Medication
Dec 09, 2021 · Medicines that doctors recommend to treat microscopic colitis include corticosteroids , also called steroids, most commonly in the form of budesonide aminosalicylates antidiarrheal medicines bile acid binders immunosuppressants biologics Doctors prescribe medicines to improve microscopic colitis symptoms. Surgery
Procedures
Common medications include: Bulking agents, such as psyllium, to make your poop more solid and slow down its transit time. Anti-diarrheals that slow down your bowel contractions, such as loperamide or diphenoxylate. Bismuth Subsalicylate (Pepto Bismol®) for …
Nutrition
8 rows · May 24, 2008 · Microscopic colitis – including collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis – causes chronic ...
Does microscopic colitis ever go away?
Jan 20, 2021 · Medications that may be linked to the condition include: Pain relievers, such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve) Proton pump inhibitors including lansoprazole (Prevacid), esomeprazole (Nexium), pantoprazole (Protonix), rabeprazole... Selective serotonin ...
What should I eat when I have microscopic colitis?
The most common therapy for use in microscopic colitis is budesonide (Entocort®), which works inside the intestines to reduce inflammation and symptoms of the disease.
How dangerous is microscopic colitis?
May 02, 2022 · How can I help prevent microscopic colitis? Wash your hands. Wash your hands in warm, soapy water for 20 seconds before and after you handle food. Wash your hands... Clean food and areas that come in contact with food. Rinse fruits and vegetables in running water. Clean cutting boards,... Cook food ...
What are the lifestyle changes for microscopic colitis?
Sep 27, 2021 · There aren’t any guidelines on how to treat microscopic colitis. However, some prescription medications may be used, including cholestyramine, 5-ASA drugs, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha drugs. 5 Ischemic Colitis Medications may be used to provide some relief from the signs and symptoms of this condition.
Explore
Oct 29, 2021 · Boswellia serrata extract, one herbal treatment touted for its anti-inflammatory properties, has also been tested in the treatment of microscopic colitis. One study showed that a 6-week treatment of boswellia serrata resulted in 63% of …

Does microscopic colitis ever go away?
What is the best medicine for microscopic colitis?
What triggers microscopic colitis?
Do probiotics help microscopic colitis?
What foods to avoid if you have colitis?
- Watch Out For Fiber. Whole grain cereals and breads are difficult to digest and lead to flare ups if you have UC. ...
- Nuts And Seeds. These foods are difficult to digest and aggravate the symptoms. ...
- Dairy. ...
- Unhealthy Fats. ...
- Caffeine. ...
- Alcohol. ...
- Certain Vegetables. ...
- Spicy Foods.
Is microscopic colitis considered an autoimmune disease?
Can stress cause microscopic colitis?
Does microscopic colitis cause fatigue?
What are the best medications for microscopic colitis?
Medicines that doctors recommend to treat microscopic colitis include. corticosteroids. NIH external link. , also called steroids, most commonly in the form of budesonide. NIH external link. aminosalicylates. antidiarrheal medicines. bile acid binders. immunosuppressants.
Can you get surgery for microscopic colitis?
Doctors rarely recommend surgery to treat microscopic colitis. Surgery may be an option if microscopic colitis causes severe symptoms that don’t improve after treatment with medicines. This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health.
What doctor diagnoses microscopic colitis?
Microscopic colitis is usually diagnosed by a gastroenterologist (a specialist in diseases of the digestive system). The gastroenterologist will perform a physical examination and will ask you about your symptoms and any medications you are taking. The doctor may also order certain tests, including: Blood tests. Lab tests.
What are the symptoms of microscopic colitis?
Other symptoms include: Always feeling like you need to have a bowel movement. Fecal incontinence (leaking stool, caused by inability to control bowel movements) Bile acid malabsorption.
What are the two types of colitis?
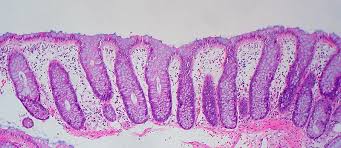
There are two types of microscopic colitis, lymphocytic colitis and collagenous colitis: Patients who have lymphocytic colitis have an increase in lymphocytes (white blood cells) in the epithelium (the lining of the colon).
