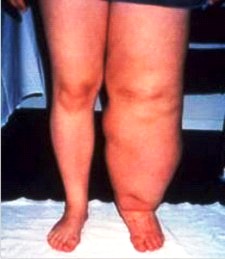
Procedures
Decongestive lymphatic therapy (DLT)
- Compression bandages and garments. Unlike blood circulation, the lymphatic system has no central pump, such as the heart, to move fluid to the lymph glands.
- Skin care. It's important to take good care of your skin to reduce your risk of developing an infection, such as cellulitis.
- Movement and exercises. ...
- Massage. ...
- Surgery. ...
- Liposuction. ...
Therapy
Top Remedies That Will Bring Quick Relief
- Flaxseed. Flax seeds have great anti-inflammatory properties which reduce the swelling within no time. ...
- Ginger. Ginger is very effective in reducing the swelling and inflammation. ...
- Fish Oil. ...
- Green Tea. ...
Self-care
- If you have a high BMI (body mass index) it’s ideal to include forms of exercise (and nutrition) that will help you reduce your body weight. ...
- Resistance training may be the best choice of exercise for reducing lymphedema. ...
- Yoga. ...
- Supervised exercise programs appear to be more beneficial to lymphedema patients than you might expect. ...
Nutrition
Hamtramck home owners or occupants are required to maintain sidewalks, alleys and other public ways near their home. This includes removal of snow, ice and filth, as well as keeping the walkways free from obstructions, encumbrances or other nuisances. Fences must also be kept free from obstructions.
What remedies can help treat lymphedema?
How to cure lymphedema naturally?
What are the best exercises for lymphedema?
What is lymphedema and how can you treat it?
What is the most effective treatment for lymphedema?
Conclusions Complete decongestive physiotherapy is a highly effective treatment for both primary and secondary lymphedema. The initial reductions in volume achieved are maintained in the majority of the treated patients.
How do I get rid of lymphedema in my legs?
There's no cure for lymphedema. Treatment focuses on reducing the swelling and preventing complications....Examples include:Exercises. ... Manual lymph drainage. ... Compression bandages. ... Compression garments. ... Sequential pneumatic compression.
What should you not do with lymphedema?
Avoid trauma or injury to the affected area. Avoid heavy lifting with the affected arm. No new tattoos in the affected area. Do not wear tight clothing, bands, shoes, or jewelry on the affected area.
What treatment is used for lymphedema?
The recommended treatment for lymphoedema is decongestive lymphatic therapy (DLT). DLT is not a cure for lymphoedema, but it can help control the symptoms. Although it takes time and effort, the treatment can be used to bring lymphoedema under control.
Is walking good for lymphedema in the legs?
Exercises. Gentle exercises, such as walking, are a great way to help the fluids in your body move a little better. Try to go for a walk every day, if you can.
What type of doctor treats the lymphatic system?
Lymphologists are doctors who are specially trained in the diagnosis of and therapy for diseases of the lymphatic system. Among other things, they examine and treat patients with lymph drainage disorders and lymphoedema (protein-rich accumulation of fluid in the tissue) at all stages of severity.
How do you get rid of lymphedema fast?
Treatment options may include:Exercise. Exercise helps to restore flexibility and strength, and it improves drainage. ... Bandage. Wearing a customized compression sleeve or elastic bandage may help to prevent an accumulation of fluid.Arm pump. ... Diet. ... Keep the arm raised. ... Infection Prevention.
What causes lymphedema to flare up?
Lymphedema occurs when the lymph vessels are not able to adequately drain lymph fluid, usually from an arm or leg. The most common causes of lymphedema include: Cancer. If cancer cells block lymph vessels, lymphedema may result.
What foods to avoid if you have lymphedema?
Limit Certain Foods Some foods can exacerbate lymphedema symptoms because of the way they are processed and the additives or high salt content they contain. These foods include added sugars — specifically fructose — refined grains, chemically modified fats and most animal and dairy products.
Can lymphedema be fixed?
There are several medical options to help treat lymphedema, especially during stage 1 and stage 2. Compression, elevation, infection prevention, physical therapy and massage can help alleviate swelling and other symptoms. Make a plan with your doctor that uses some or all of these treatments.
Can lymphoedema be cured?
There's no cure for lymphoedema, but it's usually possible to control the main symptoms using techniques to minimise fluid build-up and stimulate the flow of fluid through the lymphatic system.
What type of doctor removes lymphedema?
MSK reconstructive surgeons are highly skilled at preventing and treating lymphedema through specialized techniques.
