with infected people or things that are carrying the bacteria. This includes through contact with a contaminated wound or by sharing personal items, such as towels or razors, that have touched infected skin.
How serious is MRSA?
MRSA skin infections usually aren't serious and typically respond to treatment. But when MRSA gets inside your body, which is called invasive MRSA, it can cause a serious infection in your bloodstream or other organs. This is a life-threatening infection and more difficult to treat.Sep 3, 2019
How does MRSA make you feel?
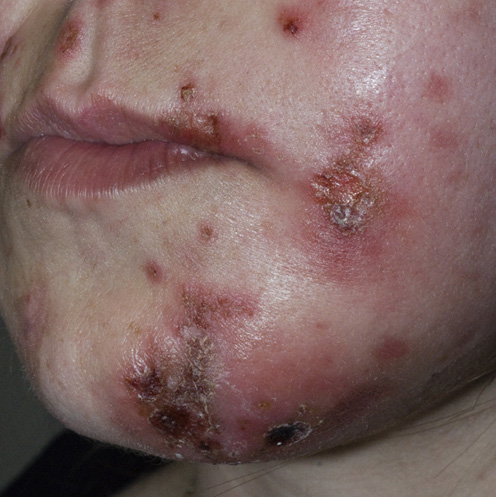
MRSA can cause a skin rash or infection that looks like a spider bite or pimples. The red, swollen bumps may feel warm and be tender to touch. The rash may ooze. MRSA can also cause deeper infections in different parts of the body.Jan 19, 2021
Is MRSA a form of Covid?
However, they also point to a meta-study that found more than 25% of all coinfections in COVID-19 patients were related to S aureus, more than half of which were MRSA. Whether some of the MRSA bacteremia events reported to NHSN in 2020 were secondary infections in COVID-19 patients remains unknown, they add.Oct 6, 2021
What is the first line treatment for MRSA?
At home — Treatment of MRSA at home usually includes a 7- to 10-day course of an antibiotic (by mouth) such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (brand name: Bactrim), clindamycin, minocycline, linezolid, or doxycycline.Nov 20, 2020
When should you suspect MRSA?
MRSA and other staph skin infections often appear as a bump or infected area on the skin that may be: > Red > Swollen or painful > Warm to the touch > Full of pus or other drainage It is especially important to contact your healthcare professional when MRSA skin infection signs and symptoms are accompanied by a fever.
Is MRSA itchy?
The sores are often itchy, but usually not painful. The sores develop into blisters that break open and ooze fluid -- this fluid contains infectious bacteria that can infect others if they have contact with it.
What is the best treatment for MRSA?
Vancomycin or daptomycin are the agents of choice for treatment of invasive MRSA infections [1]. Alternative agents that may be used for second-line or salvage therapy include telavancin, ceftaroline, and linezolid. Recent studies of treatment of MRSA bacteremia are reviewed. Vancomycin.
How much daptomycin should I take for MRSA?
This is reflected in the Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for treatment of MRSA infections, where daptomycin dosing is recommended at 8 to 10 mg/kg for complicated bacteremia and in combination with other agents if there has been prior vancomycin treatment failure [1].
How long does telavancin last?
It is bactericidal against MRSA, vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus(VISA), and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus(VRSA). It has a half-life of seven to nine hours, permitting once daily dosing. Telavancin should be avoided in patients at risk for nephrotoxicity.
When was telavancin approved?
Telavancin was approved in November 2009 in the United States for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), and in June 2013 in US for hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) caused by gram-positive pathogens including MRSA where alternative treatments are not suitable.
What is the fifth generation of cephalosporin?
Ceftaroline. Ceftaroline is a fifth-generation cephalosporin with bactericidal activity against MRSA and VISA as well as Gram-negative pathogens [14]. Ceftaroline fosamil, the pro-drug of ceftaroline, received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2010.
Is vancomycin a Gram positive drug?
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA) is a common cause of serious nosocomial infections. Vancomycin, a glycopeptide in clinical use for more than 50 years, still serves as the cornerstone of the treatment of drug-resistant Gram-positive infections. However, there are significant concerns owing to decreasing susceptibility ...
Is vancomycin bactericidal?
aureus. Furthermore, vancomycin is slowly bactericidal, which may be partly responsible for reported clinical failures in treatment of bacteremia and endocarditis.
How to treat MRSA?
What are the best home remedies for MRSA? 1 Do not share personal items such as razors, brushes, washcloths, and towels. 2 Keep your fingernails short to prevent scratches and to halt bacteria growth that can occur under the nails. 3 Wash sheets and bed linens in hot water once per week and dry on the highest heat setting after washing. 4 Wash any cuts, scrapes, or scratches immediately with antibacterial soap and keep the area covered and clean. Use hand sanitizer if soap is not readily available. 5 Wash towels and clothing after each use.
What antibiotics are used for MRSA?
Common antibiotics for treatment of MRSA include sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim, clindamycin, vancomycin, daptomycin, linezolid, tedizolid, doxycycline, minocycline, omadacycline, and delafloxacin. Your treatment may vary due to the nature of a MRSA infection, your medical history, and other prescriptions you may be taking.
What is the most common type of bacteria that is resistant to antibiotics?
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is a specific type of bacteria, also called staph, which can cause infection and has become resistant to common antibiotic treatments, such as methicillin. CDC.gov estimates that 5% of patients in United States hospitals are carriers for MRSA via their skin or nose.
What are the symptoms of MRSA?
You may notice a skin infection that resembles a spider bite, large pimple, or a red and painful bump.
How does MRSA spread?
