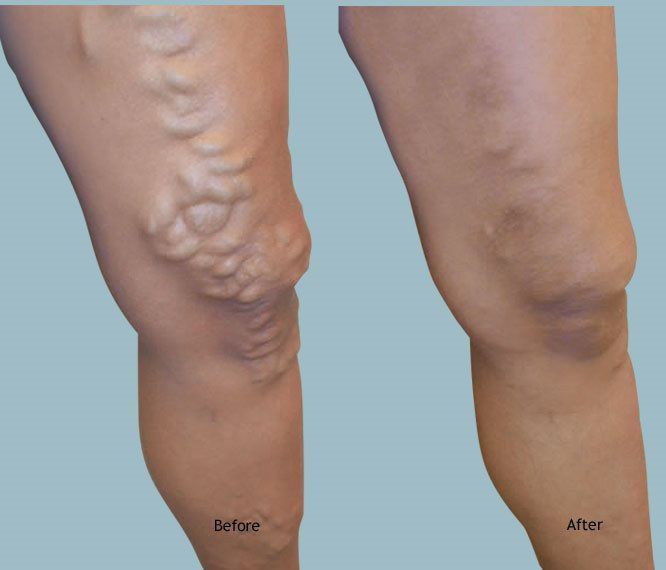
Medication
Feb 10, 2005 · For patients with newly diagnosed deep vein thrombosis (DVT), good evidence indicates that outpatient treatment is safe and effective using low-molecular-weight heparin and an oral anticoagulant until the international normalized ratio (INR) is in therapeutic range.
Self-care
May 09, 2012 · In most cases, treatment involves anticoagulant drugs alone, although other treatments like thrombolytic therapy and blood filters are an option in certain cases. With adequate treatment, most people who have DVT can recover completely. Prescriptions DVT is often treated with a combination of several medications and therapies. Anticoagulants
Nutrition
Treatment for a DVT can include: Anticoagulants ("blood thinners"). This type of medication makes it harder for your blood to clot. Anticoagulants also stop clots from getting bigger and prevent blood clots from moving. Anticoagulants do not destroy clots. Your body may naturally dissolve a clot, but sometimes clots do not completely disappear.
What do doctors prescribe to treat deep vein thrombosis?
These drugs, also called anticoagulants, are the most common treatment for DVT. They can keep a clot from growing or breaking off, and they prevent new …
Why deep vein thrombosis can be so dangerous?
The main focus of DVT treatment at home includes: taking your prescribed anticoagulant medicine safely relieving symptoms, such as leg pain …
How to treat thrombosis naturally?
Dec 22, 2020 · Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) or hormone replacement therapy. Both can increase your blood's ability to clot. Being overweight or obese. Being overweight increases the pressure in the veins in your pelvis and legs. Smoking. Smoking affects blood clotting and circulation, which can increase your risk of DVT. Cancer.
What is the optimal treatment of saphenous vein thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis can be treated with blood thinners, like heparin, warfarin, or direct anticoagulants (e.g., rivaroxaban and apixaban ). These medications work by inhibiting the clotting cascade, thereby preventing blood from clotting. In severe cases, such as with extensive blood clots or involvement of the proximal iliac veins, thrombolytic enzymes can be given to …
See more

What is the immediate treatment for DVT?
Heparin and warfarin are 2 types of anticoagulants that are used to treat DVT. Heparin is usually prescribed first because it works immediately to prevent further clotting. After this initial treatment, you may also need to take warfarin to prevent another blood clot forming.Nov 1, 2021
Can deep vein thrombosis be cured?
Depending on your general condition, thrombosis may be a singular incident or a more chronic problem. However, the good news is that generally, Thrombosis can be cured.Apr 16, 2021
How long does deep vein thrombosis take to go away?
It is important to start treatment right away for DVT. It takes about 3 to 6 months for a blood clot to go away. During this time, there are things you can do to relieve symptoms. Elevate your leg to reduce swelling.Sep 10, 2020
What are the warning signs of deep vein thrombosis?
