Treatment For Elevated Ammonia Levels
- Consuming ammonia reducing medications in appropriate dosage has been found to be beneficial. These medications allow ammonia to mix with water and get eliminated through the kidney
- Low protein diet is recommended in patients with elevated level of ammonia. ...
- Dialysis is an alternative, especially if ammonia levels in the blood are very high
What medications are used for high ammonia levels?
- Background. Cirrhosis is a chronic disorder of the liver. ...
- Review question. We investigated the use of five pharmacotherapies that specifically target ammonia for the prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis.
- Search date
- Study funding sources. ...
- Study characteristics. ...
- Key results. ...
- Quality of the evidence. ...
What medications can cause elevated ammonia levels?
- Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) – The most important, and far and away the most common cause of hyperammonemia that we will see in the ED is caused by liver disease. ...
- Portosystemic shunts – If blood from the GI tract bypasses the liver, it avoids the detoxyfying hepatocytes. ...
- Medication-induced hyperammonemia – Many different medications can cause (NCHE). ...
Why are my ammonia levels still so high?
These include:
- Hepatic encephalopathy, a condition that happens when the liver is too diseased or damaged to properly process ammonia. ...
- Reye syndrome, a serious and sometimes fatal condition that causes damage to the liver and brain. ...
- Urea cycle disorders, rare genetic defects that affect the body's ability to change ammonia into urea.
Does lactulose treat high ammonia levels?
Lactulose is also used to treat high ammonia levels in the blood due to liver disease. High ammonia levels can lead to portal-systemic encephalopathy. This drug works by drawing ammonia from your blood into your large intestine. Your large intestine then removes the ammonia through your stool.
What medication is given to reduce ammonia levels?
Lactulose is also used to reduce the amount of ammonia in the blood of patients with liver disease. It works by drawing ammonia from the blood into the colon where it is removed from the body. This medication is sometimes prescribed for other uses; ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How do you fix high ammonia levels?
What should I do?Complete a 25% water change and retest after a few hours.Treat with Ammonia Remover.When at a safe level of 0.0mg treat the tank with Fast Filter Start to boost the bacteria in your filter that process ammonia.Continue to regularly test your water.
What is the best treatment for ammonia?
There is no antidote for ammonia poisoning. Treatment consists of supportive measures. These include administration of humidified oxygen and bronchodilators and airway management; treatment of skin and eyes with copious irrigation; and dilution of ingested ammonia with milk or water.
Can ammonia be cured?
There is no antidote for ammonia poisoning, but ammonia's effects can be treated, and most victims recover. People who experience serious signs and symptoms (such as severe or constant coughing, or burns in the throat) may need hospital care.
How long does it take for ammonia levels to drop?
This process normally takes anywhere from 2-6 weeks. At temperatures below 70F, it takes even longer to cycle a tank. In comparison to other types of bacteria, Nitrifying bacteria grow slowly.
How do you lower ammonia levels naturally?
2:503:534 Ways to Lower Ammonia in the Brain - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo as a natural remedy manganese can help detoxify ammonia another natural remedy to lessen theMoreSo as a natural remedy manganese can help detoxify ammonia another natural remedy to lessen the amount of ammonia in your body is sauerkraut. Why because you're enhancing.
What is a dangerously high ammonia level?
Ammonia is highly toxic. Blood ammonia levels are usually less than 50 micromoles per liter (micromol /L), but this can vary depending on age. An increase to only 100 micromol /L can lead to changes in consciousness. A blood ammonia level of 200 micromol /L is associated with coma and convulsions.
What are the symptoms of too much ammonia in the body?
Symptoms include irritability, headache, vomiting, ataxia, and gait abnormalities in the milder cases. Seizures, encephalopathy, coma, and even death can occur in cases with ammonia levels greater than 200 micromol/L.
How much lactulose should I take for high ammonia levels?
The average lactulose dose in patients with an elevated ammonia level was 161 mL, identical to the lactulose dose in patients with a normal ammonia level. There was no correlation between lactulose dose and ammonia level (R = 0.0026).
What foods to avoid if you have high ammonia levels?
Avoid the packaged snacks, cereals, and sodas found in the middle aisles. As the body digests protein, it creates a byproduct called ammonia. When the liver is functioning properly, this is cleared without issue.
Can high ammonia levels cause permanent brain damage?
If your body can't process or eliminate ammonia, it builds up in the bloodstream. High ammonia levels in the blood can lead to serious health problems, including brain damage, coma, and even death. High ammonia levels in the blood are most often caused by liver disease.
What is the best treatment for high ammonia levels?
Patients can be treated with a special protein formula, supplements and medications such as sodium benzoate. Treating high blood ammonia levels also involves treating the underlying causes of the condition. Tests are first conducted to determine the cause of the heightened levels.
Why is ammonia high in the blood?
Cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver, and hepatitis can cause high levels of ammonia in the blood because these conditions affect the liver's ability to function properly , notes WebMD.
Can ammonia be flushed out of the body?
Ammonia cannot be flushed out of the body through urine, unlike urea. Ammonia tests can help check the effects of treatments, such as high-calorie intravenous nutrition, on a patient's liver, but urine tests can also provide a way to monitor high blood ammonia levels, according to WebMD.
What are the aims of hyperammonemia treatment?
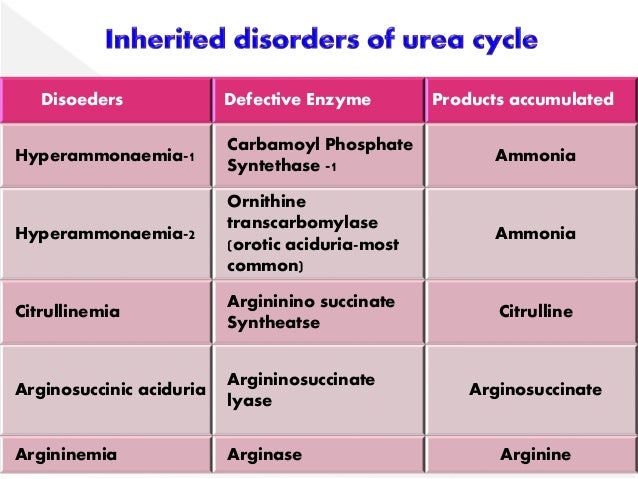
The aims of treatment for hyperammonemia are to correct biochemical abnormalities and ensure adequate nutritional intake. Treatment involves compounds that increase the removal of nitrogen waste. These compounds convert nitrogen into products other than urea, which are then excreted; hence, the load on the urea cycle is reduced. The first compounds to be used were sodium benzoate and arginine. Later, phenylacetate was used, which has now been replaced by phenylbutyrate.
What are the compounds that are used in the urea cycle?
The first compounds to be used were sodium benzoate and arginine. Later, phenylacetate was used, which has now been replaced by phenylbutyrate. Protein intake should be stopped.
Is it necessary to restrict physical activity for hyperammonemia?
Restricting physical activity of children with hyperammonemia is not necessary; however, caloric intake should be sufficient to avoid protein breakdown.
Can arginine be used for hyperammonemia?
Intravenous arginine should be provided. Corticosteroids are not indicated for the management of increased intracranial pressure in hyperammonemia because they induce negative nitrogen balance. Mannitol is not effective in treating cerebral edema induced by hyperammonemia.
Is liver transplantation good for hyperammonemia?
Neurologic outcomes correlated closely with status prior to transplantation. Thus, liver transplantation is a good option for patients with urea cycle defects who have not suffered major brain injury.
What is an Ammonia Level Test?
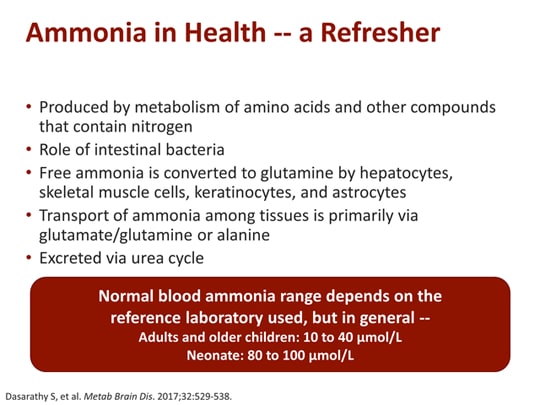
Ammonia is a by-product of protein breakdown and gas produced by the body during protein metabolism. The liver and kidneys produce ammonia, and an ammonia buffer system in the kidneys helps reduce the body’s ammonia concentration.
Symptoms of high ammonia levels
Having high ammonia levels can cause stinging or burning in the eyes. Additional symptoms may include:
Why You May Need an Ammonia Level Test
A high ammonia level test can serve as a diagnostic and monitoring tool. Among these are:
Causes of high ammonia levels
Different things can cause ammonia levels to rise. Here are a few common ones:
Treatment for high ammonia levels
Blood ammonia levels can rise in some cases, especially in infants, and then go down independently. More severe cases of ammonia buildup can lead to severe problems. The following methods can help remove excess ammonia from the blood:
Summary
You should not substitute medical advice for the information in this article. Keep this in mind. Before dealing with excessive ammonia levels, you should determine what’s causing them.
What is the name of the medication that lowers ammonia levels?
Lactulose is the only medication used to lower ammonia levels in the body. However, it is sold under a variety of brand names, including Duphalac, Enulose, Generlac, Constulose, and Kristalose.
Why is it important to reduce ammonia levels?
It is important to reduce ammonia levels that are above normal. Having too much ammonia in the blood can cause severe health problems, such as decreased brain function.
How to get rid of ammonia in the blood?
3. Take Lactulose. Lactulose is a constipation medication that is used to treat high levels of ammonia in the blood. Lactulose works by removing ammonia from the blood and moving it into the colon. Once in the colon, the ammonia is eliminated from the body when you go to the bathroom.
Why is ammonia elevated?
If you have elevated ammonia levels, it is typically due to a problem with your liver function. However, there are ways to decrease your ammonia levels and to improve your liver function.
What happens if you have high ammonia levels?
When you have high ammonia levels in the body, it is a signal that your body systems are not working correctly. This can cause a variety of health problems due to lack of essential vitamins and minerals.
How to lower ammonia levels in liver?
These include taking medication, supplementing your diet, and changing what you eat. With a combination of these methods, you can lower the ammonia levels in your body. Steps.
What is high ammonia?
High ammonia levels are a common symptom of advanced liver disease, known as cirrhosis, Reye's syndrome, and severe cases of hepatitis. If you have one of these diseases, it is likely that you will need to work on reducing your ammonia levels. ...
How to treat hyperammonemia?
The current therapeutic options to treat hyperammonemia target either the reduction of ammoniagenesis and its absorption in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, or the activation of ammonia removal by upregulating ureagenesis through treatment with N-carbamylglutamate or supplementation of urea cycle intermediates and glutamine synthesis (Figure 2) [19]. First, we will cover the current standard treatment of hyperammonemia caused by both liver disease and inborn urea cycle disorder. Additionally, treatments that were promising in clinical trials and treatments that were tried but were not efficacious are also mentioned briefly (Table 1).
What happens when ammonia levels rise?
When ammonia levels rise quickly within the brain, the glutamine synthetase enzyme located in the astrocytes rapidly synthesizes glutamine from ammonia, causing an excess of glutamine production in the brain which can disrupt the symbiotic relationship between neurons and astrocytes [14]. Such changes result in alterations of the astrocytic volume and in increased extracellular concentrations of excitatory and inhibitory substances. The subsequent intracellular osmolarity increase can also cause astrocyte swelling and loss [15]. Besides astrocyte morphological changes, increased brain ammonia concentrations also alter the expression levels of astrocyte proteins such as glial fibrillary acidic protein, glutamate, glycine transporters, and “peripheral-types” benzodiazepine receptors [16]. As a result, inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and interferon, are released from the astrocytes [16]. Ammonia also can affect energy production mechanism in the astrocytes. Ammonia inhibits α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase or oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, and the depletion of carboxylic acids, which are used for glutamine synthesis, paralyzes the Krebs cycle. The production of adenosine 5′-triphosphate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced form) in the Krebs cycle is decreased, and pyruvate conversion to lactate is increased [17]. Elevated lactate levels in the astrocytes were related to the development of brain edema. The decreased expression of glutamate receptors in the astrocytes causes glutamate increase and, possibly, seizures. Moreover, cerebral blood flow increases, cerebral autoregulation is lost, and cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension (ICH) may develop [18].
What happens to glutamine in hyperammonemia?
When in the hyperammonemia condition, the renal ammoniagenesis is decreased and excretion into urine is increased [12]. In addition, the muscles and brain convert excess ammonia to glutamine. Under normal physiological conditions, glutamine is deaminated to glutamate in neurons, which is stored in vesicles and then released into the synaptic clefts where it initiates an excitatory signal by binding to the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. Glutamate is then cleared from the synaptic clefts by the Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter-2 (EAAT-2) and is recycled to glutamine by the astrocytes, which results in the functional compartmentalization of glutamate and glutamine [13] (Figure 1).
How is ammonia produced?
Ammonia is constantly produced as a metabolic waste from amino acid catabolism in mammals. Ammonia, the toxic waste metabolite, is resolved in the liver where the urea cycle converts free ammonia to urea. Liver malfunctions cause hyperammonemia that leads to central nervous system (CNS) dysfunctions, such as brain edema, convulsions, and coma. The current treatments for hyperammonemia, such as antibiotics or lactulose, are designed to decrease the intestinal production of ammonia and/or its absorption into the body and are not effective, besides being often accompanied by side effects. In recent years, increasing evidence has shown that modifications of the gut microbiota could be used to treat hyperammonemia. Considering the role of the gut microbiota and the physiological characteristics of the intestine, the removal of ammonia from the intestine by modulating the gut microbiota would be an ideal approach to treat hyperammonemia. In this review, we discuss the significance of hyperammonemia and its related diseases and the efficacy of the current management methods for hyperammonemia to understand the mechanism of ammonia transport in the human body. The possibility to use the gut microbiota as pharmabiotics to treat hyperammonemia and its related diseases is also explored.
What are the consequences of hyperammonemia?
The direct consequence of hyperammonemia is represented by neurological disorders which include alterations of mood and personality, cognitive impairment, ataxia, convulsions, and coma [6] . The severity of the neurological dysfunction depends upon the chronic or acute type of hyperammonemia, the degree of hyperammonaemia, and the age of the patient. Neuropathological studies revealed that Alzheimer type II astrocytosis was observed in the adult hyperammonaemic patient, whereas hyperammonemia in the infant with congenital urea cycle-related genes defects or Reye syndrome was always accompanied by cerebral atrophy, neuronal loss, and cerebral edema [6]. Reye syndrome, a rapidly progressive encephalopathy, is a rare but serious pediatric condition [7]. It was much more common among children and teenagers when aspirin was commonly prescribed to them, but virtually disappeared after warnings about prescribing aspirin to children and teenagers [7]. In the USA, it is advised that anyone under 19 years of age should not be given any medication containing aspirin unless on the advice of a doctor [8]. Likewise, in the UK, aspirin should not be given to anyone under the age of 16 years unless on the advice of doctors [9].
How does ammonia get into the brain?
The flux that moves into the brain is most likely both by diffusion of gaseous NH3and by mediated transport of NH4+by channels and transporters through plasma membrane crossing, which will have a direct effect on the pH. Furthermore, NH4+competes with K+on K+transporters, affecting the membrane potentials. A cascade of secondary effects and encephalopathy will result from these direct effects of elevated ammonia concentrations on the brain [10].
