
Medication
Medications, shocking the heart back into rhythm, or even a procedure to potentially cure atrial fibrillation, called a catheter ablation, may be necessary. Certainly, with A-fib, an ounce of prevention is definitely worth a pound of cure!
Procedures
What you can do
- Be aware of any pre-appointment restrictions. ...
- Write down any symptoms you're experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to atrial fibrillation.
- Write down key personal information, including any family history of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure or diabetes, and any major stresses or recent life changes.
Nutrition
- Adgey AA, Geddes JS, Mulholland HC, Keegan DA, Pantridge JF. ...
- Adgey AA, Scott ME, Allen JD, Nelson PG, Geddes JS, Zaidi SA. ...
- Beard OW, Hipp HR, Robins M, Verzolini VR. ...
- BERKSON J, GAGE RP. ...
- DAY HW. ...
- Druss RG, Kornfeld DS. ...
- Dupont B, Flensted-Jensen E, Sandoe E. ...
- Geddes JS, Adgey AA, Pantridge JF. ...
- HONEY GE, TRUELOVE SC. ...
- Lawrie DM. ...
How to get rid of atrial fibrillation once and for all?
Usually, these drugs are grouped into three large categories:
- Drugs that slow the heart rate
- Heart rhythm medications called antiarrhythmic drugs
- Blood thinners
How do you manage AFIB?
What are the medications for ventricular fibrillation?
What medications are used for atrial fibrillation?
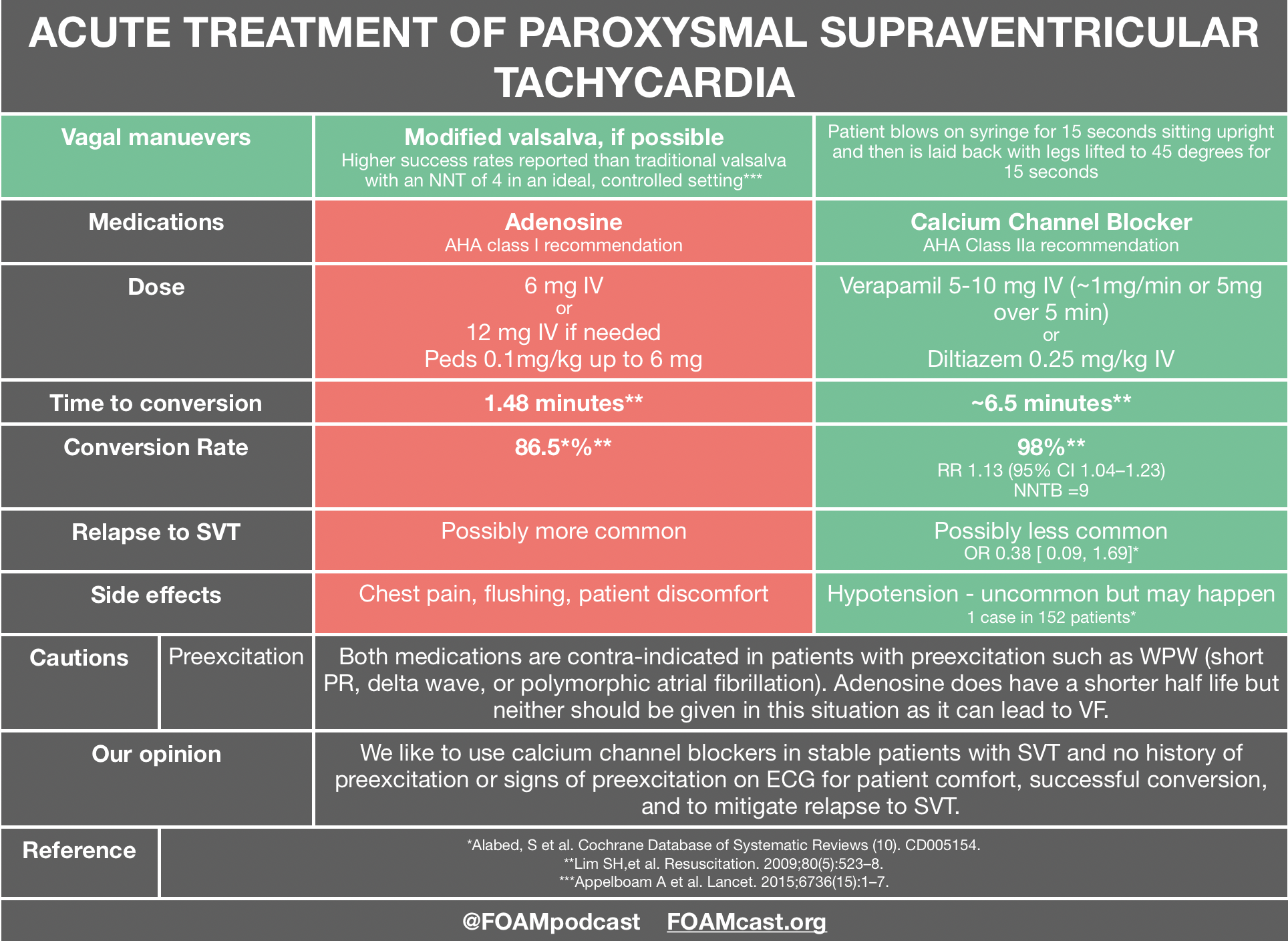
What is best treatment for atrial fibrillation?