Can Lymphedema Be Prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent all cases of lymphedema, but there are ways to lower the risk of it developing. For example, when lymph nodes need...
When Does Lymphedema develop?
Lymphedema can start right after surgery. This is called temporary (or short-term) lymphedema. It’s usually mild and goes away in the next month or...
Know What’S Normal For You
If you’ve had lymph nodes removed or radiation treatment, look closely at your body in front of a mirror. Compare both sides of your body and look...
What is the best treatment for lymphedema?
Decongestive treatment is commonly recommended for the first two stages of lymphedema. Treatment options may include: Exercise. Exercise helps to restore flexibility and strength, and it improves drainage. Specific exercises will be recommended by your doctor and/or physical therapist. Bandage.
Why does lymphedema occur?
More rarely, lymphedema can occur as birth defect or symptom of infection.
What is lymphatic anastomosis?
Lymphaticovenous anastomosis (also referred to as lymphovenous bypass). The surgeon rewires the lymphatic system by connecting lymphatic channels directly to tiny veins nearby. This is an outpatient procedure with very small and minimal incisions and very little blood loss.
What is the lymphatic system made of?
The lymphatic system is made up of many vessels that carry fluid throughout the body. Lymphedema is an abnormal buildup of protein-rich fluid in any part of the body as a result of malfunction in the lymphatic system. You can be born with it (primary lymphedema) or develop it as a result of damage to the lymphatic system, ...
How to prevent fluid accumulation in arm?
Wearing a customized compression sleeve or elastic bandage may help to prevent an accumulation of fluid. Arm pump. Applying an arm pump often helps to increase the fluid flow in the lymphatic vessels and keeps fluid from collecting in the arm. Diet.
What is the stage 3 of a swollen limb?
Stage 3: Permanent swelling that does not resolve with elevation. Pressing on the area no longer leaves a dent. Changes in the skin with scarring and thickening. Stage 4: Elephantiasis (large deformed limb), skin thickening with “wart-like” growth and extensive scarring.
How to treat a swollen arm?
Maintaining Proper Hygiene. Clean the skin of the affected arm daily and apply lotion. When drying the arm, be gentle but thorough. Take proper care of the fingernails and avoid cutting cuticles. Clean all cuts with soap and water, and then apply antibacterial ointment and a sterile dressing.
What is the goal of lymphedema treatment?
The goal is to maintain clean and well-moisturized skin to ward off infection.
What is primary lymphedema?
Primary lymphedema is lymphedema that happens on its own, not caused by another condition or injury. It can occur in children born with impaired or missing lymph nodes. Globally, a common cause of lymphedema is an infection by Wuchereria bancrofti roundworms. This is known as lymphatic filariasis.
What is lymphatic drainage?
Manual lymphatic drainage, which is targeted massage or manipulation of soft tissue, can aid in draining lymphatic fluid. Your CDT provider will likely massage you and also show you some techniques that you can perform on yourself to promote drainage.
What is the difference between primary and secondary lymphedema?
For example, up to 40 percent of those who undergo surgery for breast cancer will experience it, as this surgery usually involves a sentinel lymph node biopsy. This type of lymphedema is called secondary lymphedema. Primary lymphedema is lymphedema that happens on its own, not caused by another condition or injury.
How many people have lymphedema?
According to the World Health Organization. Trusted Source. , it’s responsible for causing lymphedema in over 15 million people worldwide. Lymphatic filariasis is one of the world’s leading causes of disability. Trusted Source. . No matter the origin, everyone with lymphedema experiences pain and discomfort.
How long do you have to wrap your body for lymphatic drainage?
Affected body parts usually need to stay wrapped up 24 hours a day — except during bathing.
How to improve drainage?
It’s important to stay as active as you can, as physical activity is one of the most effective ways to promote drainage. Your doctor will help you determine which types of exercises are right for you. Most will include stimulation of arm or leg muscles.
What is primary lymphedema?
Primary lymphedema is a rare, inherited condition caused by problems with the development of lymph vessels in your body. Specific causes of primary lymphedema include: Milroy's disease (congenital lymphedema). This disorder begins in infancy and causes lymph nodes to form abnormally.
What are the complications of lymphedema in the arm?
Complications. Lymphedema in your arm or leg can lead to serious complications, such as: Infections . Possible infections that can result from lymphedema include a serious bacterial infection of the skin (cellulitis) and an infection of the lymph vessels (lymphangitis).
Why do my arms and legs swell?