What is the difference between lymphocytic colitis and collagenous colitis?
Patients who have lymphocytic colitis have an increase in lymphocytes (white blood cells) in the epithelium (the lining of the colon). In patients who have collagenous colitis, the layer of collagen (fibrous connective tissue) under the epithelium becomes thicker.
What is the safest medication for colitis?
Budesonide is believed to be the safest and most effective medication for treating microscopic colitis. Cholestyramine resin (Locholest®, Questran®), which blocks bile acids. Antibiotics. Mesalamine (Apriso®, Asacol®) and sulfasalazine (Azulfidine®) to reduce swelling.
What tests are done to check colon?
The doctor may also order certain tests, including: Blood tests. Lab tests. Stool tests. Imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and upper GI (the patient has an X-ray after drinking a barium solution, which causes the organs to show up more sharply) of the colon.
What is the test for colon cancer?
Imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and upper GI (the patient has an X-ray after drinking a barium solution, which causes the organs to show up more sharply) of the colon.
Is mesalamine used for colitis?
Mesalamine, commonly used to treat inflammatory bowel disease, has also been studied for the treatment of microscopic colitis. An open-label, randomized trial (9) demonstrated high clinical and histological responses to mesalamine treatment, with a maintained response over six months and minimal adverse events.
What is the name of the disease that causes diarrhea in older people?
Collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis, the two subtypes of microscopic colitis, typically cause diarrhea in middle-aged or older individuals. They share many epidemiological and clinical features, but are distinguished by their histological features.
Is celiac disease a comorbidity?
Celiac disease is a common comorbidity in patients with microscopic colitis, occurring in 15% to 20% of patients (2,3). Patients with microscopic colitis should be screened for celiac disease using serology. A small bowel biopsy is required to confirm the diagnosis. Those patients determined to have celiac disease should be treated ...
Can you have gluten free diet with celiac disease?
Those patients determined to have celiac disease should be treated with a gluten-free diet. Because there is a considerable overlap of symptoms between celiac disease and microscopic colitis, a gluten-free diet often leads to improvement in diarrhea and other symptoms shared by the two disorders. MEDICAL THERAPY.
What is bismuth subsalicylate used for?
Bismuth subsalicylate is an over-the-counter agent used for various gastrointestinal complaints. It has been studied for the treatment of microscopic colitis, and been found to improve both clinical and histological activity of the disease over the short term, without significant adverse events (6,7).
Is cholestyramine a monotherapy?
Cholestyramine may be effective as monotherapy or when used in conjunction with mesalamine for patients with microscopic colitis (9–11). Budesonide. Budesonide, a steroid with extensive first-pass metabolism, has the strongest evidence from clinical trials for treating patients with microscopic colitis.
Is Budesonide a corticosteroid?
Despite the best evidence for efficacy, budesonide should not necessarily be the first-line therapy for all patients with microscopic colitis. It is a corticosteroid; therefore, there is a potential for significant adverse events. Cost and drug coverage issues may also be a limiting factor for some patients.
What to do if microscopic colitis doesn't work?
If these treatments don't work, you may need medications to suppress the immune system, such as azathioprine ( Imuran ). Surgery for microscopic colitis is an option, but very few people ever need it. For most people with microscopic colitis, treatment generally works well.
What is microscopic colitis?
In this Article. Symptoms. Causes. Treatment. Microscopic colitis is a type of inflammation of the colon, or large intestine, that can cause watery diarrhea and cramping. It can be painful and unpleasant. But in most cases, it's much less severe than other types of inflammatory bowel disease. It's called microscopic because ...
Why is microscopic colitis called microscopic?
But in most cases, it's much less severe than other types of inflammatory bowel disease. It's called microscopic because the inflammation is too small to see with the naked eye.
What are the two types of colitis?
There are two types of microscopic colitis: Collagenous colitis. Lymphocytic colitis. The differences are minor, and the symptoms and treatments are the same. But the tissues of the two types of microscopic colitis look different under a microscope. Microscopic colitis is not related to the more serious types of bowel disease: ulcerative colitis ...
Is colitis a disease under a microscope?
Microscopic colitis is not related to the more serious types of bowel disease: ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Microscopic colitis doesn’t make you more likely to get cancer.