Heart rate controlling medicines, such as beta-blockers that include Coreg (Carvedilol) and Lopressor and Toprol (Metoprolol), is the best way to treat AFib. These medications can control or slow the rapid heart rate so that the heart can function in a better way.
How is atrial fibrillation treated in a hospital?
Atrial fibrillation treatment may involve a number of options:Medication. Drugs for atrial fibrillation can help keep the normal heart rhythm, slow down a fast heart rate, or prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of stroke.Cardioversion. ... Catheter ablation, also known as cardiac ablation. ... Surgical ablation.
What is the first line treatment for AFib?
Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers are first-line agents for rate control in AF. These drugs can be administered either intravenously or orally. They are effective at rest and with exertion.
What triggers atrial fibrillation?
drinking excessive amounts of alcohol, particularly binge drinking. being overweight (read about how to lose weight) drinking lots of caffeine, such as tea, coffee or energy drinks. taking illegal drugs, particularly amphetamines or cocaine.
What is the main cause of atrial fibrillation?
The basic cause of AFib is disorganized signals that make your heart's two upper chambers (the atria) squeeze very fast and out of sync. They contract so quickly that the heart walls quiver, or fibrillate. Damage to your heart's electrical system can cause AFib.
How do you stop AFib immediately?
6 Ways to Stop an AFib EpisodeEngage in deep, mindful breathing. ... Get some exercise. ... Valsalva maneuver. ... Practice yoga. ... Put some cold water on your face. ... Contact a health professional.
What is the life expectancy of a person with AFib?
Whether or not Afib shortens a person's lifespan depends on whether or not he or she can get their heart rate and anticoagulation under control. If controlled, then Afib doesn't shorten a person's lifespan. If these two things are not under control then Afib can shorten one's lifespan.
Does a pacemaker stop AFib?
Treatment Overview The pacemaker does not treat atrial fibrillation itself. The pacemaker is used to treat a slow heart rate (bradycardia) that happens in some people who have atrial fibrillation.
How to treat atrial fibrillation?
Heart rate medicines: The most common way to treat atrial fibrillation is with drugs that control your heartbeat. These slow your rapid heart rate so your heart can pump better. You may need other drugs. Some are called beta-blockers. They also slow your heart rate.
How to reduce AFIB?
Go for fruits, veggies, and whole grains. Get more exercise -- more physical activity strengthens your heart. They'll probably suggest that you make other changes to lower your odds of heart disease, as well as conditions like diabetes and lung disease that can contribute to AFib: Quit smoking.
How to treat AFIB without surgery?
If medicines don't work or they cause side effects, you can try one of two procedures called cardioversion or ablation. These treat AFib without surgery. Electrical cardioversion: The doctor gives your heart a shock to regulate your heartbeat. They’ll use paddles or stick patches called electrodes onto your chest.
What is the procedure that a doctor uses to guide a catheter?
The doctor makes several small cuts between your ribs and uses a camera to guide catheters for either cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation. Some hospitals offer robot-assisted surgery that uses smaller cuts and allows for greater precision. Your doctor will put a video camera or tiny robot into your chest.
What is AFIB and how does it affect your heart?
Living With AFib. Atrial fibrillation is a problem with your heart 's electrical activity. You and your doctor have treatment options if your symptoms become too severe. With AFib, your heart quivers, beats irregularly, or skips beats. It can't pump blood through its chambers and out to your body as well as it should.
How does a doctor destroy the AV node?
Your doctor will insert a catheter into a vein in your groin and slide it up to the AV node, a nerve that conducts electrical impulses between the top and bottom chambers of your heart. They’ll send radiofrequency energy through the catheter to destroy the AV node. This stops the signals from reaching your ventricle.