The spread of MRSA in the general community is typically through the sharing of personal items such as razors, washcloths, towels, or other items that may have come into contact with the infected skin.
How long does it take for a lab to get results?
Some healthcare providers have access to tests that provide them with accurate results within a matter of hours, while many others may require 48 hours for lab processing. You may also need to provide a nasal secretion sample so that your healthcare provider can check for antibiotic resistance.
Can you take antibiotics for MRSA?
Depending on your specific antibiotic resistance with a MRSA infection, you may be given one or more antibiotic treatments to try. Antibiotics are the most commonly used and accepted form of treatment for MRSA patients because the condition is caused by bacteria.
How to get rid of MRSA?
Shower immediately after working out or participating in activities that increase your risk of MRSA exposure. Use disinfecting sprays that kill germs to wipe down high-touch areas like light switches, remote controls and athletic equipment. Check labels to find disinfectants that kill staph bacteria.
Where does MRSA colonize?
The bacterium remains within the skin or mucosa where it has established colonization. Problems arise when MRSA on the skin surface in a colonized person enters the skin through a wound or other opening and invades deeper structures.
What does MRSA look like?
MRSA can cause a skin rash or infection that looks like a spider bite or pimples. The red, swollen bumps may feel warm and be tender to touch. The rash may ooze. MRSA can also cause deeper infections in different parts of the body.
Where does staph live?
Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria live in the nose or on skin. You can harbor staph bacteria, including MRSA, and not know it. A healthcare expert might refer to this as bacterial colonization. Colonized people (carriers) may one day develop an MRSA infection, or they might stay healthy.
What is the treatment for Staph aureus?
Antibiotic treatment: The antibiotic used to treat the infection depends on whether the Staph aureus infection is or is not an MRSA infection.
Is MRSA a serious infection?
Most MRSA skin infections clear up with treatment. MRSA is most dangerous if it enters the bloodstream. MRSA bloodstream infections can be serious. A bloodstream infection requires immediate medical attention.
Can you get a staph infection from your nose?
Many people carry Staph aureus or MRSA bacteria in their skin or noses for varying periods of time and never know it. This is not a problem. In some people, MRSA bacteria cause painful skin infections or more serious invasive infections. People in hospitals or nursing homes are at increased risk for MRSA infections. But you can pick up the bacteria in community settings, too. Contact your healthcare provider if you develop a skin infection or show signs of MRSA.
How long does it take for MRSA to develop?
It is important to discuss a follow-up plan with your patients in case they develop systemic symptoms or worsening local symptoms, or if symptoms do not improve within 48 hours.
What is the purpose of obtaining specimens for culture and susceptibility testing?
Obtaining specimens for culture and susceptibility testing is useful to guide therapy , particularly for those with more severe infections and those who fail to respond adequately to initial management.
Is MRSA a skin infection?
Recent data suggest that MRSA as a cause of skin infections in the general community remains at high probability. The spectrum of disease caused by MRSA appears to be similar to that of Staphylococcus aureus in the community. SSTIs, specifically furuncles (abscessed hair follicles or “boils”), carbuncles (coalesced masses of furuncles), ...
Do you need antibiotics for boils?
Antibiotics, however, aren't always necessary. If you have a small skin boil caused by MRSA, your doctor may just make an incision and drain it. If you are prescribed antibiotics, follow your health care provider's instructions precisely. Never stop taking your medicine, even if you're feeling better.
Do antibiotics work for MRSA?
But other kinds of antibiotics still work. If you have a severe infection, or MRSA in the bloodstream, you will need intravenous antibiotics. Unfortunately, there is emerging antibiotic resistance being seen with some of these medications. Antibiotics, however, aren't always necessary.
What is the best treatment for MRSA?
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed as a treatment for MRSA skin infections, either by themselves or along with draining of the infection by a healthcare professional. Antibiotics are also the standard medical therapy for internal MRSA infections. Antibiotic therapy is often prescribed for the following types of infections:
What antibiotics are used for MRSA?
Antibiotic therapy is often prescribed for the following types of infections: Because MRSA is becoming more resistant, and it’s more common for antibiotic treatments to fail, and treatment may require the use of newer antibiotics, such as the “glycopeptides” which includes Vancomycin and Zyvox.
What are the side effects of Zyvox?
Other side-effects are pseudomembranous colitis, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, skin rashes and more. 2. Linezolid (Brand Names: Zyvox, Zyvoxid or Zyvoxam) Folliculitis is a common type of MRSA skin infection often treated with oral antibiotics. Approved for use in the year 2000, Linezolid is FDA approved for treating soft tissue ...
What is the best antibiotic for MRSA?
1. Clindamycin. It has been successfully and widely used for the treatment of soft tissue and skin infections as well as bone, joint and abscesses caused by Staph and MRSA.
Is MRSA resistant to clindamycin?
MRSA is becoming increasingly resistant to clindamycin in the United States. Resistance: MRSA is becoming increasingly resistant to clindamycin in the United States . Side Effects and Precautions: Diarrhea is the most common side effect, and it can promote C. difficile overgrowth infections in the colon.
What is Linezolid used for?
Approved for use in the year 2000, Linezolid is FDA approved for treating soft tissue and skin infections, including those caused by MRSA. It is often prescribed for CA-MRSA pneumonia and in particular, HA-MRSA pneumonia.
Is trimethoprim a sulfamethoxazole?
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (Brand Name: Septra or Bactrim) It is not FDA-approved for the treatment of Staphylococcal infections (including MRSA). However, laboratory tests have shown most CA-MRSA strains are susceptible and so this drug has become a treatment option for Staph and MRSA.