Sometimes both arms or both legs swell. Lymphedema is most commonly caused by the removal of or damage to your lymph nodes as a part of cancer treatment. It results from a blockage in your lymphatic system, which is part of your immune system. The blockage prevents lymph fluid from draining well, and the fluid buildup leads to swelling.
What causes lymph nodes to form abnormally?
Specific causes of primary lymphedema include: Milroy's disease (congenital lymphedema). This disorder begins in infancy and causes lymph nodes to form abnormally.
What is the lymphatic system?
Your body's lymphatic system is part of your immune system, which protects you against infection and disease. The lymphatic system includes your spleen, thymus, lymph nodes and lymph channels, as well as your tonsils and adenoids.
What to do if you have cancer surgery?
If you have had or you are going to have cancer surgery, ask your doctor whether your procedure will involve your lymph nodes or lymph vessels. Ask if your radiation treatment will be aimed at lymph nodes, so you'll be aware of the possible risks. To reduce your risk of lymphedema, try to: Protect your arm or leg.
What to do if you have swelling in your arm?
Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice persistent swelling in your arm or leg. If you already have the diagnosis of lymphedema of a limb, see your doctor if there is a sudden dramatic increase in the size of the involved limb, as it may suggest a new process is occurring.
What causes lymphedema in cancer patients?
Lymphedema can occur when the lymph system is damaged, which can prevent the lymph fluid from returning to the blood. For people with cancer, the build-up of lymph fluid can be caused by: 1 Cancer surgery, especially when lymph nodes are removed 2 Radiation therapy that can damage nearby lymph nodes or lymph vessels 3 Infections that damage surrounding tissue or cause scarring 4 Other health conditions, such as heart or vascular disease, arthritis, and eczema 5 Gene changes or mutations that involve the lymph system 6 Injury or trauma to a certain area of the body 7 Increased white blood cells from leukemia
How do you know if you have lymphedema?
Common signs and symptoms of lymphedema can include: Swelling in part of the body (such as your breast, chest, shoulder, arm, or leg) Skin feeling tight or hard, changing in texture, looking red, or feeling hot. New aching, tingling, numbness, or other discomfort in the area. The area might also feel full or heavy.
What are the lymph nodes in the body?
Lymph nodes are small, bean-sized glands along the lymph vessels that work to help filter foreign substances, such as tumor cells and infections. Lymph nodes are in many parts of the body, including the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen (belly), and groin. The tonsils, adenoids, spleen, and thymus are also parts of the lymph system.
What is the lymph system?
It is a network of lymph nodes, ducts or vessels, and organs that work together to collect and carry clear lymph fluid through the body tissues to the blood. This is much like how veins collect blood from distant parts of the body ...
Why do people with cancer have lymph nodes?
For people with cancer, the build-up of lymph fluid can be caused by: Cancer surgery, especially when lymph nodes are removed . Radiation therapy that can damage nearby lymph nodes or lymph vessels. Infections that damage surrounding tissue or cause scarring.
What is the function of lymph fluid?
Lymph fluid circulates through the body and contains proteins, salts, and water, as well as white blood cells, which help fight infection. Lymph vessels or ducts have one-way valves that work with body muscles to help move the fluid through the body and control the flow.
What is the stage 1 of a swollen arm?
Stage 1: Swelling of the affected area. There is increased size or stiffness of the arm or leg or affected area. For the arms or legs, the swelling improves when the arm or leg is raised. Stage 2: More swelling than stage 1, which does not improve when the arm or leg is elevated.
What is lymphedema in the body?
Lymphedema is swelling due to build-up of lymph fluid in the body. Lymph nodes act like a drain in your sink. If the drain is clogged, the fluid cannot drain. It usually happens in the arms or legs, but can occur in other parts of the body.
How does a lymphedema machine work?
A machine inflates a sleeve that you place on your swollen arm or leg, helping lymph fluid flow out. Weight loss. In patients who are overweight, lymphedema related to breast cancer may improve with weight loss. Surgery. If your lymphedema is severe, your doctor may suggest that you get an operation.
What is the test to see if lymph vessels are blocked?
Lymphoscintigraphy is a test that uses radioactive material to see if the lymph vessels are blocked. Computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can take pictures of the swollen area to find out why the lymph vessels are blocked. This photo shows a person with lymphedema in the left leg.
How to treat swollen arm?
The goal of treatment is to reduce the swelling or keep it from getting worse, and to relieve symptoms. Your doctor can help you figure out which treatments are best for you. Lymphedema can be treated with—. Exercise. Moving your swollen arm or leg may help the lymph fluid to drain, thus reducing the swelling.
What does it feel like to have lymphedema on your arm?