Is microscopic colitis related to cancer?
Microscopic colitis is not related to the more serious types of bowel disease: ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Microscopic colitis doesn’t make you more likely to get cancer.
How to diagnose microscopic colitis?
To help diagnose microscopic colitis, your doctor may ask you to have a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. Both procedures use a tube with a camera on it to inspect the colon. During the procedure, your doctor collects tissue samples to check for signs of microscopic colitis.
What are the symptoms of microscopic colitis?
Signs and symptoms of microscopic colitis include: Chronic watery diarrhea. Abdominal pain, cramps or bloating. Weight loss. Nausea. Fecal incontinence. Dehydration. The symptoms of microscopic colitis can come and go frequently.
Can microscopic colitis cause autoimmune disease?
People with microscopic colitis sometimes also have an autoimmune disorder, such as celiac disease, thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes or psoriasis. Genetic link. Research suggests that there may be a connection between microscopic colitis and a family history of irritable bowel syndrome. Smoking.
How does colitis get its name?
The disorder gets its name from the fact that it's necessary to examine colon tissue under a microscope to identify it, since the tissue may appear normal with a colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy. There are different subtypes of microscopic colitis: Collagenous colitis, in which a thick layer of protein (collagen) develops in colon tissue.
Is microscopic colitis more common in men or women?
Microscopic colitis is most common in people ages 50 to 70. Sex. Women are more likely to have microscopic colitis than are men. Some studies suggest an association between post-menopausal hormone therapy and microscopic colitis. Autoimmune disease.
Can smoking cause microscopic colitis?
Recent research studies have shown an association between tobacco smoking and microscopic colitis, especially in people ages 16 to 44. Some research studies indicate that using certain medications may increase your risk of microscopic colitis. But not all studies agree.
What causes inflammation in the colon?
Bacteria that produce toxins that irritate the lining of the colon. Viruses that trigger inflammation. Autoimmune disease associated with microscopic colitis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease or psoriasis. Autoimmune disease occurs when your body's immune system attacks healthy tissues.
Why does my colon itch?
Researchers believe that the causes may include: Medications that can irritate the lining of the colon. Bacteria that produce toxins that irritate the lining of the colon. Viruses that trigger inflammation. Autoimmune disease associated with microscopic colitis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease or psoriasis.
Why is colitis called a microscopy?
This condition is known as "microscopic" colitis because physicians usually can't see the inflammation without a microscope. When looked at through an endoscope—a camera mounted at the end of a long, flexible tube that's inserted in the rectum—either during a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, the colon appears entirely normal.
Is microscopic colitis the same as ulcerative colitis?
Microscopic colitis, which includes collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis, is characterized by chronic watery diarrhea caused by inflammation in the colon. It is not related to ulcerative colitis or to Crohn's disease, and there is no evidence to suggest that microscopic colitis carries the same increased risk for colon cancer as ulcerative ...
How to tell if you have microscopic colitis?
Common symptoms of microscopic colitis 1 Chronic diarrhea, which can be severe. Up to 22% of patients with microscopic colitis can have more than 10 bowel movements per day, making prompt recognition and diagnosis important. 2 Abdominal pain
Is microscopic colitis the same as colon cancer?
It is not related to ulcerative colitis or to Crohn's disease, and there is no evidence to suggest that microscopic colitis carries the same increased risk for colon cancer as ulcerative colitis. This condition is known as "microscopic" colitis because physicians usually can't see the inflammation without a microscope.
Can Crohn's disease cause microscopic colitis?
As with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, the exact cause of microscopic colitis has yet to be identified. But bacteria, bacterial toxins, and viruses are leading candidates in research. Some experts have suggested that use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin or ibuprofen, might be the actual culprits.
How many bowel movements can a microscopic colitis patient have?
Common symptoms of microscopic colitis. Chronic diarrhea, which can be severe. Up to 22% of patients with microscopic colitis can have more than 10 bowel movements per day, making prompt recognition and diagnosis important. Abdominal pain.
How long does it take to get diarrhea out of your colon?
Without these diagnostic steps, it could take weeks, months, or even years to discover the reason for the chronic diarrhea.
What tests show if you have colitis?