Is rifaximin good for hyperammonemia?
Rifaximin has become the most effective antibiotic of choice in the treatment of hyperammonemia because of its safety, efficacy, and tolerability [62]. Rifaximin is a nonsystemic, GI site-specific antibiotic as a result of the addition of a nonabsorbable pyridoimidazole ring. However, it retains the potential to cross the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria and inhibits RNA synthesis by binding to the β subunit of the bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme [63] The beneficial effects of rifaximin in hyperammonemia treatment have been shown by several clinical trials [22,23,64]. However, the risk of accumulation was raised for HE patients with liver cirrhosis because only a small fraction of rifaximin is eliminated by the liver. The most common adverse reactions of rifaximin are nausea, bloating, and diarrhea [65].
When should ammonia be a candidate cause?
Ammonia should be a candidate cause when human sources and activities, site observations or observed biological effects support portions of the source-to-impairment pathways (see Figure 2).
What causes higher ammonia concentrations in the hypolimnion?
Lack of turbulence and mixing will decrease volatilization of ammonia, resulting in higher ammonia concentrations downstream. Thermal stratification in impoundments can lead to higher concentrations of ammonia in the hypolimnion which, with bottom-release dams, can result in increased ammonia in downstream waters.
Why is ammonia in water so high?
Slow-moving water: Slow-moving or stagnant water (see Figure 5) may have high ammonia concentrations because of lack of turbulence and volatilization and greater accumulation of metabolic waste and decomposition products —including ammonia (WHO 1986).
How is ammonia affected by human activities?
The more extensive the relevant sources and activities, the more likely it is that ammonia will reach concentrations that can impair surface waters.
What causes ammonia in sediment?
Ammonia in sediments typically results from bacterial decomposition of organic matter that accumulates in sediment. Sediment microbiota mineralize organic nitrogen or (less commonly) produce ammonia by dissimilatory nitrate reduction. Ammonia is especially prevalent in anoxic sediments because nitrification (the oxidation of ammonia to nitrite [NO 2-] and nitrate [NO 3- ]) is inhibited. Ammonia generated in sediment may be toxic to benthic or surface water biota (Lapota et al. 2000).
How does high algal production affect ammonia?
High plant production: High algal or plant production can decrease ammonia by assimilation, increase ammonia by nitrogen fixation, or increase pH toxicity by CO 2 uptake, resulting in a shift to more unionized ammonia. Top of Page.
What is the cause of ammonia in septic systems?
Septic seepage and failed package plants: Seepage from failed septic tanks or their leach fields, and discharges from poorly–functioning package sewage treatment plants may contribute significant amounts of ammonia to streams and lakes.
Why is my ammonia level high?
In infants, high ammonia levels may be a sign of a genetic disease of the urea cycle or a condition called hemolytic disease of the newborn. This disorder happens when a mother develops antibodies to her baby's blood cells.
What does it mean when your blood test shows high ammonia levels?
If your results show high ammonia levels in the blood, it may be a sign of one of the following conditions: In children and teens, it may be a sign of Reye syndrome. In infants, high ammonia levels may be a sign of a genetic disease of the urea cycle or a condition called hemolytic disease of the newborn.
What is the purpose of ammonia test?
An ammonia levels test may be used to diagnose and/or monitor conditions that cause high ammonia levels. These include: Hepatic encephalopathy, a condition that happens when the liver is too diseased or damaged to properly process ammonia. In this disorder, ammonia builds up in the blood and travels to the brain.
What happens if you don't get ammonia?
Urea is passed through the body in urine. If your body can't process or eliminate ammonia, it builds up in the bloodstream. High ammonia levels in the blood can lead to serious health problems, including brain damage, coma, and even death. High ammonia levels in the blood are most often caused by liver disease.