The arm or leg with lymphedema feels heavy . Clothing and jewelry fit more tightly on the affected area. The skin looks thicker or leathery. If you notice any swelling after cancer treatment, talk to your doctor about what is causing it and how best to treat it.
How do you know if you have lymphedema?
The symptoms of lymphedema may include—. Your arm, leg, or other part of your body has a little swelling at first, but gets bigger over time. The skin in that area feels tight, and sometimes has a tingling sensation. The arm or leg with lymphedema feels heavy. Clothing and jewelry fit more tightly on the affected area.
Can cancer cause lymphedema?
Lymphedema can be caused by cancer or by cancer treatment. Sometimes a cancerous tumor can get big enough to block the lymph system. Surgery to remove cancer may also remove lymph nodes or some of the vessels that carry the lymph fluid. This can cause the fluid to build up in surrounding tissues. Radiation treatment can damage ...
How to get rid of lymphedema?
Exercises: With compression, special exercises will help to pump lymph out of the swollen area. Skin Care: Keeping the skin clean and moisturized will help prevent infections that often can happen with lymphedema. Self-Care Management and Training: Learning how to manage your lymphedema at home.
Why does lymphedema occur?
Lymphedema occurs as a result of damage to the lymph nodes or lymph vessels. The lymph vessels run very close to the blood vessels in our bodies and move fluid from the body through the lymph nodes and then into the blood. Lymph nodes work as filters to fight infection and help regulate swelling.
How to treat lymphatic drainage?
How long does treatment last? 1 In order to prevent the area from swelling constant attention is needed. 2 Elastic compression garments that fit like a second skin are worn during the day. 3 Often bandages with foam are worn at night to decrease daily daytime swelling. 4 Exercises are done while wearing compression. 5 Self manual lymphatic drainage is done for 20 minutes per day.
Why do lymph nodes work?
Lymph nodes work as filters to fight infection and help regulate swelling. Lymphedema is chronic swelling that happens when the lymph is not moving properly. This can happen when lymph nodes are removed due to cancer. Lymph nodes can also be removed in other non-cancer surgeries.
Why does lymphedema cause swelling?
Lymphedema results in chronic swelling that leads to tissue inflammation and scarring. The swollen body part feels harder to touch and is heavier than the non-swollen side.
Can lymph nodes be removed?
Lymph nodes can also be removed in other non-cancer surgeries. Lymph nodes and vessels can also be damaged with radiation therapy for cancer or through an injury to a body part. Some people are born with poorly working lymph systems. In some cases lymphedema is caused by damaged leg veins or a history of blood clots.
What is lymphedema in the legs?
Treatment. Lymphedema is swelling that’s caused by a collection of too much lymph fluid. It usually happens in your arms and legs, but it can happen in other parts of your body, as well. This swelling may cause pain and limit how well the affected area moves. Lymph is a protein -rich fluid that moves throughout your body in lymph vessels.
What causes lymphedema in the lymphatic system?
Causes and Types. If your lymphatic system is damaged or a blockage exists, the fluid can build up in the soft tissue beneath your skin. There are two types of lymphedema: Secondary lymphedema is caused by another condition or disease that damages your lymph vessels or nodes. Secondary lymphedema may be caused by:
What is the best way to move fluid from swelling?
Massage: A specially trained professional can do light massage to help move fluid from areas of swelling to other areas where working lymph vessels may carry it away. You can even learn how to use these massage techniques on yourself. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on Pinterest Email Print.
What is the best way to diagnose a swollen lymph node?
A lymphoscintigraphy is a scan that can detect blockages or missing lymph vessels. It is done by injecting radioactive material. Other tests to investigate the cause of your swelling include MRI, CT scan, and ultrasound.
How do you know if you have lymphedema?
Symptoms. The most common symptom of lymphedema is swelling in one or both arms or legs. This swelling, which can extend into the fingers or toes, usually develops gradually over time. At first, the swelling is soft and fluid. In time, it can become more dense and fibrous, and it may make your skin look grainy.
How to help lymphatic drainage?
Exercise: Gentle exercises may promote lymph drainage and strengthen your affected limb. Bandages: Wrapped in just the right way, these may help push lymph fluid toward the trunk of your body. You may also wear them to help prevent lymph fluid from going back into your affected limb.
Why do lymph nodes filter fluid?
Your lymph nodes then filter the fluid to get the impurities out of your body. You could get lymphedema for any number of reasons. There are treatments to help bring down the swelling so you feel and move better.
How many people develop lymphedema after lymph node removal?
Of four patients undergoing lymph node removal during cancer treatment, only one will develop lymphedema; the risk is about 26-33%. We think part of the answer lies in the small, but different ways lymphatic vessels form in one person to the next.
Where does fluid go in lymphedema?
A: Normally as blood flows through the body, fluid seeps out of blood vessels and into the body’s tissues. This fluid drains into the lymphatic vessels, then moves to the lymph nodes to be filtered. Eventually the fluid returns to the veins and back into circulation. In lymphedema, however, the lymphatic system fails to keep up with ...
Why does lymphatic fluid build up in the arm?
That’s because the lymphatic vessels – the places where they’d normally drain – have been damaged. As a result, this fluid builds up and causes swelling, typically in an arm or a leg, and can result in chronic inflammation. Damage to the lymphatic vessels most commonly occurs because of cancer treatment.
Why do lymphatic vessels get damaged?
Damage to the lymphatic vessels most commonly occurs because of cancer treatment. A surgeon will often remove the lymph nodes near a tumor to prevent the spread of cancer. In that process, lymphatic vessels get severed, and this is what can start the problem.
What is holding back lymphatic care?
One of the biggest things holding back lymphatic care is that there is nothing we can do right now to get a quick assessment of the lymphatic system. If you have chest pain, within an hour we can have sophisticated measurements of heart function. Nothing like that exists right now for measuring lymphatic function.
Is there a cure for lymphedema?
A: There is currently no cure for lymphedema. The standard treatment is called compression. A patient wears a pressurized sleeve over the arm or leg to compress it, and that helps the fluid drain. The problem is that it’s not feasible to wear these sleeves 24/7.
Can lymphedema cause swelling?
Its main symptom is swelling of the arms or legs, but if left untreated, lymphedema can lead to severe discomfort and life-threatening infections. The swelling associated with the disease is caused by a failure of the lymphatic system, a lesser known part of the body’s circulatory system. In research funded in part by the National Heart, Lung, ...
Why is it important to treat lymphedema?
It’s important to begin lymphedema treatment as soon as possible to prevent the condition from worsening. Untreated lymphedema can lead to skin thickening and scarring, which can be permanent. Figuring out a treatment plan and lifestyle adjustments can help you move forward and live well.
How to treat lymphedema in legs?
Nonsurgical treatments for lymphedema in the legs include: 1 Wrap: A bandage or compression garment can help reduce swelling and get lymph fluid moving back up from your legs toward your heart. People with lymphedema may wrap their leg with a bandage or wear compression stockings during waking hours, particularly during exercise. It’s also a good idea to use compression at night, too, if possible. 2 Exercise: Specific, gentle lymphedema exercises for the legs can help improve lymph fluid drainage. A lymphedema therapist can teach you how to do these exercises. 3 Pneumatic pump: A pneumatic pump for the legs is similar to a long blood pressure cuff that fits over the entire leg and applies pressure in waves up the leg. The pressure encourages fluid to flow back toward the heart. A lymphedema pump is most often used in combination with another treatment, rather than alone. 4 Massage: Lymphedema massage can encourage lymph drainage and loosen any soft tissue tightness that may be contributing to fluid blockage.
How to help lymphedema at night?
It’s also a good idea to use compression at night, too, if possible. Exercise: Specific, gentle lymphedema exercises for the legs can help improve lymph fluid drainage. A lymphedema therapist can teach you how to do these exercises. Pneumatic pump: A pneumatic pump for the legs is similar to a long blood pressure cuff that fits over ...
What causes lymphedema in the legs?
Common causes of secondary lymphedema include: Injury: A traumatic sports injury or a deep cut can damage lymph nodes and vessels and increase the risk of lymphedema. Surgical injury or removal of lymph nodes can also cause lymphedema in the legs.
How to get lymph fluid back up from legs?
Wrap: A bandage or compression garment can help reduce swelling and get lymph fluid moving back up from your legs toward your heart. People with lymphedema may wrap their leg with a bandage or wear compression stockings during waking hours, particularly during exercise.
What is it called when lymph fluid doesn't drain?
But lymph fluid can become blocked and develop into abnormal swelling when the fluid doesn’t drain properly. This condition is called lymphedema, which commonly occurs in the legs but can develop anywhere that lymph nodes and vessels are located.
How to treat a cut on the foot?
Use lotion to keep your skin moisturized. Avoid any type of cut, scrape or burn, which can lead to infection. Use sunscreen and bug spray. Don’t walk around barefoot. If you do have an injury, treat it right away—clean the area, use antibacterial ointment, and apply a bandage.