DVT signs and symptoms can include:Swelling in the affected leg. Rarely, there's swelling in both legs.Pain in your leg. The pain often starts in your calf and can feel like cramping or soreness.Red or discolored skin on the leg.A feeling of warmth in the affected leg.Dec 22, 2020
How do you get deep vein thrombosis?
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis Being sedentary due to bed rest or sitting too long without moving, such as during travel. Family history of blood clots. Having a long-term (indwelling) catheter, a tube in a blood vessel. Obesity.
What are the first signs of a blood clot?
Arms, LegsSwelling. This can happen in the exact spot where the blood clot forms, or your entire leg or arm could puff up.Change in color. You might notice that your arm or leg takes on a red or blue tinge, or gets or itchy.Pain. ... Warm skin. ... Trouble breathing. ... Lower leg cramp. ... Pitting edema. ... Swollen, painful veins.Jun 17, 2020
What are the first signs of a blood clot in the leg?
Signs that you may have a blood clotleg pain or discomfort that may feel like a pulled muscle, tightness, cramping or soreness.swelling in the affected leg.redness or discoloration of the sore spot.the affected area feeling warm to the touch.a throbbing sensation in the affected leg.Jun 23, 2021
Can aspirin dissolve a blood clot?
Working With Your Doctor for Vein Health In some cases, aspirin will not provide enough protection. Additionally, it may not work to dissolve a clot properly. Instead, it may be better as a preventative measure after a clot has been thoroughly dissolved by another medication.Mar 18, 2019
What is the best treatment for DVT?
When DVT is present, immediate treatment with anticoagulation therapy ( blood thinners) will help prevent further blood clotting in the leg veins while reducing the chances of developing a pulmonary embolism. There are several different types of anticoagulant drugs.
What is the goal of DVT treatment?
The goal of DVT treatment is to prevent the blood clot in your leg from growing bigger and prevent it from breaking loose and traveling to your lungs. Longer-term treatment focuses on preventing both complications and future clots.
How to know if you have a syringe?
During treatment, keep an eye out for warning signs of excessive bleeding, such as: 1 Coughing or vomiting blood 2 Dizziness or weakness 3 Severe headache or stomachache 4 Blood in urine or bowel movements 5 Heavy menstrual bleeding
What is DVT 2021?
If you've experienced symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), it is important to contact your doctor or local emergency room. DVT is a serious condition that can lead to a life-threatening pulmonary embolism.
Where is the inferior vena cava filter placed?
If preexisting conditions prevent you from taking anticoagulants, your doctor may recommend an inferior vena cava filter. This small, wiry device is inserted through a catheter placed in a vein in your groin or neck. The device is placed inside a large vein known as the inferior vena cava .
How long does it take for heparin to work?
Your doctor may start you on an oral anticoagulant, like Coumadin (warfarin), which can take a few days to reach therapeutic levels.
What is the best treatment for pulmonary embolism?
Anticoagulants. Anticoagulant drugs, often called blood thinners, are used to prevent abnormal blood clotting. 1 Although these drugs cannot dissolve blood clots that have already formed, they are an important and potentially life-saving medication for people with DVT or pulmonary embolism (PE).
How to get around with DVT?
A DVT may make it harder for you to get around at first. You should slowly return to your normal activities. If your legs feel swollen or heavy, lie in bed with your heels propped up about 5 to 6 inches. This helps improve circulation and decreases swelling.
How to treat a blood clot in the leg?
The main goals of treatment are to: Stop the clot from getting bigger. Prevent the clot from breaking off in your vein and moving to your lungs.
Why do my leg veins swell?
The swelling is often because the valves in the leg veins are damaged or the vein is blocked by the DVT.Most compression stockings are worn just below the knee. These stockings are tight at the ankle and become more loose as they go up the leg. This causes gentle pressure (compression) on your leg.
What is a DVT?
