
What are the treatment options for necrotizing fasciitis?
If necrotizing fasciitis is diagnosed, the patient should be transferred to the OR immediately for formal debridement. Alternatively, if necrotizing fasciitis is excluded, then the skin can be closed with a few sutures. An example of surgical exploration is on YouTube here.
Is necrotizing fasciitis a monomicrobial infection?
Background and aims: Necrotizing fasciitis (NF) although rare, is a potentially fatal infection. The majority of cases are polymicrobial, although a recent surge has been reported in monomicrobial NF caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae (KP-NF).
How is necrotizing fasciitis diagnosed?
No laboratory or imaging studies, alone or in combination, are sufficiently sensitive and specific to definitively diagnose or rule out necrotizing fasciitis. An urgent surgical consultation should be obtained as soon as the diagnosis is suspected.
Is oxygen therapy pointless for Type II necrotizing fasciitis?
Oxygen is toxic to these bacteria. Therefore, administration of higher levels of oxygen could increase tissue oxygen levels and thereby discourage the spread of these anaerobic bacteria. ( 33278180) Oxygen therapy is probably pointless for Type II necrotizing fasciitis due to group A streptococci (which are aerobic).
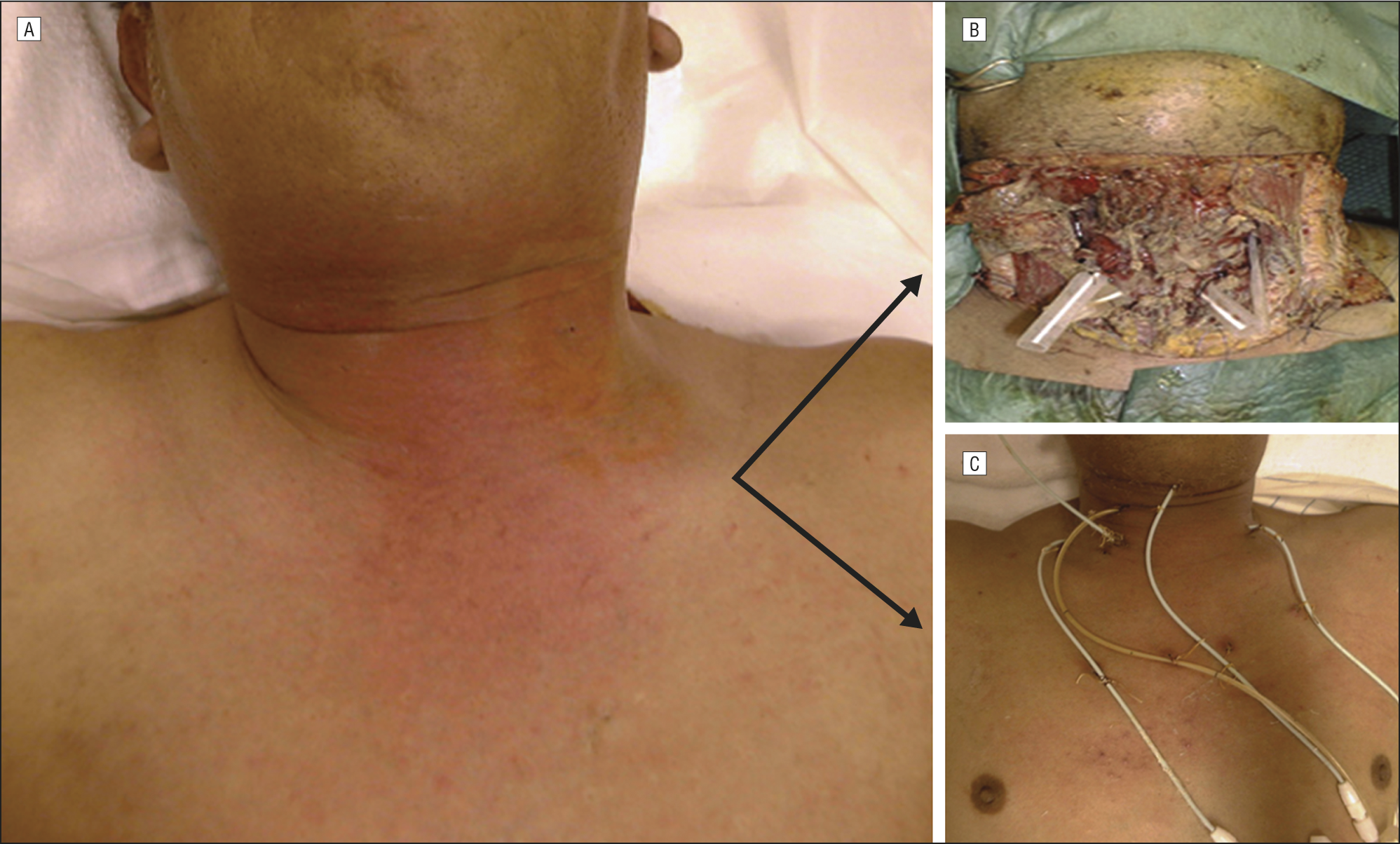
What is the best treatment for treating necrotizing fasciitis?
Doctors treat necrotizing fasciitis with IV antibiotics. Necrotizing fasciitis is a very serious illness that requires care in a hospital. Antibiotics and surgery are typically the first lines of defense if a doctor suspects a patient has necrotizing fasciitis.
What is the standard treatment for necrotizing fasciitis?
Primary treatment of necrotizing fasciitis is early and aggressive surgical exploration and debridement of necrotic tissue. Surgery is coupled with appropriate broad-spectrum parenteral antibiotic therapy. Upon first exploration, extensive incisions that go beyond the area of apparent involvement are usually necessary.
What is the best antibiotic for necrotizing fasciitis?
For necrotizing infections of the skin, fascia, and muscle, the IDSA guideline recommend pipercillin-tazobactam and vancomycin, a carbapenem (meropenem, imipenem, ertapenem), or cefotaxime and metronidazole or clindamycin.
How is perineum necrotizing fasciitis treated?
Results: Treatment of the perineal necrotizing fasciitis is combined--surgery and therapeutic management. Surgery should be performed at first within the first 24 hours as an emergency including a lot of incisions, necrectomy and effective drainage. All patients had to undergo more than four surgical interventions.
Can you treat necrosis with antibiotics?
Since antibiotics cannot penetrate into the necrotic infected tissue, surgical debridement is the first priority of treatment. However, antibiotic therapy is essential in helping to control sepsis and prevent the further spread of the infection.
Can necrotizing fasciitis be cured?
Necrotizing fasciitis is a treatable disease. Only certain rare bacterial strains are able to cause necrotizing fasciitis, but these infections progress rapidly so the sooner one seeks medical care, the better the chances of survival.
How long is antibiotic treatment for necrotizing fasciitis?
Antibiotics should be administered for up to 5 days after local signs and symptoms have resolved (62). The mean duration of antibiotic therapy for NF is 4–6 weeks. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) has recently been described as a reasonable and desirable option for neutralizing streptococcal toxins (63).
What are the most common complications of necrotizing fasciitis?
What are complications of necrotizing fasciitis?Renal failure.Septic shock with cardiovascular collapse.Scarring with cosmetic deformity.Limb loss.Sepsis.Toxic shock syndrome.
What is the most common cause of necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis is commonly caused by group A streptococcus (GAS) bacteria. That's the same type of bacteria that causes strep throat. But, several types of bacteria, such as staphylococcus and others, have also been linked to the disease.
Does doxycycline treat necrotizing fasciitis?
A combination of doxycycline plus either ceftriaxone or cefotaxime has been recommended for necrotizing fasciitis due to Vibrio vulnificus.
How fast does necrotizing fasciitis progress?
The symptoms of necrotising fasciitis develop quickly over hours or days. They may not be obvious at first and can be similar to less serious conditions, such as flu, gastroenteritis or cellulitis.
Why does clindamycin treat necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis: Subtherapeutic amounts of clindamycin may have activity against toxin production by S aureus and toxin-producing streptococci. In in vitro and animal models, clindamycin decreases toxin production in necrotizing fasciitis caused by invasive group A streptococci.