Blood tests may show if you have an infection. A bowel movement sample may show what germ is causing your illness. A colonoscopy may show what is causing your colitis. A tube with a light and camera on the end will be put into your anus, and moved forward into your intestine.
Can colitis cause diarrhea?
Inflammation can damage the lining of your colon and cause long-term diarrhea. Microscopic colitis may be caused by an infection, higher levels of acid in your colon, or the cause may not be known.
How to get rid of diarrhea fast?
Ask how much liquid to drink each day. You may need to drink an oral rehydration solution (ORS). An ORS contains a balance of water, salt, and sugar to replace body fluids lost during diarrhea. Start to exercise when you feel better. Regular exercise helps your bowels work normally.
How to get rid of diarrhea from a bowel movement?
You may need to drink an oral rehydration solution (ORS). An ORS contains a balance of water, salt, and sugar to replace body fluids lost during diarrhea. Start to exercise when you feel better. Regular exercise helps your bowels work normally. Ask about the best exercise plan for you. Ask about probiotics.
How to kill bacteria in meat?
Use a meat thermometer to make sure meat is heated to a temperature that will kill bacteria. Do not eat raw or undercooked chicken, turkey, seafood, or meat. Store food properly. Refrigerate or freeze fruits and vegetables, cooked foods, and leftovers. Drink safe water.
What to drink when you have diarrhea?
Good liquids to drink include water, juice, and broth. Ask how much liquid to drink each day. You may need to drink an oral rehydration solution (ORS). An ORS contains a balance of water, salt, and sugar to replace body fluids lost during diarrhea. Start to exercise when you feel better.
There are various causes of colitis and each has different treatments
Amber J. Tresca is a freelance writer and speaker who covers digestive conditions, including IBD. She was diagnosed with ulcerative colitis at age 16.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
For some of the causes of colitis, part of the treatment plan may include care that can be done at home. Changes to diet might also be used for some conditions, either long-term or for a short period of time.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Therapies
There aren't many over-the-counter remedies that may be recommended to treat the cause of colitis. Vitamin and mineral supplements might be recommended in some cases.
Prescriptions
There are many prescription medications and therapies used to treat colitis. The treatments used will be different based on the cause of colitis. In most cases, therapies are aimed at treating the underlying cause of the inflammation.
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
Surgery may be used to treat colitis that’s caused by IBD. This includes either the partial or the total removal of the colon. Surgery might be used when medications have failed to control the disease or there is a risk of colon cancer.
Summary
The treatments for colitis will depend on the underlying cause. For most types, medication and a change in diet are used. For some types, surgery may be needed.
A Word From Verywell
The reasons for the development of colitis are varied, as are the treatments. The key is to get the cause of colitis diagnosed so that it can be treated early and effectively. One of the most important things to know about the early diagnosis and treatment is that bleeding from the rectum is not normal.
What medications are used for microscopic colitis?
There is also a strong association between microscopic colitis and the use of various medications including: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and ibuprofen. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like Celexa, Paxil and Zoloft. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) like Prilosec and Prevacid.
What is microscopic colitis?
This is what those with microscopic colitis deal with on a nearly daily basis. This inflammatory condition of the colon, broken down into two forms—collagenous and lymphocytic colitis—is becoming increasingly common, with more people seeking quick relief.
Why is colitis called microscopic?
Sufferers may experience over 10 bowel movements a day. It’s referred to as “microscopic” because it can only be identified under a microscope. A colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy will not detect it.
What is the LC in colitis?
Microscopic colitis is broken down into two specific types: Lymphocytic Colitis (LC): This form is identified by an excessive amount of inflammatory cells or lymphocytes, specifically more than one-fifth of the cells found in the tissues of the colon.
Does smoking cause colitis?
There is also a strong association between microscopic colitis and the use of various medications including: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and ibuprofen.
Is boswellia serrata good for colitis?
Boswellia serrata extract, one herbal treatment touted for its anti-inflammatory properties, has also been tested in the treatment of microscopic colitis. One study showed that a 6-week treatment of boswellia serrata resulted in 63% of patients in remission versus 27% in the placebo group.
Does low fat help with colitis?
A low-fat and low-fiber diet is often recommended to help relieve diarrhea. You may also want to eat several smaller meals rather than a few large meals.