What is deep vein thrombosis? Deep vein thrombosis (DVT, also called venous thrombosis) is a blood clot that develops in a vein deep in the body. The clot may partially or completely block blood flow through the vein. Most DVTs occur in the lower leg, thigh or pelvis, although they also can occur in other parts of the body including the arm, brain, ...
Where are blood clots found?
You have a blood clot in an unusual location, such as in a vein from the intestines, liver, kidney or brain. You have a strong family history of blood clots.
What are the causes of DVT?
The following conditions can increase your risk of a DVT: An inherited (genetic) condition that increases your risk of blood clots. Cancer and some of its treatments (chemotherapy) Limited blood flow in a deep vein, due to injury, surgery, or immobilization. Long periods of inactivity that decrease blood flow, such as:
What is the most common test for DVT?
A duplex venous ultrasound. This is the most common test used to diagnose a DVT. It shows the blood flow in the veins and any blood clots that exist. An ultrasound technician will apply pressure while scanning your arm or leg. If the pressure does not cause the vein to compress, it could mean there is a blood clot.
What is the best treatment for DVT?
Blood Thinners. These drugs, also called anticoagulants, are the most common treatment for DVT. They can keep a clot from growing or breaking off, and they prevent new clots from forming. But they can't thin your blood, despite their name. And they won’t get rid of an existing clot.
What to do after pulmonary embolism surgery?
After the surgery, you may need pain medicine. When it’s time to go home, you’ll need a friend or family member to drive you. An IVC filter traps blood clots before they cause a pulmonary embolism and is used only to prevent pulmonary embolisms. It doesn’t protect against DVT or treat the condition itself.
What is the IVC filter?
Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter. An IVC filter is a small metal device that looks like an upside-down umbrella and can stop blood clots in your veins from moving. It goes in your body’s main vein, called the inferior vena cava (IVC). This vein runs through your belly.
How long does it take to take warfarin?
You may also take warfarin by pill once a day, starting while you're on heparin and then usually for 3 to 6 months or more. While you take it, you'll need regular blood tests to make sure you've got the right amount in your system. Too little won't prevent clots, and too much makes dangerous bleeding more likely.
Where do blood clots move?
Blood clots that move from place to place (mobile thrombus) DVT in your inferior vena cava and iliac veins. These are the veins that run from your heart to your lower body and pelvis. There are two types of IVC filters. One stays in your body permanently.
Does warfarin cause birth defects?
It can also interact with other medicines, vitamins, and foods with a lot of vitamin K, which is another good reason to get your blood checked often. Let your doctor know if you're pregnant because warfarin can cause birth defects.
Can you take warfarin while pregnant?
Let your doctor know if you're pregnant because warfarin can cause birth defects. You'll have to take something else. Newer anti-clotting medicines, known as Xa inhibitors, work as well as warfarin for most people. You won't have to get blood tests, change your dose, or remember what foods you ate.
What is the treatment for DVT?
Once you receive a diagnosis of DVT, you’ll likely be prescribed medications known as anticoagulants, or blood thinners. These work to keep the clot from growing and to prevent further clots.
Why is it important to make changes to your lifestyle to prevent DVT?
Along with managing your symptoms , it’s important to make changes to your lifestyle in order to prevent DVT happening again. Certain people are at a higher risk of developing DVT, including: people who are having surgery in the lower extremities. heavy smokers.
What is a DVT?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition that happens when a blood clot forms in a vein. A deep vein blood clot can occur anywhere in the body, but most often forms in the calf or thigh. Treating DVT is important because of the risk of a life-threatening complication known as pulmonary embolism. This occurs when the blood clot breaks ...
How long do you have to take anticoagulant?
You may have to take the anticoagulant medication for three to six months, sometimes longer. Make sure to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Taking too much of an anticoagulant medication like warfarin can thin the blood too much and lead to bleeding problems.
What is the best medicine for stroke?
Acetyl salicylic acid, which is derived from salicylate and is commonly known as aspirin, is used to prevent stroke. Ginger is a common ingredient in many recipes. It can also be made into a tea. Ginger has many other health benefits as well.