How does AFIB work?
It’s connected to one or two wires that are inserted through a vein and sit in your heart. It delivers painless electric pulses that make your heart beat. Treating the Causes of AFib. If problems such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, or an overactive thyroid caused your AFib, you'll need to treat the root cause.
Why is ventricular fibrillation considered an emergency?
The goal of emergency treatment is to restore blood flow as quickly as possible to prevent organ and brain damage.
What test is used to diagnose ventricular fibrillation?
Tests to diagnose and determine the cause of ventricular fibrillation include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of your heart.
What to do if you are not trained to use an AED?
If you're not trained to use an AED, a 911 operator or another emergency medical operator may be able to give you instructions. Public-use AEDs are programmed to recognize ventricular fibrillation and send a shock only when needed.
How to control high blood pressure?
Maintaining a healthy body weight can help control blood pressure and cholesterol. Take medications as prescribed to manage high blood pressure or high cholesterol. Limit alcohol.
What are some ways to keep your heart healthy?
Heart-healthy foods include fruits, vegetables and whole grains, as well as lean protein sources such as soy, beans, nuts, fish, skinless poultry and low-fat dairy products.
How to do CPR?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). CPR mimics the pumping motion of the heart and keeps blood flowing through the body. First call 911 or your local emergency number. Then start CPR by pushing hard and fast on the person's chest — about 100 to 120 compressions a minute.
What are the goals of AFIB treatment?
Your treatment plan will likely address three goals: restore your normal heart rate. restore your normal heart rhythm. Medications can help achieve all three of these goals.
How to reduce the risk of AFIB?
These changes can help reduce your risk of complications from AFib. You should stop or refrain from smoking and limit your intake of alcohol and caffeine. Also, you should avoid cough and cold medications that contain stimulants. If you’re not sure which to avoid, ask your pharmacist.
How does AFIB work?
Two types of medication can help with this. They work by slowing down electrical signals in your heart. These medications are: Sodium channel blockers such as flecainide (Tambocor) and quinidine.
How to slow down heart rate?
Slowing down your heart rate is another important step in treatment. Your doctor may prescribe medications for this purpose. Three types of medications can be used to restore your normal heart rate: 1 Beta-blockers such as atenolol (Tenormin), carvedilol (Coreg), and propranolol (Inderal) 2 Calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem (Cardizem) and verapamil (Verelan) 3 Digoxin (Lanoxin)
What is the best medicine for slowing down heart rate?
Three types of medications can be used to restore your normal heart rate: Beta-blockers such as atenolol (Tenormin), carvedilol (Coreg), and propranolol (Inderal) Calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem (Cardizem) ...
Why are NOACs recommended over warfarin?
These NOACs are now recommended over the traditionally prescribed warfarin (Coumadin) because they have no known food interactions and don’t require frequent monitoring. People who take warfarin require frequent blood testing and need to monitor their intake of foods rich in vitamin K.
How to restore sinus rhythm?
Another option for restoring sinus rhythm when medications fail is called catheter ablation. A narrow catheter is threaded through a blood vessel into your heart. The catheter uses radiofrequency energy to destroy a small number of tissue cells in your heart that send out signals that cause your abnormal heart rhythm.
What is the best medicine for AFIB?
Heart rate controlling medicines, such as beta-blockers that include Coreg ( Carvedilol) and Lopressor and Toprol ( Metoprolol ), is the best way to treat AFib.
What are the symptoms of AFIB?
Early warning signs and symptoms of atrial fibrillation include chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness. Treatment for atrial fibrillation includes medical procedures, surgery, and medication.
How do you know if you have AFIB?
Symptoms of AFib are confusion, anxiety, fatigue, a fluttering in the chest, and the feeling that you may pass out or faint. Atrial fibrillation is treated with medications, cardioversion therapy, and surgery.
What is the name of the heart condition that causes heart palpitations?
Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is an abnormality in the heart rhythm, which involves irregular and often rapid beating of the heart. Symptoms may include heart palpitations, dizziness, fainting, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Atrial fibrillation treatment may include medication or procedures like cardioversion or ablation ...
What is the name of the condition where blood clots form inside the heart and travel to the brain?
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) occurs when the two smaller, upper chambers of the heart (the atria) beat irregularly instead of rhythmically. This abnormal condition can allow blood clots to form inside the heart and later travel to the brain and cause a stroke.
What is the name of the medication that is used to treat ventricular arrhythmias?
Sotylize ( sotalol hydrochloride) Sotylize (fluorouracil) is a prescription medication used to treat life-threatening heart rhythm problems called ventricular arrhythmias and to increase the amount of time between having symptoms of heart rhythm disorders called atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
What is AF in medical terms?
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm characterized by an irregular and fast heartbeat. The upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat chaotically, and can cause pooling and clotting of blood in the atria, instead of it emptying into the lower chamber (ventricles).
What is the most common test for atrial fibrillation?
The most commonly used tests to diagnose atrial fibrillation include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): The ECG draws a picture on graph paper of the electrical impulses traveling through the heart muscle. An EKG provides an electrical “snapshot” of the heart.
Where does atrial fibrillation occur?
Because atrial fibrillation usually begins in the pulmonary veins or at their attachment to the left atrium, energy is applied around the connections of the pulmonary veins to the left atrium during the pulmonary vein ablation procedure.
What is electrical cardioversion?
Electrical Cardioversion: A cardioversion electrically “resets” the heart. Medications alone are not always effective in converting atrial fibrillation to a more normal rhythm. Sometimes cardioversion is used to restore a normal heart rhythm and allow the medication to successfully maintain the normal rhythm.
What is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria?
Atrial fibrillation ( AF or AFib) is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria. Instead of the SA node (sinus node) directing the electrical rhythm, many different impulses rapidly fire at once, causing a very fast, chaotic rhythm in the atria.
What is a pulmonary vein ablation?
Pulmonary Vein Ablation: Pulmonary vein ablation (also called pulmonary vein antrum isolation or PVAI) may be an option for people who cannot tolerate medications or when medications are not effective in treating atrial fibrillations.
What is an ECG recording of atrial fibrillation?
An ECG recording of atrial fibrillation. Instead of the impulse traveling in an orderly fashion through the heart, many impulses begin at the same time and spread through the atria, competing for a chance to travel through the AV node.
Why is AV node ablation used?
Because the patient will continue to have atrial fibrillation, an anticoagulant medication is prescribed to reduce the risk of stroke. Important note: Due to better treatment alternatives, AV node ablation is rarely used to treat atrial fibrillation.
How to treat atrial fibrillation?
It may be possible for you to be treated by a GP, or you may be referred to a heart specialist (a cardiologist).
What factors are taken into consideration when treating atrial fibrillation?
Factors that will be taken into consideration include: your age. your overall health. the type of atrial fibrillation you have. your symptoms.
What are some alternatives to warfarin?
Alternative anticoagulants. Rivaroxaban, dabigatran, apixaban and edoxaban are alternatives to warfarin. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has approved these medicines for use in treating atrial fibrillation.
Why do you need a pacemaker for atrial fibrillation?
It's usually used to stop your heart beating too slowly, but in atrial fibrillation it may be used to help your heart beat regularly. Having a pacemaker fitted is usually a minor surgical procedure carried out under a local anaesthetic (the area being operated on is numbed and you're conscious during the procedure).
How long before cardioversion should you take anticoagulant?
In this case, you'll be given an anticoagulant for 3 to 4 weeks before cardioversion, and for at least 4 weeks afterwards to minimise the chance of having a stroke. In an emergency, pictures of the heart can be taken to check for blood clots, and cardioversion can be carried out without going on medicine first.
What is the best way to reduce heart rate?
Controlling the rate of the heartbeat. The aim is to reduce your heart rate to less than 90 beats per minute when you are resting. A beta blocker, such as bisoprolol or atenolol, or a calcium channel blocker, such as verapamil or diltiazem, will be prescribed.
What is the best medicine to restore heart rhythm?
Restoring a normal heart rhythm. A variety of medicines are available to restore normal heart rhythm, including: flecainide. beta blockers, particularly sotalol. An alternative medicine may be recommended if a particular medicine does not work or the side effects are troublesome.

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Clinical Trials
- Following a heart-healthy lifestyle can help prevent or treat conditions such as high blood pressure and heart disease. Lifestyle changes often include: 1. Eating heart-healthy foods.Eat a healthy diet that's low in salt and solid fats and rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains. 2. Exercising regularly.Exercise daily and increase physical activity. 3. Quitting smoking.If you smo…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- If you have an irregular or pounding heartbeat, make an appointment with your family doctor. If atrial fibrillation is found early, treatment may be easier and more effective. You may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared for your appointment. Here'…
Coping and Support
- Ventricular fibrillation is always diagnosed in an emergency situation. A pulse check will reveal no pulse if sudden cardiac death occurred. Tests to diagnose and determine the cause of ventricular fibrillation include: 1. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of your heart. Sticky patches (electrodes) are placed on your chest and someti…