How to get blood out of your leg?
Wear graduated compression stockings. These specially fitted stockings are tight at the feet and become gradually looser up on the leg, creating gentle pressure that keeps blood from pooling and clotting. Elevate the affected leg. Make sure your foot is higher than your hip. Take walks.
Can DVT cause leg pain?
DVT doesn’t always cause symptoms, but it can sometimes result in leg pain or swelling. The pain usually occurs in the calf and feels like an intense cramp. To ease the pain and swelling of a DVT, you can try the following at home: Wear graduated compression stockings.
What does it feel like to have a deep vein thrombosis?
The pain often starts in your calf and can feel like cramping or soreness. Red or discolored skin on the leg. A feeling of warmth in the affected leg. Deep vein thrombosis can occur without noticeable symptoms.
What are the complications of DVT?
Complications. Complications of DVT can include: Pulmonary embolism (PE). PE is a potentially life-threatening complication associated with DVT. It occurs when a blood vessel in your lung becomes blocked by a blood clot (thrombus) that travels to your lung from another part of your body, usually your leg.
How do you know if you have a pulmonary embolism?
The warning signs and symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include: Sudden shortness of breath. Chest pain or discomfort that worsens when you take a deep breath or when you cough. Feeling lightheaded or dizzy, or fainting. Rapid pulse. Rapid breathing. Coughing up blood.
What causes blood clots?
The main causes of DVT are damage to a vein from surgery or trauma and inflammation due to infection or injury.
Can a DVT cause pulmonary embolism?
However, pulmonary embolism can occur with no evidence of DVT. When DVT and pulmonary embolism occur together, it's called venous thromboembolism (VTE).
What is PE in medical terms?
When to see a doctor. Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot gets lodged in an artery in the lung, blocking blood flow to part of the lung. Blood clots most often start in the legs and travel up through the right side of the heart and into the lungs. This is called DVT.
How long does it take for blood clots to go away after birth?
Women with an inherited clotting disorder are especially at risk. The risk of blood clots from pregnancy can continue for up to six weeks after you have your baby. Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) or hormone replacement therapy. Both can increase your blood's ability to clot.
What is deep vein thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, occurs when a blood clot, or thrombus, develops in one of the large veins of the upper or lower limbs. These veins typically run deep between muscles, as opposed to superficial veins, which lie closer to the skin.
What causes deep vein thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis typically occurs as a result of a combination of risk factors that increase the risk of developing thrombosis. These factors are collectively known as Virchow’s triad, and include hypercoagulability, slowed venous blood flow, and damage to the inner lining of blood vessels.
What are the warning signs of deep vein thrombosis?
Warning signs of DVT can include a throbbing or cramping pain in the affected limb, usually in the calf or thigh; swelling; warm skin around the painful area; and swollen veins that are hard or sore to the touch.
What are the signs and symptoms of deep vein thrombosis?
Signs and symptoms of DVT vary depending on the extent and location of the blood clot. In some cases, DVT can develop silently; however, the most common symptoms include redness, swelling, and pain on the affected limb.
How is deep vein thrombosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of DVT begins by taking a thorough medical history and performing a physical exam. If a DVT is suspected, a Wells score can be obtained to determine the pretest probability of DVT, which is the likelihood that an individual has a DVT before any further testing occurs.
How is deep vein thrombosis treated?
Deep vein thrombosis can be treated with blood thinners, like heparin, warfarin, or direct anticoagulants (e.g., rivaroxaban and apixaban ). These medications work by inhibiting the clotting cascade, thereby preventing blood from clotting.
How is deep vein thrombosis prevented?
DVTs can be prevented by using compression stockings and doing frequent calf exercises during long periods of inactivity in order to help blood move through the veins and prevent stasis. Additionally, individuals with a higher risk of DVT or PE and lower risk of bleeding may be given long-term anticoagulant therapy.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment